Japanese Battleship Mishima on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
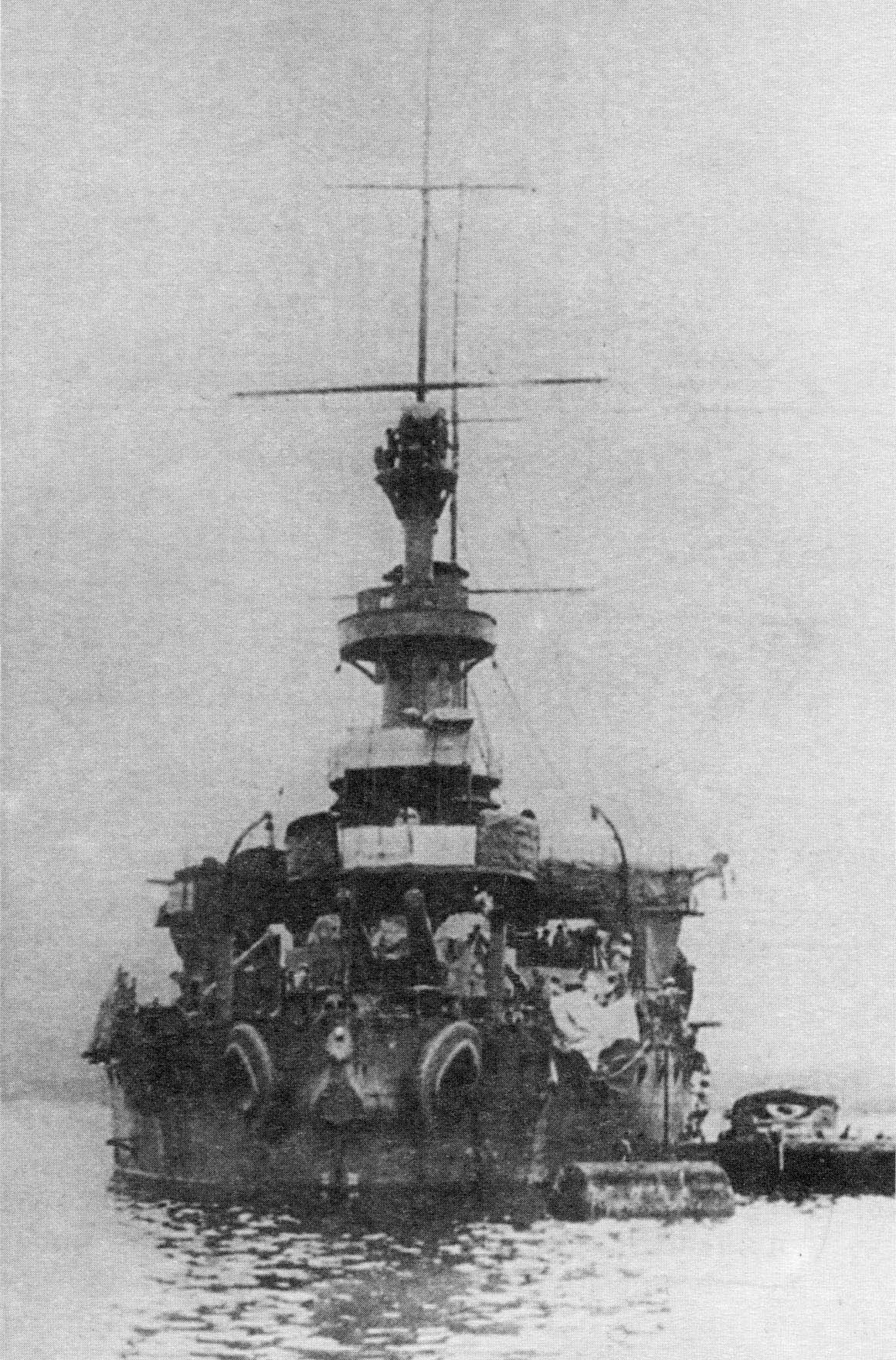 ''Admiral Seniavin'' (), was a built for
''Admiral Seniavin'' (), was a built for
 ''Admiral Seniavin'' (), was a built for
''Admiral Seniavin'' (), was a built for Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until being dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution and the declaration of ...
during the 1890s. She was one of eight Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
n pre-dreadnought battleship
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built from the mid- to late- 1880s to the early 1900s. Their designs were conceived before the appearance of in 1906 and their classification as "pre-dreadnought" is retrospectively appli ...
s captured by the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, Potsdam Declaration, when it was dissolved followin ...
from the Russians during the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 – 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the ...
of 1904–1905. She subsequently served in the Japanese Navy under the name until sunk as a target in 1936.
In Russian service
Initially assigned to the RussianBaltic Fleet
The Baltic Fleet () is the Naval fleet, fleet of the Russian Navy in the Baltic Sea.
Established 18 May 1703, under Tsar Peter the Great as part of the Imperial Russian Navy, the Baltic Fleet is the oldest Russian fleet. In 1918, the fleet w ...
, she was later reclassed as a coastal defence ship
Coastal defence ships (sometimes called coastal battleships or coast defence ships) were warships built for the purpose of coastal defence, mostly during the period from 1860 to 1920. They were small, often cruiser-sized warships that sacrifi ...
.
The three obsolete ''Ushakov''s (, , and ''Admiral Senyavin'') were rejected for inclusion in the Second Pacific Squadron assembled by Admiral Zinovy Rozhestvensky
Zinovy Petrovich Rozhestvensky (, tr. ; – January 14, 1909) was a Russian admiral of the Imperial Russian Navy. He was in command of the Second Pacific Squadron in the Battle of Tsushima, during the Russo-Japanese War.
Under Admiral Rozh ...
to reinforce the existing Russian squadron based at Port Arthur after the outbreak of the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 – 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the ...
as Rozhestvensky felt they were unsuitable for such an extreme blue-water operation. Nevertheless, all three were selected to form part of Admiral Nebogatov's Third Pacific Squadron which was subsequently sent out to reinforce Rozhestvensky on his journey to the Far East after political agitation following his departure. This Third Pacific Squadron transited the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal (; , ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, Indo-Mediterranean, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest ...
and the two Russian squadrons rendezvoused at Cam Ranh Bay
Cam Ranh Bay () is a deep-water bay in Vietnam in Khánh Hòa Province. It is located at an inlet of the South China Sea situated on the southeastern coast of Vietnam, between Phan Rang and Nha Trang, approximately 290 kilometers (180 miles) nor ...
after a cruise that became known as the "Voyage of the Damned", and from there Rozhestvensky set course through the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by South China, in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan island, Taiwan and northwestern Philippines (mainly Luz ...
towards the Korea Strait
The Korea Strait is a strait, sea passage in East Asia between the Korean Peninsula and Japan. It connects the East China Sea, the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan in the northwest Pacific Ocean. The strait is split by Tsushima Island into two par ...
, where they were discovered by the Japanese.
At the resulting Battle of Tsushima
The Battle of Tsushima (, ''Tsusimskoye srazheniye''), also known in Japan as the , was the final naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War, fought on 27–28 May 1905 in the Tsushima Strait. A devastating defeat for the Imperial Russian Navy, the ...
(27–28 May 1905), the three ships survived the first phase of the engagement on the evening of 27 May largely due to the Japanese concentrating their efforts on Rozhestvensky's modern battleships (concentrated in the First and Second Divisions of the Russian squadron) and their subsequent almost-total destruction left the Russian fleet in tatters. Nebogatov's Third Division was largely able to keep itself together during the night, although ''Admiral Seniavin''s sister ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same Ship class, class or of virtually identical design to another ship. Such vessels share a nearly identical hull and superstructure layout, similar size, and roughly comparable features and equipment. They o ...
''Admiral Ushakov
Admiral Fyodor Fyodorovich Ushakov ( rus, Фёдор Фёдорович Ушаков, Fëdor Fëdorovič Ušakov, p=ʊʂɐˈkof; – ) was an Imperial Russian Navy officer best known for his service in the French Revolutionary and Napoleoni ...
'' strayed from formation and was sunk by the Japanese. The morning of 28 May found the Russian survivors surrounded by an apparently undamaged Japanese force, and Nebogatov surrendered. Thus ''Admiral Seniavin'' and ''General Admiral Graf Apraksin'' were captured as prizes of war.
Japanese service
''General Admiral Graf Apraxin'' was commissioned into the Imperial Japanese Navy under the name ''Okinoshima'' and ''Admiral Seniavin'' became the second-class coastal defense vessel ''Mishima''. ''Mishima'' was named for the small island ofMishima Mishima may refer to:
Places
* Mishima, Fukushima, a town in Fukushima Prefecture
* Mishima, Kagoshima, a village in Kagoshima Prefecture
* Mishima, Niigata, a town in Niigata Prefecture
* Mishima, Shizuoka, a city in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japa ...
, offshore from Hagi in Yamaguchi prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Chūgoku region of Honshu. Yamaguchi Prefecture has a population of 1,377,631 (1 February 2018) and has a geographic area of 6,112 Square kilometre, km2 (2,359 Square mile, sq mi). ...
, not far from the location of the Battle of Tsushima. ''Mishima'' retained her original four 10-inch 45 caliber guns, six 6-inch 40 caliber Armstrong Z guns and two 47 mm guns.
''Mishima'' was part of the Japanese Second Fleet in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, participating in the Battle of Tsingtao
The siege of Tsingtao (; ; zh, s=青岛战役, t=青島戰役) was the attack on the German port of Qingdao (Tsingtao) from Jiaozhou Bay during World War I by Japan and the United Kingdom. The siege was waged against Imperial Germany between 2 ...
against the small number of Imperial German Navy
The Imperial German Navy or the ''Kaiserliche Marine'' (Imperial Navy) was the navy of the German Empire, which existed between 1871 and 1919. It grew out of the small Prussian Navy (from 1867 the North German Federal Navy), which was mainly for ...
ships left behind by Admiral von Spee
Maximilian Johannes Maria Hubert Reichsgraf von Spee (22 June 1861 – 8 December 1914) was a German naval officer in the Imperial German Navy (''Kaiserliche Marine)'', who commanded the East Asia Squadron during World War I. Spee entered the n ...
's East Asia Squadron
The German East Asia Squadron () was an Imperial German Navy cruiser squadron which operated mainly in the Pacific Ocean between the mid-1890s until 1914, when it was destroyed at the Battle of the Falkland Islands. It was based at Germany's Ji ...
''.
After the end of the war, ''Mishima'' supported the Japanese Siberian Intervention against the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
in eastern Russia by covering the landings of Japanese forces, and by acting as an icebreaker
An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters, and provide safe waterways for other boats and ships. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller ...
to keep the sea lanes
A sea lane, sea road or shipping lane is a regularly used navigable route for large water vessels (ships) on wide waterways such as oceans and large lakes, and is preferably safe, direct and economic. During the Age of Sail, they were determined ...
between Japan and Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( ; , ) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai and the capital of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. It is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area o ...
open.
On 1 April 1921, ''Mishima'' was re-classified as a submarine tender
A submarine tender, in British English a submarine depot ship, is a type of depot ship that supplies and supports submarines.
Development
Submarines are small compared to most oceangoing vessels, and generally cannot carry large amounts of foo ...
.
''Mishima'' was decommissioned on 10 October 1935. She was sunk as a target by aircraft from the aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and hangar facilities for supporting, arming, deploying and recovering carrier-based aircraft, shipborne aircraft. Typically it is the ...
on 5 May 1936 off Toino Misaki ( Cape Toi), Miyazaki Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyūshū. Miyazaki Prefecture has a population of 1,028,215 as of 1 January 2025 and has a geographic area of 7,735 Square kilometre, km2 (2,986 sq mi). Miyazaki Prefectur ...
, Japan, at .
See also
*List of battleships of Japan
Between the 1890s and 1940s, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) built a series of battleships as it expanded its fleet. Previously, the Empire of Japan had acquired a few ironclad warships from foreign builders, although it had adopted the naval ...
Notes
References
* * * * *External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Admiral Seniavin Battleships of the Imperial Russian Navy Ships built at the Baltic Shipyard 1894 ships Russo-Japanese War battleships of Russia Captured ships Ships sunk as targets Naval ships captured by Japan during the Russo-Japanese War Maritime incidents in 1936 Shipwrecks in the Philippine Sea