Iron-making on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
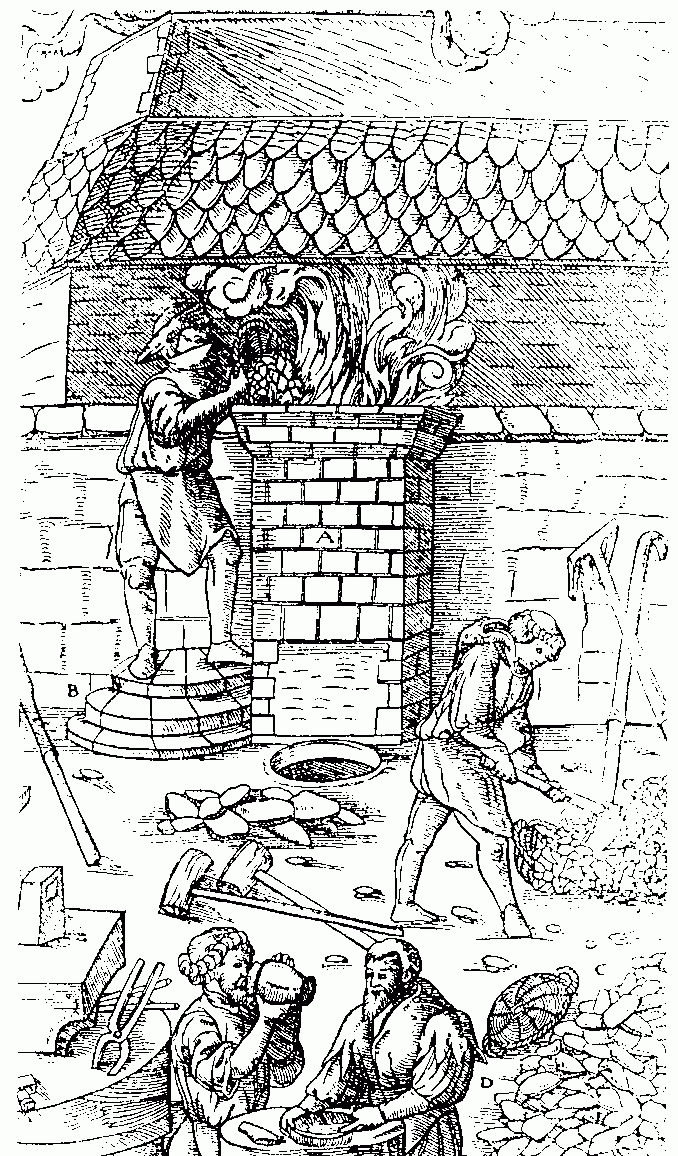 Ferrous metallurgy is the
Ferrous metallurgy is the

 Iron was extracted from iron–nickel alloys, which comprise about 6% of all meteorites that fall on the
Iron was extracted from iron–nickel alloys, which comprise about 6% of all meteorites that fall on the
 About 1500 BC, increasing numbers of non-meteoritic, smelted iron objects appeared in
About 1500 BC, increasing numbers of non-meteoritic, smelted iron objects appeared in
Online version
accessed on 2010-02-11. Although iron objects dating from the
 The history of ferrous metallurgy in the Indian subcontinent began in the 2nd millennium BC. Archaeological sites in the Gangetic plains have yielded iron implements dated between 1800 and 1200 BC. By the early 13th century BC, iron smelting was practiced on a large scale in India. In
The history of ferrous metallurgy in the Indian subcontinent began in the 2nd millennium BC. Archaeological sites in the Gangetic plains have yielded iron implements dated between 1800 and 1200 BC. By the early 13th century BC, iron smelting was practiced on a large scale in India. In  Perhaps as early as 500 BC, although certainly by 200 AD, high-quality steel was produced in southern India by the crucible technique. In this system, high-purity wrought iron, charcoal, and glass were mixed in a crucible and heated until the iron melted and absorbed the carbon. Iron chain was used in Indian suspension bridges as early as the 4th century.
Wootz steel was produced in India and
Perhaps as early as 500 BC, although certainly by 200 AD, high-quality steel was produced in southern India by the crucible technique. In this system, high-purity wrought iron, charcoal, and glass were mixed in a crucible and heated until the iron melted and absorbed the carbon. Iron chain was used in Indian suspension bridges as early as the 4th century.
Wootz steel was produced in India and
 Numerous scholars have suggested that the Afanasievo culture may be responsible for the introduction of
Numerous scholars have suggested that the Afanasievo culture may be responsible for the introduction of 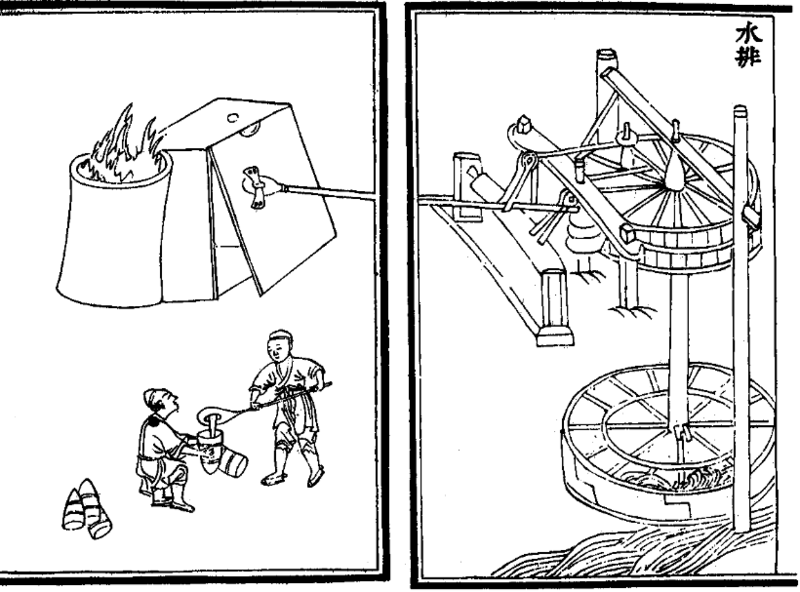 During the
During the
 Archaeometallurgical scientific knowledge and technological development originated in numerous centers of Africa; the centers of origin were located in
Archaeometallurgical scientific knowledge and technological development originated in numerous centers of Africa; the centers of origin were located in
51
��59. Inhabitants of Termit, in eastern
53
��54. Similarly, smelting in bloomery-type furnaces appear in the
 The preferred method of iron production in Europe until the development of the puddling (metallurgy), puddling process in 1783–84. Cast iron development lagged in Europe because wrought iron was the desired product and the intermediate step of producing cast iron involved an expensive blast furnace and further refining of pig iron to cast iron, which then required a labor and capital intensive conversion to wrought iron.
Through a good portion of the Middle Ages, in Western Europe, iron was still being made by the working of iron blooms into wrought iron. Some of the earliest casting of iron in Europe occurred in Sweden, in two sites, Lapphyttan and Vinarhyttan, between 1150 and 1350. Some scholars have speculated the practice followed the Mongols across Russia to these sites, but there is no clear proof of this hypothesis, and it would certainly not explain the pre-Mongol datings of many of these iron-production centres. In any event, by the late 14th century, a market for cast iron goods began to form, as a demand developed for cast iron cannonballs.
The preferred method of iron production in Europe until the development of the puddling (metallurgy), puddling process in 1783–84. Cast iron development lagged in Europe because wrought iron was the desired product and the intermediate step of producing cast iron involved an expensive blast furnace and further refining of pig iron to cast iron, which then required a labor and capital intensive conversion to wrought iron.
Through a good portion of the Middle Ages, in Western Europe, iron was still being made by the working of iron blooms into wrought iron. Some of the earliest casting of iron in Europe occurred in Sweden, in two sites, Lapphyttan and Vinarhyttan, between 1150 and 1350. Some scholars have speculated the practice followed the Mongols across Russia to these sites, but there is no clear proof of this hypothesis, and it would certainly not explain the pre-Mongol datings of many of these iron-production centres. In any event, by the late 14th century, a market for cast iron goods began to form, as a demand developed for cast iron cannonballs.
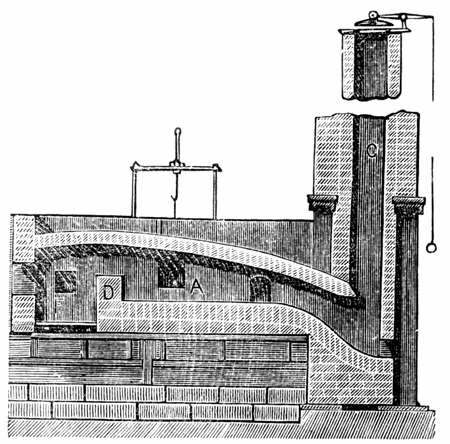 It was only after this that economically viable means of converting pig iron to bar iron began to be devised. A process known as potting and stamping was devised in the 1760s and improved in the 1770s, and seems to have been widely adopted in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands from about 1785. However, this was largely replaced by Henry Cort's puddling process, patented in 1784, but probably only made to work with grey pig iron in about 1790. These processes permitted the great expansion in the production of iron that constitutes the Industrial Revolution for the iron industry.
In the early 19th century, Hall discovered that the addition of iron oxide to the charge of the puddling furnace caused a violent reaction, in which the pig iron was decarburization, decarburised, this became known as 'wet puddling'. It was also found possible to produce steel by stopping the puddling (metallurgy), puddling process before decarburisation was complete.
It was only after this that economically viable means of converting pig iron to bar iron began to be devised. A process known as potting and stamping was devised in the 1760s and improved in the 1770s, and seems to have been widely adopted in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands from about 1785. However, this was largely replaced by Henry Cort's puddling process, patented in 1784, but probably only made to work with grey pig iron in about 1790. These processes permitted the great expansion in the production of iron that constitutes the Industrial Revolution for the iron industry.
In the early 19th century, Hall discovered that the addition of iron oxide to the charge of the puddling furnace caused a violent reaction, in which the pig iron was decarburization, decarburised, this became known as 'wet puddling'. It was also found possible to produce steel by stopping the puddling (metallurgy), puddling process before decarburisation was complete.
 Apart from some production of puddled steel, English steel continued to be made by the cementation process, sometimes followed by remelting to produce crucible steel. These were batch-based processes whose raw material was bar iron, particularly Swedish oregrounds iron.
The problem of mass-producing cheap steel was solved in 1855 by Henry Bessemer, with the introduction of the Bessemer process, Bessemer converter at his steelworks in Sheffield, England. (An early converter can still be seen at the city's Kelham Island Museum). In the Bessemer process, molten pig iron from the blast furnace was charged into a large crucible, and then air was blown through the molten iron from below, igniting the dissolved carbon from the coke. As the carbon burned off, the melting point of the mixture increased, but the heat from the burning carbon provided the extra energy needed to keep the mixture molten. After the carbon content in the melt had dropped to the desired level, the air draft was cut off: a typical Bessemer converter could convert a 25-ton batch of pig iron to steel in half an hour.
In the 1860s development of regenerative furnaces and higher temperature refractory lining allowed to melt steel in an open hearth. That was slow and energy intensive, but allowed to better control the chemical makeup of the product and recycle iron scrap.
The acidic refractory lining of Bessemer converters and early open hearths didn't allow to remove phosphorus from steel with lime, which prolonged the life of puddling furnaces in order to utilize phosphorous iron ores abundant in Continental Europe. However, in the 1870s Gilchrist–Thomas process was developed, and later basic lining was adopted for the open hearths as well.
Finally, the Basic oxygen steelmaking, basic oxygen process was introduced at the Voest-Alpine works in 1952; a modification of the basic Bessemer process, it lances oxygen from above the steel (instead of bubbling air from below), reducing the amount of nitrogen uptake into the steel. The basic oxygen process is used in all modern steelworks; the last Bessemer converter in the U.S. was retired in 1968. Furthermore, the last three decades have seen a massive increase in the mini-mill business, where scrap steel only is melted with an electric arc furnace. These mills only produced bar products at first, but have since expanded into flat and heavy products, once the exclusive domain of the integrated steelworks.
Until these 19th-century developments, steel was an expensive commodity and only used for a limited number of purposes where a particularly hard or flexible metal was needed, as in the cutting edges of tools and springs. The widespread availability of inexpensive steel powered the Second Industrial Revolution and modern society as we know it. Mild steel ultimately replaced wrought iron for almost all purposes, and wrought iron is no longer commercially produced. With minor exceptions, alloy steels only began to be made in the late 19th century. Stainless steel was developed on the eve of World War I and was not widely used until the 1920s.
Apart from some production of puddled steel, English steel continued to be made by the cementation process, sometimes followed by remelting to produce crucible steel. These were batch-based processes whose raw material was bar iron, particularly Swedish oregrounds iron.
The problem of mass-producing cheap steel was solved in 1855 by Henry Bessemer, with the introduction of the Bessemer process, Bessemer converter at his steelworks in Sheffield, England. (An early converter can still be seen at the city's Kelham Island Museum). In the Bessemer process, molten pig iron from the blast furnace was charged into a large crucible, and then air was blown through the molten iron from below, igniting the dissolved carbon from the coke. As the carbon burned off, the melting point of the mixture increased, but the heat from the burning carbon provided the extra energy needed to keep the mixture molten. After the carbon content in the melt had dropped to the desired level, the air draft was cut off: a typical Bessemer converter could convert a 25-ton batch of pig iron to steel in half an hour.
In the 1860s development of regenerative furnaces and higher temperature refractory lining allowed to melt steel in an open hearth. That was slow and energy intensive, but allowed to better control the chemical makeup of the product and recycle iron scrap.
The acidic refractory lining of Bessemer converters and early open hearths didn't allow to remove phosphorus from steel with lime, which prolonged the life of puddling furnaces in order to utilize phosphorous iron ores abundant in Continental Europe. However, in the 1870s Gilchrist–Thomas process was developed, and later basic lining was adopted for the open hearths as well.
Finally, the Basic oxygen steelmaking, basic oxygen process was introduced at the Voest-Alpine works in 1952; a modification of the basic Bessemer process, it lances oxygen from above the steel (instead of bubbling air from below), reducing the amount of nitrogen uptake into the steel. The basic oxygen process is used in all modern steelworks; the last Bessemer converter in the U.S. was retired in 1968. Furthermore, the last three decades have seen a massive increase in the mini-mill business, where scrap steel only is melted with an electric arc furnace. These mills only produced bar products at first, but have since expanded into flat and heavy products, once the exclusive domain of the integrated steelworks.
Until these 19th-century developments, steel was an expensive commodity and only used for a limited number of purposes where a particularly hard or flexible metal was needed, as in the cutting edges of tools and springs. The widespread availability of inexpensive steel powered the Second Industrial Revolution and modern society as we know it. Mild steel ultimately replaced wrought iron for almost all purposes, and wrought iron is no longer commercially produced. With minor exceptions, alloy steels only began to be made in the late 19th century. Stainless steel was developed on the eve of World War I and was not widely used until the 1920s.
 The steel industry is often considered an indicator of economic progress, because of the critical role played by steel in infrastructural and overall economic development. In 1980, there were more than 500,000 U.S. steelworkers. By 2000, the number of steelworkers had fallen to 224,000.
The boom and bust, economic boom in China and India caused a massive increase in the demand for steel. Between 2000 and 2005, world steel demand increased by 6%. Since 2000, several Indian and Chinese steel firms have risen to prominence, such as Tata Steel (which bought Corus Group in 2007), Baosteel Group and Shagang Group. , though, ArcelorMittal is the world's List of steel producers, largest steel producer. In 2005, the British Geological Survey stated China was the top steel producer with about one-third of the world share; Japan, Russia, and the US followed respectively.
The large production capacity of steel results in a significant amount of carbon dioxide emissions inherent related to the main production route. In 2019, it was estimated that 7 to 9% of the global carbon dioxide emissions resulted from the steel industry. Reduction of these emissions are expected to come from a shift in the main production route using cokes, more recycling of steel and the application of carbon capture and storage or carbon capture and utilization technology.
In 2008, steel began commodity market, trading as a commodity on the London Metal Exchange. At the end of 2008, the steel industry faced a sharp downturn that led to many cut-backs.
The steel industry is often considered an indicator of economic progress, because of the critical role played by steel in infrastructural and overall economic development. In 1980, there were more than 500,000 U.S. steelworkers. By 2000, the number of steelworkers had fallen to 224,000.
The boom and bust, economic boom in China and India caused a massive increase in the demand for steel. Between 2000 and 2005, world steel demand increased by 6%. Since 2000, several Indian and Chinese steel firms have risen to prominence, such as Tata Steel (which bought Corus Group in 2007), Baosteel Group and Shagang Group. , though, ArcelorMittal is the world's List of steel producers, largest steel producer. In 2005, the British Geological Survey stated China was the top steel producer with about one-third of the world share; Japan, Russia, and the US followed respectively.
The large production capacity of steel results in a significant amount of carbon dioxide emissions inherent related to the main production route. In 2019, it was estimated that 7 to 9% of the global carbon dioxide emissions resulted from the steel industry. Reduction of these emissions are expected to come from a shift in the main production route using cokes, more recycling of steel and the application of carbon capture and storage or carbon capture and utilization technology.
In 2008, steel began commodity market, trading as a commodity on the London Metal Exchange. At the end of 2008, the steel industry faced a sharp downturn that led to many cut-backs.
 Ferrous metallurgy is the
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
of iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
and its alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s. The earliest surviving prehistoric
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron-making, iron, copper extraction, copper ...
of iron from ores began, but by the end of the 2nd millennium BC iron was being produced from iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the f ...
s in the region from Greece to India,Riederer, Josef; Wartke, Ralf-B.: "Iron", Cancik, Hubert; Schneider, Helmuth (eds.): Brill's New Pauly, Brill 2009Early Antiquity By I.M. Drakonoff. 1991. University of Chicago Press
The University of Chicago Press is the university press of the University of Chicago, a Private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. It is the largest and one of the oldest university presses in the United States. It pu ...
. . p. 372 The use of wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.05%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4.5%), or 0.25 for low carbon "mild" steel. Wrought iron is manufactured by heating and melting high carbon cast iron in an ...
(worked iron) was known by the 1st millennium BC, and its spread defined the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
. During the medieval period, smiths in Europe found a way of producing wrought iron from cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
, in this context known as pig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate good used by the iron industry in the production of steel. It is developed by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with si ...
, using finery forge
A finery forge is a forge used to produce wrought iron from pig iron by decarburization in a process called "fining" which involved liquifying cast iron in a fining hearth and decarburization, removing carbon from the molten cast iron through Redo ...
s. All these processes required charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ca ...
as fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work (physics), work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chem ...
.
By the 4th century BC southern India had started exporting wootz steel, with a carbon content between pig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate good used by the iron industry in the production of steel. It is developed by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with si ...
and wrought iron, to ancient China, Africa, the Middle East, and Europe. Archaeological evidence of cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
appears in 5th-century BC China. New methods of producing it by carburizing bars of iron in the cementation process were devised in the 17th century. During the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, new methods of producing bar iron by substituting coke for charcoal emerged, and these were later applied to produce steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
, ushering in a new era of greatly increased use of iron and steel that some contemporaries described as a new "Iron Age".
In the late 1850s Henry Bessemer invented a new steelmaking process which involved blowing air through molten pig-iron to burn off carbon, and so producing mild steel. This and other 19th-century and later steel-making processes have displaced wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.05%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4.5%), or 0.25 for low carbon "mild" steel. Wrought iron is manufactured by heating and melting high carbon cast iron in an ...
. Today, wrought iron is no longer produced on a commercial scale, having been displaced by the functionally equivalent mild or low-carbon steel.
Meteoric iron

Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. That source can often be identified with certainty because of the unique crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
line features (Widmanstätten pattern
Widmanstätten patterns (), also known as Thomson structures, are figures of long Phase (matter), phases of nickel–iron, found in the octahedrite shapes of iron meteorite crystals and some pallasites.
Iron meteorites are very often formed ...
s) of that material, which are preserved when the metal is worked cold or at low temperature. Those artifacts include, for example, a bead from the 5th millennium BC found in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and spear tips and ornaments from ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
and Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
around 4000 BC.Tylecote (1992). p. 3.
These early uses appear to have been largely ceremonial or decorative. Meteoric iron is very rare, and the metal was probably very expensive, perhaps more expensive than gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
. The early Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
are known to have barter
In trade, barter (derived from ''bareter'') is a system of exchange (economics), exchange in which participants in a financial transaction, transaction directly exchange good (economics), goods or service (economics), services for other goods ...
ed iron (meteoric or smelted) for silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, at a rate of 40 times the iron's weight, with Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
in the first centuries of the second millennium BC.
Meteoric iron was also fashioned into tools in the Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
when the Thule people of Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
began making harpoons, knives, ulus and other edged tools from pieces of the Cape York meteorite
The Cape York meteorite, also known as the Innaanganeq meteorite, is one of the largest known iron meteorites, classified as a medium octahedrite in chemical group IIIAB meteorites, IIIAB. In addition to many small fragments, at least eight large ...
. Typically pea-size bits of metal were cold-hammered into disks and fitted to a bone handle. These artifacts were also used as trade goods with other Arctic peoples: tools made from the Cape York meteorite have been found in archaeological sites more than distant. When the American polar explorer Robert Peary shipped the largest piece of the meteorite to the American Museum of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. Located in Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 21 interconn ...
in New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
in 1897, it still weighed over 33 tons. Another example of a late use of meteoric iron is an adze from around 1000 AD found in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
.
Native iron
Native iron in the metallic state occurs rarely as small inclusions in certainbasalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
rocks. Besides meteoritic iron, Thule people of Greenland have used native iron from the Disko region.
Iron smelting and the Iron Age
Iron smelting—the extraction of usable metal fromoxidized
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
iron ores—is more difficult than tin and copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
smelting. While these metals and their alloys can be cold-worked or melted in relatively simple furnaces (such as the kilns used for pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
) and cast into molds, smelted iron requires hot-working and can be melted only in specially designed furnaces. Iron is a common impurity in copper ores and iron ore was sometimes used as a flux
Flux describes any effect that appears to pass or travel (whether it actually moves or not) through a surface or substance. Flux is a concept in applied mathematics and vector calculus which has many applications in physics. For transport phe ...
, thus it is not surprising that humans mastered the technology of smelted iron only after several millennia of bronze metallurgy.
The place and time for the discovery of iron smelting is not known, partly because of the difficulty of distinguishing metal extracted from nickel-containing ores from hot-worked meteoritic iron. The archaeological evidence seems to point to the Middle East area, during the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
in the 3rd millennium BC. However, wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.05%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4.5%), or 0.25 for low carbon "mild" steel. Wrought iron is manufactured by heating and melting high carbon cast iron in an ...
artifacts remained a rarity until the 12th century BC.
The Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
is conventionally defined by the widespread replacement of bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
weapons and tools with those of iron and steel.Waldbaum (1978). pp. 56–58. That transition happened at different times in different places, as the technology spread. Mesopotamia was fully into the Iron Age by 900 BC. Although Egypt produced iron artifacts, bronze remained dominant until its conquest by Assyria in 663 BC. The Iron Age began in India about 1200 BC, in Central Europe about 800 BC, and in China about 300 BC. Around 500 BC, the Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
ns, who had learned from the Assyrians the use of iron and were expelled from Egypt, became major manufacturers and exporters of iron.
Ancient Near East
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, Anatolia and Egypt. Nineteen meteoric iron objects were found in the tomb
A tomb ( ''tumbos'') or sepulchre () is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called '' immurement'', alth ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
ian ruler Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun or Tutankhamen, (; ), was an Egyptian pharaoh who ruled during the late Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Born Tutankhaten, he instituted the restoration of the traditional polytheistic form of an ...
, who died in 1323 BC, including an iron dagger with a golden hilt, an Eye of Horus
The Eye of Horus, also known as left ''wedjat'' eye or ''udjat'' eye, specular to the Eye of Ra (right ''wedjat'' eye), is a concept and symbol in ancient Egyptian religion that represents well-being, healing, and protection. It derives from th ...
, the mummy's head-stand and sixteen models of an artisan's tools. An Ancient Egyptian sword bearing the name of pharaoh Merneptah
Merneptah () or Merenptah (reigned July or August 1213–2 May 1203 BCE) was the fourth pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty of Ancient Egypt. According to contemporary historical records, he ruled Egypt for almost ten y ...
as well as a battle axe with an iron blade and gold-decorated bronze shaft were both found in the excavation of Ugarit
Ugarit (; , ''ủgrt'' /ʾUgarītu/) was an ancient port city in northern Syria about 10 kilometers north of modern Latakia. At its height it ruled an area roughly equivalent to the modern Latakia Governorate. It was discovered by accident in 19 ...
.Richard Cowen, ''The Age of Iron'', Chapter 5 in a series of essays on Geology, History, and People prepares for a course of the University of California at DavisOnline version
accessed on 2010-02-11. Although iron objects dating from the
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
have been found across the Eastern Mediterranean, bronzework appears to have greatly predominated during this period.Waldbaum (1978): 23. As the technology spread, iron came to replace bronze as the dominant metal used for tools and weapons across the Eastern Mediterranean (the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, Anatolia and Egypt).
Iron was originally smelted in bloomeries, furnaces where bellows were used to force air through a pile of iron ore and burning charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ca ...
. The carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
produced by the charcoal reduced the iron oxide
An iron oxide is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Ferric oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of which is rust.
Iron ...
from the ore to metallic iron. The bloomery, however, was not hot enough to melt the iron, so the metal collected in the bottom of the furnace as a spongy mass, or ''bloom''. Workers then repeatedly beat and folded it to force out the molten slag
The general term slag may be a by-product or co-product of smelting (pyrometallurgical) ores and recycled metals depending on the type of material being produced. Slag is mainly a mixture of metal oxides and silicon dioxide. Broadly, it can be c ...
. This laborious, time-consuming process produced wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.05%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4.5%), or 0.25 for low carbon "mild" steel. Wrought iron is manufactured by heating and melting high carbon cast iron in an ...
, a malleable but fairly soft alloy.
Concurrent with the transition from bronze to iron was the discovery of carburization, the process of adding carbon to wrought iron. While the iron bloom contained some carbon, the subsequent hot-working oxidized
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
most of it. Smiths in the Middle East discovered that wrought iron could be turned into a much harder product by heating the finished piece in a bed of charcoal, and then quenching it in water or oil. This procedure turned the outer layers of the piece into steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
, an alloy of iron and iron carbides, with an inner core of less brittle iron.
Theories on the origin of iron smelting
The development of iron smelting was traditionally attributed to theHittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
of Anatolia of the Late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
.Muhly, James D. 'Metalworking/Mining in the Levant' pp. 174–183 in ''Near Eastern Archaeology'' ed. Suzanne Richard (2003), pp. 179–180. It was believed that they maintained a monopoly on iron working, and that their empire had been based on that advantage. According to that theory, the ancient Sea Peoples, who invaded the Eastern Mediterranean and destroyed the Hittite empire at the end of the Late Bronze Age, were responsible for spreading the knowledge through that region. This theory is no longer held in the mainstream of scholarship, since there is no archaeological evidence of the alleged Hittite monopoly. While there are some iron objects from Bronze Age Anatolia, the number is comparable to iron objects found in Egypt and other places of the same time period, and only a small number of those objects were weapons.
A more recent theory claims that the development of iron technology was driven by the disruption of the copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
and tin trade routes, due to the collapse of the empires at the end of the Late Bronze Age. These metals, especially tin, were not widely available and metal workers had to transport them over long distances, whereas iron ores were widely available. However, no known archaeological evidence suggests a shortage of bronze or tin in the Early Iron Age. Bronze objects remained abundant, and these objects have the same percentage of tin as those from the Late Bronze Age.
Indian subcontinent
Southern India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
(present day Mysore
Mysore ( ), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of Mysore district and Mysore division. As the traditional seat of the Wadiyar dynasty, the city functioned as the capital of the ...
) iron was in use 12th to 11th centuries BC. The technology of iron metallurgy advanced in the politically stable Maurya period and during a period of peaceful settlements in the 1st millennium BC.
Iron artifacts such as spikes, knives, dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually one or two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a cutting or stabbing, thrusting weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or ...
s, arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers c ...
-heads, bowls
Bowls, also known as lawn bowls or lawn bowling, is a sport in which players try to roll their ball (called a bowl) closest to a smaller ball (known as a "jack" or sometimes a "kitty"). The bowls are shaped (biased), so that they follow a curve ...
, spoons, saucepans, axe
An axe (; sometimes spelled ax in American English; American and British English spelling differences#Miscellaneous spelling differences, see spelling differences) is an implement that has been used for thousands of years to shape, split, a ...
s, chisel
A chisel is a hand tool with a characteristic Wedge, wedge-shaped cutting edge on the end of its blade. A chisel is useful for carving or cutting a hard material such as woodworking, wood, lapidary, stone, or metalworking, metal.
Using a chi ...
s, tongs
Tongs are a type of tool used to grip and lift objects instead of holding them directly with hands. There are many forms of tongs adapted to their specific use. Design variations include resting points so that the working end of the tongs d ...
, door fittings, etc., dated from 600 to 200 BC, have been discovered at several archaeological sites of India.Marco Ceccarelli (2000). ''International Symposium on History of Machines and Mechanisms: Proceedings HMM Symposium''. Springer. . p. 218 The Greek historian Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
wrote the first western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
account of the use of iron in India. The Indian mythological texts, the Upanishad
The Upanishads (; , , ) are late Vedic and post-Vedic Sanskrit texts that "document the transition from the archaic ritualism of the Veda into new religious ideas and institutions" and the emergence of the central religious concepts of Hind ...
s, have mentions of weaving, pottery and metallurgy, as well. The Romans had high regard for the excellence of steel from India in the time of the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an Indian empire during the classical period of the Indian subcontinent which existed from the mid 3rd century to mid 6th century CE. At its zenith, the dynasty ruled over an empire that spanned much of the northern Indian ...
.
 Perhaps as early as 500 BC, although certainly by 200 AD, high-quality steel was produced in southern India by the crucible technique. In this system, high-purity wrought iron, charcoal, and glass were mixed in a crucible and heated until the iron melted and absorbed the carbon. Iron chain was used in Indian suspension bridges as early as the 4th century.
Wootz steel was produced in India and
Perhaps as early as 500 BC, although certainly by 200 AD, high-quality steel was produced in southern India by the crucible technique. In this system, high-purity wrought iron, charcoal, and glass were mixed in a crucible and heated until the iron melted and absorbed the carbon. Iron chain was used in Indian suspension bridges as early as the 4th century.
Wootz steel was produced in India and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
from around 300 BC. Wootz steel is famous from Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
for its durability and ability to hold an edge. When asked by King Porus to select a gift, Alexander
Alexander () is a male name of Greek origin. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here ar ...
is said to have chosen, over gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
or silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, thirty pounds of steel. Wootz steel was originally a complex alloy with iron as its main component together with various trace element
__NOTOC__
A trace element is a chemical element of a minute quantity, a trace amount, especially used in referring to a micronutrient, but is also used to refer to minor elements in the composition of a rock, or other chemical substance.
In nutr ...
s. Recent studies have suggested that its qualities may have been due to the formation of carbon nanotubes
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range (nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized:
* ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''SWC ...
in the metal. According to Will Durant, the technology passed to the Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
and from them to Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
s who spread it through the Middle East.Will Durant (), '' The Story of Civilization I: Our Oriental Heritage'' In the 16th century, the Dutch carried the technology from South India to Europe, where it was mass-produced.
Steel was produced in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
from 300 BC by furnaces blown by the monsoon winds. The furnaces were dug into the crests of hills, and the wind was diverted into the air vents by long trenches. This arrangement created a zone of high pressure at the entrance, and a zone of low pressure at the top of the furnace. The flow is believed to have allowed higher temperatures than bellows-driven furnaces could produce, resulting in better-quality iron. Steel made in Sri Lanka was traded extensively within the region and in the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
.
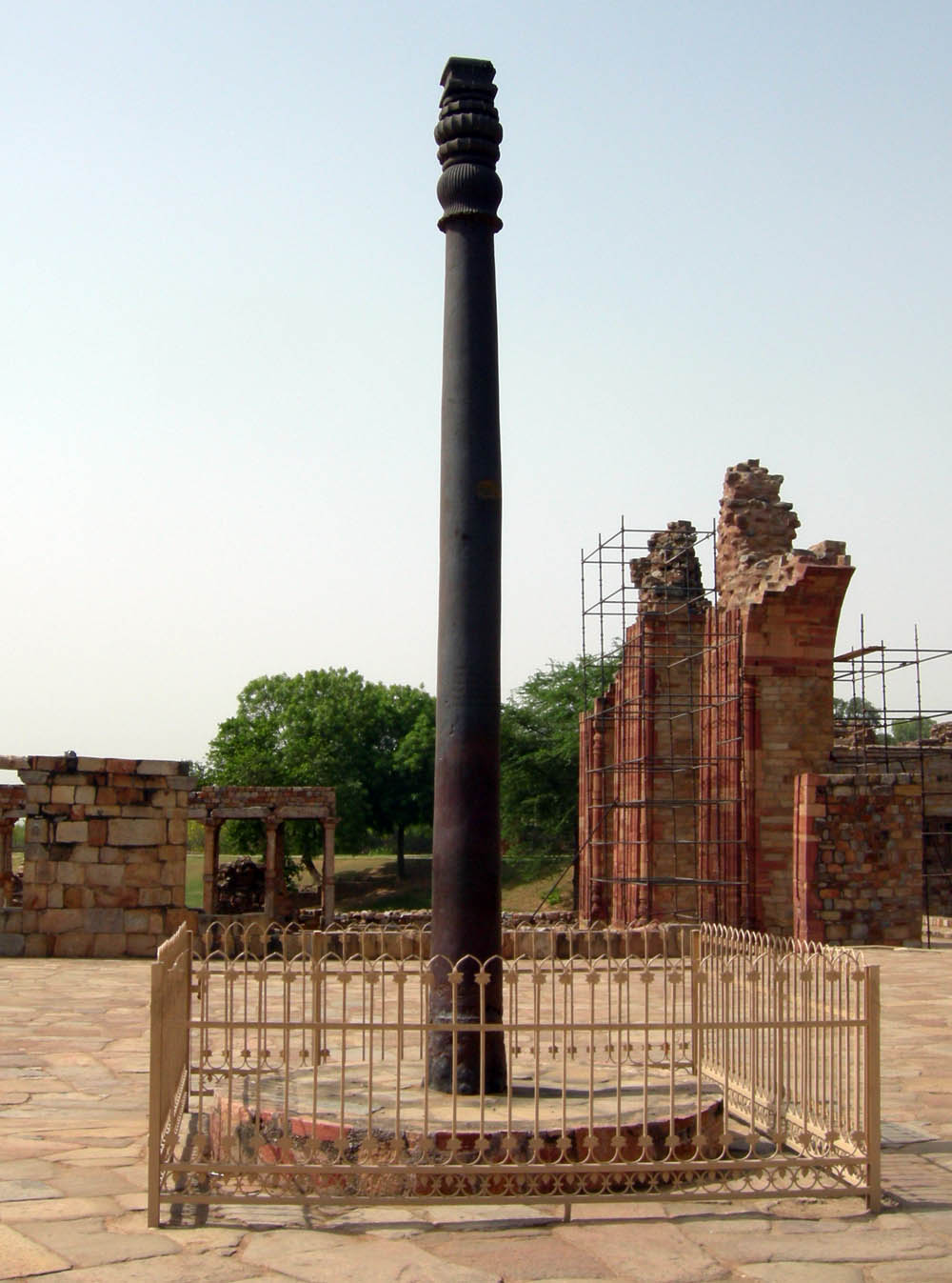
One of the world's foremost metallurgical curiosities is an iron pillar located in the Qutb complex in Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
. The pillar is made of wrought iron (98% Fe), is almost seven meters high and weighs more than six tonnes. The pillar was erected by Chandragupta II
Chandragupta II (r.c. 375–415), also known by his title Vikramaditya, as well as Chandragupta Vikramaditya, was an emperor of the Gupta Empire. Modern scholars generally identify him with King Chandra of the Iron pillar of Delhi, Delhi iron ...
Vikramaditya and has withstood 1,600 years of exposure to heavy rains with relatively little corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
.
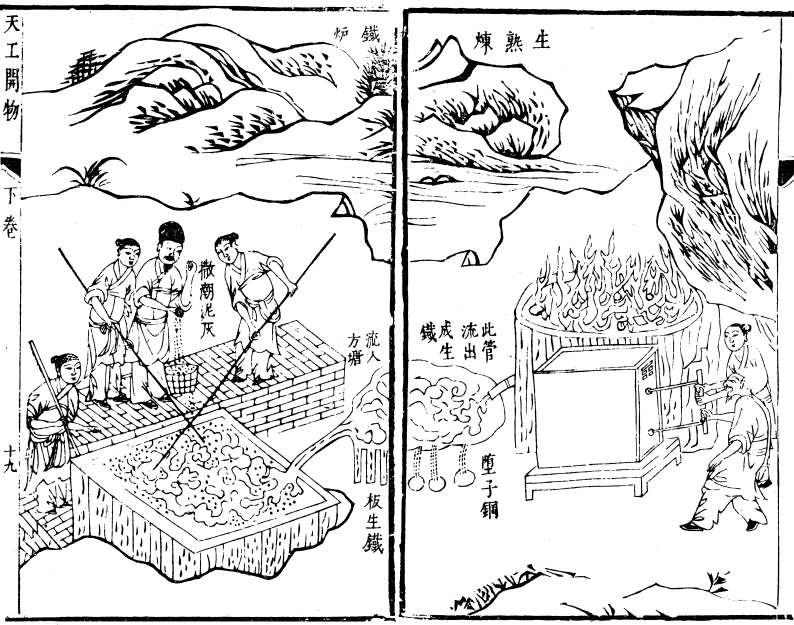
China
 Numerous scholars have suggested that the Afanasievo culture may be responsible for the introduction of
Numerous scholars have suggested that the Afanasievo culture may be responsible for the introduction of metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
to China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. In particular, contacts between the Afanasievo culture and the Majiayao culture
The Majiayao culture was a group of Neolithic communities who lived primarily in the upper Yellow River region in eastern Gansu, eastern Qinghai and northern Sichuan, China. The culture existed from 3300 to 2000 BC. The Majiayao culture represent ...
and the Qijia culture are considered for the transmission of bronze technology.
In 2008, two iron fragments were excavated at the Mogou site, in Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
. They have been dated to the 14th century BC, belonging to the period of Siwa culture. One of the fragments was made of bloomery iron rather than meteoritic iron.p. xl, Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, J, Woronoff & I. Spence
The earliest iron artifacts made from bloomeries in China date to end of the 9th century BC. Cast iron was used in ancient China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
for warfare, agriculture and architecture. Around 500 BC, metalworkers in the southern state of Wu achieved a temperature of 1130 °C. At this temperature, iron combines with 4.3% carbon and melts. The liquid iron can be cast
Cast may refer to:
Music
* Cast (band), an English alternative rock band
* Cast (Mexican band), a progressive Mexican rock band
* The Cast, a Scottish musical duo: Mairi Campbell and Dave Francis
* ''Cast'', a 2012 album by Trespassers William ...
into molds, a method far less laborious than individually forging each piece of iron from a bloom.
Cast iron is rather brittle and unsuitable for striking implements. It can be ''decarburized'' to steel or wrought iron by heating it in air for several days. In China, these iron working methods spread northward, and by 300 BC, iron was the material of choice throughout China for most tools and weapons. A mass grave in Hebei
Hebei is a Provinces of China, province in North China. It is China's List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, sixth-most populous province, with a population of over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. It bor ...
province, dated to the early 3rd century BC, contains several soldiers buried with their weapons and other equipment. The artifacts recovered from this grave are variously made of wrought iron, cast iron, malleabilized cast iron, and quench-hardened steel, with only a few, probably ornamental, bronze weapons.
 During the
During the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
(202 BC–220 AD), the government established ironworking as a state monopoly, repealed during the latter half of the dynasty and returned to private entrepreneurship, and built a series of large blast furnaces in Henan
Henan; alternatively Honan is a province in Central China. Henan is home to many heritage sites, including Yinxu, the ruins of the final capital of the Shang dynasty () and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the historical capitals of China, Lu ...
province, each capable of producing several tons of iron per day. By this time, Chinese metallurgists had discovered how to fine molten pig iron, stirring it in the open air until it lost its carbon and could be hammered (wrought). In modern Mandarin- Chinese, this process is now called ''chao'', literally stir frying. Pig iron is known as 'raw iron', while wrought iron is known as 'cooked iron'. By the 1st century BC, Chinese metallurgists had found that wrought iron and cast iron could be melted together to yield an alloy of intermediate carbon content, that is, steel.
According to legend, the sword of Liu Bang
Emperor Gaozu of Han (2561 June 195 BC), also known by his given name Liu Bang, was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning from 202 to 195 BC. He is considered by traditional Chinese historiography to be one o ...
, the first Han emperor, was made in this fashion. Some texts of the era mention "harmonizing the hard and the soft" in the context of ironworking; the phrase may refer to this process. The ancient city of Wan ( Nanyang) from the Han period forward was a major center of the iron and steel industry. Along with their original methods of forging steel, the Chinese had also adopted the production methods of creating Wootz steel, an idea imported from India to China by the 5th century AD.
During the Han dynasty, the Chinese were also the first to apply hydraulic power (i.e. a waterwheel) in working the bellows of the blast furnace. This was recorded in the year 31 AD, as an innovation by the Chinese mechanical engineer and politician Du Shi
Du Shi (, d. 38'' Book of Later Han'', vol. 31Crespigny, 183.) was a Chinese hydrologist, inventor, mechanical engineer, metallurgist, and politician of the Eastern Han dynasty. Du Shi is credited with being the first to apply hydraulic power ...
, Prefect
Prefect (from the Latin ''praefectus'', substantive adjectival form of ''praeficere'': "put in front", meaning in charge) is a magisterial title of varying definition, but essentially refers to the leader of an administrative area.
A prefect' ...
of Nanyang. Although Du Shi was the first to apply water power to bellows in metallurgy, the first drawn and printed illustration of its operation with water power appeared in 1313 AD, in the Yuan dynasty era text called the ''Nong Shu''.
In the 11th century, there is evidence of the production of steel in Song China using two techniques: a "berganesque" method that produced inferior, heterogeneous steel and a precursor to the modern Bessemer process that utilized partial decarbonization via repeated forging under a cold blast. By the 11th century, there was a large amount of deforestation in China due to the iron industry's demands for charcoal.(2006). 158. By this time however, the Chinese had learned to use bituminous coke to replace charcoal, and with this switch in resources many acres of prime timberland in China were spared.
Iron Age Europe
The earliest iron objects found in Europe date from the 3rd millennium BC, and are assigned to the Yamnaya culture and Catacomb culture. Eastern Europe, especially the Cis-Ural region, shows the highest concentration of early and middle Bronze Age iron objects in western Eurasia, though most of these are thought to consist of meteoric Iron. A knife blade from the Catacomb culture dated to c. 2300 BC is thought to have been made from smelted iron. During most of the Middle and LateBronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
in Central Europe, iron was present, though scarce. It was used for personal ornaments and small knives, for repairs on bronzes, and for bimetallic items. Early smelted iron finds from central Europe include an iron knife or sickle from Ganovce in Slovakia, possibly dating from the 18th-15th century BC, an iron ring from Vorwohlde in Germany dating from circa the 15th century BC, and an iron chisel from Heegermühle in Germany dating from circa 1000 BC. Smelted iron objects are known from Eastern Europe dating from after 1200 BC.
In the 11th century BC iron swords replaced bronze swords in Southern Europe, especially in Greece, and in the 10th century BC iron became the prevailing metal in use. In the Carpathian Basin there is a significant increase in iron finds dating from the 10th century BC onwards, with some finds possibly dating as early as the 12th century BC. Iron swords have been found in central Europe dating from the 10th century BC; however, the Iron Age began in earnest with the Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe (Hallst ...
from 800 BC. Steel was produced from circa 800 BC as part of the production of swords, and swords made entirely of high-carbon steel are known from pre-Roman period. Evidence for iron metallurgy in Britain dates from the 10th century BC, with the beginning of the Iron Age dated to the 8th century BC. The production of high-carbon steel is attested in Britain from circa 490 BC. Iron metallurgy began to be practised in Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
during the later Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
from at least the 9th century BC, with evidence for steel production from 800–700 BC. Iron and steel artefacts, including high-carbon steel, were manufactured in northern Sweden, Finland and Norway (in the Cap of the North) from c. 200–50 BC. Evidence for iron metallurgy in Italy and Sardinia dates from the Late Bronze Age (c. 1350-950 BC). High-carbon steel tools were produced in Iberia (Portugal) from c. 900 BC.
From 500 BC the La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a Iron Age Europe, European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman Republic, Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age ...
saw a significant increase in iron production, with iron metallurgy also becoming common in southern Scandinavia. The spread of ironworking in Central and Western Europe is associated with Celtic expansion. By the 1st century BC, Noric steel was famous for its quality and sought-after by the Roman military. The annual output of iron in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
is estimated at 84,750 tonnes
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
.
The production of ultrahigh carbon steel is attested at the Germanic site of Heeten
Raalte () is a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality and a town in the heart of the region of Salland in the Netherlands, Dutch Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Overijssel.
Population centres
The municipality consists of the ...
in the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
from the 2nd to 4th/5th centuries AD, in the Late Roman Iron Age.
Sub-Saharan Africa
 Archaeometallurgical scientific knowledge and technological development originated in numerous centers of Africa; the centers of origin were located in
Archaeometallurgical scientific knowledge and technological development originated in numerous centers of Africa; the centers of origin were located in West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
, Central Africa
Central Africa (French language, French: ''Afrique centrale''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''África central''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''África Central'') is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries accordin ...
, and East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
; consequently, as these origin centers are located within inner Africa, these archaeometallurgical developments are thus native African technologies. Iron metallurgical development occurred 2631 BCE – 2458 BCE at Lejja, in Nigeria, 2136 BCE – 1921 BCE at Obui, in Central Africa Republic, 1895 BCE – 1370 BCE at Tchire Ouma 147, in Niger, and 1297 BCE – 1051 BCE at Dekpassanware, in Togo.
Though there is some uncertainty, some archaeologists believe that iron metallurgy was developed independently in sub-Saharan Africa (possibly in West Africa).Eggert (2014). pp51
��59. Inhabitants of Termit, in eastern
Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
, smelted iron around 1500 BC.
In the region of the Aïr Mountains
The Aïr Mountains or Aïr Massif (Air Tamajeq language, Tamajăq: ''Ayǝr''; Hausa language, Hausa: Eastern ''Azbin'', Western ''Abzin'') is a triangular massif, located in northern Niger, within the Sahara. Part of the West Sa ...
in Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
there are also signs of independent copper smelting between 2500 and 1500 BC. The process was not in a developed state, indicating smelting was not foreign. It became mature about 1500 BC.
Archaeological sites containing iron smelting furnaces and slag have also been excavated at sites in the Nsukka region of southeast Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
in what is now Igboland
Igbo land ( Standard ) is a cultural and common linguistic region in southeastern Nigeria which is the indigenous homeland of the Igbo people. Geographically, it is divided into two sections, eastern (the larger of the two) and western. Its popu ...
: dating to 2000 BC at the site of Lejja (Eze-Uzomaka 2009) and to 750 BC and at the site of Opi (Holl 2009). The site of Gbabiri (in the Central African Republic) has yielded evidence of iron metallurgy, from a reduction furnace and blacksmith workshop; with earliest dates of 896–773 BC and 907–796 BC respectively.Eggert (2014). pp53
��54. Similarly, smelting in bloomery-type furnaces appear in the
Nok culture
The Nok culture is a population whose material remains are named after the Ham people, Ham village of Nok in Southern Kaduna, southern Kaduna State of Nigeria, where their terracotta sculptures were first discovered in 1928. The Nok people and ...
of central Nigeria by about 550 BC and possibly a few centuries earlier.
There is also evidence that carbon steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states:
* no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt ...
was made in Western Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
by the ancestors of the Haya people as early as 2,300 to 2,000 years ago (about 300 BC or soon after) by a complex process of "pre-heating" allowing temperatures inside a furnace to reach 1300 to 1400 °C.
Iron and copper working spread southward through the continent, reaching the Cape
A cape is a clothing accessory or a sleeveless outer garment of any length that hangs loosely and connects either at the neck or shoulders. They usually cover the back, shoulders, and arms. They come in a variety of styles and have been used th ...
around AD 200. The widespread use of iron revolutionized the Bantu-speaking farming communities who adopted it, driving out and absorbing the rock tool using hunter-gatherer societies they encountered as they expanded to farm wider areas of savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
. The technologically superior Bantu-speakers spread across southern Africa and became wealthy and powerful, producing iron for tools and weapons in large, industrial quantities.
The earliest records of bloomery-type furnaces in East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
are discoveries of smelted iron and carbon in Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
that date back between the 7th and 6th centuries BC, particularly in Meroe where there are known to have been ancient bloomeries that produced metal tools for the Nubians and Kushites and produced surplus for their economy.

Medieval Islamic world
Iron technology was further advanced by severalinventions in medieval Islam
The following is a list of inventions, discoveries and scientific advancements made in the medieval Muslim world, Islamic world, especially during the Islamic Golden Age,George Saliba (1994), ''A History of Arabic Astronomy: Planetary Theories Du ...
, during the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century.
This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign o ...
. By the 11th century, every province throughout the Muslim world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
had these industrial mills in operation, from Al-Andalus, Islamic Spain and North Africa in the west to the Middle East and Central Asia in the east. There are also 10th-century references to cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
, as well as archeological evidence of blast furnaces being used in the Ayyubid and Mamluk empires from the 11th century, thus suggesting a diffusion of Chinese metal technology to the Islamic world.
One of the most famous steels produced in the medieval Near East was Damascus steel used for swordmaking, and mostly produced in Damascus, Syria, in the period from 900 to 1750. This was produced using the crucible steel method, based on the earlier Indian wootz steel. This process was adopted in the Middle East using locally produced steels. The exact process remains unknown, but it allowed carbides to precipitate out as micro particles arranged in sheets or bands within the body of a blade. Carbides are far harder than the surrounding low carbon steel, so swordsmiths could produce an edge that cut hard materials with the precipitated carbides, while the bands of softer steel let the sword as a whole remain tough and flexible. A team of researchers based at the Technische Universität Dresden, Technical University of Dresden that uses X-rays and electron microscopy to examine Damascus steel discovered the presence of cementite nanowires and carbon nanotubes. Peter Paufler, a member of the Dresden team, says that these nanostructures give Damascus steel its distinctive properties and are a result of the forging process.
Medieval and early modern Europe
There was no fundamental change in the technology of iron production in Europe for many centuries. European metal workers continued to produce iron in bloomeries. However, the Medieval period brought two developments—the use of water power in the bloomery process in various places (outlined above), and the first European production in cast iron.Powered bloomeries
Sometime in the medieval period, water power was applied to the bloomery process. It is possible that this was at the Cistercian Abbey of Clairvaux Abbey, Clairvaux as early as 1135, but it was certainly in use in early 13th century France and Sweden. In England, the first clear documentary evidence for this is the accounts of a forge of the Bishop of Durham, near Bedburn in 1408, but that was certainly not the first such ironworks. In the Furness district of England, powered bloomeries were in use into the beginning of the 18th century, and near Garstang until about 1770. The Catalan Forge was a variety of powered bloomery. Bloomeries with hot blast were used in upstate New York State, New York in the mid-19th century.Blast furnace
 The preferred method of iron production in Europe until the development of the puddling (metallurgy), puddling process in 1783–84. Cast iron development lagged in Europe because wrought iron was the desired product and the intermediate step of producing cast iron involved an expensive blast furnace and further refining of pig iron to cast iron, which then required a labor and capital intensive conversion to wrought iron.
Through a good portion of the Middle Ages, in Western Europe, iron was still being made by the working of iron blooms into wrought iron. Some of the earliest casting of iron in Europe occurred in Sweden, in two sites, Lapphyttan and Vinarhyttan, between 1150 and 1350. Some scholars have speculated the practice followed the Mongols across Russia to these sites, but there is no clear proof of this hypothesis, and it would certainly not explain the pre-Mongol datings of many of these iron-production centres. In any event, by the late 14th century, a market for cast iron goods began to form, as a demand developed for cast iron cannonballs.
The preferred method of iron production in Europe until the development of the puddling (metallurgy), puddling process in 1783–84. Cast iron development lagged in Europe because wrought iron was the desired product and the intermediate step of producing cast iron involved an expensive blast furnace and further refining of pig iron to cast iron, which then required a labor and capital intensive conversion to wrought iron.
Through a good portion of the Middle Ages, in Western Europe, iron was still being made by the working of iron blooms into wrought iron. Some of the earliest casting of iron in Europe occurred in Sweden, in two sites, Lapphyttan and Vinarhyttan, between 1150 and 1350. Some scholars have speculated the practice followed the Mongols across Russia to these sites, but there is no clear proof of this hypothesis, and it would certainly not explain the pre-Mongol datings of many of these iron-production centres. In any event, by the late 14th century, a market for cast iron goods began to form, as a demand developed for cast iron cannonballs.
Finery forge
An alternative method of decarburization, decarburisingpig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate good used by the iron industry in the production of steel. It is developed by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with si ...
was the finery forge
A finery forge is a forge used to produce wrought iron from pig iron by decarburization in a process called "fining" which involved liquifying cast iron in a fining hearth and decarburization, removing carbon from the molten cast iron through Redo ...
, which seems to have been devised in the region around Namur (city), Namur in the 15th century. By the end of that century, this Walloon process spread to the ''Pay de Bray'' on the eastern boundary of Normandy, and then to England, where it became the main method of making wrought iron by 1600. It was introduced to Sweden by Louis De Geer (1587–1652), Louis de Geer in the early 17th century and was used to make the oregrounds iron favoured by English steelmakers.
A variation on this was the Finery forge#German forge, German forge. This became the main method of producing bar iron in Sweden.
Cementation process
In the early 17th century, ironworkers in Western Europe had developed the cementation process for carburization, carburizingwrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.05%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4.5%), or 0.25 for low carbon "mild" steel. Wrought iron is manufactured by heating and melting high carbon cast iron in an ...
. Wrought iron bars and charcoal were packed into stone boxes, then sealed with clay to be held at a red heat continually tended in an oxygen-free state immersed in nearly pure carbon (charcoal) for up to a week. During this time, carbon diffused into the surface layers of the iron, producing ''cement steel'' or ''blister steel''—also known as case hardened, where the portions wrapped in iron (the pick or axe blade) became harder, than say an axe hammer-head or shaft socket which might be insulated by clay to keep them from the carbon source. The earliest place where this process was used in England was at Coalbrookdale from 1619, where Sir Basil Brooke had two cementation furnaces (recently excavated in 2001–2005). For a time in the 1610s, he owned a patent on the process, but had to surrender this in 1619. He probably used Forest of Dean iron as his raw material, but it was soon found that oregrounds iron was more suitable. The quality of the steel could be improved by faggoting (metalworking), faggoting, producing the so-called shear steel.
Crucible steel
In the 1740s, Benjamin Huntsman found a means of melting blister steel, made by the cementation process, in crucibles. The resulting crucible steel, usually cast in ingots, was more homogeneous than blister steel.Tylecote (1992).Transition to coke in England
Beginnings
Early iron smelting used charcoal as both the heat source and the reducing agent. By the 18th century, the availability of wood for making charcoal was limiting the expansion of iron production, so that England became increasingly dependent for a considerable part of the iron required by its industry, on Sweden (from the mid-17th century) and then from about 1725 also on Russia. Smelting with coal (or its derivative coke (fuel), coke) was a long sought objective. The production of pig iron with coke was probably achieved by Dud Dudley around 1619, and with a mixed fuel made from coal and wood again in the 1670s. However this was probably only a technological rather than a commercial success. Shadrach Fox may have smelted iron with coke at Coalbrookdale in Shropshire in the 1690s, but only to make cannonballs and other cast iron products such as shells. However, in the peace after the Nine Years War, there was no demand for these.Abraham Darby and his successors
In 1707, Abraham Darby I patented a method of making cast iron pots. His pots were thinner and hence cheaper than those of his rivals. Needing a larger supply of pig iron he leased the blast furnace at Coalbrookdale in 1709. There, he made iron using coke, thus establishing the first successful business in Europe to do so. His products were all of cast iron, though his immediate successors attempted (with little commercial success) to fine this to bar iron. Wrought iron, Bar iron thus continued normally to be made with charcoal pig iron until the mid-1750s. In 1755 Abraham Darby II (with partners) opened a new coke-using furnace at Horsehay in Shropshire, and this was followed by others. These supplied coke pig iron to finery forges of the traditional kind for the production of wrought iron, bar iron. The reason for the delay remains controversial.New forge processes
 It was only after this that economically viable means of converting pig iron to bar iron began to be devised. A process known as potting and stamping was devised in the 1760s and improved in the 1770s, and seems to have been widely adopted in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands from about 1785. However, this was largely replaced by Henry Cort's puddling process, patented in 1784, but probably only made to work with grey pig iron in about 1790. These processes permitted the great expansion in the production of iron that constitutes the Industrial Revolution for the iron industry.
In the early 19th century, Hall discovered that the addition of iron oxide to the charge of the puddling furnace caused a violent reaction, in which the pig iron was decarburization, decarburised, this became known as 'wet puddling'. It was also found possible to produce steel by stopping the puddling (metallurgy), puddling process before decarburisation was complete.
It was only after this that economically viable means of converting pig iron to bar iron began to be devised. A process known as potting and stamping was devised in the 1760s and improved in the 1770s, and seems to have been widely adopted in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands from about 1785. However, this was largely replaced by Henry Cort's puddling process, patented in 1784, but probably only made to work with grey pig iron in about 1790. These processes permitted the great expansion in the production of iron that constitutes the Industrial Revolution for the iron industry.
In the early 19th century, Hall discovered that the addition of iron oxide to the charge of the puddling furnace caused a violent reaction, in which the pig iron was decarburization, decarburised, this became known as 'wet puddling'. It was also found possible to produce steel by stopping the puddling (metallurgy), puddling process before decarburisation was complete.
Hot blast
The efficiency of the blast furnace was improved by the change to hot blast, patented by James Beaumont Neilson in Scotland in 1828. This further reduced production costs. Within a few decades, the practice was to have a 'stove' as large as the furnace next to it into which the waste gas (containing CO) from the furnace was directed and burnt. The resultant heat was used to preheat the air blown into the furnace.Industrial steelmaking
 Apart from some production of puddled steel, English steel continued to be made by the cementation process, sometimes followed by remelting to produce crucible steel. These were batch-based processes whose raw material was bar iron, particularly Swedish oregrounds iron.
The problem of mass-producing cheap steel was solved in 1855 by Henry Bessemer, with the introduction of the Bessemer process, Bessemer converter at his steelworks in Sheffield, England. (An early converter can still be seen at the city's Kelham Island Museum). In the Bessemer process, molten pig iron from the blast furnace was charged into a large crucible, and then air was blown through the molten iron from below, igniting the dissolved carbon from the coke. As the carbon burned off, the melting point of the mixture increased, but the heat from the burning carbon provided the extra energy needed to keep the mixture molten. After the carbon content in the melt had dropped to the desired level, the air draft was cut off: a typical Bessemer converter could convert a 25-ton batch of pig iron to steel in half an hour.
In the 1860s development of regenerative furnaces and higher temperature refractory lining allowed to melt steel in an open hearth. That was slow and energy intensive, but allowed to better control the chemical makeup of the product and recycle iron scrap.
The acidic refractory lining of Bessemer converters and early open hearths didn't allow to remove phosphorus from steel with lime, which prolonged the life of puddling furnaces in order to utilize phosphorous iron ores abundant in Continental Europe. However, in the 1870s Gilchrist–Thomas process was developed, and later basic lining was adopted for the open hearths as well.
Finally, the Basic oxygen steelmaking, basic oxygen process was introduced at the Voest-Alpine works in 1952; a modification of the basic Bessemer process, it lances oxygen from above the steel (instead of bubbling air from below), reducing the amount of nitrogen uptake into the steel. The basic oxygen process is used in all modern steelworks; the last Bessemer converter in the U.S. was retired in 1968. Furthermore, the last three decades have seen a massive increase in the mini-mill business, where scrap steel only is melted with an electric arc furnace. These mills only produced bar products at first, but have since expanded into flat and heavy products, once the exclusive domain of the integrated steelworks.
Until these 19th-century developments, steel was an expensive commodity and only used for a limited number of purposes where a particularly hard or flexible metal was needed, as in the cutting edges of tools and springs. The widespread availability of inexpensive steel powered the Second Industrial Revolution and modern society as we know it. Mild steel ultimately replaced wrought iron for almost all purposes, and wrought iron is no longer commercially produced. With minor exceptions, alloy steels only began to be made in the late 19th century. Stainless steel was developed on the eve of World War I and was not widely used until the 1920s.
Apart from some production of puddled steel, English steel continued to be made by the cementation process, sometimes followed by remelting to produce crucible steel. These were batch-based processes whose raw material was bar iron, particularly Swedish oregrounds iron.
The problem of mass-producing cheap steel was solved in 1855 by Henry Bessemer, with the introduction of the Bessemer process, Bessemer converter at his steelworks in Sheffield, England. (An early converter can still be seen at the city's Kelham Island Museum). In the Bessemer process, molten pig iron from the blast furnace was charged into a large crucible, and then air was blown through the molten iron from below, igniting the dissolved carbon from the coke. As the carbon burned off, the melting point of the mixture increased, but the heat from the burning carbon provided the extra energy needed to keep the mixture molten. After the carbon content in the melt had dropped to the desired level, the air draft was cut off: a typical Bessemer converter could convert a 25-ton batch of pig iron to steel in half an hour.
In the 1860s development of regenerative furnaces and higher temperature refractory lining allowed to melt steel in an open hearth. That was slow and energy intensive, but allowed to better control the chemical makeup of the product and recycle iron scrap.
The acidic refractory lining of Bessemer converters and early open hearths didn't allow to remove phosphorus from steel with lime, which prolonged the life of puddling furnaces in order to utilize phosphorous iron ores abundant in Continental Europe. However, in the 1870s Gilchrist–Thomas process was developed, and later basic lining was adopted for the open hearths as well.
Finally, the Basic oxygen steelmaking, basic oxygen process was introduced at the Voest-Alpine works in 1952; a modification of the basic Bessemer process, it lances oxygen from above the steel (instead of bubbling air from below), reducing the amount of nitrogen uptake into the steel. The basic oxygen process is used in all modern steelworks; the last Bessemer converter in the U.S. was retired in 1968. Furthermore, the last three decades have seen a massive increase in the mini-mill business, where scrap steel only is melted with an electric arc furnace. These mills only produced bar products at first, but have since expanded into flat and heavy products, once the exclusive domain of the integrated steelworks.
Until these 19th-century developments, steel was an expensive commodity and only used for a limited number of purposes where a particularly hard or flexible metal was needed, as in the cutting edges of tools and springs. The widespread availability of inexpensive steel powered the Second Industrial Revolution and modern society as we know it. Mild steel ultimately replaced wrought iron for almost all purposes, and wrought iron is no longer commercially produced. With minor exceptions, alloy steels only began to be made in the late 19th century. Stainless steel was developed on the eve of World War I and was not widely used until the 1920s.
Modern steel industry
 The steel industry is often considered an indicator of economic progress, because of the critical role played by steel in infrastructural and overall economic development. In 1980, there were more than 500,000 U.S. steelworkers. By 2000, the number of steelworkers had fallen to 224,000.
The boom and bust, economic boom in China and India caused a massive increase in the demand for steel. Between 2000 and 2005, world steel demand increased by 6%. Since 2000, several Indian and Chinese steel firms have risen to prominence, such as Tata Steel (which bought Corus Group in 2007), Baosteel Group and Shagang Group. , though, ArcelorMittal is the world's List of steel producers, largest steel producer. In 2005, the British Geological Survey stated China was the top steel producer with about one-third of the world share; Japan, Russia, and the US followed respectively.
The large production capacity of steel results in a significant amount of carbon dioxide emissions inherent related to the main production route. In 2019, it was estimated that 7 to 9% of the global carbon dioxide emissions resulted from the steel industry. Reduction of these emissions are expected to come from a shift in the main production route using cokes, more recycling of steel and the application of carbon capture and storage or carbon capture and utilization technology.
In 2008, steel began commodity market, trading as a commodity on the London Metal Exchange. At the end of 2008, the steel industry faced a sharp downturn that led to many cut-backs.
The steel industry is often considered an indicator of economic progress, because of the critical role played by steel in infrastructural and overall economic development. In 1980, there were more than 500,000 U.S. steelworkers. By 2000, the number of steelworkers had fallen to 224,000.
The boom and bust, economic boom in China and India caused a massive increase in the demand for steel. Between 2000 and 2005, world steel demand increased by 6%. Since 2000, several Indian and Chinese steel firms have risen to prominence, such as Tata Steel (which bought Corus Group in 2007), Baosteel Group and Shagang Group. , though, ArcelorMittal is the world's List of steel producers, largest steel producer. In 2005, the British Geological Survey stated China was the top steel producer with about one-third of the world share; Japan, Russia, and the US followed respectively.
The large production capacity of steel results in a significant amount of carbon dioxide emissions inherent related to the main production route. In 2019, it was estimated that 7 to 9% of the global carbon dioxide emissions resulted from the steel industry. Reduction of these emissions are expected to come from a shift in the main production route using cokes, more recycling of steel and the application of carbon capture and storage or carbon capture and utilization technology.
In 2008, steel began commodity market, trading as a commodity on the London Metal Exchange. At the end of 2008, the steel industry faced a sharp downturn that led to many cut-backs.
See also
* Bintie, a type of refined iron * Steel#History of steelmaking, History of steelmaking *Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
* List of alloys
* Nok culture
The Nok culture is a population whose material remains are named after the Ham people, Ham village of Nok in Southern Kaduna, southern Kaduna State of Nigeria, where their terracotta sculptures were first discovered in 1928. The Nok people and ...
* Non-ferrous extractive metallurgy
* Roman metallurgy
Citations
Bibliography
* Ebrey, Walthall, Palais (2006). ''East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History''. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company. * * * Needham, Joseph (1986). ''Science and Civilization in China: Volume 4, Part 2''; Needham, Joseph (1986). ''Science and Civilization in China: Volume 4, Part 3''. * *Further reading
* Knowles, Anne Kelly. (2013). ''Mastering Iron: The Struggle to Modernize an American Industry, 1800–1868'' (University of Chicago Press) 334 pages * Lam, Wengcheong (2014). ''Everything Old is New Again? Rethinking the transition to Cast Iron Production in the Plains of Central China'', Chinese University of Hong Kong * Pleiner, R. (2000). ''Iron in Archaeology. The European Bloomery Smelters'', Praha, Archeologický Ústav Av Cr. * Pounds, Norman J. G. (1957). "Historical Geography of the Iron and Steel Industry of France". ''Annals of the Association of American Geographers'' 47#1, pp. 3–14. . * Wagner, Donald (1996). ''Iron and Steel in Ancient China''. Leiden: E.J. Brill. * Woods, Michael and Mary B. Woods (2000). ''Ancient Construction (Ancient Technology)'' Runestone PressExternal links
* {{Authority control 4th-millennium BC establishments History of metallurgy Steelmaking