Intraventricular Administration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Intracerebroventricular injection (often abbreviated as ICV injection) is a route of administration for drugs via injection into the
Intracerebroventricular injection (often abbreviated as ICV injection) is a route of administration for drugs via injection into the
 Many factors must be considered with intracerebroventricular injection to maintain safety. Some of these factors include osmolarity, pH, volume, and the presence of preservatives in the drug solution. Also, intracranial pressure, cerebrospinal fluid bulk flow rate, and buffering capacity have an impact on the distribution and safety of the injected drug. A major concern of ICV injection is neurovascular injury and intracranial hemorrhage. The risk of these conditions increases with each additional injection or "tap". For this reason, if repeated taps are needed, a catheter-based device can be implanted. These devices are connected to a subcutaneous reservoir, the most common being the
Many factors must be considered with intracerebroventricular injection to maintain safety. Some of these factors include osmolarity, pH, volume, and the presence of preservatives in the drug solution. Also, intracranial pressure, cerebrospinal fluid bulk flow rate, and buffering capacity have an impact on the distribution and safety of the injected drug. A major concern of ICV injection is neurovascular injury and intracranial hemorrhage. The risk of these conditions increases with each additional injection or "tap". For this reason, if repeated taps are needed, a catheter-based device can be implanted. These devices are connected to a subcutaneous reservoir, the most common being the
 Intracerebroventricular injection (often abbreviated as ICV injection) is a route of administration for drugs via injection into the
Intracerebroventricular injection (often abbreviated as ICV injection) is a route of administration for drugs via injection into the cerebral ventricles
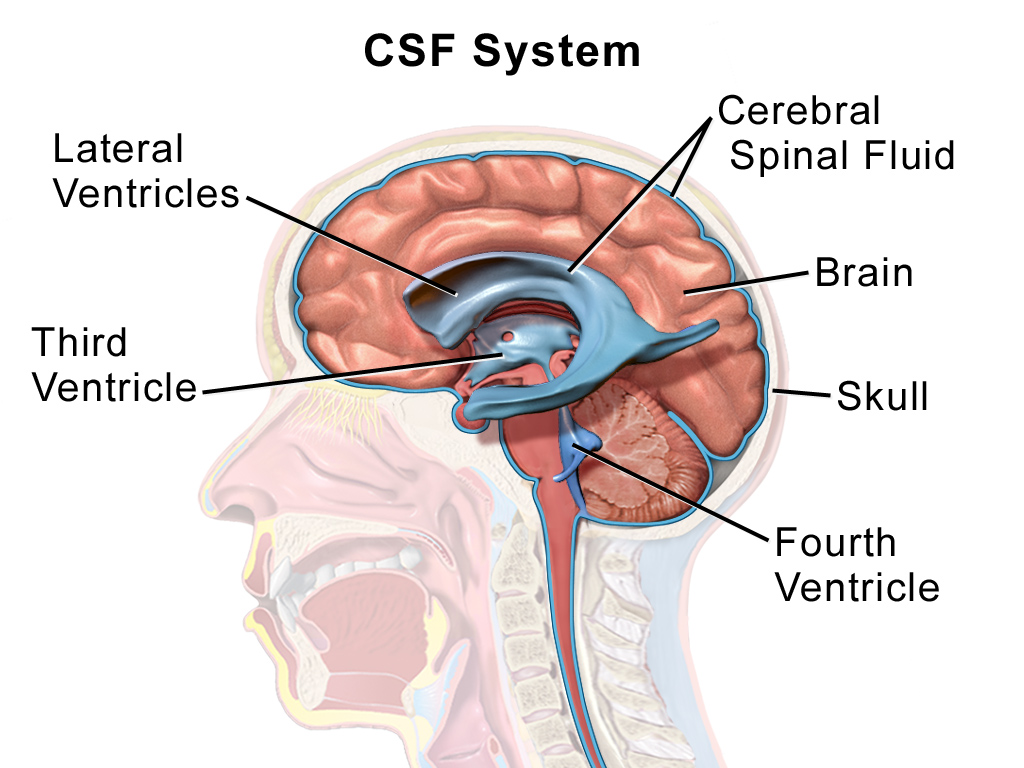
In neuroanatomy, the ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricu ...
so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
(CSF). This route of administration is often used to bypass the blood-brain barrier because it can prevent important medications from reaching the central nervous system. This injection method is widely used in diseased mice models to study the effect of drugs, plasmid DNA, and viral vectors on the central nervous system. In humans, ICV injection can be used for the administration of drugs for various reasons. Examples include the treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that results in the loss of motor neurons and progressive muscle wasting. It is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and if left untreated it is the most common geneti ...
(SMA), the administration of chemotherapy in glioma
A glioma is a type of primary tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or spinal cord. They are malignant but some are extremely slow to develop. Gliomas comprise about 30% of all brain and central nervous system tumors and 80% of ...
s, and the administration of drugs for long-term pain management
Pain management is an aspect of medicine and health care involving relief of pain (pain relief, analgesia, pain control) in various dimensions, from acute (medicine), acute and simple to chronic condition, chronic and challenging. Most physici ...
. ICV injection is also used in the creation of diseased animal models specifically to model neurological disorders.
Uses
Creation of Animal Models
Intracerebroventricular injection has been used to inject drugs that induce a diseased state to create animal models for a variety of diseases. Of these,Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
(AD) animal models are heavily represented in the literature.
ICV injection of Streptozotocin
Streptozotocin or streptozocin ( INN, USP) (STZ) is a naturally occurring alkylating antineoplastic agent that is particularly toxic to the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas in mammals. It is used in medicine for treating certain can ...
has been used to create a metabolic model of Alzheimer's disease. This protocol works by damaging the control level of cerebral glucose metabolism to mimic Alzheimer's disease symptoms. An early sign of AD is glucose hypometabolism and impaired insulin signaling has been seen in AD patients. Streptozotocin has also largely been used to create diabetes animal models, by injecting either intravenously or intraperitoneally. These ICV injections result in models for the sporadic Alzheimer's disease (sAD) form, rather than familial. A characteristic of sAD is an insulin-resistant brain state (IRBS). Streptozotocin is a beta-cytotoxic drug and by injecting it directly into the cerebral ventricles, the treated mice develop symptoms that align with sAD symptoms in humans. Some of these symptoms include IRBS-associated memory impairment, glucose hypometabolism, oxidative stress, and neurodegeneration.
More recently, a model for AD that represents both familial and sporadic AD has emerged. In the clinic, as well as independent experiments, an increase in amyloid beta (Aβ) levels in the brain has been seen to cause Alzheimer-like symptoms. To create an animal model of AD, Aβ can be injected using ICV injection. A benefit of this pathogen-induced model is that it shows Alzheimer's-like symptoms, while also exhibiting Aβ pathology. This is present in both familial and sporadic AD, making it a more inclusive model. Additionally, the level of Aβ can be controlled, making it an ideal candidate for AD investigation. However, damage to the brain tissue during ICV injection must be minimized to prevent neuronal injury. This requires a highly trained individual or surgeon.
Testing in Animals
Intracerebroventricular injection has also been used to test therapeutics and other drugs in animals. Examples of these studies include injection ofbromodeoxyuridine
Bromodeoxyuridine (5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine, BrdU, BUdR, BrdUrd, broxuridine) is a synthetic nucleoside analogue with a chemical structure similar to thymidine. BrdU is commonly used to study cell proliferation in living tissues and has been s ...
for proliferation tracing, Apelin-13 for cerebral ischemia
Brain ischemia is a condition in which there is insufficient bloodflow to the brain to meet metabolic demand. This leads to poor oxygen supply in the brain and may be temporary such as in transient ischemic attack or permanent in which there is ...
, and α-interferon for its antiviral and antibiotic properties.
ICV injection of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) has been used to determine the effectiveness of this injection method compared to intraperitoneal administration. BrdU is a widely used marker to detect proliferative cells in the brain. It is assumed that the number of labeled nuclei after BrdU administration is an indicator of the intensity of cell proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation ...
. In the study, there was an increase in BrdU-positive nuclei in the parenchyma for ICV injection compared to the levels for intraperitoneal administration. This indicates a greater level of the tracer is introduced when injected directly into the ventricular cerebrospinal fluid.
Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is the main pathophysiological process present in ischemic stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop ...
. Apelin regulates many physiological functions including cardiovascular function, endocrine function, nervous system function, and feeding behavior. This regulation occurs through combination with the APJ receptor, and this system is present in many brain regions. In previous studies, lateral ICV injection of Apelin-13 was done to observe apoptosis during cerebral I/R injury. This route of administration allows for the necessary level of Apelin-13 to reach the brain regions that are impacted by ischemia and hypoxia.
ICV injection of α-Interferon has been used for the treatment of intracranial malignancies in the clinic. α-Interferon has antiviral, antibacterial, and immunostimulatory properties. However, severe central nervous system symptoms occur after injection for ICV, intravenous, and intramuscular routes of administration. Additionally, only .09-.18% of the total Interferon dose was seen to pass through the blood-brain barrier when injected intramuscularly. In one study, intraperitoneal injection of α-Interferon was done on mice and there was no impact on monoamine levels. Another study conducted a similar experiment using the ICV injection method. This study showed reduced monoamine levels in the frontal cortex, in a dose-dependent manner. This indicates that ICV injection increases the percentage of the dose that reaches the mouse brain.
Human Therapeutics
In recent years, gene andcell therapy
Cell therapy (also called cellular therapy, cell transplantation, or cytotherapy) is a therapy in which viable cells are injected, grafted or implanted into a patient in order to effectuate a medicinal effect, for example, by transplanting T- ...
therapeutic options have become increasingly present in the clinic. For some of these therapeutics, the administration of the drug directly into the central nervous system is optimal for the treatment of neurological disorders, while avoiding a severe immune response. Additionally, most of the dose is introduced directly into the target area with ICV injection. In addition to these therapies, ICV injection has been used for the delivery of chemotherapies
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a cura ...
, treatment of carcinomatous meningitis, and other neurological disorder
Neurological disorders represent a complex array of medical conditions that fundamentally disrupt the functioning of the nervous system. These disorders affect the brain, spinal cord, and nerve networks, presenting unique diagnosis, treatment, and ...
s.
In the design of gene therapies
Gene therapy is medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells.
The first attempt at modifying human DNA was performed in 1 ...
, the proper adeno-associated virus
Adeno-associated viruses (AAV) are small viruses that infect humans and some other primate species. They belong to the genus '' Dependoparvovirus'', which in turn belongs to the family ''Parvoviridae''. They are small (approximately 26 nm in ...
(AAV) serotype
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or Cell (biology), cells are classified together based on their shared reactivity ...
must be selected. AAV is effective at transporting genetic material in vivo, and there are more than 100 serotypes for AAV that have been identified. Each serotype has a different binding capacity to cell surface receptors. Three serotypes have been identified for their promising specificity to the central nervous system. In a 2017 study, AAV2/1, AAVDJ8, and AAV9 were administered to neonatal mice via ICV injection. The brains of these mice were analyzed for GFP expression following this procedure. The results of this showed that AAV2/1 had higher expression in the cortical layers while penetrating less to the midbrain compared to the AAVDJ8 and AAV9 serotypes. The results indicate that ICV injection of AAV vectors is successful for having a lasting expression of the transgene.
Primary malignant brain tumors (PMBT) and brain metastases have a high impact on patients with both high morbidity and mortality rates. For patients impacted by this, treatment consists primarily of palliative care. However, multimodal therapy using intra-CSF chemotherapy has shown promise in overt leukemic or lymphomatous meningeosis and primary CNS lymphomas. This form of chemotherapy is less toxic while maintaining similar efficacy to cranial irradiation, by preventing the infiltration and proliferation of leukemic and tumor cells into the leptomeninges.
In a 2019 study, autologous non-genetically modified adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction (ADSVF) was injected into 24 patients using an ICV injection procedure. Seven other patients were injected through ventriculoperitoneal shunts. These seven patients were being treated for varying neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer's disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results i ...
(ALS), progressive multiple sclerosis (MS-P), Parkinson's
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become more prevalen ...
, spinal cord injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. It is a destructive neurological and pathological state that causes major motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunctions.
Symptoms of ...
, traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumati ...
, and stroke. A total of 113 injections were performed on the 31 patients, with one patient having up to 15 injections over three years. Follow-up was conducted for each participant, with varying follow-up times. One patient developed an infection from their implant, and four patients required hospitalization after their injections. Overall, the results indicate that ICV injections, both single and repeat, are safe.
Pain Management
Intracerebroventricular injection has also been historically used for pain management. These procedures are primarily focused on refractory head and facial pain, peripheral nerve injury, and other persistent pain conditions. Six patients with either refractory trigeminal neuralgia or cluster headaches were treated with an ICV opiate infusion pump. Visual analog scores (VAS) were obtained before and after injection to measure effectiveness. When compared, VAS scores improved from an average of 7.8 to 2.8 after the procedure. Most complications that occurred from this procedure consisted of nausea and drowsiness. These symptoms went away after the pump was adjusted. ICV pumps are typically kept in and replaced every four to five years, making the procedure ideal for patients with chronic pain. The CTK 01512-2 peptide toxin can act as avoltage-gated calcium channel
Voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), also known as voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), are a group of voltage-gated ion channels found in the membrane of excitable cells (''e.g.'' muscle, glial cells, neurons) with a permeability to ...
(VGCC) blocker. In previous studies, it was shown to have a prolonged effect on preventing and reducing the processing of harmful stimuli by the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. To strengthen this finding, the CTK 01512-2 toxin was tested on two models of persistent pain. These models include chronic post-ischemia pain (CPIP) and paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. Additionally, the peptide was injected using three routes of administration: intravenous, intrathecal, and intracerebroventricular. This approach is beneficial for patients who do not respond to traditional pain management approaches. This also addresses the side effects that occur when using opioid agents. The results of this study showed that pain-reducing effects were observed with all three methods of administration.
The drugs gabapentin
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropath ...
and pregabalin
Pregabalin, sold under the brand name Lyrica among others, is an anticonvulsant, analgesic, and anxiolytic amino acid medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, restless legs syndrome, opioid withdrawal, generalized anx ...
have long since been used for the treatment of neuropathic pain conditions. The mechanism behind the effectiveness of these drugs is not fully known. However, gabapentin and pregabalin were demonstrated to have supraspinal-mediated analgesic effects after peripheral nerve injury. This is due to the noradrenergic pain inhibitory system that is employed by these drugs, coupled with spinal receptors that produce analgesic effects. The results of this study indicate that ICV injection of these drugs decreases thermal and mechanical hypersensitivity in a murine chronic pain model that has partial ligation of the sciatic nerve.
Complications
 Many factors must be considered with intracerebroventricular injection to maintain safety. Some of these factors include osmolarity, pH, volume, and the presence of preservatives in the drug solution. Also, intracranial pressure, cerebrospinal fluid bulk flow rate, and buffering capacity have an impact on the distribution and safety of the injected drug. A major concern of ICV injection is neurovascular injury and intracranial hemorrhage. The risk of these conditions increases with each additional injection or "tap". For this reason, if repeated taps are needed, a catheter-based device can be implanted. These devices are connected to a subcutaneous reservoir, the most common being the
Many factors must be considered with intracerebroventricular injection to maintain safety. Some of these factors include osmolarity, pH, volume, and the presence of preservatives in the drug solution. Also, intracranial pressure, cerebrospinal fluid bulk flow rate, and buffering capacity have an impact on the distribution and safety of the injected drug. A major concern of ICV injection is neurovascular injury and intracranial hemorrhage. The risk of these conditions increases with each additional injection or "tap". For this reason, if repeated taps are needed, a catheter-based device can be implanted. These devices are connected to a subcutaneous reservoir, the most common being the Ommaya reservoir
An Ommaya reservoir is an intraventricular catheter system that can be used for the aspiration of cerebrospinal fluid or for the delivery of drugs (e.g. chemotherapy) into the cerebrospinal fluid. It consists of a catheter in one lateral ventric ...
. This can be accessed multiple times, with a sterile puncture through the scalp into the reservoir. There is also an associated risk of infection with this method, but it is less likely than other methods of accessing the intraventricular space. Other rare complications with this method include leukoencephalopathy, white matter necrosis, and intracerebral hemorrhage.
Other complications can occur with this procedure, and they can be divided into infectious and noninfectious categories. Of the noninfectious complications, the most frequently reported were CSF leaks, hemorrhage, catheter malposition, catheter obstruction, and device malfunction. In one study, the most likely cause for device removals was due to infectious complications (73.75 percent). Of the infections, the most common cause was skin flora. The aseptic technique during insertion and handling has been shown to decrease the occurrence of these complications. Also, in some cases of infection, antibiotics could be given through the ICV system, avoiding the need for removal.
Administration Technique
Anatomy
The blood-brain barrier protects the brain by restricting the ability of large molecules to cross the barrier between the blood, CSF, and interstitial fluid of the brain. ICV injection circumvents this barrier, to be able to deliver drugs to the CSF. An ICV device is implanted under the scalp, into the subgaleal space where it is then connected to the ventricles with an outlet catheter. This allows for repeated doses of the drug without having to re-puncture the scalp. Production of CSF is at a rate of about .3 mL/minute and occurs at theependyma
The ependyma is the thin neuroepithelial ( simple columnar ciliated epithelium) lining of the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. The ependyma is one of the four types of neuroglia in the central nervous s ...
l and parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
l regions and the choroid plexus
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central ...
. Up to 80 percent of CSF production comes from the choroid plexus, which is present within the lateral, third, and fourth ventricles. The choroid is lined with epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
with tight junctions at the ventricular side of the cells. This comprises the blood-CSF barrier. Whereas the blood-brain barrier is made up of vascular endothelium in capillary beds throughout the CNS parenchyma.
Insertion
For insertion in mice, a permanent ICV guide cannula must be inserted 1 mm above the lateral ventricle. A trained surgeon is ideal for insertion, and a stereotaxic frame and bone cement are needed. The cannula is implanted through the hindlimb area of the cerebral cortex. The surgeon must be careful to minimize damage to the surrounding brain tissue during this process. A catheter connected to a subcutaneous reservoir is implanted for permanent access in humans. The reservoir used is most commonly the Ommaya reservoir. A 25-gauge needle is used to puncture the scalp into the reservoir. A few milliliters of CSF are withdrawn before injecting the drug. This technique is typically used for long-term drug administration. Rarely will repeated taps be conducted to administer drugs due to the risk of damaging brain tissue.References
{{reflist Medical treatments Routes of administration Injection (medicine) Ventricular system