Irditoxin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Irditoxin is a
Irditoxin is a
 Irditoxin is a
Irditoxin is a three-finger toxin
Three-finger toxins (abbreviated 3FTx) are a protein superfamily of small toxin proteins found in the venom of snakes. Three-finger toxins are in turn members of a larger superfamily of three-finger protein domains which includes non-toxic prote ...
(3FTx) protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
found in the venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a sti ...
of the brown tree snake
The brown tree snake (''Boiga irregularis''), also known as the brown catsnake, is an arboreal rear-fanged colubrid snake native to eastern and northern coastal Australia, eastern Indonesia (Sulawesi to Papua), Papua New Guinea, and many island ...
(''Boiga irregularis'') and likely in other members of the genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
''Boiga
''Boiga'' is a large genus of rear-fanged, mildly venomous snakes, known commonly as cat-eyed snakes or simply cat snakes, in the family Colubridae. Species of the genus ''Boiga'' are native to southeast Asia, India, and Australia, but due to ...
''. It is a heterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex or multimer formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ...
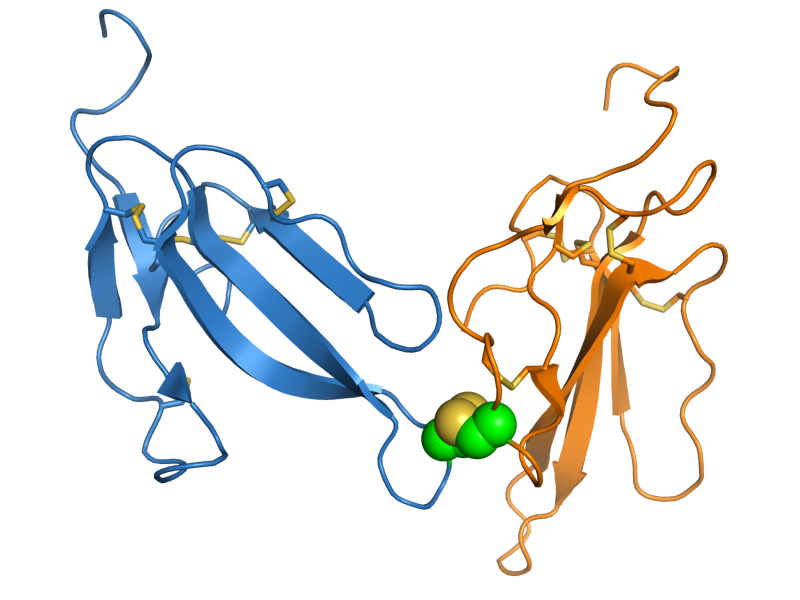
composed of two distinct protein chains, each of the three-finger protein fold, linked by an intermolecular disulfide bond
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups.
In inor ...
. This structure is unusual for 3FTx proteins, which are most commonly monomeric.
Structure
Three-finger toxin
Three-finger toxins (abbreviated 3FTx) are a protein superfamily of small toxin proteins found in the venom of snakes. Three-finger toxins are in turn members of a larger superfamily of three-finger protein domains which includes non-toxic prote ...
(3FTx) proteins canonically consist of approximately 60-80 amino acid residue
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s that assume a structure with three "finger"-like beta strand
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common structural motif, motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone chain, backbon ...
-containing loops projecting from a core stabilized by four intramolecular disulfide bonds. Irditoxin is a covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
heterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex or multimer formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ...
in which two subunits are linked by an intermolecular disulfide bond
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups.
In inor ...
. Each subunit is of the three-finger toxin
Three-finger toxins (abbreviated 3FTx) are a protein superfamily of small toxin proteins found in the venom of snakes. Three-finger toxins are in turn members of a larger superfamily of three-finger protein domains which includes non-toxic prote ...
(3FTx) protein superfamily
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping (clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred (see homology (biology), homology). Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if n ...
and is most closely related to the "non-conventional" 3FTx subclass, characterized by the presence of an additional disulfide bond in the first of the canonical three "finger" loops. Each subunit thus contains 11 cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as ...
residues: the eight canonical residues that form the core disulfide bonds, the two in the first loop forming the non-conventional disulfide, and the one that forms the dimeric linkage. Irditoxin subunits A and B are 75 and 77 amino acid residue
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s long, respectively, and each possess a seven-residue extension with a pyroglutamic acid
Pyroglutamic acid (also known as PCA, 5-oxoproline, pidolic acid) is a ubiquitous but understudied natural amino acid derivative in which the free amino group of glutamic acid or glutamine cyclizes to form a lactam. The names of pyroglutamic acid ...
post-translational modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biolog ...
at the N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amin ...
.
Irditoxin's structure is highly unusual within the 3FTx superfamily. Most 3FTx proteins are monomers. The best-studied exception is kappa-bungarotoxin, a non-covalent homodimer with a very different protein-protein interaction surface; the recently described alpha-cobratoxin also forms both covalent homodimers and low-abundance covalent heterodimers with other 3FTx proteins found in monocled cobra
The monocled cobra (''Naja kaouthia''), also called monocellate cobra and Indian spitting cobra, is a venomous cobra species widespread across South and Southeast Asia. It is characterized by a distinctive circular or "monocle"-shaped marking on ...
(''Naja kaouthia'') venom. It is as yet unclear how irditoxin's two subunits contribute to its biological activities.
Function
Irditoxin is an abundant protein in the venom of the brown tree snake and accounts for about 10% of the protein found in venom samples of brown treesnakes collected fromGuam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
, where they are an invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
. Irditoxin's toxic effects are highly species-dependent; in laboratory tests, it is highly toxic to lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic isla ...
s and bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s but not to mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s. Although the molecular mechanism of toxicity is not clear, irditoxin produces robust post- synaptic blockade of signaling in the avian neuromuscular junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation to ...
.
Discovery and nomenclature
Irditoxin was first described in 2009 after isolation from samples of venom from thebrown tree snake
The brown tree snake (''Boiga irregularis''), also known as the brown catsnake, is an arboreal rear-fanged colubrid snake native to eastern and northern coastal Australia, eastern Indonesia (Sulawesi to Papua), Papua New Guinea, and many island ...
. Its name is a contraction of "''B. irregularis'' dimeric toxin". Other ''Boiga
''Boiga'' is a large genus of rear-fanged, mildly venomous snakes, known commonly as cat-eyed snakes or simply cat snakes, in the family Colubridae. Species of the genus ''Boiga'' are native to southeast Asia, India, and Australia, but due to ...
'' species, and possibly other colubrid
Colubridae (, commonly known as colubrids , from , 'snake') is a family of snakes. With 249 genera, it is the largest snake family. The earliest fossil species of the family date back to the Late Eocene epoch, with earlier origins suspected. Colu ...
snakes, likely possess homologous proteins.
References
{{reflist, 32em Neurotoxins