intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
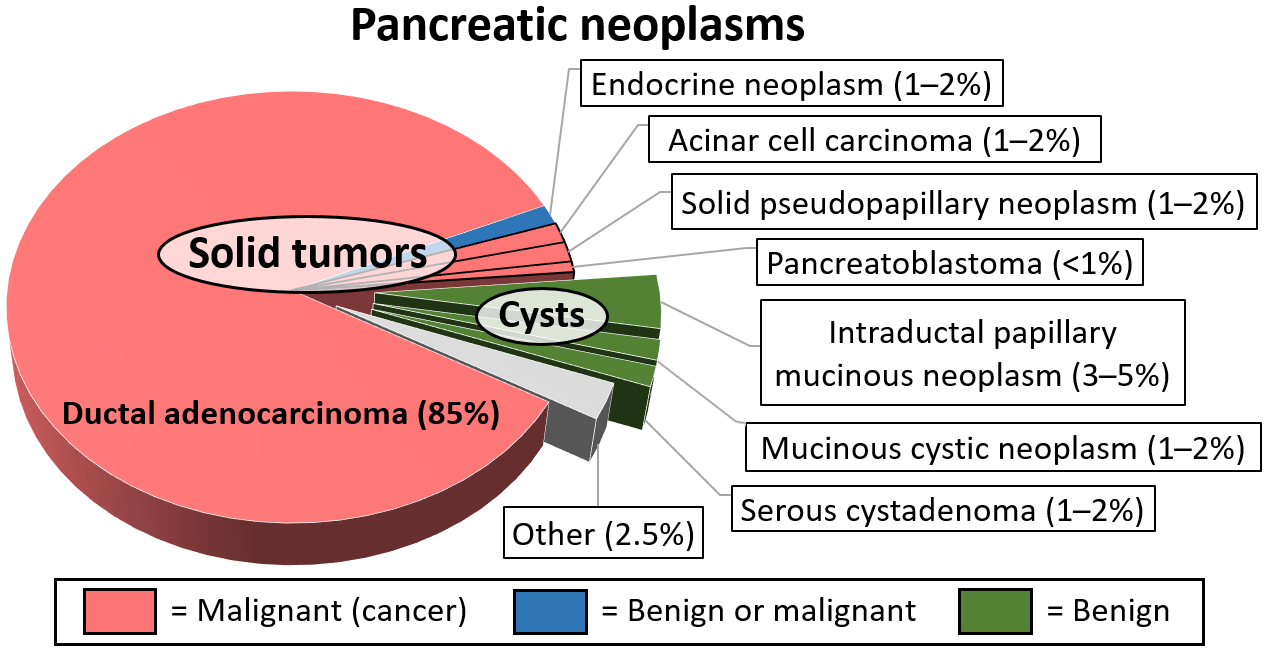
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a type of tumor that can occur within the cells of the pancreatic duct. IPMN tumors produce mucus, and this mucus can form
 In most cases, IPMNs are diagnosed based on clinical and radiographic criteria. If fluid from the cyst is aspirated, the CEA level is typically elevated. Confirmation of the diagnosis with tissue is rarely necessary.
By
In most cases, IPMNs are diagnosed based on clinical and radiographic criteria. If fluid from the cyst is aspirated, the CEA level is typically elevated. Confirmation of the diagnosis with tissue is rarely necessary.
By
 Side branch IPMNs are the most common pancreatic cysts. IPMNs occur more often in men than women, and often occur in the 6th and 7th decade of life.
Side branch IPMNs are the most common pancreatic cysts. IPMNs occur more often in men than women, and often occur in the 6th and 7th decade of life.
pancreatic cyst
A pancreatic cyst is a fluid filled sac within the pancreas.
Causes range from benign to malignant. Pancreatic cysts can occur in the setting of pancreatitis, though they are only reliably diagnosed 6 weeks after the episode of acute pancreati ...
s. Although intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms are benign tumors, they can progress to pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of t ...
. As such IPMN is viewed as a precancerous condition. Once an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm has been found, the management options include close monitoring and pre-emptive surgery.
Histology
IPMNs are lined with mucin-secreting columnar epithelium.Diagnosis
 In most cases, IPMNs are diagnosed based on clinical and radiographic criteria. If fluid from the cyst is aspirated, the CEA level is typically elevated. Confirmation of the diagnosis with tissue is rarely necessary.
By
In most cases, IPMNs are diagnosed based on clinical and radiographic criteria. If fluid from the cyst is aspirated, the CEA level is typically elevated. Confirmation of the diagnosis with tissue is rarely necessary.
By histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Spe ...
, IPMN is characterized on light microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of micr ...
by Mucinous epithelial cells, and growth within the pancreatic ducts. Mucin 5AC is a useful immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to an ...
marker. Characteristic genetic alterations are those of KRAS and GNAS.
Further subtyping of IPMN can be done as either:
* Gross pathology: Main duct, branch duct, and mixed duct lesions, which determines surgical management. Main duct lesion is the segmental or diffuse dilatation of main pancreatic duct greater than 5 mm without other causes of obstruction. Meanwhile, branch duct lesion is the pancreatic cyst more than 5 mm that communicates with the main duct. The mixed duct lesions fulfills both criteria above.
*By light microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of micr ...
and immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to an ...
: Gastric, intestinal, pancreaticbiliary, and oncocytic.
Treatment
The treatment of choice for main-duct IPMNs is resection due to approximately 50% chance of malignancy. Side-branch IPMNs are occasionally monitored with regular CT or MRIs, but most are eventually resected, with a 30% rate of malignancy in these resected tumors. Indications for surgical resection include obstructive jaundice, an enhancing mural nodule >5 mm, and pancreatic duct dilation (>10 mm). Surgery can include the removal of the head of the pancreas (a pancreaticoduodenectomy), removal of the body and tail of the pancreas (a distal pancreatectomy), or rarely removal of the entire pancreas (a total pancreatectomy). In selected cases the surgery can be performed using minimally invasive techniques such as laparoscopy or robotic surgery. A study using Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Registry (SEER) data suggested that increased lymph node counts harvested during the surgery were associated with better survival in invasive IPMN patients.Prognosis
Survival 5 years after resection of an IPMN without malignancy is approximately 80%, 85% with malignancy but no lymph node spread and 0% with malignancy spreading to lymph nodes.Epidemiology
 Side branch IPMNs are the most common pancreatic cysts. IPMNs occur more often in men than women, and often occur in the 6th and 7th decade of life.
Side branch IPMNs are the most common pancreatic cysts. IPMNs occur more often in men than women, and often occur in the 6th and 7th decade of life.
History
In 1982, IPMN was reported as a "mucin-producing tumor" by Kazuhiko Ohashi of the Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research.See also
* Pancreatic serous cystadenoma * Solid pseudopapillary neoplasmReferences
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm Gastrointestinal cancer Pancreas disorders Pancreatic cancer