Iostat (Unix) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
iostat (''input/output statistics'') is a computer
FreeBSD iostat(8) manual page
Mac OS X iostat manual page
Unix file system-related software System monitors Computer performance System administration
system monitor
A system monitor is a hardware or software component used to monitor system resources and performance in a computer system.
Among the management issues regarding use of system monitoring tools are resource usage and privacy.
Overview
Software ...
tool used to collect and show operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
storage
Storage may refer to:
Goods Containers
* Dry cask storage, for storing high-level radioactive waste
* Food storage
* Intermodal container, cargo shipping
* Storage tank
Facilities
* Garage (residential), a storage space normally used to store car ...
input and output statistics. It is often used to identify performance issues with storage devices, including local disks, or remote disks accessed over network file systems such as NFS. It can also be used to provide information about terminal (TTY) input and output, and also includes some basic CPU information.
Syntax and availability
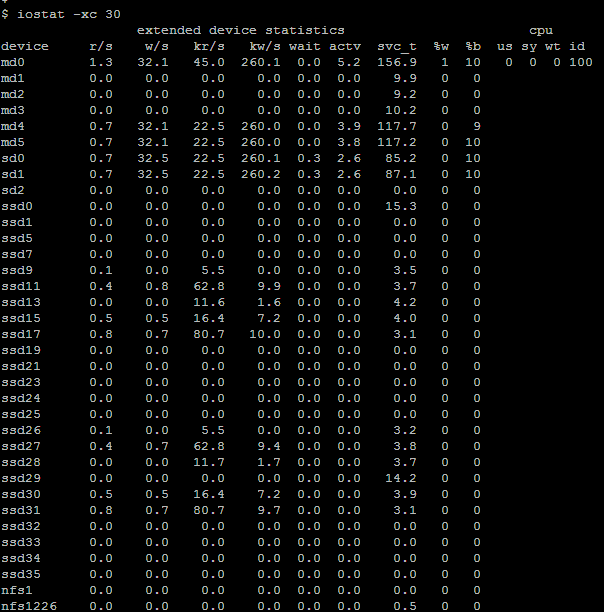
iostat -x displays output where each line (row) gives numerical data for one device. The first column lists the device name, and subsequent columns show various statistics for that device. Columns include the average service time (''svc_t'', which includes not only the time a request is in the service queue, but also the seek time and transfer time), the average busy percentage (''%b'', essentially the proportion of time that the device is in use), and the percentage of time that the queue is not empty (''%w'', which means the proportion of time in which requests from the device have not yet been fulfilled).
It is best to run iostat specifying a time interval in seconds (for example iostat -x 30) in order to see the results over time. This is because otherwise, the output will reflect the values over the entire timespan since the system was last rebooted.
The iostat tool is available on most Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, a ...
and Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X or *nix) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-li ...
operating systems, such as FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), which was based on Research Unix. The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993. In 2005, FreeBSD was the most popular ...
, macOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of ...
(''com.apple.pkg.Core'' package), Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which i ...
( sysstat package), and Solaris. The syntax and output of iostat often differs slightly between them.
Output of the command
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. (Sun for short) was an American technology company that sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services and created the Java programming language, the Solaris operating system, ZFS, ...
stated that high values in the ''wait'' and ''svc_t'' fields suggest a lack of overall throughput in the system, indicating that "the system is overloaded with I/O operations". Consistently high values in the ''kr/s'', ''kw/s'', ''%w'' and ''%b'' fields also indicate "a possible I/O bottleneck".
In versions of Solaris before Solaris 7, iostat can give misleading information in the ''wait'' field on multiprocessor
Multiprocessing is the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor or the ability to allocate tasks between them. There ar ...
systems. This is because iostat can misinterpret one processor being in a state where it is waiting for I/O, as meaning that all processors in the system are having to wait.
It is also advisable to disregard high values in the ''svc_t'' field for disks that have very low rates of activity (less than 5%). This is because the ''fsflush'' process can force up the average service time when synchronising data on disk with what is in memory.
iostat does not display information about the individual volumes on each disk if a volume manager is used . The ''vxstat'' command can be used to show this information instead. In contrast, when using Linux LVM as a volume manager, iostat does display volume information individually, because each logical volume has its own device mapper (dm) device.
See also
* Disk-drive performance characteristics * mpstat * netstat * sar (Unix) * systat * vmstatReferences
{{ReflistExternal links
FreeBSD iostat(8) manual page
Mac OS X iostat manual page
Unix file system-related software System monitors Computer performance System administration