J.A.R. Newlands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
John Alexander Reina Newlands (26 November 1837 – 29 July 1898) was a British chemist who worked concerning the periodicity of elements.
 Newlands was born in
Newlands was born in 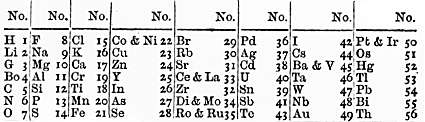 After
After  John Newlands died due to complications of surgery at his home in Lower Clapton, Middlesex and was buried at West Norwood Cemetery. His businesses was continued after his death by his younger brother, Benjamin.
John Newlands died due to complications of surgery at his home in Lower Clapton, Middlesex and was buried at West Norwood Cemetery. His businesses was continued after his death by his younger brother, Benjamin.
Cartage biography
Newlands on classification of elements
{{DEFAULTSORT:Newlands, John Alexander Reina 1837 births 1898 deaths People from Southwark English chemists Analytical chemists Burials at West Norwood Cemetery People involved with the periodic table English people of Scottish descent English people of Italian descent
Biography
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
in England, at West Square in Southwark
Southwark ( ) is a district of Central London situated on the south bank of the River Thames, forming the north-western part of the wider modern London Borough of Southwark. The district, which is the oldest part of South London, developed ...
, the son of a Scottish Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
minister and his Italian wife.
Newlands was home-schooled by his father, and later studied at the Royal College of Chemistry file:The Royal College of Chemistry; the laboratories. Lithograph Wellcome V0013588.jpg, The Royal College of Chemistry: the laboratories. Lithograph
The Royal College of Chemistry (RCC) was a college originally based on Oxford Street in central Lo ...
, now part of Imperial College London
Imperial College London, also known as Imperial, is a Public university, public research university in London, England. Its history began with Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, Prince Albert, husband of Queen Victoria, who envisioned a Al ...
. He was interested in social reform and during 1860 served as a volunteer with Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as (). In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as () or (). 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, revolutionary and republican. H ...
in his military campaign to unify Italy. Returning to London, Newlands established himself as an analytical chemist in 1864. In 1868 he became chief chemist of James Duncan's London sugar refinery
A sugar refinery is a refinery which processes raw sugar from cane or sugar extracted from beets into white refined sugar.
Cane sugar mills traditionally produce raw sugar, which is sugar that still contains molasses, giving it color ...
, where he introduced a number of improvements in processing. Later he quit the refinery and again became an analyst with his brother, Benjamin.
Newlands was the first person to devise a periodic table of chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
s arranged in order of their relative atomic mass
Atomic mass ( or ) is the mass of a single atom. The atomic mass mostly comes from the combined mass of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with minor contributions from the electrons and nuclear binding energy. The atomic mass of atoms, ...
es published in ''Chemical News'' in February 1863. Continuing Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner's work with triads and Jean-Baptiste Dumas
Jean Baptiste André Dumas (; 14 July 180010 April 1884) was a French chemist, best known for his works on organic analysis and synthesis, as well as the determination of atomic weights (relative atomic masses) and molecular weights by measuri ...
' families of similar elements, he published in 1865 his " Law of Octaves", which stated that "any given element will exhibit analogous behaviour to the eighth element following it in the table." Newlands arranged all of the known elements, starting with hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
and ending with thorium
Thorium is a chemical element; it has symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is a weakly radioactive light silver metal which tarnishes olive grey when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and ha ...
(atomic weight 232), into eight groups of seven, which he likened to octaves of music. In Newlands' table, the elements were ordered by the atomic weights that were known at the time and were numbered sequentially to show their order. Groups were shown going across the table, with periods going down – the opposite from the modern form of the periodic table.
The incompleteness of the table alluded to the possible existence of additional, undiscovered elements. However, the Law of Octaves was ridiculed by some of Newlands' contemporaries, and the Society of Chemists did not accept his work for publication.
 After
After Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev ( ; ) was a Russian chemist known for formulating the periodic law and creating a version of the periodic table of elements. He used the periodic law not only to correct the then-accepted properties of some known ele ...
and Lothar Meyer received the Davy Medal from the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
for their later 'discovery' of the periodic table in 1882, Newlands fought for recognition of his earlier work and eventually received the Davy Medal in 1887.
 John Newlands died due to complications of surgery at his home in Lower Clapton, Middlesex and was buried at West Norwood Cemetery. His businesses was continued after his death by his younger brother, Benjamin.
John Newlands died due to complications of surgery at his home in Lower Clapton, Middlesex and was buried at West Norwood Cemetery. His businesses was continued after his death by his younger brother, Benjamin.
Works
*See also
* History of the periodic tableReferences
Further reading
*External links
Cartage biography
Newlands on classification of elements
{{DEFAULTSORT:Newlands, John Alexander Reina 1837 births 1898 deaths People from Southwark English chemists Analytical chemists Burials at West Norwood Cemetery People involved with the periodic table English people of Scottish descent English people of Italian descent