Intranasal Drug Delivery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Intranasal drug delivery occurs when particles are inhaled into the nasal cavity and transported directly into the nervous system. Though pharmaceuticals can be injected into the nose, some concerns include injuries, infection, and safe disposal. Studies demonstrate improved

 The nasal cavity is highly vascularized, allowing efficient transfer of molecules directly to the nervous system. Compared to other administration routes, nasal drug delivery increases bioavailability and reduces systemic exposure risks. The nasal cavity’s slightly acidic environment and enzymes can affect drug degradation, making delivery systems with neutral to acidic pH ideal. The respiratory region, with its large surface area and high vascularization, is the primary site for drug absorption into systemic circulation. Targeting the olfactory region enhances nose-to-brain drug delivery, as particles can travel via the olfactory nerve to the brain. This route offers potential for treating brain diseases and mental health conditions.
The nasal cavity is highly vascularized, allowing efficient transfer of molecules directly to the nervous system. Compared to other administration routes, nasal drug delivery increases bioavailability and reduces systemic exposure risks. The nasal cavity’s slightly acidic environment and enzymes can affect drug degradation, making delivery systems with neutral to acidic pH ideal. The respiratory region, with its large surface area and high vascularization, is the primary site for drug absorption into systemic circulation. Targeting the olfactory region enhances nose-to-brain drug delivery, as particles can travel via the olfactory nerve to the brain. This route offers potential for treating brain diseases and mental health conditions.
 The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a semipermeable membrane that separates the blood from the brain’s interstitial fluid. It is formed by tight junctions between endothelial cells, astrocytes, and pericytes in the brain’s capillaries, and has high electrical resistance. The BBB is crucial for protecting the brain from pathogens and toxic substances, maintaining homeostasis, and preventing alterations to neuronal functions. However, some diseases can damage the BBB, causing leakage. Research suggests that increasing intake of vitamins and antioxidants, as well as reducing stress, can help restore the BBB. Due to its selective nature, the BBB restricts the passive diffusion of solutes, large and hydrophilic molecules, and immune factors, making it challenging to deliver pharmaceuticals directly to the brain.
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a semipermeable membrane that separates the blood from the brain’s interstitial fluid. It is formed by tight junctions between endothelial cells, astrocytes, and pericytes in the brain’s capillaries, and has high electrical resistance. The BBB is crucial for protecting the brain from pathogens and toxic substances, maintaining homeostasis, and preventing alterations to neuronal functions. However, some diseases can damage the BBB, causing leakage. Research suggests that increasing intake of vitamins and antioxidants, as well as reducing stress, can help restore the BBB. Due to its selective nature, the BBB restricts the passive diffusion of solutes, large and hydrophilic molecules, and immune factors, making it challenging to deliver pharmaceuticals directly to the brain.
 Nanoparticles are drug delivery systems ranging from 1–1000 nm in diameter. Lipid-based and polymer-based nanocarriers are commonly used for nose-to-brain delivery as they exert high stability, solubility, and adherence. Exosomes and dendrimers are other potential nanocarriers. Nanosystems can be synthesized either using physical or chemical methods. A few physical methods include evaporation-condensation reaction and laser ablation. Irradiation, microemulsion, and chemical reduction are common chemical techniques to develop nanoparticles. Sonication, electroporation, and incubation are common methods to load drugs into nanocarriers.
Coating these nanosystems with mucoadhesive agents, stimulus-sensitive materials, or antibodies can enhance biocompatibility, clearance rates, specificity, and bioavailability. Penetration and absorption enhancers can significantly increase the overall efficacy of the system. Imaging studies along with measurement of drug transfer efficiency and bioavailability can further support the role of these drug delivery systems.
Nanoparticles are drug delivery systems ranging from 1–1000 nm in diameter. Lipid-based and polymer-based nanocarriers are commonly used for nose-to-brain delivery as they exert high stability, solubility, and adherence. Exosomes and dendrimers are other potential nanocarriers. Nanosystems can be synthesized either using physical or chemical methods. A few physical methods include evaporation-condensation reaction and laser ablation. Irradiation, microemulsion, and chemical reduction are common chemical techniques to develop nanoparticles. Sonication, electroporation, and incubation are common methods to load drugs into nanocarriers.
Coating these nanosystems with mucoadhesive agents, stimulus-sensitive materials, or antibodies can enhance biocompatibility, clearance rates, specificity, and bioavailability. Penetration and absorption enhancers can significantly increase the overall efficacy of the system. Imaging studies along with measurement of drug transfer efficiency and bioavailability can further support the role of these drug delivery systems.
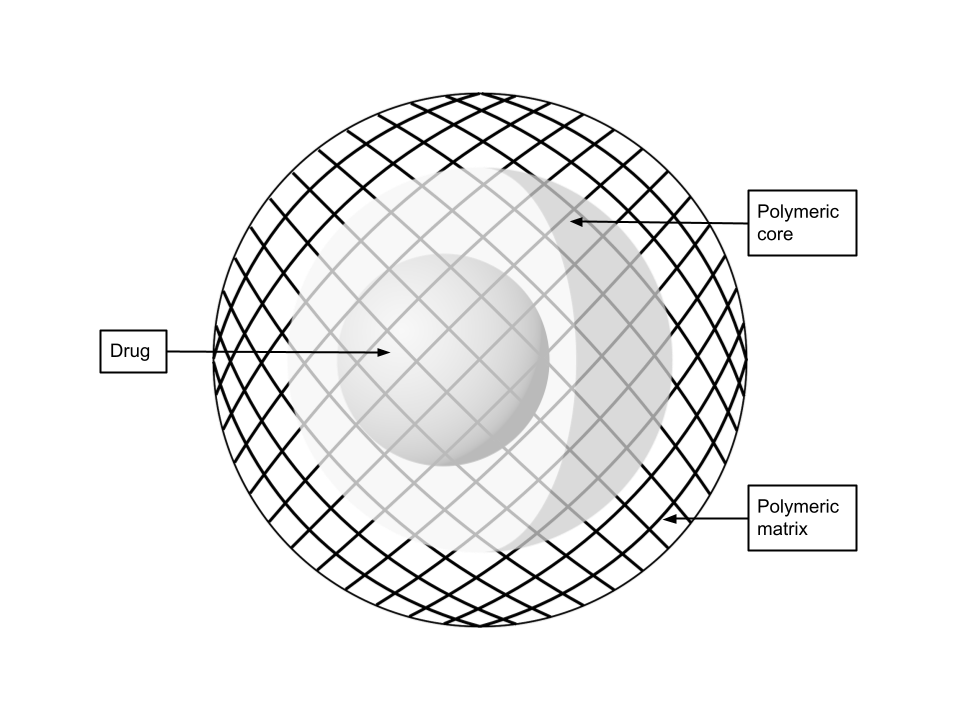
 Polymer-based nanoparticles can be made from either natural or synthetic sources. Nanospheres and nanocapsules are polymeric nanoparticle systems. Natural polymers can be found in the environment or human body. On the other hand, synthetic polymers do not occur naturally and are artificially developed polymers with chemical modifications. Natural polymer-based nanoparticles can be made up of chitosan,
Polymer-based nanoparticles can be made from either natural or synthetic sources. Nanospheres and nanocapsules are polymeric nanoparticle systems. Natural polymers can be found in the environment or human body. On the other hand, synthetic polymers do not occur naturally and are artificially developed polymers with chemical modifications. Natural polymer-based nanoparticles can be made up of chitosan,
 Exosomes are vesicular structures containing genetic information. Recently, exosomes are being utilized as drug carriers. These systems are observed to be stable, specific, and safe. Moreover, delivery of exosomes shows less immunogenic affects. Further surface modifications and conjugation with liposomes enhances the therapeutic effects. Based on a previous study, intranasal delivery of exosomes loaded with a
Exosomes are vesicular structures containing genetic information. Recently, exosomes are being utilized as drug carriers. These systems are observed to be stable, specific, and safe. Moreover, delivery of exosomes shows less immunogenic affects. Further surface modifications and conjugation with liposomes enhances the therapeutic effects. Based on a previous study, intranasal delivery of exosomes loaded with a 
patient compliance
In medicine, patient compliance (also adherence, capacitance) describes the degree to which a person correctly follows medical advice. Most commonly, it refers to medication or drug compliance, but it can also apply to other situations such as me ...
with inhalation. Treating brain diseases has been a challenge due to the blood brain barrier
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is compo ...
. Previous studies evaluated the efficacy of delivery therapeutics through intranasal route for brain diseases and mental health conditions. Intranasal administration is a potential route associated with high drug transfer from nose to brain and drug bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. H ...
.
History of drug delivery
Drug delivery
Drug delivery involves various methods and technologies designed to transport pharmaceutical compounds to their target sites helping therapeutic effect. It involves principles related to drug preparation, route of administration, site-specif ...
is a process of administering therapeutics to treat human diseases. The first drug delivery system is often dated to the 1950s, when Smith Kline & French Laboratories introduced the Spansule technology. Between 1950s and 1980s, there were four drug release systems developed for oral and transdermal applications: dissolution, diffusion, osmosis, and ion-exchange controlled release. Later in the 1980s, the Lupron Depot technology further advanced the field by offering zero-order and long-term release systems. The intranasal route gained interest towards the end of the 20th century with treating cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. During the late 1980s, William Frey II studied the intranasal route for treating brain diseases. Ever since, it has become a potential route for nose-to-brain delivery.
Anatomy
Intranasal delivery pathway

 The nasal cavity is highly vascularized, allowing efficient transfer of molecules directly to the nervous system. Compared to other administration routes, nasal drug delivery increases bioavailability and reduces systemic exposure risks. The nasal cavity’s slightly acidic environment and enzymes can affect drug degradation, making delivery systems with neutral to acidic pH ideal. The respiratory region, with its large surface area and high vascularization, is the primary site for drug absorption into systemic circulation. Targeting the olfactory region enhances nose-to-brain drug delivery, as particles can travel via the olfactory nerve to the brain. This route offers potential for treating brain diseases and mental health conditions.
The nasal cavity is highly vascularized, allowing efficient transfer of molecules directly to the nervous system. Compared to other administration routes, nasal drug delivery increases bioavailability and reduces systemic exposure risks. The nasal cavity’s slightly acidic environment and enzymes can affect drug degradation, making delivery systems with neutral to acidic pH ideal. The respiratory region, with its large surface area and high vascularization, is the primary site for drug absorption into systemic circulation. Targeting the olfactory region enhances nose-to-brain drug delivery, as particles can travel via the olfactory nerve to the brain. This route offers potential for treating brain diseases and mental health conditions.
Blood brain barrier
 The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a semipermeable membrane that separates the blood from the brain’s interstitial fluid. It is formed by tight junctions between endothelial cells, astrocytes, and pericytes in the brain’s capillaries, and has high electrical resistance. The BBB is crucial for protecting the brain from pathogens and toxic substances, maintaining homeostasis, and preventing alterations to neuronal functions. However, some diseases can damage the BBB, causing leakage. Research suggests that increasing intake of vitamins and antioxidants, as well as reducing stress, can help restore the BBB. Due to its selective nature, the BBB restricts the passive diffusion of solutes, large and hydrophilic molecules, and immune factors, making it challenging to deliver pharmaceuticals directly to the brain.
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a semipermeable membrane that separates the blood from the brain’s interstitial fluid. It is formed by tight junctions between endothelial cells, astrocytes, and pericytes in the brain’s capillaries, and has high electrical resistance. The BBB is crucial for protecting the brain from pathogens and toxic substances, maintaining homeostasis, and preventing alterations to neuronal functions. However, some diseases can damage the BBB, causing leakage. Research suggests that increasing intake of vitamins and antioxidants, as well as reducing stress, can help restore the BBB. Due to its selective nature, the BBB restricts the passive diffusion of solutes, large and hydrophilic molecules, and immune factors, making it challenging to deliver pharmaceuticals directly to the brain.
Recent studies on nose-to-brain drug delivery
Alzheimer's
Neurodegenerative disease
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Neuronal damage may also ultimately result in their death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, mul ...
s occur from loss of neuronal structure and function. This progressive degeneration of neurons is irreversible. Alzheimer's
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
is a neurodegenerative disease that begins with short-term memory loss progressing to loss of control over heartbeat and breathing. It has been over 100 years since Alois Alzheimer first presented the world disease to the world in 1906. There is evidence for the efficacy of intranasal delivery to treat Alzheimer's. Intranasal delivery of insulin showed greater memory improvement in patients with Alzheimer's than in healthy individuals. Increased microglial activation inflammation are characteristics of Alzheimer's. Animal studies show intranasal administration of pro-resolving lipid mediators decreased both factors, slowing pathogenesis
In pathology, pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes .
Descript ...
of this disease. Delivering a novel peptide via intranasal route reduced amyloid beta plaques, a defining trait of Alzheimer's and enhanced cognitive functions. Intranasal delivery of anti-Alzheimer's drug dispersed through hydrogel in rabbits demonstrated higher bioavailability compared to oral tablets. MiR132 is an RNA molecule that regulates neuronal morphology and maintains survival. This molecule is downregulated with Alzheimer's. A study administered PEG-PLA nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At ...
s loaded with this miRNA to mice through the nasal route. This novel therapy showed increased expression of miR132 and improved memory function. To strengthen the effectiveness of intranasal delivery, there are studies to develop permeation enhancers to better improve drug transport across the blood brain barrier.
Glioblastoma
Abnormal cell growth and formation of mass in the brain tissue or nearby regions may cause brain cancer. Constant headaches, seizures, and blurred vision are common symptoms.Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nons ...
(GBM) is the most fast-growing and deadliest brain tumor. Though the main cause of glioblastoma remains unknown, it originates when astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" and , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of en ...
s mutate and multiply uncontrollably forming tumors in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. The challenge with current therapeutics is to initiate tumor cell apoptosis with no toxic effects to healthy brain tissue. Nanoparticles loaded with chemotherapeutics delivered through the intranasal route show promising results in treating glioblastoma. PLGA
PLGA, PLG, or poly(lactic-''co''-glycolic) acid (CAS Registry Number, CAS: ) is a copolymer which is used in a host of Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved therapeutic devices, owing to its biodegradation, biodegradability and biocompatibi ...
-based nanoparticles loaded with paclitaxel
Paclitaxel, sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer, and pancreatic cancer. It is administered b ...
or doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used toge ...
conjugated with a RGD sequence targeted the glioblastoma microenvironment and reduced tumor volume through cell death. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) inhibits pro-apoptotic genes increasing progression of glioblastoma. Self-assembling nanoparticles produced with anti-tumor peptides were administered intranasally and reduced miR-21 levels increasing tumor cell apoptosis.
Epilepsy
Infection, head injury, or strokes can cause sudden bursts of neuronal activity leading to abnormal behaviors, muscle movement, and mood changes. This condition is known as seizure.Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
is characterized by recurring seizures. Some possible causes of epilepsy include imbalance or disruption of neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
s, strokes, or brain injury. Intranasal delivery of carbamazepine
Carbamazepine, sold under the brand name Tegretol among others, is an anticonvulsant medication used in the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It is used as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia along with other medications and as ...
nanoparticles increase antiepileptic drug bioavailability. Administering a self-assembling hydrogel with neuroactive drugs to treat Parkinson's disease appears to be biocompatible, low in toxicity, and have a good recovery capacity. Nasal delivery of this gel demonstrated increased drug concentration in the brain. Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Present in animals since early stages of evolution, in humans it plays roles in behavior that include Human bonding, ...
is a hormone which is observed to alleviate anxiety symptoms in people with autism. Intranasal administration indicated efficient transfer of pharmacologically active oxytocin from nasal cavity to brain.
Parkinson's
Similar to Alzheimer's,Parkinson's
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become more prevalen ...
is the most common neurodegenerative disease associated with balance and coordination issues, muscle stiffness, and tremors. During the early 1800s, James Parkinson medically defined this disease. A study observed improvement in locomotor abilities in rats with Parkinson's after intranasal delivery of conjugated mitochondrial systems. Another study demonstrated delivery of neuroactive drugs in a hydrogel increased residence times in the nasal cavity and concentration in the brain. Administering therapeutics combined with nanocarriers is shown to directly transfer drugs to the target cells and enhance accumulation. The observed effects include improved neuronal signaling and locomotion. Furthermore, intranasal delivery of biodegradable nanoparticles surface-modified with lactoferrin
Lactoferrin (LF), also known as lactotransferrin (LTF), is a multifunctional protein of the transferrin family. Lactoferrin is a globular proteins, globular glycoprotein with a molecular mass of about 80 Atomic mass unit, kDa that is widely repre ...
increase accumulation in the brain and cellular uptake.
Depression
Characterized by loss ofneuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity or just plasticity, is the ability of neural networks in the brain to change through neurogenesis, growth and reorganization. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to reorganize and rewir ...
, depression is a common mood disorder causing persistent negative emotions and changes in lifestyle. Intranasal delivery of relaxin-3
Relaxin-3 is a neuropeptide that was discovered in 2001, and which is highly conserved in species ranging from flies, fish, rodents and humans. Relaxin-3 is a member and ancestral gene of the relaxin family of peptides, which includes the namesa ...
mimetics demonstrated significant anti-depressant activity in behavior paradigms of rat models. Delivering a thermoresponsive hydrogel loaded with berberine intranasally exhibited high bioavailability in hippocampus and anti-depressant activity.
Anxiety
Anxiety can impair hippocampus function which increases risk of depression and dementia.Anxiolytic
An anxiolytic (; also antipanic or anti-anxiety agent) is a medication or other intervention that reduces anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiogenic agents which increase anxiety. Anxiolytic medications are used for the treatment of anxie ...
effects were observed in animal models post-intranasal delivery of a loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Another study indicated intranasal delivery of neuropeptide Y
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a 36 amino-acid neuropeptide that is involved in various physiological and homeostatic processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. It is secreted alongside other neurotransmitters such as GABA and glu ...
lowered anxiety in rats.
Anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa (AN), often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by Calorie restriction, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin.
Individuals wit ...
(AN) is a common eating disorder characterized by low intake of food from fear of weight gain. Several complications are associated with this chronic disorder such as fatigue, insomnia, and low blood pressure. Intranasal administration of oxytocin in patients with AN significantly lowered food anticipation and eating concern.
Substance use disorder
Uncontrolled and continuous use of a substance, drugs or alcohol, is known as substance use disorder. Substances can interfere with neuronal signaling and potentially disrupt the brain circuit. Addiction to these substances impairs thinking, behavior, and other biological functions. Intranasal delivery of insulin is associated with improvement in brain metabolic activities and alleviate impulsivity.Opioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
addiction is prevalent and associated with many substance abuse deaths. A study observed high biodistribution in the brain and reduction in opioid overdose in rats administered with naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand name Narcan among others, is an opioid antagonist, a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. For example, it is used to restore breathing after an opioid overdose. Effects begin within two ...
-loaded lipid nanoparticles.
Post-traumatic stress disorder
Witnessing a devastating or terrifying situation can lead topost-traumatic stress disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental disorder that develops from experiencing a Psychological trauma, traumatic event, such as sexual assault, domestic violence, child abuse, warfare and its associated traumas, natural disaster ...
(PTSD). This mental health condition triggers anxiety, depression, and extreme fear with memories. Intranasal administration of temperature-sensitive hydrogels loaded with PTSD medications showed enhanced brain targeting effects and tissue distribution. Similarly, another study observed anti-PTSD effects with intranasal administration of loaded hydrogels.
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f ...
is a chronic mental health condition caused by changes in brain chemistry and structure. Genetics and environment are hypothesized to play a key role in development of this disorder. Research suggests impaired gene expression or chemical imbalance may impact this condition. Anxiety can increase risk of schizophrenia and symptoms include hallucinations, disorganized speech, and abnormal behavior. Davunetide (NAP) is a segment of activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP). ADNP is reported be downregulated with schizophrenia. A study observed decreased hyperactivity in mice when treated with NAP via the intranasal route.
Migraine
Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
occurs with episodes of intense headache causing nausea and throbbing pain. Stress and hormonal changes can be a trigger migraine. A nasal spray containing sumatriptan demonstrated a significant reduction of migraine pain. Further clinical studies of intranasal administration of sumatriptan
Sumatriptan, sold under the brand name Imitrex among others, is a medication used to treat migraine headaches and cluster headaches. It is taken Oral administration, orally, Nasal administration, intranasally, or by Subcutaneous injection, su ...
(ST) can help evaluate efficacy and safety of such delivery systems. Since its approval by the FDA in 2021, dihydroergotamine mesylate has been administered through nasal sprays to treat migraines.
Nanosystems for Intranasal Drug Delivery
 Nanoparticles are drug delivery systems ranging from 1–1000 nm in diameter. Lipid-based and polymer-based nanocarriers are commonly used for nose-to-brain delivery as they exert high stability, solubility, and adherence. Exosomes and dendrimers are other potential nanocarriers. Nanosystems can be synthesized either using physical or chemical methods. A few physical methods include evaporation-condensation reaction and laser ablation. Irradiation, microemulsion, and chemical reduction are common chemical techniques to develop nanoparticles. Sonication, electroporation, and incubation are common methods to load drugs into nanocarriers.
Coating these nanosystems with mucoadhesive agents, stimulus-sensitive materials, or antibodies can enhance biocompatibility, clearance rates, specificity, and bioavailability. Penetration and absorption enhancers can significantly increase the overall efficacy of the system. Imaging studies along with measurement of drug transfer efficiency and bioavailability can further support the role of these drug delivery systems.
Nanoparticles are drug delivery systems ranging from 1–1000 nm in diameter. Lipid-based and polymer-based nanocarriers are commonly used for nose-to-brain delivery as they exert high stability, solubility, and adherence. Exosomes and dendrimers are other potential nanocarriers. Nanosystems can be synthesized either using physical or chemical methods. A few physical methods include evaporation-condensation reaction and laser ablation. Irradiation, microemulsion, and chemical reduction are common chemical techniques to develop nanoparticles. Sonication, electroporation, and incubation are common methods to load drugs into nanocarriers.
Coating these nanosystems with mucoadhesive agents, stimulus-sensitive materials, or antibodies can enhance biocompatibility, clearance rates, specificity, and bioavailability. Penetration and absorption enhancers can significantly increase the overall efficacy of the system. Imaging studies along with measurement of drug transfer efficiency and bioavailability can further support the role of these drug delivery systems.
Lipid-based nanoparticles
Lipid-based nanoparticles (LNP) can deliver molecules with low toxicity and controlled release. Liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN), nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC), and nanoemulsions are examples. Liposomes are made up of phospholipids forming spherical vesicles. This property enables liposomes to exhibit high biocompatibility and biodegradability. Studies report potential application of liposomes to treat brain diseases due to increased retention and absorption in nasal cavity, and high brain biodistribution. A previous study developed acationic
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
liposome loaded with mRNA and green fluorescent protein (GFP). Intranasal delivery of this formulation in murine models demonstrated high brain biodistribution and expression of mRNA-GFP.
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) are made up of solid lipids forming a matrix and stabilized by surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word ''surfactant'' is a Blend word, blend of "surface-active agent",
coined in ...
s. They exhibit high physical stability and remain in solid state at different temperatures. Sometimes burst release may occur due to rigidity and less flexibility in shape.
Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) are synthesized by a mixture of solid and aqueous lipids. NLC's are developed from SLNs, thus referred to as second generation LNPs. Intranasal administration of NLC loaded with curcumin
Curcumin is a bright yellow chemical produced by plants of the ''Curcuma longa'' species. It is the principal curcuminoid of turmeric (''Curcuma longa''), a member of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is sold as a herbal supplement, cosmetic ...
(CRM) increased biodistribution and concentration in brain after emerging as a potential system for brain cancer.
Small colloidal systems made of micelle
A micelle () or micella () ( or micellae, respectively) is an aggregate (or supramolecular assembly) of surfactant amphipathic lipid molecules dispersed in a liquid, forming a colloidal suspension (also known as associated colloidal system). ...
s containing oil, aqueous phases, and emulsifiers are called nanoemulsions. Intranasal delivery of gel nanoemulsion loaded with temozolomide
Temozolomide, sold under the brand name Temodar among others, is an anticancer medication used to treat brain tumors such as glioblastoma and anaplastic astrocytoma. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency ...
is observed to exhibit sustained release and better permeation from nose to brain to treat glioblastoma.
Polymer-based nanoparticles

 Polymer-based nanoparticles can be made from either natural or synthetic sources. Nanospheres and nanocapsules are polymeric nanoparticle systems. Natural polymers can be found in the environment or human body. On the other hand, synthetic polymers do not occur naturally and are artificially developed polymers with chemical modifications. Natural polymer-based nanoparticles can be made up of chitosan,
Polymer-based nanoparticles can be made from either natural or synthetic sources. Nanospheres and nanocapsules are polymeric nanoparticle systems. Natural polymers can be found in the environment or human body. On the other hand, synthetic polymers do not occur naturally and are artificially developed polymers with chemical modifications. Natural polymer-based nanoparticles can be made up of chitosan, hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (; abbreviated HA; conjugate base hyaluronate), also called hyaluronan, is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminog ...
, alginate, and gelatin. Natural polymers exhibit excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability, and low toxicity. Synthetic polymer-based nanoparticles can consist of polyglycolic acid
Polyglycolide or poly(glycolic acid) (PGA), also spelled as polyglycolic acid, is a biodegradable, thermoplastic polymer and the simplest linear, aliphatic polyester. It can be prepared starting from glycolic acid by means of polycondensation or ...
(PGA), poly (lactic acid) (PLA), and poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
PLGA, PLG, or poly(lactic-''co''-glycolic) acid ( CAS: ) is a copolymer which is used in a host of Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved therapeutic devices, owing to its biodegradability and biocompatibility. PLGA is synthesized by means ...
(PLGA).
A study evaluated chitosan nanoparticles loaded with an anti-epileptic drug, phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anticonvulsant, anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence se ...
(PHT), to treat epilepsy. Observations suggested high stability, sustained release, and bioavailability when these particles where administered via the intranasal route. Similarly, administering PLGA nanoparticles loaded lamotrigine
Lamotrigine ( ), sold under the brand name Lamictal among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and stabilize mood in bipolar disorder. For epilepsy, this includes focal seizures, tonic-clonic seizures, and seizures in Lennox-Gastau ...
(LTG), polymer-based nanoparticle, showed better permeation through BBB and higher bioavailability.
Exosomes
 Exosomes are vesicular structures containing genetic information. Recently, exosomes are being utilized as drug carriers. These systems are observed to be stable, specific, and safe. Moreover, delivery of exosomes shows less immunogenic affects. Further surface modifications and conjugation with liposomes enhances the therapeutic effects. Based on a previous study, intranasal delivery of exosomes loaded with a
Exosomes are vesicular structures containing genetic information. Recently, exosomes are being utilized as drug carriers. These systems are observed to be stable, specific, and safe. Moreover, delivery of exosomes shows less immunogenic affects. Further surface modifications and conjugation with liposomes enhances the therapeutic effects. Based on a previous study, intranasal delivery of exosomes loaded with a Stat3
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT3'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family.
Function
STAT3 is a member of the STAT protein family. In respon ...
inhibitor reduced brain inflammation and slowed brain tumor growth.

Dendrimers
Dendrimers are polymeric macromolecules with a branched network similar to a tree structure. Generally, they are spherical and homogeneous. Surface charge and molecule chemistry can play crucial role with drug interaction and release. Poly(amidoamine) ( PAMAM) dendrimers are the most commonly used system. A study investigated potential application of dendrimer-based formulation ofhaloperidol
Haloperidol, sold under the brand name Haldol among others, is a typical antipsychotic medication. Haloperidol is used in the treatment of schizophrenia, tics in Tourette syndrome, mania in bipolar disorder, delirium, agitation, acute psychos ...
. Intranasal administration showed improved targeting, and solubility as well as high concentrations in the brain. Drugs can be loaded in dendrimers through formulation and nanoconstruct.
Importance of physiochemical properties
For drug delivery systems to bypass the blood brain barrier, modifications of physiochemical properties can enhance safety and efficacy. Size, surface charge, andlipophilicity
Lipophilicity (from Greek λίπος "fat" and φίλος "friendly") is the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such compounds are called lipophilic (translated ...
play a major role in substance bypassing the blood brain barrier. Smaller, positively charged, or more lipophilic molecules enhance efficacy of nose-to-brain delivery. Decrease in delivery system size increases permeation. As the membrane is negatively charged, a particle with positive surface charge interacts electrostatically which enhances bioadhesion. Carriers with more lipophilicity exert better mucoadhesion and residence time. Drug system pH, solubility, and hydrogen bonding potential are other physiochemical properties which should be evaluated.
References
{{reflist Drug delivery devices