International Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere Data Set on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The International Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere Data Set (ICOADS) is a digital
The International Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere Data Set (ICOADS) is a digital
 The International Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere Data Set (ICOADS) is a digital
The International Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere Data Set (ICOADS) is a digital database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spa ...
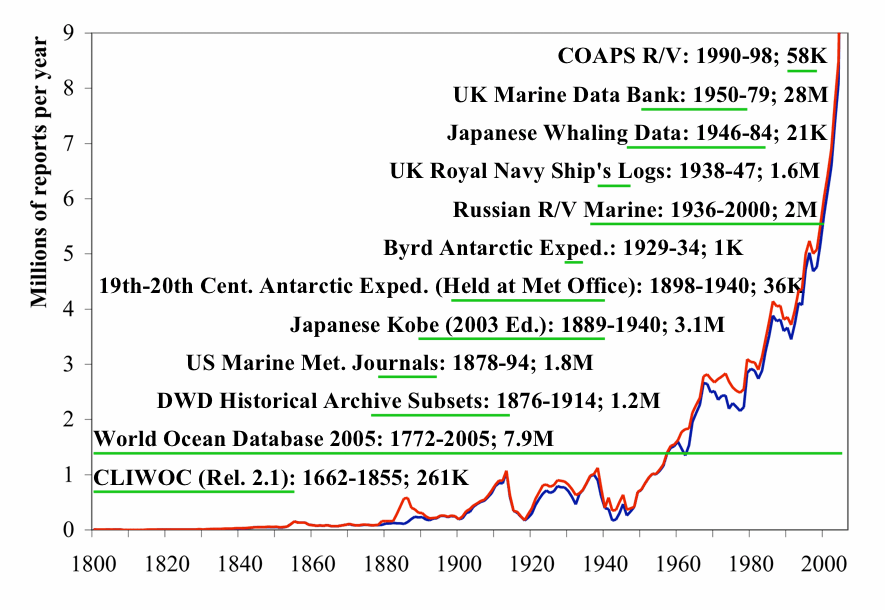
of 261 million weather observations made by ship
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguishe ...
s, weather ship
A weather ship, or ocean station vessel, was a ship stationed in the ocean for surface and upper air meteorological observations for use in weather forecasting. They were primarily located in the north Atlantic and north Pacific oceans, reportin ...
s, and weather buoy
Weather buoys are instruments which collect weather and ocean data within the world's oceans, as well as aid during emergency response to chemical spills, legal proceedings, and engineering design. Moored buoys have been in use since 1951, wh ...
s spanning the years 1662 to 2007. The database was initially constructed in 1985 and continues to be expanded upon and updated on a regular basis. From the original data, gridded datasets were created. ICOADS information has been useful in determining the reliability of ship and buoy wind measurements, helping to determine temperature trends in the sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the ocean temperature close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air ma ...
field, and updating the Atlantic hurricane database.
History
Beginning in 1981, the Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere data set (COADS) began construction within theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
. In April 1985, the first version of this database was created, including 70 million reports covering the years of 1854 through 1979. Each year thereafter, recent data was added to the dataset to extend its length towards the present. In November 1996, the first gridded datasets were created, using a one degree latitude by one degree longitude grid for the years 1960 through 1993. The following November, they were revised and extended to cover years through 1995. In November 1999, they were extended into 1997. In March 2002, two degree grids were created on a monthly basis for the years 1800 through 1949, and in recognition of input from other countries such as the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, the database was renamed ICOADS. In November 2000, the database was extended backward to 1784. In September 2002, this data became available through the internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a ''internetworking, network of networks'' that consists ...
. In late 2005, data from weather buoys were added into the database. In July 2009, the database was extended back to 1662. Data updates to include recent observations were begun on a monthly basis. The total number of observations in the database is now 261 million.
Available information
ICOADS has a variety of marine meteorological information within it, such as airtemperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on ...
, sea surface temperature, wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ...
, pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
, humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
, and cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
iness. Data in the time frame from 1662 through the early 1800s in quite sparse, as ship voyages covered only small areas of the globe in those days.
Related research
Based upon data from ICOADS, wind reports from moored weather buoys were determined to have smaller error than those from ships. The use of winds and pressures from ocean observations within ICOADS has led to a refinement of the Atlantic hurricane database as part of the North Atlantic hurricane reanalysis. Sea surface temperature data from ICOADS have been used to detect 20th century trends within that field. Global atmospheric reanalyses of past years have utilized the data within ICOADS.See also
* Atmospheric Circulation Reconstructions over the EarthReferences
{{reflist, 2 Climate and weather statistics Historical climatology Meteorological data and networks Numerical climate and weather models