Ipswich QLD (4) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ipswich () is a port town and
"England's Oldest Town"
Retrieved 2 August 2015. The settlement was of great economic importance to the
 The modern town took shape in Anglo-Saxon times (7th–8th centuries) around the
The modern town took shape in Anglo-Saxon times (7th–8th centuries) around the
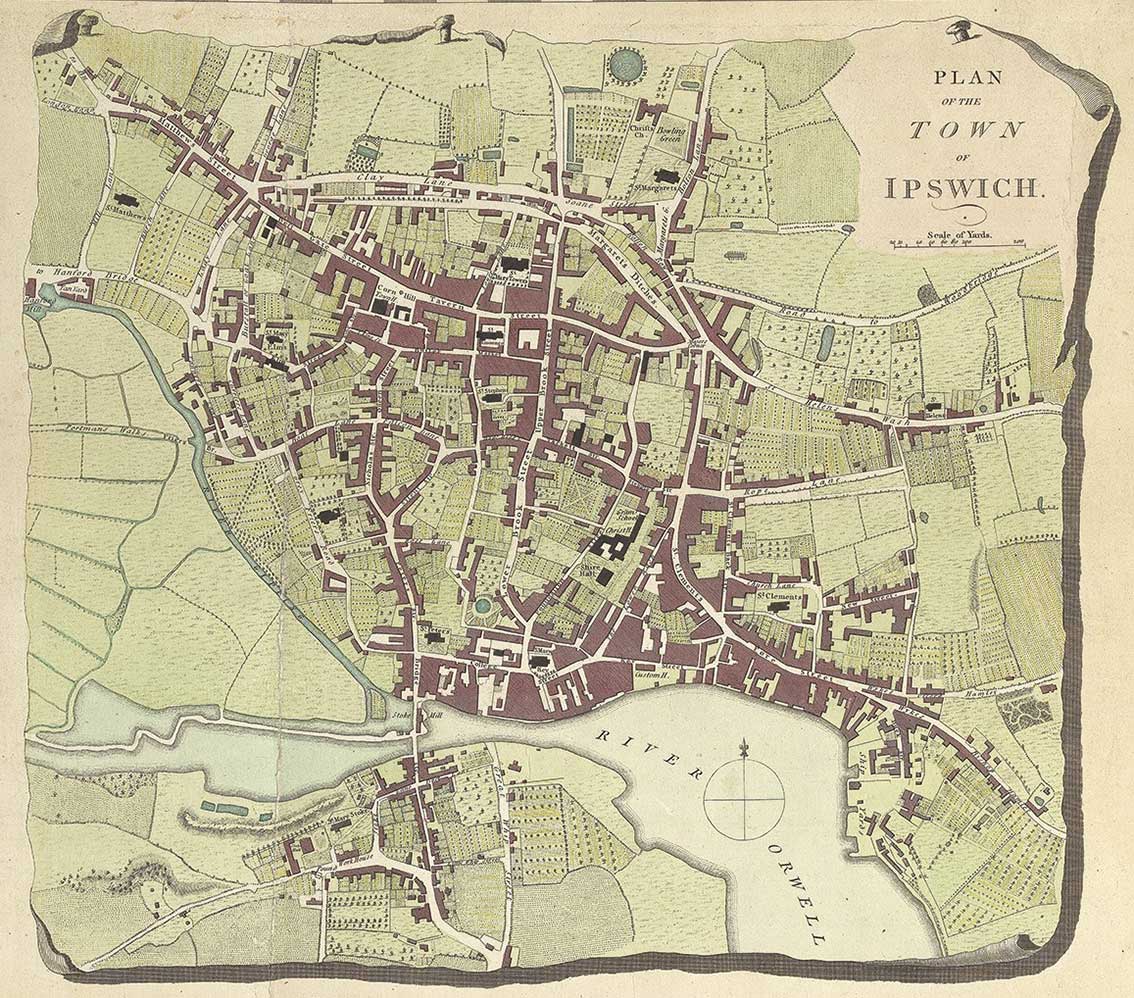 During the 14th to 17th centuries Ipswich was a
During the 14th to 17th centuries Ipswich was a  The painter Thomas Gainsborough lived and worked in Ipswich. In 1835, Charles Dickens stayed in Ipswich and used it as a setting for scenes in his novel ''The Pickwick Papers''. The hotel where he resided first opened in 1518; it was then known as The Tavern and later became known as the Great White Horse Hotel. Dickens made the hotel famous in chapter XXII of ''The Pickwick Papers'', vividly describing the hotel's meandering corridors and stairs.
The painter Thomas Gainsborough lived and worked in Ipswich. In 1835, Charles Dickens stayed in Ipswich and used it as a setting for scenes in his novel ''The Pickwick Papers''. The hotel where he resided first opened in 1518; it was then known as The Tavern and later became known as the Great White Horse Hotel. Dickens made the hotel famous in chapter XXII of ''The Pickwick Papers'', vividly describing the hotel's meandering corridors and stairs.
 Ipswich is home to many artists and has a number of galleries, the most prominent of which are at Christchurch Mansion, the Town Hall, Ancient House, Ipswich, Ancient House and the Artists' Gallery in Electric House. The visual arts are further supported with many sculptures at easily accessible sites. The Borough Council promotes the creation of new public works of art and has been known to make this a condition of planning permission. The town has three museums:
Ipswich is home to many artists and has a number of galleries, the most prominent of which are at Christchurch Mansion, the Town Hall, Ancient House, Ipswich, Ancient House and the Artists' Gallery in Electric House. The visual arts are further supported with many sculptures at easily accessible sites. The Borough Council promotes the creation of new public works of art and has been known to make this a condition of planning permission. The town has three museums:
 In addition to the Christchurch Mansion and Ancient House, Ipswich in the 21st century has some important cultural buildings including the New Wolsey Theatre and the Regent Theatre, Ipswich, Regent Theatre—the largest theatre venue in East Anglia where, in 1964, the Beatles performed when it was still known as the Gaumont. There is also the Corn Exchange, Ipswich, Corn Exchange in King Street which was completed in 1882.
There are several medieval Ipswich churches but the grandest is Ipswich Minster (previously known as St. Mary-le-Tower), rebuilt by the Victorians. Holy Trinity Church by the waterfront is one of the few churches in the country which was built during the reign of William IV and whilst the outside looks plain, the interior is quite spectacular. The world's oldest circle of church bells is housed in St Lawrence Church, Ipswich, St Lawrence Church, which is maintained by the Ipswich Historic Churches Trust.
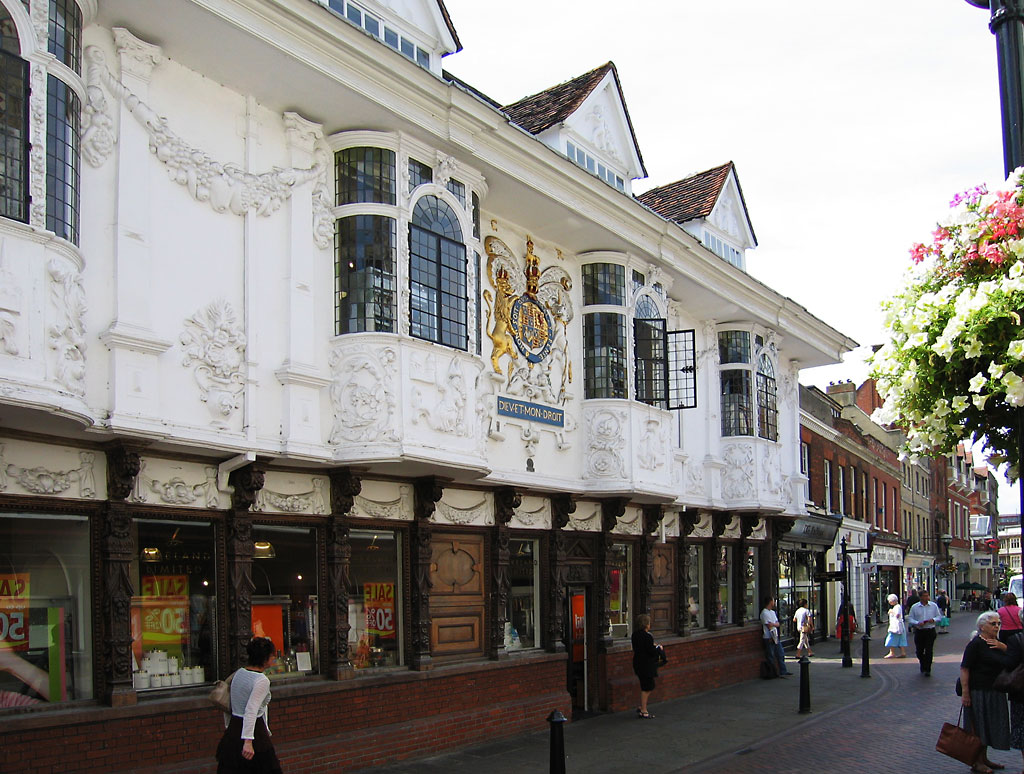
The Ancient House, Ipswich, Ancient House in the Buttermarket Centre, Ipswich, Buttermarket is an example of a merchant house which features tudor pargeting and the Ipswich window.
The former East Suffolk County Hall is just east of the centre of Ipswich. It is listed as a building at risk by the Victorian Society. The Town Hall remains in use as an arts centre and events venue; it dates from 1866 (architects: Bellamy & Hardy of Lincoln). The 18th Century Grade II listed Old Post Office, which was built in 1881, has been renovated and is now home to the Botanist bar.
Modern buildings include Endeavour House (headquarters of Suffolk County Council and formerly home of the TXU Corporation), Grafton House (home of Ipswich Borough Council) and Ipswich Crown Court, all located on Russell Road (Ipswich), Russell Road in the area known as the Ipswich Village Development, which includes Portman Road stadium. The stadium has hosted England under-21, under-23, and international soccer matches, as well as rugby union and hockey matches.
In the waterfront area The Mill (Ipswich), The Mill is the List of tallest buildings and structures in Ipswich, tallest building in
In addition to the Christchurch Mansion and Ancient House, Ipswich in the 21st century has some important cultural buildings including the New Wolsey Theatre and the Regent Theatre, Ipswich, Regent Theatre—the largest theatre venue in East Anglia where, in 1964, the Beatles performed when it was still known as the Gaumont. There is also the Corn Exchange, Ipswich, Corn Exchange in King Street which was completed in 1882.
There are several medieval Ipswich churches but the grandest is Ipswich Minster (previously known as St. Mary-le-Tower), rebuilt by the Victorians. Holy Trinity Church by the waterfront is one of the few churches in the country which was built during the reign of William IV and whilst the outside looks plain, the interior is quite spectacular. The world's oldest circle of church bells is housed in St Lawrence Church, Ipswich, St Lawrence Church, which is maintained by the Ipswich Historic Churches Trust.
The Ancient House, Ipswich, Ancient House in the Buttermarket Centre, Ipswich, Buttermarket is an example of a merchant house which features tudor pargeting and the Ipswich window.
The former East Suffolk County Hall is just east of the centre of Ipswich. It is listed as a building at risk by the Victorian Society. The Town Hall remains in use as an arts centre and events venue; it dates from 1866 (architects: Bellamy & Hardy of Lincoln). The 18th Century Grade II listed Old Post Office, which was built in 1881, has been renovated and is now home to the Botanist bar.
Modern buildings include Endeavour House (headquarters of Suffolk County Council and formerly home of the TXU Corporation), Grafton House (home of Ipswich Borough Council) and Ipswich Crown Court, all located on Russell Road (Ipswich), Russell Road in the area known as the Ipswich Village Development, which includes Portman Road stadium. The stadium has hosted England under-21, under-23, and international soccer matches, as well as rugby union and hockey matches.
In the waterfront area The Mill (Ipswich), The Mill is the List of tallest buildings and structures in Ipswich, tallest building in
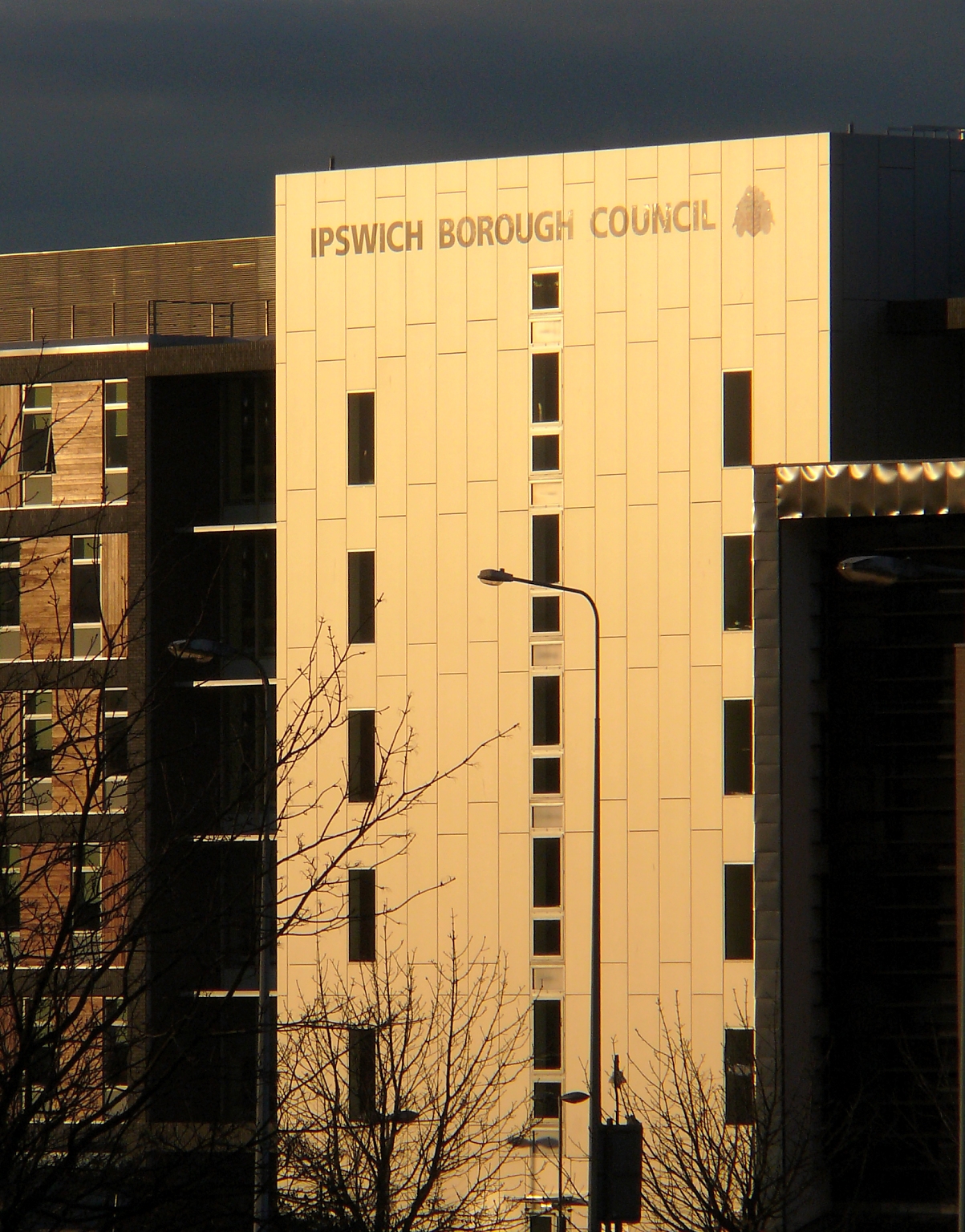 Ipswich is governed locally by a two-tier council system. Ipswich Borough Council fulfils non-metropolitan district, district council functions such as refuse collection, housing and planning and Suffolk County Council provides the County Council, county council services such as transport, education and social services.
The town is covered by two parliamentary constituencies: Ipswich (UK Parliament constituency), Ipswich, which is represented by Labour MP Jack Abbott (politician), Jack Abbott and covers about 75% of the town, and Central Suffolk and North Ipswich (UK Parliament constituency), Central Suffolk & North Ipswich, which covers the remaining 25% and is represented by Conservative MP Patrick Spencer.
In April 2006 the Non-metropolitan district, borough council initiated public discussions about the idea of turning the borough into a Unitary authority#United Kingdom, unitary authority; Ipswich had constituted a county borough from 1889 to 1974, independent of the administrative county of East Suffolk (county), East Suffolk, and this status was not restored by the Local Government Commission for England (1992), Banham/Cooksey Commission in the 1990s. Ipswich, Norwich, Exeter and Oxford united to campaign for unitary authority status for the four towns. In March 2007, it was announced that Ipswich was one of 16 shortlisted councils. In December 2007 plans were put into doubt as the government announced that it had "delayed" the unitary bids for Ipswich and Exeter. In July 2008 the Boundary Committee for England, Boundary Committee announced its preferred option was for a unitary authority covering Ipswich and the south eastern corner of Suffolk, including Felixstowe.
Ipswich is governed locally by a two-tier council system. Ipswich Borough Council fulfils non-metropolitan district, district council functions such as refuse collection, housing and planning and Suffolk County Council provides the County Council, county council services such as transport, education and social services.
The town is covered by two parliamentary constituencies: Ipswich (UK Parliament constituency), Ipswich, which is represented by Labour MP Jack Abbott (politician), Jack Abbott and covers about 75% of the town, and Central Suffolk and North Ipswich (UK Parliament constituency), Central Suffolk & North Ipswich, which covers the remaining 25% and is represented by Conservative MP Patrick Spencer.
In April 2006 the Non-metropolitan district, borough council initiated public discussions about the idea of turning the borough into a Unitary authority#United Kingdom, unitary authority; Ipswich had constituted a county borough from 1889 to 1974, independent of the administrative county of East Suffolk (county), East Suffolk, and this status was not restored by the Local Government Commission for England (1992), Banham/Cooksey Commission in the 1990s. Ipswich, Norwich, Exeter and Oxford united to campaign for unitary authority status for the four towns. In March 2007, it was announced that Ipswich was one of 16 shortlisted councils. In December 2007 plans were put into doubt as the government announced that it had "delayed" the unitary bids for Ipswich and Exeter. In July 2008 the Boundary Committee for England, Boundary Committee announced its preferred option was for a unitary authority covering Ipswich and the south eastern corner of Suffolk, including Felixstowe.
 Being the county town of agricultural Suffolk, industry around Ipswich has had a strong farming bias with Ransomes, Sims & Jefferies, Ransomes, Sims & Jefferies Ltd, one of the most famous agricultural manufacturers, located in the town. The world's first commercial lawnmower, motorised lawnmower was built by Ransomes in 1902. Ransomes & Rapier was a major British manufacturer of railway equipment and later cranes, from 1869 to 1987. There was a sugar beet factory at Ipswich for many years; it was closed in 2001 as part of a rationalisation by British Sugar. This agricultural link is preserved in the Ipswich Town F.C., local football club's nickname "The Tractor Boys". Phillips & Piper Ltd on Old Foundry Road employed many women who sewed equestrian and hunt jackets for Harrods, Pytchley, and other labels for 130 years, finally closing down in June 1982.
Being the county town of agricultural Suffolk, industry around Ipswich has had a strong farming bias with Ransomes, Sims & Jefferies, Ransomes, Sims & Jefferies Ltd, one of the most famous agricultural manufacturers, located in the town. The world's first commercial lawnmower, motorised lawnmower was built by Ransomes in 1902. Ransomes & Rapier was a major British manufacturer of railway equipment and later cranes, from 1869 to 1987. There was a sugar beet factory at Ipswich for many years; it was closed in 2001 as part of a rationalisation by British Sugar. This agricultural link is preserved in the Ipswich Town F.C., local football club's nickname "The Tractor Boys". Phillips & Piper Ltd on Old Foundry Road employed many women who sewed equestrian and hunt jackets for Harrods, Pytchley, and other labels for 130 years, finally closing down in June 1982.
 The British Telecom, British Telecom Research Laboratories were located to the east of the town in 1975 at
The British Telecom, British Telecom Research Laboratories were located to the east of the town in 1975 at
 Ipswich railway station is on the Great Eastern Main Line from Liverpool Street railway station, London to Norwich railway station, Norwich, the East Suffolk Line to Lowestoft railway station, Lowestoft and the Felixstowe Branch Line. Trains are run by Greater Anglia, which operates direct services to cities including London, Cambridge railway station, Cambridge, Chelmsford railway station, Chelmsford, Norwich railway station, Norwich and Peterborough railway station, Peterborough. Ipswich engine shed opened in 1846 and closed in 1968. Ipswich is still a signing-on point for locomotive crews and a Motive power depot#Stabling and fuelling points, stabling point. The town has a smaller suburban station at Derby Road railway station, Derby Road east of the town centre, on the Felixstowe branch line.
Ipswich is close to the A12 road (England), A12 and the A14 road (England), A14 roads. The Orwell Bridge which carries the A14 over the River Orwell connects it to the Port of Felixstowe, a major container port to the east.
Bus services in Ipswich are operated by Ipswich Buses, First Bus East of England, First Eastern Counties, Beestons and several smaller companies. Town services operate mainly from Tower Ramparts bus station and regional services from the Ipswich Old Cattle Market bus station. Ipswich Airport closed in 1996.
Ipswich is on Sustrans's National Cycle Route 1 and National Cycle Route 51.
Ipswich railway station is on the Great Eastern Main Line from Liverpool Street railway station, London to Norwich railway station, Norwich, the East Suffolk Line to Lowestoft railway station, Lowestoft and the Felixstowe Branch Line. Trains are run by Greater Anglia, which operates direct services to cities including London, Cambridge railway station, Cambridge, Chelmsford railway station, Chelmsford, Norwich railway station, Norwich and Peterborough railway station, Peterborough. Ipswich engine shed opened in 1846 and closed in 1968. Ipswich is still a signing-on point for locomotive crews and a Motive power depot#Stabling and fuelling points, stabling point. The town has a smaller suburban station at Derby Road railway station, Derby Road east of the town centre, on the Felixstowe branch line.
Ipswich is close to the A12 road (England), A12 and the A14 road (England), A14 roads. The Orwell Bridge which carries the A14 over the River Orwell connects it to the Port of Felixstowe, a major container port to the east.
Bus services in Ipswich are operated by Ipswich Buses, First Bus East of England, First Eastern Counties, Beestons and several smaller companies. Town services operate mainly from Tower Ramparts bus station and regional services from the Ipswich Old Cattle Market bus station. Ipswich Airport closed in 1996.
Ipswich is on Sustrans's National Cycle Route 1 and National Cycle Route 51.
 Ipswich's sole professional association football club is Ipswich Town F.C., Ipswich Town, which was established in 1878 and play at the 30,300-capacity Portman Road, Portman Road stadium. They have competed in the Premier League since the 2024–25 Premier League, 2024–25 season, following their promotion as runners-up from the EFL Championship in the 2023–24 EFL Championship, 2023–24 season. Elected to the English Football League, Football League in 1938, they have a strong East Anglian derby, rivalry with Norwich City F.C., Norwich City, and were the previous club of the two most successful England national football team, England managers; Alf Ramsey, who was buried in the Old Cemetery in the town on his death in 1999, and Bobby Robson. Ipswich won the First Division title in 1961–62 Football League, 1961–62 in their first season as a top division club during Ramsey's reign, as well as the 1977–78 FA Cup, 1978 FA Cup and the 1980–81 UEFA Cup, 1981 UEFA Cup under Robson. The club are also undefeated at home in all European competitions, having won 25 and drawn six of 31 matches.
Ipswich is also home to several non-League football clubs, including Ipswich Wanderers F.C., Ipswich Wanderers and Whitton United F.C., Whitton United in the Eastern Counties Football League, Eastern Counties League, and Achilles F.C., Achilles, Crane Sports F.C., Crane Sports, and Ransomes Sports F.C., Ransomes Sports among others in the Suffolk and Ipswich Football League, Suffolk & Ipswich League. The town has representation in both codes of Rugby football, rugby. There are two rugby union teams – Ipswich RFC, who play in London 2 North East League, and Ipswich YM RUFC – and one rugby league side – Ipswich Rhinos, who play in the Rugby League Conference. Ipswich Cardinals are an American football team, playing in the South-East Conference of BAFACL 1; the second tier of the BAFA Community Leagues.
The Motorcycle speedway, speedway team, the Ipswich Witches, have ridden at Foxhall Stadium on the outskirts of Ipswich since 1951 and have won the top-tier league title four times, the knock-out cup five times and the second-tier knock-out cup twice. The stadium is also used regularly for Hot Rods (oval racing), Hot Rod, Stock car racing in the United Kingdom, Stock Car and Banger racing events, hosting major events throughout the year on the stadium's outer tarmac oval.
Ipswich Gymnastics Centre is one of only three fully London Organising Committee for the Olympic Games, Olympic accredited gymnastics facilities in the United Kingdom, UK.
Ipswich has a rich history of public swimming. During the 1830s, there were at least three designated swimming places – one was near St Cement's, the second was next to St Mary-at-the-Quay Church, Ipswich, St Mary-At-The Quay and the third not far from Stoke Bridge. These were all closed in the late 1830s during the building of the wet dock. A designated enclosed area of the River Orwell, called Stoke Bathing Place, was created to cater for the swimmers. It was damaged in the floods of 1953 but maps show the swimming place still in situ as late as 1973. Ipswich Swimming, formed in 1884 as Ipswich Swimming Club, used the Stoke Swimming Place. Fore Street Swimming Pool opened in 1894. The pool is still in use and is the second oldest swimming pool in is in the UK. Pipers Vale Pool opened in 1937 after replacing the West End Bathing Place, which had closed in 1936 due to fears that it was polluting the River Orwell. Broomhill Pool, Broom Hill pool opened, in 1986, which was prompted to serve the western side of the town. It closed in 2002 but is about to be restored with the plan of opening again in 2025/26. St Matthew's Baths was opened in 1924 and closed in 1984 when Crown Pools opened, which is still in use. The Ipswich Swimming Club, is based there although they use the Fore Street Swimming Pool, Fore Street swimming pool, too. The most successful Ipswich Swimming Club member is FINA World Aquatics Championships, World Championship gold medallist Karen Pickering. There are plans for a new "low carbon aquatics centre" with the intention of opening next to Ipswich Town F.C., Ipswich Town Football Club in 2027.
Ipswich had a Ipswich Racecourse, racecourse which ran a mix of flat and National Hunt races.
Ipswich's sole professional association football club is Ipswich Town F.C., Ipswich Town, which was established in 1878 and play at the 30,300-capacity Portman Road, Portman Road stadium. They have competed in the Premier League since the 2024–25 Premier League, 2024–25 season, following their promotion as runners-up from the EFL Championship in the 2023–24 EFL Championship, 2023–24 season. Elected to the English Football League, Football League in 1938, they have a strong East Anglian derby, rivalry with Norwich City F.C., Norwich City, and were the previous club of the two most successful England national football team, England managers; Alf Ramsey, who was buried in the Old Cemetery in the town on his death in 1999, and Bobby Robson. Ipswich won the First Division title in 1961–62 Football League, 1961–62 in their first season as a top division club during Ramsey's reign, as well as the 1977–78 FA Cup, 1978 FA Cup and the 1980–81 UEFA Cup, 1981 UEFA Cup under Robson. The club are also undefeated at home in all European competitions, having won 25 and drawn six of 31 matches.
Ipswich is also home to several non-League football clubs, including Ipswich Wanderers F.C., Ipswich Wanderers and Whitton United F.C., Whitton United in the Eastern Counties Football League, Eastern Counties League, and Achilles F.C., Achilles, Crane Sports F.C., Crane Sports, and Ransomes Sports F.C., Ransomes Sports among others in the Suffolk and Ipswich Football League, Suffolk & Ipswich League. The town has representation in both codes of Rugby football, rugby. There are two rugby union teams – Ipswich RFC, who play in London 2 North East League, and Ipswich YM RUFC – and one rugby league side – Ipswich Rhinos, who play in the Rugby League Conference. Ipswich Cardinals are an American football team, playing in the South-East Conference of BAFACL 1; the second tier of the BAFA Community Leagues.
The Motorcycle speedway, speedway team, the Ipswich Witches, have ridden at Foxhall Stadium on the outskirts of Ipswich since 1951 and have won the top-tier league title four times, the knock-out cup five times and the second-tier knock-out cup twice. The stadium is also used regularly for Hot Rods (oval racing), Hot Rod, Stock car racing in the United Kingdom, Stock Car and Banger racing events, hosting major events throughout the year on the stadium's outer tarmac oval.
Ipswich Gymnastics Centre is one of only three fully London Organising Committee for the Olympic Games, Olympic accredited gymnastics facilities in the United Kingdom, UK.
Ipswich has a rich history of public swimming. During the 1830s, there were at least three designated swimming places – one was near St Cement's, the second was next to St Mary-at-the-Quay Church, Ipswich, St Mary-At-The Quay and the third not far from Stoke Bridge. These were all closed in the late 1830s during the building of the wet dock. A designated enclosed area of the River Orwell, called Stoke Bathing Place, was created to cater for the swimmers. It was damaged in the floods of 1953 but maps show the swimming place still in situ as late as 1973. Ipswich Swimming, formed in 1884 as Ipswich Swimming Club, used the Stoke Swimming Place. Fore Street Swimming Pool opened in 1894. The pool is still in use and is the second oldest swimming pool in is in the UK. Pipers Vale Pool opened in 1937 after replacing the West End Bathing Place, which had closed in 1936 due to fears that it was polluting the River Orwell. Broomhill Pool, Broom Hill pool opened, in 1986, which was prompted to serve the western side of the town. It closed in 2002 but is about to be restored with the plan of opening again in 2025/26. St Matthew's Baths was opened in 1924 and closed in 1984 when Crown Pools opened, which is still in use. The Ipswich Swimming Club, is based there although they use the Fore Street Swimming Pool, Fore Street swimming pool, too. The most successful Ipswich Swimming Club member is FINA World Aquatics Championships, World Championship gold medallist Karen Pickering. There are plans for a new "low carbon aquatics centre" with the intention of opening next to Ipswich Town F.C., Ipswich Town Football Club in 2027.
Ipswich had a Ipswich Racecourse, racecourse which ran a mix of flat and National Hunt races.
 State-funded secondary schools include comprehensive schools such as Copleston High School, St Alban's Catholic High School, Ipswich, St Alban's Catholic High School, Holbrook Academy, Holbrook Primary and Northgate High School, Ipswich, Northgate High School and academies such as Ipswich Academy and Chantry Academy. Ipswich is also home to several independent schools, including Royal Hospital School,
State-funded secondary schools include comprehensive schools such as Copleston High School, St Alban's Catholic High School, Ipswich, St Alban's Catholic High School, Holbrook Academy, Holbrook Primary and Northgate High School, Ipswich, Northgate High School and academies such as Ipswich Academy and Chantry Academy. Ipswich is also home to several independent schools, including Royal Hospital School,
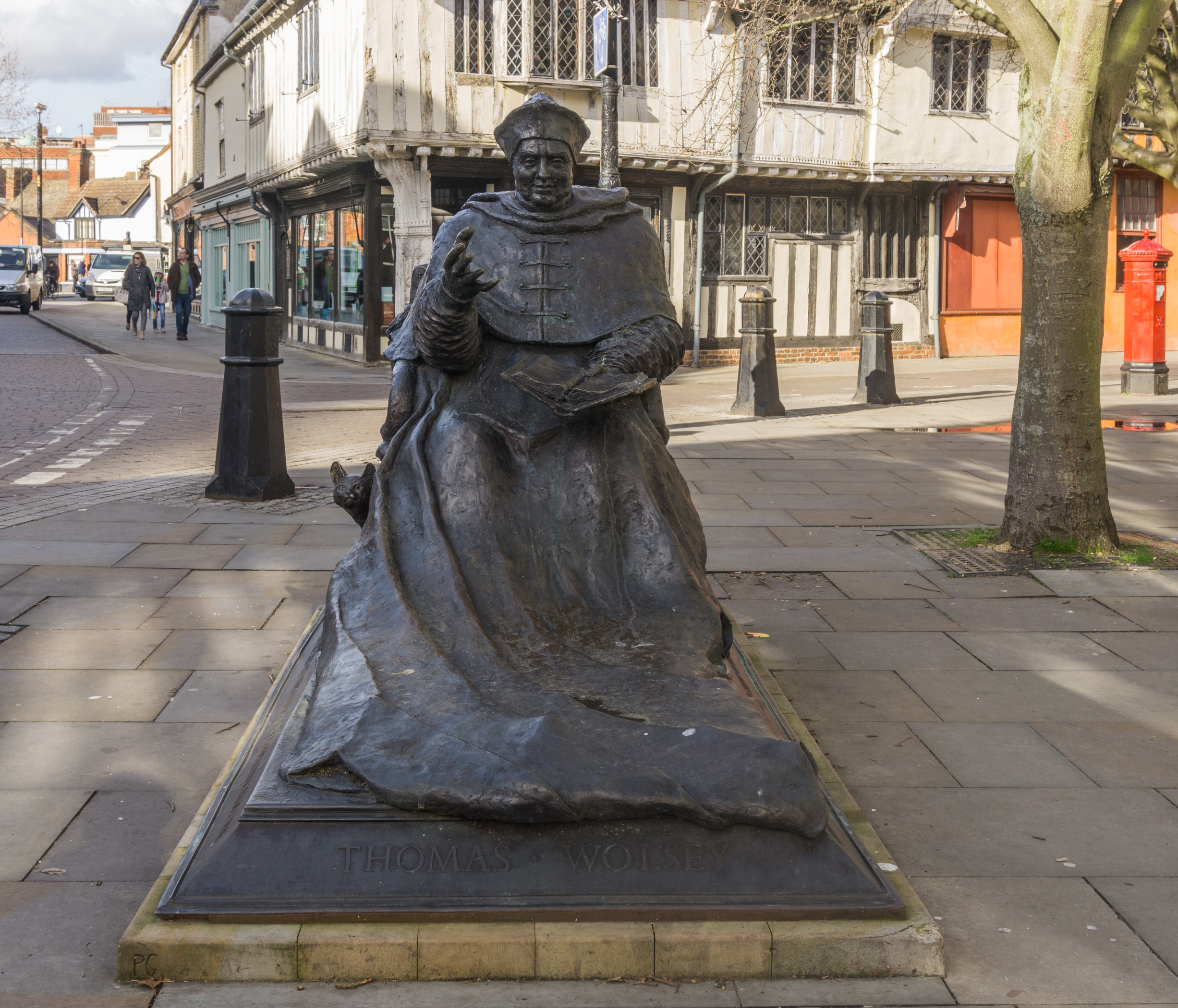 The Tudor Cardinal
The Tudor Cardinal
Ipswich Borough Council
* {{Authority control Ipswich, Towns in Suffolk County towns in England Non-metropolitan districts of Suffolk Port cities and towns of the North Sea River Orwell Trading posts of the Hanseatic League Unparished areas in Suffolk Populated places established in the 1st millennium Former civil parishes in Suffolk Boroughs in England
borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English language, English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
...
in Suffolk
Suffolk ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Norfolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Essex to the south, and Cambridgeshire to the west. Ipswich is the largest settlement and the county ...
, England. It is the county town
In Great Britain and Ireland, a county town is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county, and the place where public representatives are elected to parliament. Following the establishment of county councils in ...
, and largest in Suffolk, followed by Lowestoft
Lowestoft ( ) is a coastal town and civil parish in the East Suffolk (district), East Suffolk district of Suffolk, England.OS Explorer Map OL40: The Broads: (1:25 000) : . As the List of extreme points of the United Kingdom, most easterly UK se ...
and Bury St Edmunds
Bury St Edmunds (), commonly referred to locally as ''Bury,'' is a cathedral as well as market town and civil parish in the West Suffolk District, West Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England.OS Explorer map 211: Bury St. Edmunds an ...
, and the third-largest population centre in East Anglia
East Anglia is an area of the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, with parts of Essex sometimes also included.
The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, ...
, after Peterborough
Peterborough ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in the City of Peterborough district in the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire, England. The city is north of London, on the River Nene. A ...
and Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of the county of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. It lies by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. The population of the Norwich ...
. It is northeast of London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
and in 2011 had a population of 144,957. The Ipswich built-up area
This is a list of the most populous urban areas in the United Kingdom based on the 2011 census, as defined by the Office for National Statistics (ONS).
Definition
The methodology used by ONS in 2011 is set out in ''2011 Built-up Areas – Meth ...
is the fourth-largest in the East of England
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sunrise, Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact ...
and the 42nd-largest in England and Wales. It includes the towns and villages of Kesgrave
Kesgrave is a town and civil parish in the East Suffolk district of Suffolk, England. The town is close to both Ipswich and Woodbridge. Kesgrave forms part of the wider Ipswich Built-up area.
History
The area was recorded as ''Gressgrava'' in ...
, Woodbridge
Woodbridge may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Woodbridge, Western Australia formerly called ''West Midland''
*Woodbridge, Tasmania
Canada
*Woodbridge, Ontario
England
*Woodbridge, Suffolk, the location of
**Woodbridge (UK Parliament constituency ...
, Bramford
Bramford is a village in the Mid Suffolk district of Suffolk, England. It is three miles west of Ipswich of which it forms part of the wider Ipswich Built-up area. It was recorded in the Domesday Book as "Brunfort" or "Branfort". The River Gip ...
and Martlesham Heath
Martlesham Heath is a village in Suffolk, England. It is east of Ipswich, This was an ancient area of heathland and latterly the site of Martlesham Heath Airfield. A "new village" was established there in the mid-1970s and this has developed in ...
.
Ipswich was first recorded during the medieval period as ''Gippeswic'', the town has also been recorded as ''Gyppewicus'' and ''Yppswyche''. It has been continuously inhabited since the Saxon
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
period, and is believed to be one of the oldest towns in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
.Hills, Catherine"England's Oldest Town"
Retrieved 2 August 2015. The settlement was of great economic importance to the
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from the late 9th century, when it was unified from various Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to f ...
throughout its history, particularly in trade, with the town's historical dock, Ipswich Waterfront
The Ipswich Waterfront is a cultural and historically significant area surrounding the marina in the town of Ipswich, Suffolk, England. The modern dock was constructed in 1842 and the area was a functioning dock up until the 1970s. At the time ...
, known as the largest and most important dock in the Kingdom.K. Wade, 'Gipeswic – East Anglia's first economic capital, 600–1066', in N. Salmon and R. Malster (eds), ''Ipswich From The First To The Third Millennium'' (Ipswich, 2001), 1–6.
Ipswich is divided into various quarters, with the town centre and the waterfront drawing the most footfall. The town centre features the retail shopping district and the historic town square
A town square (or public square, urban square, city square or simply square), also called a plaza or piazza, is an open public space commonly found in the heart of a traditional town or city, and which is used for community gatherings. Relat ...
, known as the Cornhill. The waterfront, south of the town centre on a meander of the River Orwell, offers a picturesque setting with a marina
A marina (from Spanish , Portuguese and Italian : "related to the sea") is a dock or basin with moorings and supplies for yachts and small boats.
A marina differs from a port in that a marina does not handle large passenger ships or cargo ...
, luxury yachts, high-rise apartment buildings, and a variety of restaurants and cafes. The waterfront is also home to the University of Suffolk
The University of Suffolk is a public university situated in Suffolk and Norfolk, England. The university was established in 2007 as University Campus Suffolk (UCS), founded as a collaboration between the University of East Anglia and the Unive ...
campus.
Ipswich is adjacent to the Suffolk & Essex Coast & Heaths National Landscape
The Suffolk & Essex Coast & Heaths National Landscape is an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in Suffolk and Essex, England.
The AONB covers ancient woodland, commercial forestry, the estuaries of the Alde, Blyth, Deben, Orwell and Stour ...
AONB
An Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB; , AHNE) is one of 46 areas of countryside in England, Wales, or Northern Ireland that has been designated for conservation due to its significant landscape value. Since 2023, the areas in England an ...
and is close to Dedham Vale AONB. The town has a tourist sector, with 3.5 million people reported to have visited the town in 2016. In 2020, Ipswich was ranked as an emerging global tourist destination by TripAdvisor
Tripadvisor is an American company that operates online travel agency, travel agencies, comparison shopping websites, and mobile apps with user-generated content.
Its namesake brand, Tripadvisor.com, operates in 40 countries and 20 languages, and ...
.
History
Ipswich is one of England's oldest towns, and is claimed to be the oldest still continuing town to have been established and developed by theEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Culture, language and peoples
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
* ''English'', an Amish ter ...
, with continuous settlement since early Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
times.
Roman settlement
A largeRoman fort
''Castra'' () is a Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discuss ...
, part of the coastal defences of Britain, stood at Walton Walton may refer to:
People
* Walton (given name)
* Walton (surname)
* Susana, Lady Walton (1926–2010), Argentine writer
Places
Canada
* Walton, Nova Scotia, a community
** Walton River (Nova Scotia)
*Walton, Ontario, a hamlet
United Kingd ...
near Felixstowe
Felixstowe ( ) is a port town and civil parish in the East Suffolk District, East Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England. The estimated population in 2017 was 24,521. The Port of Felixstowe is the largest Containerization, containe ...
(, and the largest Roman villa
A Roman villa was typically a farmhouse or country house in the territory of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, sometimes reaching extravagant proportions.
Nevertheless, the term "Roman villa" generally covers buildings with the common ...
in Suffolk (possibly an administrative complex) stood at Castle Hill (north-west Ipswich).
Middle Ages
 The modern town took shape in Anglo-Saxon times (7th–8th centuries) around the
The modern town took shape in Anglo-Saxon times (7th–8th centuries) around the Port of Ipswich
The Port of Ipswich can be dated to c.625. The name Ipswich was originally Gippeswyc, referring to the River Gipping, River Gyppes with a suffix derived from the Scandinavian term vik, which had evolved from meaning bay or inlet to mean landing-p ...
. As the coastal states of north-western Europe emerged from the collapse of the Roman Empire, essential North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
trade and communication between eastern Britain and the continent (especially to Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
, and through the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
) passed through the former Roman ports of London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
(serving the kingdoms of Mercia
Mercia (, was one of the principal kingdoms founded at the end of Sub-Roman Britain; the area was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlan ...
, the East Saxons
The Kingdom of the East Saxons (; ), referred to as the Kingdom of Essex , was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex ...
, Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Gr ...
) and York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a Yor ...
(Eoforwic) (serving the Kingdom of Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland.
The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Sout ...
).
''Gipeswic'' (also in other spellings such as ''Gippeswich'') arose as the equivalent to these, serving the Kingdom of East Anglia
The Kingdom of the East Angles (; ), informally known as the Kingdom of East Anglia, was a small independent Monarchy, kingdom of the Angles (tribe), Angles during the History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon period comprising what are now t ...
, its early imported wares dating to the time of King Rædwald, ruler of the East Angles (616–624). The famous ship-burial and treasure at Sutton Hoo
Sutton Hoo is the site of two Anglo-Saxon cemeteries dating from the 6th to 7th centuries near Woodbridge, Suffolk, England. Archaeology, Archaeologists have been excavating the area since 1938, when an undisturbed ship burial containing a wea ...
nearby () is probably his grave. The Ipswich Museum
Ipswich Museum is a registered museum of culture, history and natural heritage, located in a Grade II* listed building on High Street in Ipswich, the county town of Suffolk. It was historically the leading regional museum in Suffolk, housing ...
houses replica
A replica is an exact (usually 1:1 in scale) copy or remake of an object, made out of the same raw materials, whether a molecule, a work of art, or a commercial product. The term is also used for copies that closely resemble the original, without ...
s of the Roman Mildenhall and Sutton Hoo treasure
Sutton Hoo is the site of two Anglo-Saxon cemeteries dating from the 6th to 7th centuries near Woodbridge, Suffolk, England. Archaeologists have been excavating the area since 1938, when an undisturbed ship burial containing a wealth of Anglo- ...
s. A gallery devoted to the town's origins includes Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
weapon
A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime (e.g., murder), law ...
s, jewellery
Jewellery (or jewelry in American English) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment such as brooches, ring (jewellery), rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the ...
and other artefacts.
The seventh-century town was centred near the quay. Around 700 AD, Frisian potters from the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
area settled in Ipswich and set up the first large-scale potteries in England since Roman times. Their wares were traded far across England, and the industry was unique to Ipswich for 200 years. With growing prosperity, in about 720 AD a large new part of the town was laid out in the Buttermarket area. Ipswich was becoming a place of national and international importance. Parts of the ancient road plan still survive in its modern streets.
After the invasion of 869, Ipswich fell under Viking
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
rule. The earth ramparts circling the town centre were probably raised by Vikings in Ipswich around 900 to prevent its recapture by the English. They were unsuccessful. The town operated a mint
Mint or The Mint may refer to:
Plants
* Lamiaceae, the mint family
** ''Mentha'', the genus of plants commonly known as "mint"
Coins and collectibles
* Mint (facility), a facility for manufacturing coins
* Mint condition, a state of like-new ...
under royal licence from King Edgar
Edgar is a commonly used masculine English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Edgar'' (composed of ''wikt:en:ead, ead'' "rich, prosperous" and ''Gar (spear), gar'' "spear").
Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the Late Midd ...
in the 970s, which continued through the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
until the time of King John, in about 1215. The abbreviation ''Gipes'' appears on the coins.
King John granted the town its first charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the ...
in 1200, laying the medieval foundations of its modern civil government. Thenceforth Ipswich strongly maintained its jurisdiction over the Liberty of Ipswich, an administrative area extending over about 35 square kilometres centred on the town.
In the next four centuries it made the most of its wealth. Five large religious houses, including two Augustinian Priories (St Peter and St Paul, and Holy Trinity, both mid-12th century), and those of the Ipswich Greyfriars
Ipswich Greyfriars was a mediaeval monastic house of Friars Minor (Franciscans) founded during the 13th century in Ipswich, Suffolk. It was said conventionally to have been founded by Sir Robert Tibetot of Nettlestead, Suffolk (before 1230–1298) ...
(Franciscans
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor being the largest conte ...
, before 1298), Ipswich Whitefriars
Ipswich Whitefriars was the medieval religious house of Carmelite friars (under a prior) which formerly stood near the centre of the town of Ipswich, the county town of Suffolk, UK. It was the last of the three principal mendicant communities to be ...
(Carmelites
The Order of the Brothers of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Mount Carmel (; abbreviated OCarm), known as the Carmelites or sometimes by synecdoche known simply as Carmel, is a mendicant order in the Catholic Church for both men and women. Histo ...
founded 1278–79) and Ipswich Blackfriars (Dominicans
Dominicans () also known as Quisqueyans () are an ethnic group, ethno-nationality, national people, a people of shared ancestry and culture, who have ancestral roots in the Dominican Republic.
The Dominican ethnic group was born out of a fusio ...
, before 1263), stood in medieval Ipswich. The last Carmelite Prior of Ipswich was the celebrated John Bale
John Bale (21 November 1495 – November 1563) was an English churchman, historian controversialist, and Bishop of Ossory in Ireland. He wrote the oldest known historical verse drama in English (on the subject of King John), and developed and ...
, author of the oldest English historical verse-drama (''Kynge Johan'', ). There were also several hospitals, including the leper hospital of St Mary Magdalene, founded before 1199.
During the Middle Ages the Marian Shrine of Our Lady of Grace
Our Lady of Grace is a Titles of Mary, Title of Mary. The feast day associated with this title is February 7. The title of Our Lady of Grace is venerated in many countries throughout the world under various aspects. Many parishes, churches, and sc ...
was a famous pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a travel, journey to a holy place, which can lead to a personal transformation, after which the pilgrim returns to their daily life. A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) w ...
destination, and attracted many pilgrims including Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
and Katherine of Aragon
Catherine of Aragon (also spelt as Katherine,
historical Spanish: , now: ; 16 December 1485 – 7 January 1536) was Queen of England as the first wife of King Henry VIII from their marriage on 11 June 1509 until its annulment on 23 May ...
. At the Reformation the statue was taken away to London to be burned, though some claim that it survived and is preserved at Nettuno
Nettuno is a town and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Rome in the Lazio region of central Italy, south of Rome. A resort city and agricultural center on the Tyrrhenian Sea, it has a population of approximately 50,000.
Economy
It has a ...
, Italy.
Around 1380, Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer ( ; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He w ...
satirised the merchants of Ipswich in ''The Canterbury Tales
''The Canterbury Tales'' () is a collection of 24 stories written in Middle English by Geoffrey Chaucer between 1387 and 1400. The book presents the tales, which are mostly written in verse, as part of a fictional storytelling contest held ...
''. Thomas Wolsey
Thomas Wolsey ( ; – 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic cardinal (catholic), cardinal. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's Lord High Almoner, almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and ...
, the future cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal most commonly refers to
* Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of three species in the family Cardinalidae
***Northern cardinal, ''Cardinalis cardinalis'', the common cardinal of ...
, was born in Ipswich in 1473 as the son of a wealthy landowner. One of Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
's closest political allies, he founded a college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further education institution, or a secondary sc ...
in the town in 1528, which was for its brief duration one of the homes of the Ipswich School
Ipswich School is a public school (English fee-charging boarding and day school) for pupils aged 3 to 18 in Ipswich, Suffolk, England.
North of the town centre, Ipswich School has four parts on three adjacent sites. The Pre-Prep and Nur ...
. He remains one of the town's most famed figures.
Early-modern era
 During the 14th to 17th centuries Ipswich was a
During the 14th to 17th centuries Ipswich was a kontor
A ''kontor'' (also Kontor; ) was a major foreign trading post of the Hanseatic League. Kontors were legal entities established in a foreign city (i.e. a city that did not belong to the Hanseatic League), with a degree of legal autonomy. Most kon ...
for the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
, the port being used for imports and exports to the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
.
In the time of Queen Mary the Ipswich Martyrs
The Ipswich Martyrs were nine people burnt at the stake for their Lollard or Protestant beliefs around 1515-1558. The executions were mainly carried out in the centre of Ipswich, Suffolk on The Cornhill, the square in front of Ipswich Town Hall. ...
were burnt at the stake on the Cornhill for their Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
beliefs. A monument commemorating this event now stands in Christchurch Park
Christchurch Park is a historical area of rolling lawns, wooded areas, and delicately created arboretum, arboreta close to the town centre in Ipswich, Suffolk. The park hosts various facilities such as a children's play area, tennis courts, table ...
. Ipswich was a printing, bookseller
Bookselling is the commercial trading of books, which is the retail and distribution end of the publishing process.
People who engage in bookselling are called booksellers, bookdealers, book people, bookmen, or bookwomen.
History
The foundi ...
centre, and an entrepôt for continental books in the 16th century. From 1611 to 1634 Ipswich was a major centre for emigration to New England. This was encouraged by the Town Lecturer, Samuel Ward (minister), Samuel Ward. His brother Nathaniel Ward was first minister of Ipswich, Massachusetts, Ipswich, Massachusetts, where a promontory was named 'Castle Hill' after the place of that name in north-west Ipswich, UK. Ipswich was also one of the main ports of embarkation for puritans leaving other East Anglia
East Anglia is an area of the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, with parts of Essex sometimes also included.
The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, ...
n towns and villages for the Massachusetts Bay Colony during the 1630s and what has become known as the Great Migration (Puritan), Great Migration.
 The painter Thomas Gainsborough lived and worked in Ipswich. In 1835, Charles Dickens stayed in Ipswich and used it as a setting for scenes in his novel ''The Pickwick Papers''. The hotel where he resided first opened in 1518; it was then known as The Tavern and later became known as the Great White Horse Hotel. Dickens made the hotel famous in chapter XXII of ''The Pickwick Papers'', vividly describing the hotel's meandering corridors and stairs.
The painter Thomas Gainsborough lived and worked in Ipswich. In 1835, Charles Dickens stayed in Ipswich and used it as a setting for scenes in his novel ''The Pickwick Papers''. The hotel where he resided first opened in 1518; it was then known as The Tavern and later became known as the Great White Horse Hotel. Dickens made the hotel famous in chapter XXII of ''The Pickwick Papers'', vividly describing the hotel's meandering corridors and stairs.
19th and 20th centuries
In 1824 Dr George Birkbeck, with support from several local businessmen, founded one of the first Mechanics' Institutes, which survives to this day as the independent Ipswich Institute reading room and library. The building is located at 15 Tavern Street. In the mid-19th century coprolite (fossilised animal dung) was discovered; the material was mined and then dissolved in acid, the resulting mixture forming the basis of Fisons fertiliser business. The Tolly Cobbold brewery, built in the 18th century and rebuilt in 1894–96, is one of the finest Victorian era, Victorian brewery, breweries in the UK. There was a Cobbold brewery in the town from 1746 until 2002 when Ridley's Brewery, Ridley's Breweries took Tolly Cobbold over. Felix Thornley Cobbold presented Christchurch Mansion to the town in 1896. Smaller breweries include St Jude's Brewery, situated in an 18th-century coach-house near the town centre. Ipswich was subject to bombing by German Zeppelins during World War I but the greatest damage by far occurred during the German bombing raids of World War II. The area in and around the docks was especially devastated. Eighty civilians died by enemy action in the Ipswich county borough area during the latter war. The last bombs to fall on Ipswich landed on Seymour Road at 2a.m. on 2 March 1945, killing nine people and destroying six houses. The Willis Building (Ipswich), Willis Building is a glass-clad building owned by Willis Group Holdings, Willis. Designed by Norman Foster, Baron Foster of Thames Bank, Norman Foster, the building dates from 1974, when it was known as the Willis Faber & Dumas building. It became the youngest grade I listed building in Britain in 1991, being at the time one of only two listed buildings to be less than thirty years old. In September 1993, Ipswich and Arras, Nord Pas-de-Calais, France, became twin towns, and a square in the new Buttermarket development was named Arras Square to mark the relationship. Ipswich formerly had a Ipswich Airport, municipal airport to the south-east of the town, which was opened in 1929 by the Ipswich Corporation. The airport was controversially closed in 1996. The site was redeveloped for housing as the Ravenswood estate.21st century
Ipswich has experienced a building boom in the early part of the 21st century. Construction has mainly concentrated around the Deindustrialization, former industrial dock which is now known as theIpswich Waterfront
The Ipswich Waterfront is a cultural and historically significant area surrounding the marina in the town of Ipswich, Suffolk, England. The modern dock was constructed in 1842 and the area was a functioning dock up until the 1970s. At the time ...
. Regeneration to the area has made it a hub of culture in Ipswich, the area boasts fine dining restaurants, a boutique hotel, and the new regional university, the University of Suffolk
The University of Suffolk is a public university situated in Suffolk and Norfolk, England. The university was established in 2007 as University Campus Suffolk (UCS), founded as a collaboration between the University of East Anglia and the Unive ...
. The new high rise buildings of the Regatta Quay development has topped the list of the List of tallest buildings and structures in Ipswich, tallest buildings in Ipswich. The mixed-use high rise building, The Mill (building), The Mill, is currently the tallest building in Suffolk.
Ipswich has made several unsuccessful bids for City status in the United Kingdom, city status. The town does not have a cathedral, so the Bishop of St Edmundsbury and Ipswich is based at Bury St Edmunds
Bury St Edmunds (), commonly referred to locally as ''Bury,'' is a cathedral as well as market town and civil parish in the West Suffolk District, West Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England.OS Explorer map 211: Bury St. Edmunds an ...
, the former county town
In Great Britain and Ireland, a county town is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county, and the place where public representatives are elected to parliament. Following the establishment of county councils in ...
of West Suffolk (county), West Suffolk.
Ipswich is the largest town in Suffolk, followed by Lowestoft
Lowestoft ( ) is a coastal town and civil parish in the East Suffolk (district), East Suffolk district of Suffolk, England.OS Explorer Map OL40: The Broads: (1:25 000) : . As the List of extreme points of the United Kingdom, most easterly UK se ...
and Bury St Edmunds
Bury St Edmunds (), commonly referred to locally as ''Bury,'' is a cathedral as well as market town and civil parish in the West Suffolk District, West Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England.OS Explorer map 211: Bury St. Edmunds an ...
, and the third-largest population centre in East Anglia
East Anglia is an area of the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, with parts of Essex sometimes also included.
The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, ...
, after Peterborough
Peterborough ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in the City of Peterborough district in the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire, England. The city is north of London, on the River Nene. A ...
and Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of the county of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. It lies by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. The population of the Norwich ...
. It is northeast of London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
and in 2011 had a population of 144,957. The Ipswich built-up area
This is a list of the most populous urban areas in the United Kingdom based on the 2011 census, as defined by the Office for National Statistics (ONS).
Definition
The methodology used by ONS in 2011 is set out in ''2011 Built-up Areas – Meth ...
is the fourth-largest in the East of England
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sunrise, Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact ...
and the 42nd-largest in England and Wales. It includes the towns and villages of Kesgrave
Kesgrave is a town and civil parish in the East Suffolk district of Suffolk, England. The town is close to both Ipswich and Woodbridge. Kesgrave forms part of the wider Ipswich Built-up area.
History
The area was recorded as ''Gressgrava'' in ...
, Woodbridge
Woodbridge may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Woodbridge, Western Australia formerly called ''West Midland''
*Woodbridge, Tasmania
Canada
*Woodbridge, Ontario
England
*Woodbridge, Suffolk, the location of
**Woodbridge (UK Parliament constituency ...
, Bramford
Bramford is a village in the Mid Suffolk district of Suffolk, England. It is three miles west of Ipswich of which it forms part of the wider Ipswich Built-up area. It was recorded in the Domesday Book as "Brunfort" or "Branfort". The River Gip ...
and Martlesham Heath
Martlesham Heath is a village in Suffolk, England. It is east of Ipswich, This was an ancient area of heathland and latterly the site of Martlesham Heath Airfield. A "new village" was established there in the mid-1970s and this has developed in ...
.
Localities
The waterfront is now devoted primarily to leisure use and includes extensive recent development of residential apartment blocks and a university campus. Businesses operated from the dock include luxury boats and a timber merchant. Other industries have been established to the south of the wet dock. The area was flooded in 2013 during a tidal surge. In February 2019 a Floodgate, flood gate, which protects the "New Cut", was unveiled. The flood barrier, similar in design to the Thames Barrier, cost £67m. The Ipswich Village Development, begun in 2002 around Russell Road, is home to Suffolk County Council and Ipswich Borough Council. Holywells Ward, Ipswich is the area around Holywells Park, Ipswich, Holywells Park, a public park situated near the docks, and the subject of a painting by Thomas Gainsborough. Alexandra Park is the nearest park to the waterfront's northern quay, and situated on Back Hamlet, adjacent toUniversity of Suffolk
The University of Suffolk is a public university situated in Suffolk and Norfolk, England. The university was established in 2007 as University Campus Suffolk (UCS), founded as a collaboration between the University of East Anglia and the Unive ...
.
Localities outside the town centre include Bixley Farm, Broke Hall, California, Suffolk, California, Castle Hill, Ipswich, Suffolk, Castle Hill, Chantry, Suffolk, Chantry, The Dales, Gainsborough, Suffolk, Gainsborough, Greenwich, Maidenhall, Pinewood, Suffolk, Pinewood, Priory Heath, Racecourse, Suffolk, Racecourse, Ravenswood, Ipswich, Ravenswood (built on a former airfield), Rose Hill, Suffolk, Rose Hill, Rushmere, Ipswich, Rushmere, Springvale, Ipswich, Springvale, St Margarets, Ipswich, St Margarets, Stoke, Suffolk, Stoke, Warren Heath, Westbourne, Suffolk, Westbourne, Whitehouse, Ipswich, Whitehouse and Whitton, Ipswich, Whitton.
To the east of the town is Trinity Park, Suffolk, Trinity Park near Bucklesham the home of the annual Suffolk Show, a typical County shows in United Kingdom, county show. The 'Trinity' is the name given to the three animals native to the county of Suffolk, namely Red Poll cattle, the powerful Suffolk Punch horse and the black-faced Suffolk (sheep), Suffolk sheep.
Culture

 Ipswich is home to many artists and has a number of galleries, the most prominent of which are at Christchurch Mansion, the Town Hall, Ancient House, Ipswich, Ancient House and the Artists' Gallery in Electric House. The visual arts are further supported with many sculptures at easily accessible sites. The Borough Council promotes the creation of new public works of art and has been known to make this a condition of planning permission. The town has three museums:
Ipswich is home to many artists and has a number of galleries, the most prominent of which are at Christchurch Mansion, the Town Hall, Ancient House, Ipswich, Ancient House and the Artists' Gallery in Electric House. The visual arts are further supported with many sculptures at easily accessible sites. The Borough Council promotes the creation of new public works of art and has been known to make this a condition of planning permission. The town has three museums: Ipswich Museum
Ipswich Museum is a registered museum of culture, history and natural heritage, located in a Grade II* listed building on High Street in Ipswich, the county town of Suffolk. It was historically the leading regional museum in Suffolk, housing ...
, the Ipswich Transport Museum and Christchurch Mansion.
For a town of its size, Ipswich has an impressive arts community, home to outstanding local, regional, and internationally renowned organisations.
The New Wolsey Theatre is a 400-seat theatre situated on Civic Drive. Although the Wolsey Theatre was built in 1979, The New Wolsey Company took on the management and running of the Wolsey Theatre in 2000, opening its first production in February 2001.
Established in 1983 as Suffolk Dance, DanceEast celebrated its 40th birthday in 2023. Today, they are one of the UK’s leading dance organisations.
Brighten The Corners is a not for profit organisation set up by the team at Out Loud Music CIC. Brighten the Corners operates three full-time venues, is the name of the annual town centre festival in Ipswich, Suffolk and promotes gigs by independent and emerging artists/musicians.
Spill Festival of Performance was launched in Ipswich in 2007 and creates events for the people of Ipswich, East Anglia, and further afield, and work with artists to develop their practice. They bring internationally significant and ground-breaking artists’ work to Ipswich and the UK. They also run year-round events and activities in the SPILL Think Tank venue, next door to Ipswich Museum.
Eastern Angles Theatre Company is based at its community hub the Eastern Angles Centre in Ipswich. In 2022 it celebrated its 40th anniversary. The group engages in rural tours and seasonal performances.
Gecko (theatre company), Gecko Theatre an award-winning and internationally acclaimed physical theatre company, led by Artistic Director Amit Lahav.
Red Rose Chain a not for profit theatre company based at The Avenue Theatre in Ipswich, delivering a vibrant professional and community programme.
Regent Theatre, Ipswich, The Regent Theatre is a theatre and concert venue located at St Helen's Street in Ipswich, Suffolk, England. It is East Anglia
East Anglia is an area of the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, with parts of Essex sometimes also included.
The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, ...
's largest theatre. It has also been known as the Gaumont Theatre. It was designated as a Grade II listed building in 2000.
All play a key role in shaping the town’s cultural landscape.
Media
Television
Ipswich is covered by ''BBC Look East'' and ''ITV News Anglia'', both broadcast fromNorwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of the county of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. It lies by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. The population of the Norwich ...
.
Radio
The town has five local radio stations, BBC Radio Suffolk which broadcast from its studios on St Matthews Street in the town, the commercial station Heart East which was founded in 1975 as Radio Orwell covering the A14 corridor in Suffolk, and Ipswich 102 who took over the FM frequency in 2018, until 2020 when it rebranded as Greatest Hits Radio Ipswich & Suffolk. Then in September 2022, the station was rebranded again as Nation Radio Suffolk where it has one local show on weekday afternoons 1pm-4pm, hosted by Rob Chandler (who hosted the local afternoon show prior to the rebrand). The younger audience was catered for with Suffolk-based Kiss 105-108, until September 2023 when its 106.4 frequency flipped over to carrying Greatest Hits Radio East, Greatest Hits Radio Ipswich & Suffolk. Ipswich Community Radio was launched in 2007.Newspapers
The town's daily newspaper is the ''Ipswich Star'', a sister title to the county's daily newspaper the ''East Anglian Daily Times''.Buildings
 In addition to the Christchurch Mansion and Ancient House, Ipswich in the 21st century has some important cultural buildings including the New Wolsey Theatre and the Regent Theatre, Ipswich, Regent Theatre—the largest theatre venue in East Anglia where, in 1964, the Beatles performed when it was still known as the Gaumont. There is also the Corn Exchange, Ipswich, Corn Exchange in King Street which was completed in 1882.
There are several medieval Ipswich churches but the grandest is Ipswich Minster (previously known as St. Mary-le-Tower), rebuilt by the Victorians. Holy Trinity Church by the waterfront is one of the few churches in the country which was built during the reign of William IV and whilst the outside looks plain, the interior is quite spectacular. The world's oldest circle of church bells is housed in St Lawrence Church, Ipswich, St Lawrence Church, which is maintained by the Ipswich Historic Churches Trust.
The Ancient House, Ipswich, Ancient House in the Buttermarket Centre, Ipswich, Buttermarket is an example of a merchant house which features tudor pargeting and the Ipswich window.
The former East Suffolk County Hall is just east of the centre of Ipswich. It is listed as a building at risk by the Victorian Society. The Town Hall remains in use as an arts centre and events venue; it dates from 1866 (architects: Bellamy & Hardy of Lincoln). The 18th Century Grade II listed Old Post Office, which was built in 1881, has been renovated and is now home to the Botanist bar.
Modern buildings include Endeavour House (headquarters of Suffolk County Council and formerly home of the TXU Corporation), Grafton House (home of Ipswich Borough Council) and Ipswich Crown Court, all located on Russell Road (Ipswich), Russell Road in the area known as the Ipswich Village Development, which includes Portman Road stadium. The stadium has hosted England under-21, under-23, and international soccer matches, as well as rugby union and hockey matches.
In the waterfront area The Mill (Ipswich), The Mill is the List of tallest buildings and structures in Ipswich, tallest building in
In addition to the Christchurch Mansion and Ancient House, Ipswich in the 21st century has some important cultural buildings including the New Wolsey Theatre and the Regent Theatre, Ipswich, Regent Theatre—the largest theatre venue in East Anglia where, in 1964, the Beatles performed when it was still known as the Gaumont. There is also the Corn Exchange, Ipswich, Corn Exchange in King Street which was completed in 1882.
There are several medieval Ipswich churches but the grandest is Ipswich Minster (previously known as St. Mary-le-Tower), rebuilt by the Victorians. Holy Trinity Church by the waterfront is one of the few churches in the country which was built during the reign of William IV and whilst the outside looks plain, the interior is quite spectacular. The world's oldest circle of church bells is housed in St Lawrence Church, Ipswich, St Lawrence Church, which is maintained by the Ipswich Historic Churches Trust.
The Ancient House, Ipswich, Ancient House in the Buttermarket Centre, Ipswich, Buttermarket is an example of a merchant house which features tudor pargeting and the Ipswich window.
The former East Suffolk County Hall is just east of the centre of Ipswich. It is listed as a building at risk by the Victorian Society. The Town Hall remains in use as an arts centre and events venue; it dates from 1866 (architects: Bellamy & Hardy of Lincoln). The 18th Century Grade II listed Old Post Office, which was built in 1881, has been renovated and is now home to the Botanist bar.
Modern buildings include Endeavour House (headquarters of Suffolk County Council and formerly home of the TXU Corporation), Grafton House (home of Ipswich Borough Council) and Ipswich Crown Court, all located on Russell Road (Ipswich), Russell Road in the area known as the Ipswich Village Development, which includes Portman Road stadium. The stadium has hosted England under-21, under-23, and international soccer matches, as well as rugby union and hockey matches.
In the waterfront area The Mill (Ipswich), The Mill is the List of tallest buildings and structures in Ipswich, tallest building in East Anglia
East Anglia is an area of the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, with parts of Essex sometimes also included.
The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, ...
, reaching 23 storeys.
On the north-west side of Ipswich lies Broomhill Pool, Ipswich, Broomhill Pool, a Grade II listed Olympic-sized lido which opened in 1938 and closed in 2002, since which time a campaign to see it restored and re-opened has been run by the Broomhill Pool Trust. On the southern side of Ipswich is historic Belstead Lodge, now the Belstead Brook Hotel.
Governance
The Municipal Borough of Ipswich was created in 1836 by the Municipal Corporations Act 1835. It was the form of local government for the ancient borough of Ipswich until the Local Government Act 1888 replaced it with the County Borough of Ipswich in 1889. Both originated from the ancient borough of Ipswich. The local authority was Ipswich Corporation. Following the passage of the Reform Act 1832, the government set up a Royal Commission in July 1833 to investigate how local councils worked. In 1974 it was replaced by the non-metropolitan district of Ipswich and Ipswich Borough Council became the local authority, with county council duties fulfilled by Suffolk County Council. Following the Local Government Act 1888, the county ofSuffolk
Suffolk ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Norfolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Essex to the south, and Cambridgeshire to the west. Ipswich is the largest settlement and the county ...
outside of Ipswich was split into East Suffolk (county), East Suffolk and West Suffolk (county), West Suffolk for administrative purposes and the term administrative county was introduced. There was a level of continuity as Ipswich was still run by the Ipswich Corporation, independently from East Suffolk (which surrounded it), although the county council was based in Ipswich at East Suffolk County Hall.
In 1974 following the Local Government Act 1972 and Ipswich became a non-metropolitan district with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in the administrative county of Suffolk
Suffolk ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Norfolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Essex to the south, and Cambridgeshire to the west. Ipswich is the largest settlement and the county ...
with the same boundaries as the abolished county borough.
 Ipswich is governed locally by a two-tier council system. Ipswich Borough Council fulfils non-metropolitan district, district council functions such as refuse collection, housing and planning and Suffolk County Council provides the County Council, county council services such as transport, education and social services.
The town is covered by two parliamentary constituencies: Ipswich (UK Parliament constituency), Ipswich, which is represented by Labour MP Jack Abbott (politician), Jack Abbott and covers about 75% of the town, and Central Suffolk and North Ipswich (UK Parliament constituency), Central Suffolk & North Ipswich, which covers the remaining 25% and is represented by Conservative MP Patrick Spencer.
In April 2006 the Non-metropolitan district, borough council initiated public discussions about the idea of turning the borough into a Unitary authority#United Kingdom, unitary authority; Ipswich had constituted a county borough from 1889 to 1974, independent of the administrative county of East Suffolk (county), East Suffolk, and this status was not restored by the Local Government Commission for England (1992), Banham/Cooksey Commission in the 1990s. Ipswich, Norwich, Exeter and Oxford united to campaign for unitary authority status for the four towns. In March 2007, it was announced that Ipswich was one of 16 shortlisted councils. In December 2007 plans were put into doubt as the government announced that it had "delayed" the unitary bids for Ipswich and Exeter. In July 2008 the Boundary Committee for England, Boundary Committee announced its preferred option was for a unitary authority covering Ipswich and the south eastern corner of Suffolk, including Felixstowe.
Ipswich is governed locally by a two-tier council system. Ipswich Borough Council fulfils non-metropolitan district, district council functions such as refuse collection, housing and planning and Suffolk County Council provides the County Council, county council services such as transport, education and social services.
The town is covered by two parliamentary constituencies: Ipswich (UK Parliament constituency), Ipswich, which is represented by Labour MP Jack Abbott (politician), Jack Abbott and covers about 75% of the town, and Central Suffolk and North Ipswich (UK Parliament constituency), Central Suffolk & North Ipswich, which covers the remaining 25% and is represented by Conservative MP Patrick Spencer.
In April 2006 the Non-metropolitan district, borough council initiated public discussions about the idea of turning the borough into a Unitary authority#United Kingdom, unitary authority; Ipswich had constituted a county borough from 1889 to 1974, independent of the administrative county of East Suffolk (county), East Suffolk, and this status was not restored by the Local Government Commission for England (1992), Banham/Cooksey Commission in the 1990s. Ipswich, Norwich, Exeter and Oxford united to campaign for unitary authority status for the four towns. In March 2007, it was announced that Ipswich was one of 16 shortlisted councils. In December 2007 plans were put into doubt as the government announced that it had "delayed" the unitary bids for Ipswich and Exeter. In July 2008 the Boundary Committee for England, Boundary Committee announced its preferred option was for a unitary authority covering Ipswich and the south eastern corner of Suffolk, including Felixstowe.
Industry
 Being the county town of agricultural Suffolk, industry around Ipswich has had a strong farming bias with Ransomes, Sims & Jefferies, Ransomes, Sims & Jefferies Ltd, one of the most famous agricultural manufacturers, located in the town. The world's first commercial lawnmower, motorised lawnmower was built by Ransomes in 1902. Ransomes & Rapier was a major British manufacturer of railway equipment and later cranes, from 1869 to 1987. There was a sugar beet factory at Ipswich for many years; it was closed in 2001 as part of a rationalisation by British Sugar. This agricultural link is preserved in the Ipswich Town F.C., local football club's nickname "The Tractor Boys". Phillips & Piper Ltd on Old Foundry Road employed many women who sewed equestrian and hunt jackets for Harrods, Pytchley, and other labels for 130 years, finally closing down in June 1982.
Being the county town of agricultural Suffolk, industry around Ipswich has had a strong farming bias with Ransomes, Sims & Jefferies, Ransomes, Sims & Jefferies Ltd, one of the most famous agricultural manufacturers, located in the town. The world's first commercial lawnmower, motorised lawnmower was built by Ransomes in 1902. Ransomes & Rapier was a major British manufacturer of railway equipment and later cranes, from 1869 to 1987. There was a sugar beet factory at Ipswich for many years; it was closed in 2001 as part of a rationalisation by British Sugar. This agricultural link is preserved in the Ipswich Town F.C., local football club's nickname "The Tractor Boys". Phillips & Piper Ltd on Old Foundry Road employed many women who sewed equestrian and hunt jackets for Harrods, Pytchley, and other labels for 130 years, finally closing down in June 1982.
 The British Telecom, British Telecom Research Laboratories were located to the east of the town in 1975 at
The British Telecom, British Telecom Research Laboratories were located to the east of the town in 1975 at Martlesham Heath
Martlesham Heath is a village in Suffolk, England. It is east of Ipswich, This was an ancient area of heathland and latterly the site of Martlesham Heath Airfield. A "new village" was established there in the mid-1970s and this has developed in ...
; it is now a science park called Adastral Park. The area was originally RAF Martlesham Heath, a World War II airfield. Part of the old airfield is now the site of Suffolk Constabulary's police headquarters.
A key employment sector is insurance, both wholesale and retail sectors. Some of the major players with a key presence in Ipswich include AXA, Axa, Churchill Insurance, Churchill, Legal & General, Liverpool Victoria, LV and Willis Towers Watson. Access to a skilled and experienced workforce has also led to the establishment of ancillary businesses serving these companies, including call centres dealing with sales and claims.
Ipswich is one of the Haven ports and is still a working port, handling several million tonnes of cargo each year. Prior to decommissioning, HMS Grafton (F80), HMS ''Grafton'' was a regular visitor to the port and has special links with the town and the county of Suffolk. HMS Orwell, HMS ''Orwell'', named after the river, is also closely linked with Ipswich.
Demography
Ethnicity
Religion
Transport
 Ipswich railway station is on the Great Eastern Main Line from Liverpool Street railway station, London to Norwich railway station, Norwich, the East Suffolk Line to Lowestoft railway station, Lowestoft and the Felixstowe Branch Line. Trains are run by Greater Anglia, which operates direct services to cities including London, Cambridge railway station, Cambridge, Chelmsford railway station, Chelmsford, Norwich railway station, Norwich and Peterborough railway station, Peterborough. Ipswich engine shed opened in 1846 and closed in 1968. Ipswich is still a signing-on point for locomotive crews and a Motive power depot#Stabling and fuelling points, stabling point. The town has a smaller suburban station at Derby Road railway station, Derby Road east of the town centre, on the Felixstowe branch line.
Ipswich is close to the A12 road (England), A12 and the A14 road (England), A14 roads. The Orwell Bridge which carries the A14 over the River Orwell connects it to the Port of Felixstowe, a major container port to the east.
Bus services in Ipswich are operated by Ipswich Buses, First Bus East of England, First Eastern Counties, Beestons and several smaller companies. Town services operate mainly from Tower Ramparts bus station and regional services from the Ipswich Old Cattle Market bus station. Ipswich Airport closed in 1996.
Ipswich is on Sustrans's National Cycle Route 1 and National Cycle Route 51.
Ipswich railway station is on the Great Eastern Main Line from Liverpool Street railway station, London to Norwich railway station, Norwich, the East Suffolk Line to Lowestoft railway station, Lowestoft and the Felixstowe Branch Line. Trains are run by Greater Anglia, which operates direct services to cities including London, Cambridge railway station, Cambridge, Chelmsford railway station, Chelmsford, Norwich railway station, Norwich and Peterborough railway station, Peterborough. Ipswich engine shed opened in 1846 and closed in 1968. Ipswich is still a signing-on point for locomotive crews and a Motive power depot#Stabling and fuelling points, stabling point. The town has a smaller suburban station at Derby Road railway station, Derby Road east of the town centre, on the Felixstowe branch line.
Ipswich is close to the A12 road (England), A12 and the A14 road (England), A14 roads. The Orwell Bridge which carries the A14 over the River Orwell connects it to the Port of Felixstowe, a major container port to the east.
Bus services in Ipswich are operated by Ipswich Buses, First Bus East of England, First Eastern Counties, Beestons and several smaller companies. Town services operate mainly from Tower Ramparts bus station and regional services from the Ipswich Old Cattle Market bus station. Ipswich Airport closed in 1996.
Ipswich is on Sustrans's National Cycle Route 1 and National Cycle Route 51.
Sport
 Ipswich's sole professional association football club is Ipswich Town F.C., Ipswich Town, which was established in 1878 and play at the 30,300-capacity Portman Road, Portman Road stadium. They have competed in the Premier League since the 2024–25 Premier League, 2024–25 season, following their promotion as runners-up from the EFL Championship in the 2023–24 EFL Championship, 2023–24 season. Elected to the English Football League, Football League in 1938, they have a strong East Anglian derby, rivalry with Norwich City F.C., Norwich City, and were the previous club of the two most successful England national football team, England managers; Alf Ramsey, who was buried in the Old Cemetery in the town on his death in 1999, and Bobby Robson. Ipswich won the First Division title in 1961–62 Football League, 1961–62 in their first season as a top division club during Ramsey's reign, as well as the 1977–78 FA Cup, 1978 FA Cup and the 1980–81 UEFA Cup, 1981 UEFA Cup under Robson. The club are also undefeated at home in all European competitions, having won 25 and drawn six of 31 matches.
Ipswich is also home to several non-League football clubs, including Ipswich Wanderers F.C., Ipswich Wanderers and Whitton United F.C., Whitton United in the Eastern Counties Football League, Eastern Counties League, and Achilles F.C., Achilles, Crane Sports F.C., Crane Sports, and Ransomes Sports F.C., Ransomes Sports among others in the Suffolk and Ipswich Football League, Suffolk & Ipswich League. The town has representation in both codes of Rugby football, rugby. There are two rugby union teams – Ipswich RFC, who play in London 2 North East League, and Ipswich YM RUFC – and one rugby league side – Ipswich Rhinos, who play in the Rugby League Conference. Ipswich Cardinals are an American football team, playing in the South-East Conference of BAFACL 1; the second tier of the BAFA Community Leagues.
The Motorcycle speedway, speedway team, the Ipswich Witches, have ridden at Foxhall Stadium on the outskirts of Ipswich since 1951 and have won the top-tier league title four times, the knock-out cup five times and the second-tier knock-out cup twice. The stadium is also used regularly for Hot Rods (oval racing), Hot Rod, Stock car racing in the United Kingdom, Stock Car and Banger racing events, hosting major events throughout the year on the stadium's outer tarmac oval.
Ipswich Gymnastics Centre is one of only three fully London Organising Committee for the Olympic Games, Olympic accredited gymnastics facilities in the United Kingdom, UK.
Ipswich has a rich history of public swimming. During the 1830s, there were at least three designated swimming places – one was near St Cement's, the second was next to St Mary-at-the-Quay Church, Ipswich, St Mary-At-The Quay and the third not far from Stoke Bridge. These were all closed in the late 1830s during the building of the wet dock. A designated enclosed area of the River Orwell, called Stoke Bathing Place, was created to cater for the swimmers. It was damaged in the floods of 1953 but maps show the swimming place still in situ as late as 1973. Ipswich Swimming, formed in 1884 as Ipswich Swimming Club, used the Stoke Swimming Place. Fore Street Swimming Pool opened in 1894. The pool is still in use and is the second oldest swimming pool in is in the UK. Pipers Vale Pool opened in 1937 after replacing the West End Bathing Place, which had closed in 1936 due to fears that it was polluting the River Orwell. Broomhill Pool, Broom Hill pool opened, in 1986, which was prompted to serve the western side of the town. It closed in 2002 but is about to be restored with the plan of opening again in 2025/26. St Matthew's Baths was opened in 1924 and closed in 1984 when Crown Pools opened, which is still in use. The Ipswich Swimming Club, is based there although they use the Fore Street Swimming Pool, Fore Street swimming pool, too. The most successful Ipswich Swimming Club member is FINA World Aquatics Championships, World Championship gold medallist Karen Pickering. There are plans for a new "low carbon aquatics centre" with the intention of opening next to Ipswich Town F.C., Ipswich Town Football Club in 2027.
Ipswich had a Ipswich Racecourse, racecourse which ran a mix of flat and National Hunt races.
Ipswich's sole professional association football club is Ipswich Town F.C., Ipswich Town, which was established in 1878 and play at the 30,300-capacity Portman Road, Portman Road stadium. They have competed in the Premier League since the 2024–25 Premier League, 2024–25 season, following their promotion as runners-up from the EFL Championship in the 2023–24 EFL Championship, 2023–24 season. Elected to the English Football League, Football League in 1938, they have a strong East Anglian derby, rivalry with Norwich City F.C., Norwich City, and were the previous club of the two most successful England national football team, England managers; Alf Ramsey, who was buried in the Old Cemetery in the town on his death in 1999, and Bobby Robson. Ipswich won the First Division title in 1961–62 Football League, 1961–62 in their first season as a top division club during Ramsey's reign, as well as the 1977–78 FA Cup, 1978 FA Cup and the 1980–81 UEFA Cup, 1981 UEFA Cup under Robson. The club are also undefeated at home in all European competitions, having won 25 and drawn six of 31 matches.
Ipswich is also home to several non-League football clubs, including Ipswich Wanderers F.C., Ipswich Wanderers and Whitton United F.C., Whitton United in the Eastern Counties Football League, Eastern Counties League, and Achilles F.C., Achilles, Crane Sports F.C., Crane Sports, and Ransomes Sports F.C., Ransomes Sports among others in the Suffolk and Ipswich Football League, Suffolk & Ipswich League. The town has representation in both codes of Rugby football, rugby. There are two rugby union teams – Ipswich RFC, who play in London 2 North East League, and Ipswich YM RUFC – and one rugby league side – Ipswich Rhinos, who play in the Rugby League Conference. Ipswich Cardinals are an American football team, playing in the South-East Conference of BAFACL 1; the second tier of the BAFA Community Leagues.
The Motorcycle speedway, speedway team, the Ipswich Witches, have ridden at Foxhall Stadium on the outskirts of Ipswich since 1951 and have won the top-tier league title four times, the knock-out cup five times and the second-tier knock-out cup twice. The stadium is also used regularly for Hot Rods (oval racing), Hot Rod, Stock car racing in the United Kingdom, Stock Car and Banger racing events, hosting major events throughout the year on the stadium's outer tarmac oval.
Ipswich Gymnastics Centre is one of only three fully London Organising Committee for the Olympic Games, Olympic accredited gymnastics facilities in the United Kingdom, UK.
Ipswich has a rich history of public swimming. During the 1830s, there were at least three designated swimming places – one was near St Cement's, the second was next to St Mary-at-the-Quay Church, Ipswich, St Mary-At-The Quay and the third not far from Stoke Bridge. These were all closed in the late 1830s during the building of the wet dock. A designated enclosed area of the River Orwell, called Stoke Bathing Place, was created to cater for the swimmers. It was damaged in the floods of 1953 but maps show the swimming place still in situ as late as 1973. Ipswich Swimming, formed in 1884 as Ipswich Swimming Club, used the Stoke Swimming Place. Fore Street Swimming Pool opened in 1894. The pool is still in use and is the second oldest swimming pool in is in the UK. Pipers Vale Pool opened in 1937 after replacing the West End Bathing Place, which had closed in 1936 due to fears that it was polluting the River Orwell. Broomhill Pool, Broom Hill pool opened, in 1986, which was prompted to serve the western side of the town. It closed in 2002 but is about to be restored with the plan of opening again in 2025/26. St Matthew's Baths was opened in 1924 and closed in 1984 when Crown Pools opened, which is still in use. The Ipswich Swimming Club, is based there although they use the Fore Street Swimming Pool, Fore Street swimming pool, too. The most successful Ipswich Swimming Club member is FINA World Aquatics Championships, World Championship gold medallist Karen Pickering. There are plans for a new "low carbon aquatics centre" with the intention of opening next to Ipswich Town F.C., Ipswich Town Football Club in 2027.
Ipswich had a Ipswich Racecourse, racecourse which ran a mix of flat and National Hunt races.
Education
Schools
 State-funded secondary schools include comprehensive schools such as Copleston High School, St Alban's Catholic High School, Ipswich, St Alban's Catholic High School, Holbrook Academy, Holbrook Primary and Northgate High School, Ipswich, Northgate High School and academies such as Ipswich Academy and Chantry Academy. Ipswich is also home to several independent schools, including Royal Hospital School,
State-funded secondary schools include comprehensive schools such as Copleston High School, St Alban's Catholic High School, Ipswich, St Alban's Catholic High School, Holbrook Academy, Holbrook Primary and Northgate High School, Ipswich, Northgate High School and academies such as Ipswich Academy and Chantry Academy. Ipswich is also home to several independent schools, including Royal Hospital School, Ipswich School
Ipswich School is a public school (English fee-charging boarding and day school) for pupils aged 3 to 18 in Ipswich, Suffolk, England.
North of the town centre, Ipswich School has four parts on three adjacent sites. The Pre-Prep and Nur ...
(both are co-educational and members of the Headmasters' and Headmistresses' Conference), Ipswich High School, Suffolk, Ipswich High School (has recently changed from girls only to girls and boys) and St Joseph's College, Ipswich, St Joseph's College (Catholic, co-educational) which hosts an international summer camp.
Further and higher education
Suffolk New College is a further education college located in Ipswich, serving students from the town and wider area. There is also a sixth form college, One (sixth form college), One, which serves students from the same area. Ipswich is the location of theUniversity of Suffolk
The University of Suffolk is a public university situated in Suffolk and Norfolk, England. The university was established in 2007 as University Campus Suffolk (UCS), founded as a collaboration between the University of East Anglia and the Unive ...
, Suffolk
Suffolk ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Norfolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Essex to the south, and Cambridgeshire to the west. Ipswich is the largest settlement and the county ...
's first Higher Education Institution (HEI), established in 2007. It was originally University Campus Suffolk, a collaborative venture involving the University of Essex in Colchester, the University of East Anglia in Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of the county of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. It lies by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. The population of the Norwich ...
, various further education colleges and Suffolk County Council. However, the university was granted its own degree awarding powers in November 2015, and in May 2016 it was awarded university status. The university was renamed to the University of Suffolk in August 2016, prior to its former name University Campus Suffolk.
Climate
Ipswich experiences an oceanic climate, like the rest of the British Isles, with a narrow range of temperature and rainfall spread evenly throughout the year. One of the two nearest for which data is available is East Bergholt, about south west of the town centre and at a similar elevation, and similar river valley/estuary situation. The average July maximum of is the third-highest for a major settlement in the country, behind London and Colchester, illustrating the relative warmth of the area during the summer part of the year. The record maximum is , set during August 2003. Typically, 24.9 days of the year will record a maximum temperature of or above, and the warmest day of the year should reach , on average. The absolute minimum is , set in January 1963, although frosts have been recorded in all months except July, August and September. In an average year, 55.33 nights will report an air frost. The lowest temperature to be recorded in recent years was during December 2010. As with much of East Anglia, rainfall is low, averaging 569.3mm in a typical year, with 103.8 days of the year reporting over 1mm of rain. All averages refer to the period 1971–2000. The weather station at Levington is even closer than East Bergholt at from the town centre further down the river estuary on the way toFelixstowe
Felixstowe ( ) is a port town and civil parish in the East Suffolk District, East Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England. The estimated population in 2017 was 24,521. The Port of Felixstowe is the largest Containerization, containe ...
. It has a slightly more marine climate than East Bergholt, with slightly lower highs and milder lows throughout the year in the 1981–2010 average period. It is slightly less prone to frosts, averaging 35.5 such occurrences in a calendar year. Sunshine levels at 1,707.7 hours per annum are relatively high for the British Isles, but not abnormal for southern parts of England.
Wattisham is from Ipswich, but has a higher altitude of . As a result, high temperatures there are a little lower than East Bergholt and Levington, but lows are similar. In average year, there are around 43 nights of frost recorded at Wattisham (as well as two days of frost), and one day when the temperature exceeds .
People
 The Tudor Cardinal
The Tudor Cardinal Thomas Wolsey
Thomas Wolsey ( ; – 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic cardinal (catholic), cardinal. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's Lord High Almoner, almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and ...
was born in the town. Sir Samuel Mayart, the judge and political theorist, was born in Ipswich in 1585. The artist Thomas Gainsborough and the cartoonist Carl Giles, "Giles" worked here, Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, Horatio, Lord Nelson, became Steward of Ipswich, and Margaret Catchpole began her adventurous career here. Alf Ramsey and Bobby Robson were both successful managers of Ipswich Town F.C., Ipswich Town. Ipswich was the birthplace in 1741 of Sarah Trimmer, née Kirby, writer and critic of children's literature and among the first to introduce pictorial material and animals and the natural world into it. Also born in Ipswich is Sam Claflin, who appeared in ''The Hunger Games (film series), The Hunger Games'' and Peaky Blinders (TV series), ''Peaky Blinders''.
Actor and director Richard Ayoade, best known for his role as Maurice Moss in ''The IT Crowd'', was brought up in Ipswich, as was the ceramic artist Blanche Georgiana Vulliamy,
and the musician Nandi Bushell.
Hugh Catchpole, a noted educationist with over 60 years of association with military schools and colleges in India and Pakistan, was born in Ipswich.
Jeremy Wade, an extreme angler known for hosting TV shows such as ''River Monsters'' and ''Dark Waters'', was born in Ipswich.
Composer Christopher Wright (composer), Christopher Wright (1954–2024) was born in Ipswich.
Twin towns
Ipswich is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with: * Arras, France, since 1994In popular culture
* In Serena Valentino's Villains novel ''Poor Unfortunate Soul: A Tale of the Sea Witch'', Ursula (The Little Mermaid), Ursula appears in Ipswich and proceeds to turn the citizens of the town into twisted sea creatures, reminiscent of the horror tales of author HP Lovecraft. She is stopped upon the arrival of King Triton. * In the Dead Parrot sketch by Monty Python's Flying Circus, the customer is sent to Bolton for a replacement but was falsely told he was in Ipswich: "C: This is Bolton, is it? O: (with a fake moustache) No, it's Ipswich." * In the 1934 Dennis Wheatley novel ''Black August (novel), Black August'' the main characters, after a series of adventures, are held prisoners in Ipswich where a local Communist government has been set up; they are sentenced to death as enemies of the State, but are freed when the revolution is overthrown.See also
* List of college towns * List of English districts * List of locations in Australia with an English name * List of tallest buildings and structures in Ipswich * List of towns in England * List of U.S. places named after non-U.S. placesReferences
Further reading
* Howgego, Caleb. ''Ipswich in 50 Buildings'' (Amberley, 2019) * Howgego, Caleb. ''Ipswich Through Time'' (Amberley, 2015) * Kindred, David. ''Ipswich Past & Present'' (The History Press, 2004) * Malster, Robert. ''A History of Ipswich'' (Phillimore, 2000) * Malster, Robert. ''Ipswich: A Pictorial History'' (Phillimore, 1991) * Twinch, Carol. ''The History of Ipswich'' (Breedon Books, 2008) * Twinch, Carol. ''Walks Through History Ipswich'' (DB Publishing, 2011)External links
*Ipswich Borough Council
* {{Authority control Ipswich, Towns in Suffolk County towns in England Non-metropolitan districts of Suffolk Port cities and towns of the North Sea River Orwell Trading posts of the Hanseatic League Unparished areas in Suffolk Populated places established in the 1st millennium Former civil parishes in Suffolk Boroughs in England