internal market on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The European single market, also known as the European internal market or the European common market, is the single market comprising mainly the member states of the
Free movement of goods: Guide to the application of Treaty provisions governing the free movement of goods
page 9, © European Union, 2010. Reproduction is authorised provided the source is acknowledged, save where otherwise stated. Published 7 July 2010, accessed 3 January 2021 Goods are only covered if they have economic value, i.e. they can be valued in money and are capable of forming the subject of commercial transactions. Works of art, coins which are no longer in circulation and water are noted as examples of "goods". Fish are goods, but a
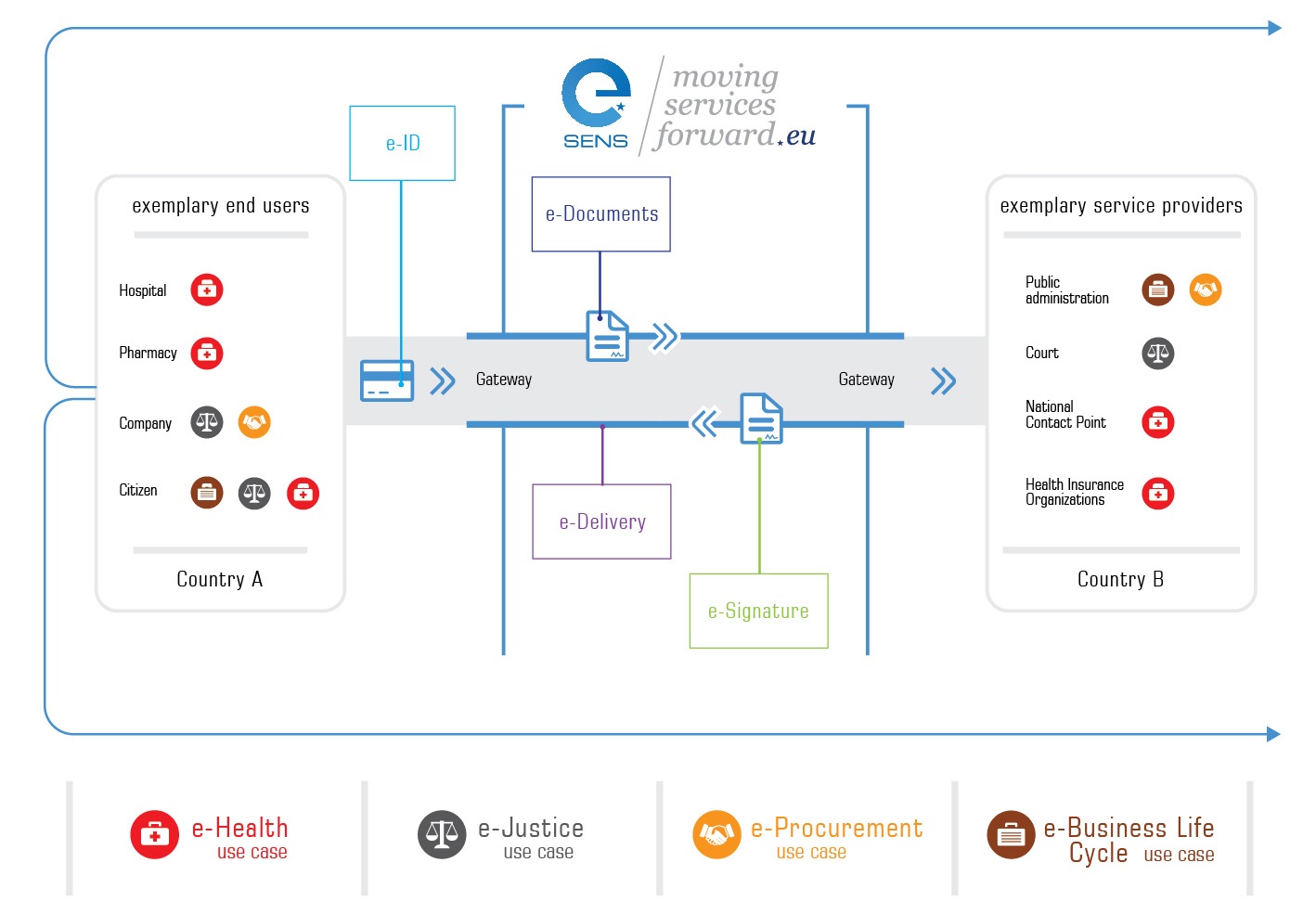 In May 2015 the Juncker Commission announced a plan to reverse the fragmentation of internet shopping and other online services by establishing a Single Digital Market that would cover digital services and goods from e-commerce to parcel delivery rates, uniform telecoms and copyright rules.
In May 2015 the Juncker Commission announced a plan to reverse the fragmentation of internet shopping and other online services by establishing a Single Digital Market that would cover digital services and goods from e-commerce to parcel delivery rates, uniform telecoms and copyright rules.
Case 43/75
0/ref> Free movement was increasingly based on " The Free Movement of Workers Regulation articles 1 to 7 set out the main provisions on equal treatment of workers. First, articles 1 to 4 generally require that workers can take up employment, conclude contracts, and not suffer discrimination compared to nationals of the member state. In a famous case, the '' Belgian Football Association v Bosman'', a Belgian footballer named Jean-Marc Bosman claimed that he should be able to transfer from R.F.C. de Liège to USL Dunkerque when his contract finished, regardless of whether Dunkerque could afford to pay Liège the habitual transfer fees. The Court of Justice held "the transfer rules constitute an obstacle to free movement" and were unlawful unless they could be justified in the public interest, but this was unlikely. In '' Groener v Minister for Education'' the Court of Justice accepted that a requirement to speak Gaelic to teach in a
The Free Movement of Workers Regulation articles 1 to 7 set out the main provisions on equal treatment of workers. First, articles 1 to 4 generally require that workers can take up employment, conclude contracts, and not suffer discrimination compared to nationals of the member state. In a famous case, the '' Belgian Football Association v Bosman'', a Belgian footballer named Jean-Marc Bosman claimed that he should be able to transfer from R.F.C. de Liège to USL Dunkerque when his contract finished, regardless of whether Dunkerque could afford to pay Liège the habitual transfer fees. The Court of Justice held "the transfer rules constitute an obstacle to free movement" and were unlawful unless they could be justified in the public interest, but this was unlikely. In '' Groener v Minister for Education'' the Court of Justice accepted that a requirement to speak Gaelic to teach in a
 First, article 4 of the Citizens Rights Directive 2004 says every citizen has the right to depart a member state with a valid
First, article 4 of the Citizens Rights Directive 2004 says every citizen has the right to depart a member state with a valid  Fourth, and more debated, article 24 requires that the longer an EU citizen stays in a host state, the more rights they have to access public and welfare services, on the basis of equal treatment. This reflects general principles of equal treatment and citizenship in TFEU articles 18 and 20. In a simple case, in '' Sala v Freistaat Bayern'' the Court of Justice held that a Spanish woman who had lived in (Germany) for 25 years and had a baby was entitled to
Fourth, and more debated, article 24 requires that the longer an EU citizen stays in a host state, the more rights they have to access public and welfare services, on the basis of equal treatment. This reflects general principles of equal treatment and citizenship in TFEU articles 18 and 20. In a simple case, in '' Sala v Freistaat Bayern'' the Court of Justice held that a Spanish woman who had lived in (Germany) for 25 years and had a baby was entitled to
 Only the EU member states are fully part of the European single market, while several other countries and territories have been granted various degrees of participation. The single market has been extended, with exceptions, to
Only the EU member states are fully part of the European single market, while several other countries and territories have been granted various degrees of participation. The single market has been extended, with exceptions, to
European Union: internal market
{{Authority control Economic integration European Union law
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
(EU). With certain exceptions, it also comprises Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
, Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
(through the Agreement on the European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Asso ...
), and Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
(through sectoral treaties). The single market seeks to guarantee the free movement of goods
In economics, goods are anything that is good, usually in the sense that it provides welfare or utility to someone. Alan V. Deardorff, 2006. ''Terms Of Trade: Glossary of International Economics'', World Scientific. Online version: Deardorffs ...
, capital, services, and people
The term "the people" refers to the public or Common people, common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. I ...
, known collectively as the "four freedoms". This is achieved through common rules and standards that all participating states are legally committed to follow.
Any potential EU accession candidates are required to agree to association agreements with the EU during the negotiation, which must be implemented prior to accession. In addition, through three individual agreements on a Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area (DCFTA) with the EU, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
have also been granted limited access to the single market in selected sectors. Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
has access to the free movement of some goods via its membership in the European Union–Turkey Customs Union. The United Kingdom left the European single market on 31 December 2020. An agreement was reached between the UK Government and European Commission to align Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
on rules for goods with the European single market, to maintain an open border on the island of Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
.
The market is intended to increase competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indi ...
, labour specialisation, and economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of Productivity, output produced per unit of cost (production cost). A decrease in ...
, allowing goods and factors of production
In economics, factors of production, resources, or inputs are what is used in the production process to produce output—that is, goods and services. The utilised amounts of the various inputs determine the quantity of output according to the rela ...
to move to the area where they are most valued, thus improving the efficiency of the allocation of resources. It is also intended to drive economic integration whereby the once separate economies of the member states become integrated within a single EU-wide economy. The creation of the internal market as a seamless, single market is an ongoing process, with the integration of the service industry still containing gaps. According to a 2019 estimate, because of the single market the GDP of member countries is on average 9 percent higher than it would be if tariff and non-tariff restrictions were in place.
History
One of the core objectives of theEuropean Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organisation created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisbo ...
(EEC) upon its establishment in 1957 was the development of a common market offering free movement of goods, service, people and capital. Free movement of goods was established in principle through the customs union between its then- six member states.
However, the EEC struggled to enforce a single market due to the absence of strong decision-making structures. Because of protectionist attitudes, it was difficult to replace intangible barriers with mutually recognized standards and common regulations.
In the 1980s, when the economy of the EEC began to lag behind the rest of the developed world, Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013), was a British stateswoman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of th ...
sent Lord Cockfield to the Delors Commission to take the initiative to attempt to relaunch the common market. Cockfield wrote and published a White Paper in 1985 identifying 300 measures to be addressed in order to complete a single market. The White Paper was well received and led to the adoption of the Single European Act
The Single European Act (SEA) was the first major revision of the 1957 Treaty of Rome. The Act set the European Community an objective of establishing a single market by 31 December 1992, and a forerunner of the European Union's Common Fore ...
, a treaty which reformed the decision-making mechanisms of the EEC and set a deadline of 31 December 1992 for the completion of a single market. In the end, it was launched on 1 January 1993.
The new approach, pioneered at the Delors Commission, combined positive and negative integration, relying upon minimum rather than exhaustive harmonisation. Negative integration consists of prohibitions imposed on member states banning discriminatory behaviour and other restrictive practices. Positive integration consists of approximating laws and standards. Especially important (and controversial) in this respect is the adoption of harmonising legislation under Article 114 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU).
The commission also relied upon the European Court of Justice
The European Court of Justice (ECJ), officially the Court of Justice (), is the supreme court of the European Union in matters of European Union law. As a part of the Court of Justice of the European Union, it is tasked with interpreting ...
's ''Cassis de Dijon'' jurisprudence, under which member states were obliged to recognise goods which had been legally produced in another member state, unless the member state could justify the restriction by reference to a mandatory requirement. Harmonisation would only be used to overcome barriers created by trade restrictions which survived the ''Cassis'' mandatory requirements test, and to ensure essential standards where there was a risk of a race to the bottom
Race to the bottom is a Socioeconomics, socio-economic concept describing a scenario in which individuals or companies compete in a manner that incrementally reduces the utility of a product or service in response to perverse incentives. This pheno ...
. Thus, harmonisation was largely used to ensure basic health and safety standards were met.
By 1992 about 90% of the issues had been resolved and in the same year the Maastricht Treaty
The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Communities, ...
set about to create an Economic and Monetary Union as the next stage of integration. Work on freedom for services took longer, and was the last freedom to be implemented, mainly through the Posting of Workers Directive (adopted in 1996)Directive 96/71/EC and the Directive on services in the internal market (adopted in 2006).Directive 2006/123/EC
In 1997 the Amsterdam Treaty abolished physical barriers across the internal market by incorporating the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) encompasses European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their common borders. As an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) policy of the European Union (EU), it ...
within the competences of the EU. The Schengen Agreement implements the abolition of border controls between most member states, common rules on visas, and police and judicial co-operation.
The official goal of the Lisbon Treaty
The Treaty of Lisbon (initially known as the Reform Treaty) is a European agreement that amends the two Treaty, treaties which form the constitutional basis of the European Union (EU). The Treaty of Lisbon, which was signed by all Member stat ...
was to establish an internal market, which would balance economic growth and price stability, a highly competitive social market economy, aiming at full employment and social progress, and a high level of protection and improvement of the quality of the environment, with also promoting scientific and technological advance. Even as the Lisbon Treaty
The Treaty of Lisbon (initially known as the Reform Treaty) is a European agreement that amends the two Treaty, treaties which form the constitutional basis of the European Union (EU). The Treaty of Lisbon, which was signed by all Member stat ...
came into force in 2009, however, some areas pertaining to parts of the four freedoms (especially in the field of services) had not yet been completely opened. Those, along with further work on the economic and monetary union, would see the EU move further to a ''European Home Market''.
In 2010, José Manuel Durão Barroso, then President of the European Commission
The president of the European Commission, also known as president of the College of Commissioners is the Head of government, head of the European Commission, the Executive (government), executive branch of the European Union (EU). The president ...
, asked former Italian Prime Minister Mario Monti to draft a report on revitalizing the European Single Market. The resulting document, known as the Monti Report, was presented in May 2010 and identified barriers to the internal market while proposing measures to strengthen economic integration and competitiveness. The report laid the groundwork for the "Single Market Act," a set of initiatives launched by the European Commission to enhance the functioning of the Single Market.
Following the Monti Report, the European Union continued to commission high-level reflections on the future of its economic integration. In April 2024, Enrico Letta, former Italian Prime Minister and President of the Jacques Delors Institute, presented the Letta Report, ''Much More Than a Market'', which called for a strategic renewal of the European Single Market to support the green and digital transitions, enhance economic cohesion, and promote a "fifth freedom" focused on knowledge and innovation. Around the same time, Mario Draghi was tasked with preparing a report on European competitiveness, addressing long-term structural reforms needed to boost productivity, resilience, and the EU's global economic standing.
Four freedoms
The "Four freedoms" of the single market are: * Free movement of goods * Free movement of capital * Freedom to establish and provide services * Free movement of labourGoods
The range of "goods" (or "products") covered by the term "free movement of goods" "is as wide as the range of goods in existence".Publications Office of the EUFree movement of goods: Guide to the application of Treaty provisions governing the free movement of goods
page 9, © European Union, 2010. Reproduction is authorised provided the source is acknowledged, save where otherwise stated. Published 7 July 2010, accessed 3 January 2021 Goods are only covered if they have economic value, i.e. they can be valued in money and are capable of forming the subject of commercial transactions. Works of art, coins which are no longer in circulation and water are noted as examples of "goods". Fish are goods, but a
European Court of Justice
The European Court of Justice (ECJ), officially the Court of Justice (), is the supreme court of the European Union in matters of European Union law. As a part of the Court of Justice of the European Union, it is tasked with interpreting ...
ruling in 1999 stated that fishing rights (or fishing permits) are not goods, but a provision of service. The ruling further explains that, both capital and service can be valued in money and are capable of forming the subject of commercial transactions, but they are not goods.
Council Regulation (EC) 2679/98 of 7 December 1998, on the functioning of the internal market in relation to the free movement of goods among the Member States, was aimed at preventing obstacles to the free movement of goods attributable to "action or inaction" by a Member State. The regulation empowered the Commission to request intervention by a Member State when the actions of private individuals were creating an "obstacle" to free movement of goods. A resolution was adopted by the Council and member state government representatives on the same day, under which the member states agreed to take action where necessary to protect the free movement of goods and other freedoms, and to issue public information where there were disruptions, including their efforts to address obstacles to free movement of goods.
Customs duties and taxation
The customs union of the European Union removes customs barriers between member states and operates a common customs policy towards third countries, with the aim "to ensure normal conditions of competition and to remove all restrictions of a fiscal nature capable of hindering the free movement of goods within the Common Market". Aspects of the EU Customs area extend to a number of non-EU-member states, namelyAndorra
Andorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, is a Sovereignty, sovereign landlocked country on the Iberian Peninsula, in the eastern Pyrenees in Southwestern Europe, Andorra–France border, bordered by France to the north and Spain to A ...
, Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, ...
, San Marino
San Marino, officially the Republic of San Marino, is a landlocked country in Southern Europe, completely surrounded by Italy. Located on the northeastern slopes of the Apennine Mountains, it is the larger of two European microstates, microsta ...
and Turkey, under separately negotiated arrangements. The United Kingdom agreed on a trade deal with the European Union on 24 December 2020, which was signed by Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
Boris Johnson
Alexander Boris de Pfeffel Johnson (born 19 June 1964) is a British politician and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of the Conservative Party from 2019 to 2022. He wa ...
on 30 December 2020.
=Customs duties
= Article 30 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union ("TFEU") prohibits border levies between member states on both European Union Customs Union produce and non-EUCU (third-country) produce. Under Article 29 of the TFEU, customs duty applicable to third country products are levied at the point of entry into EUCU, and once within the EU external border goods may circulate freely between member states. Under the operation of theSingle European Act
The Single European Act (SEA) was the first major revision of the 1957 Treaty of Rome. The Act set the European Community an objective of establishing a single market by 31 December 1992, and a forerunner of the European Union's Common Fore ...
, customs border controls between member states have been largely abandoned. Physical inspections on imports and exports have been replaced mainly by audit controls and risk analysis.
=Charges having equivalent effect to customs duties
= Article 30 of the TFEU prohibits not only customs duties but also charges having equivalent effect. TheEuropean Court of Justice
The European Court of Justice (ECJ), officially the Court of Justice (), is the supreme court of the European Union in matters of European Union law. As a part of the Court of Justice of the European Union, it is tasked with interpreting ...
defined "charge having equivalent effect" in ''Commission v Italy''.
A charge is a customs duty if it is proportionate to the value of the goods; if it is proportionate to the quantity, it is a charge having equivalent effect to a customs duty.
There are three exceptions to the prohibition on charges imposed when goods cross a border, listed in Case 18/87 Commission v Germany. A charge is not a customs duty or charge having equivalent effect if:
* it relates to a general system of internal dues applied systematically and in accordance with the same criteria to domestic products and imported products alike,
* if it constitutes payment for a service in fact rendered to the economic operator of a sum in proportion to the service, or
* subject to certain conditions, if it attaches to inspections carried out to fulfil obligations imposed by Union law.
=Taxation
= Article 110 of the TFEU provides: In the ''taxation of rum case'', the ECJ stated that:Quantitative and equivalent restrictions
Free movement of goods within theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
is achieved by a customs union and the principle of non-discrimination. The EU manages imports from non-member states, duties between member states are prohibited, and imports circulate freely. In addition under the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union article 34, 'Quantitative restrictions on imports and all measures having equivalent effect shall be prohibited between Member States'. In '' Procureur du Roi v Dassonville'' the Court of Justice held that this rule meant all "trading rules" that are "enacted by Member States" which could hinder trade "directly or indirectly, actually or potentially" would be caught by article 34. This meant that a Belgian law requiring Scotch whisky imports to have a certificate of origin was unlikely to be lawful. It discriminated against parallel importers like Mr Dassonville, who could not get certificates from authorities in France, where they bought the Scotch. This "wide test", to determine what could potentially be an unlawful restriction on trade, applies equally to actions by quasi-government bodies, such as the former " Buy Irish" company that had government appointees.
It also means states can be responsible for private actors. For instance, in '' Commission v France'' French farmer vigilantes were continually sabotaging shipments of Spanish strawberries, and even Belgian tomato imports. France was liable for these hindrances to trade because the authorities "manifestly and persistently abstained" from preventing the sabotage. Generally speaking, if a member state has laws or practices that directly discriminate against imports (or exports under TFEU article 35) then it must be justified under article 36, which outlines all of the justifiable instances. The justifications include public morality
Morality () is the categorization of intentions, Decision-making, decisions and Social actions, actions into those that are ''proper'', or ''right'', and those that are ''improper'', or ''wrong''. Morality can be a body of standards or principle ...
, policy or security, "protection of health and life of humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
, animals or plants", "national treasures" of "artistic, historic or archaeological value" and "industrial and commercial property". In addition, although not clearly listed, environmental protection can justify restrictions on trade as an over-riding requirement derived from TFEU article 11. The ''Eyssen v Netherlands c''ase from 1981 outlined a disagreement between the science community and the Dutch government whether niacin in cheese posed a public risk. As public risk falls under article 36, meaning that a quantitative restriction can be imposed, it justified the import restriction against the Eyssen cheese company by the Dutch government.
More generally, it has been increasingly acknowledged that fundamental human rights should take priority over all trade rules. So, in '' Schmidberger v Austria'' the Court of Justice held that Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
did not infringe article 34 by failing to ban a protest that blocked heavy traffic passing over the A13, Brenner Autobahn, en route to Italy. Although many companies, including Mr Schmidberger's German undertaking, were prevented from trading, the Court of Justice reasoned that freedom of association
Freedom of association encompasses both an individual's right to join or leave groups voluntarily, the right of the group to take collective action to pursue the interests of its members, and the right of an association to accept or decline membe ...
is one of the "fundamental pillars of a democratic society", against which the free movement of goods had to be balanced, and was probably subordinate. If a member state does appeal to the article 36 justification, the measures it takes have to be applied proportionately. This means the rule must be pursue a legitimate aim and (1) be suitable to achieve the aim, (2) be necessary, so that a less restrictive measure could not achieve the same result, and (3) be reasonable __NOTOC__
Reasonable may refer to:
* Reason, the capacity for rational thinking
* Reasonable accommodation, An adjustment made in a system to accommodate an individual's need
* Reasonable and non-discriminatory licensing, a licensing requirement ...
in balancing the interests of free trade with interests in article 36.
Often rules apply to all goods neutrally, but may have a greater practical effect on imports than domestic products. For such "indirect" discriminatory (or "indistinctly applicable") measures the Court of Justice has developed more justifications: either those in article 36, or additional "mandatory" or "overriding" requirements such as consumer protection
Consumer protection is the practice of safeguarding buyers of goods and services, and the public, against unfair practices in the marketplace. Consumer protection measures are often established by law. Such laws are intended to prevent business ...
, improving labour standards, protecting the environment, press diversity, fairness in commerce, and more: the categories are not closed. In the most famous case '' Rewe-Zentral AG v Bundesmonopol für Branntwein'', the Court of Justice found that a German law requiring all spirits and liqueurs (not just imported ones) to have a minimum alcohol content of 25 per cent was contrary to TFEU article 34, because it had a greater negative effect on imports. German liqueurs were over 25 per cent alcohol, but Cassis de Dijon, which Rewe-Zentrale AG wished to import from France, only had 15 to 20 per cent alcohol. The Court of Justice rejected the German government's arguments that the measure proportionately protected public health under TFEU article 36, because stronger beverages were available and adequate labelling would be enough for consumers to understand what they bought. This rule primarily applies to requirements about a product's content or packaging. In '' Walter Rau Lebensmittelwerke v De Smedt PVBA'' the Court of Justice found that a Belgian law requiring all margarine to be in cube
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional space, three-dimensional solid object in geometry, which is bounded by six congruent square (geometry), square faces, a type of polyhedron. It has twelve congruent edges and eight vertices. It i ...
shaped packages infringed article 34, and was not justified by the pursuit of consumer protection. The argument that Belgians would believe it was butter if it was not cube shaped was disproportionate: it would "considerably exceed the requirements of the object in view" and labelling would protect consumers "just as effectively".
In a 2003 case, '' Commission v Italy'' Italian law required that cocoa products that included other vegetable fats could not be labelled as "chocolate". It had to be "chocolate substitute". All Italian chocolate was made from cocoa butter
Cocoa butter, also called theobroma oil, is a pale-yellow, edible Vegetable oil, fat extracted from the cocoa bean (''Theobroma cacao''). It is used to make chocolate, as well as some ointments, toiletries, and pharmaceuticals. Cocoa butter h ...
alone, but British, Danish and Irish manufacturers used other vegetable fats. They claimed the law infringed article 34. The Court of Justice held that a low content of vegetable fat did not justify a "chocolate substitute" label. This was derogatory in the consumers' eyes. A "neutral and objective statement" was enough to protect consumers. If member states place considerable obstacles on the use of a product, this can also infringe article 34. So, in a 2009 case, '' Commission v Italy'', the Court of Justice held that an Italian law prohibiting motorcycles or mopeds from pulling trailers infringed article 34. Again, the law applied neutrally to everyone, but disproportionately affected importers, because Italian companies did not make trailers. This was not a product requirement, but the Court reasoned that the prohibition would deter people from buying it: it would have "a considerable influence on the behaviour of consumers" that "affects the access of that product to the market". It would require justification under article 36, or as a mandatory requirement.
In contrast to product requirements or other laws that hinder market access
In international trade, market access refers to a company's ability to enter a foreign market by selling its goods and services in another country. Market access is not the same as free trade, because market access is normally subject to condition ...
, the Court of Justice developed a presumption that "selling arrangements" would be presumed to not fall into TFEU article 34, if they applied equally to all sellers, and affected them in the same manner in fact. In '' Keck and Mithouard'' two importers claimed that their prosecution under a French competition law
Competition law is the field of law that promotes or seeks to maintain market competition by regulating anti-competitive conduct by companies. Competition law is implemented through public and private enforcement. It is also known as antitrust ...
, which prevented them from selling Picon beer under wholesale price, was unlawful. The aim of the law was to prevent cut throat competition, not to hinder trade. The Court of Justice held, as "in law and in fact" it was an equally applicable "selling arrangement" (not something that alters a product's content) it was outside the scope of article 34, and so did not need to be justified. Selling arrangements can be held to have an unequal effect "in fact" particularly where traders from another member state are seeking to break into the market, but there are restrictions on advertising and marketing. In '' Konsumentombudsmannen v De Agostini'' the Court of Justice reviewed Swedish bans on advertising to children under age 12, and misleading commercials for skin care products. While the bans have remained (justifiable under article 36 or as a mandatory requirement) the Court emphasised that complete marketing bans could be disproportionate if advertising were "the only effective form of promotion enabling traderto penetrate" the market. In '' Konsumentombudsmannen v Gourmet AB'' the Court suggested that a total ban for advertising alcohol on the radio, TV and in magazines could fall within article 34 where advertising was the only way for sellers to overcome consumers' "traditional social practices and to local habits and customs" to buy their products, but again the national courts would decide whether it was justified under article 36 to protect public health. Under the Unfair Commercial Practices Directive, the EU harmonised restrictions on restrictions on marketing and advertising, to forbid conduct that distorts average consumer behaviour, is misleading or aggressive, and sets out a list of examples that count as unfair. Increasingly, states have to give mutual recognition to each other's standards of regulation, while the EU has attempted to harmonise minimum ideals of best practice. The attempt to raise standards is hoped to avoid a regulatory "race to the bottom
Race to the bottom is a Socioeconomics, socio-economic concept describing a scenario in which individuals or companies compete in a manner that incrementally reduces the utility of a product or service in response to perverse incentives. This pheno ...
", while allowing consumers access to goods from around the continent.
Capital
Free movement of capital was traditionally seen as the fourth freedom, after goods, workers and persons, services and establishment. The original Treaty of Rome required that restrictions on free capital flows only be removed to the extent necessary for the common market. From theMaastricht Treaty
The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Communities, ...
, now in TFEU article 63, "all restrictions on the movement of capital between the Member States and between Member States and third countries shall be prohibited". This means capital controls of various kinds are prohibited, including limits on buying currency, limits on buying company shares or financial assets, or government approval requirements for foreign investment. By contrast, taxation of capital, including corporate tax
A corporate tax, also called corporation tax or company tax or corporate income tax, is a type of direct tax levied on the income or capital of corporations and other similar legal entities. The tax is usually imposed at the national level, but ...
, capital gains tax
A capital gains tax (CGT) is the tax on profits realized on the sale of a non-inventory asset. The most common capital gains are realized from the sale of stocks, bonds, precious metals, real estate, and property.
In South Africa, capital g ...
and financial transaction tax, are not affected so long as they do not discriminate by nationality. According to the Capital Movement Directive 1988, Annex I, 13 categories of capital which must move free are covered.
In ''Baars v Inspecteur der Belastingen Particulieren Baars is a Dutch language patronymic or toponymic surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Ab Baars (born 1955), Dutch jazz saxophonist and clarinettist
*Bernard Baars (born 1946), Dutch-born American neuroscientist
*Conrad Baars (1919– ...
'' the Court of Justice held that for investments in companies, the capital rules, rather than freedom of establishment rules, were engaged if an investment did not enable a "definite influence" through shareholder voting or other rights by the investor. That case held a Dutch Wealth Tax Act 1964 unjustifiably exempted Dutch investments, but not Mr Baars' investments in an Irish company, from the tax: the wealth tax, or exemptions, had to be applied equally. On the other hand, TFEU article 65(1) does not prevent taxes that distinguish taxpayers based on their residence or the location of an investment (as taxes commonly focus on a person's actual source of profit) or any measures to prevent tax evasion
Tax evasion or tax fraud is an illegal attempt to defeat the imposition of taxes by individuals, corporations, trusts, and others. Tax evasion often entails the deliberate misrepresentation of the taxpayer's affairs to the tax authorities to red ...
. Apart from tax cases, largely following from the opinions of Advocate General Maduro, a series of cases held that government owned golden shares were unlawful. In '' Commission v Germany'' the Commission claimed the German Volkswagen Act 1960 violated article 63, in that §2(1) restricted any party having voting rights exceeding 20% of the company, and §4(3) allowed a minority of 20% of shares held by the Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a States of Germany, German state (') in Northern Germany, northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Germany, Federal Re ...
government to block any decisions. Although this was not an impediment to the actual purchase of shares, or receipt of dividends by any shareholder, the Court of Justice's Grand Chamber agreed that it was disproportionate for the government's stated aim of protecting workers or minority shareholders. Similarly, in '' Commission v Portugal'' the Court of Justice held that Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
infringed free movement of capital by retaining golden shares in Portugal Telecom that enabled disproportionate voting rights, by creating a "deterrent effect on portfolio investments" and reducing "the attractiveness of an investment". This suggested the Court's preference that a government, if it sought public ownership or control, should nationalise in full the desired proportion of a company in line with TFEU article 345.
Capital within the EU may be transferred in any amount from one country to another (except that Greece currently has capital controls restricting outflows, and Cyprus imposed capital controls between 2013 and April 2015). All intra-EU transfers in euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
are considered as domestic payments and bear the corresponding domestic transfer costs. This includes all member States of the EU, even those outside the eurozone
The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a Monetary union, currency union of 20 Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (Euro sign, €) as their primary currency ...
providing the transactions are carried out in euro. Credit/debit card charging and ATM withdrawals within the Eurozone are also charged as domestic; however, paper-based payment orders, like cheques, have not been standardised so these are still domestic-based. The ECB has also set up a clearing system, T2 since March 2023, for large euro transactions.
The final stage of completely free movement of capital was thought to require a single currency and monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
, eliminating the transaction costs and fluctuations of currency exchange. Following a Report of the Delors Commission in 1988, the Maastricht Treaty
The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Communities, ...
made economic and monetary union an objective, first by completing the internal market, second by creating a European System of Central Banks to co-ordinate common monetary policy, and third by locking exchange rates and introducing a single currency, the euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
. Today, 20 member states have adopted the euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
, one is in the process of adopting (Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
), one has determined to opt-out (Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
) and 5 member states have delayed their accession, particularly since the Eurozone crisis. According to TFEU articles 119 and 127, the objective of the European Central Bank
The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's Big Four (banking)#International ...
and other central banks ought to be price stability. This has been criticised for apparently being superior to the objective of full employment
Full employment is an economic situation in which there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment. Full employment does not entail the disappearance of all unemployment, as other kinds of unemployment, namely structural and frictional, may ...
in the Treaty on European Union article 3.
Within the building on the Investment Plan for Europe, for a closer integration of capital markets, in 2015, the Commission adopted the Action Plan on Building a Capital Markets Union (CMU) setting out a list of key measures to achieve a true single market for capital in Europe, which deepens the existing Banking Union, because this revolves around disintermediated, market-based forms of financing, which should represent an alternative to the traditionally predominant (in Europe) bank-based financing channel. The EU's political and economic context call for strong and competitive capital markets to finance the EU economy. The CMU project is a political signal to strengthen the single market as a project of all 28 Member States, instead of just the Eurozone countries, and sent a strong signal to the UK to remain an active part of the EU, before Brexit.
Services
As well as creating rights for "workers" who generally lack bargaining power in the market, the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union or TFEU also protects the "freedom of establishment" in article 49, and "freedom to provide services" in article 56.Establishment
In '' Gebhard v Consiglio dell’Ordine degli Avvocati e Procuratori di Milano'' the Court of Justice held that to be "established" means to participate in economic life "on a stable and continuous basis", while providing "services" meant pursuing activity more "on a temporary basis". This meant that a lawyer fromStuttgart
Stuttgart (; ; Swabian German, Swabian: ; Alemannic German, Alemannic: ; Italian language, Italian: ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, largest city of the States of Germany, German state of ...
, who had set up chambers in Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
and was censured by the Milan Bar Council for not having registered, should claim for breach of establishment freedom, rather than service freedom. However, the requirements to be registered in Milan before being able to practice would be allowed if they were non-discriminatory, "justified by imperative requirements in the general interest" and proportionately applied. All people or entities that engage in economic activity, particularly the self-employed, or "undertakings" such as companies or firms, have a right to set up an enterprise without unjustified restrictions. The Court of Justice has held that both a member state government and a private party can hinder freedom of establishment, so article 49 has both "vertical" and "horizontal" direct effect. In '' Reyners v Belgium'' the Court of Justice held that a refusal to admit a lawyer to the Belgian bar because he lacked Belgian nationality was unjustified. TFEU article 49 says states are exempt from infringing others' freedom of establishment when they exercise "official authority", but this did an advocate's work (as opposed to a court's) was not official. By contrast in '' Commission v Italy'' the Court of Justice held that a requirement for lawyers in Italy to comply with maximum tariffs unless there was an agreement with a client was not a restriction. The Grand Chamber of the Court of Justice held the commission had not proven that this had any object or effect of limiting practitioners from entering the market. Therefore, there was no ''prima facie'' infringement freedom of establishment that needed to be justified.
In regard to companies, the Court of Justice held in '' R (Daily Mail and General Trust plc) v HM Treasury'' that member states could restrict a company moving its seat of business, without infringing TFEU article 49. This meant the ''Daily Mail
The ''Daily Mail'' is a British daily Middle-market newspaper, middle-market Tabloid journalism, tabloid conservative newspaper founded in 1896 and published in London. , it has the List of newspapers in the United Kingdom by circulation, h ...
'' newspaper's parent company
A holding company is a company whose primary business is holding a controlling interest in the Security (finance), securities of other companies. A holding company usually does not produce goods or services itself. Its purpose is to own Share ...
could not avoid tax by shifting its residence to the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
without first settling its tax bills in the UK. The UK did not need to justify its action, as rules on company seats were not yet harmonised. By contrast, in '' Centros Ltd v Erhversus-og Selkabssyrelsen'' the Court of Justice found that a UK limited company
In a limited company, the Legal liability, liability of members or subscribers of the company is limited to what they have invested or guaranteed to the company. Limited companies may be limited by Share (finance), shares or by guarantee. In a c ...
operating in Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
could not be required to comply with Denmark's minimum share capital rules. UK law only required £1 of capital to start a company, while Denmark's legislature took the view companies should only be started up if they had 200,000 Danish krone (around €27,000) to protect creditors
A creditor or lender is a Party (law), party (e.g., person, organization, company, or government) that has a claim on the services of a second party. It is a person or institution to whom money is owed. The first party, in general, has provided ...
if the company failed and went insolvent
In accounting, insolvency is the state of being unable to pay the debts, by a person or company ( debtor), at maturity; those in a state of insolvency are said to be ''insolvent''. There are two forms: cash-flow insolvency and balance-sheet in ...
. The Court of Justice held that Denmark's minimum capital law infringed Centros Ltd's freedom of establishment and could not be justified, because a company in the UK could admittedly provide services in Denmark without being established there, and there were less restrictive means of achieving the aim of creditor protection. This approach was criticised as potentially opening the EU to unjustified regulatory competition, and a race to the bottom
Race to the bottom is a Socioeconomics, socio-economic concept describing a scenario in which individuals or companies compete in a manner that incrementally reduces the utility of a product or service in response to perverse incentives. This pheno ...
in standards, like in the US where the state of Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
attracts most companies and is often argued to have the worst standards of accountability of boards, and low corporate taxes as a result. Similarly in '' Überseering BV v Nordic Construction GmbH'' the Court of Justice held that a German court could not deny a Dutch building company the right to enforce a contract in Germany on the basis that it was not validly incorporated in Germany. Although restrictions on freedom of establishment could be justified by creditor protection, labour rights to participate in work, or the public interest in collecting taxes, denial of capacity went too far: it was an "outright negation" of the right of establishment. However, in '' Cartesio Oktató és Szolgáltató bt'' the Court of Justice affirmed again that because corporations are created by law, they are in principle subject to any rules for formation that a state of incorporation wishes to impose. This meant that the Hungarian authorities could prevent a company from shifting its central administration to Italy while it still operated and was incorporated in Hungary. Thus, the court draws a distinction between the right of establishment for foreign companies (where restrictions must be justified), and the right of the state to determine conditions for companies incorporated in its territory, although it is not entirely clear why.
Types of service
The "freedom to provide services" under TFEU article 56 applies to people who provide services "for remuneration", especially in commercial or professional activity. For example, in '' Van Binsbergen v Bestuur van de Bedrijfvereniging voor de Metaalnijverheid'' a Dutch lawyer moved to Belgium while advising a client in asocial security
Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance ...
case, and was told he could not continue because Dutch law said only people established in the Netherlands could give legal advice. The Court of Justice held that the freedom to provide services applied, it was directly effective, and the rule was probably unjustified: having an address in the member state would be enough to pursue the legitimate aim of good administration of justice.
Case law
Case law, also used interchangeably with common law, is a law that is based on precedents, that is the judicial decisions from previous cases, rather than law based on constitutions, statutes, or regulations. Case law uses the detailed facts of ...
states that the treaty provisions relating to the freedom to provide services do not apply in situations where the service, service provider and other relevant facts are confined within a single member state. An early Council Directive from 26 July 1971 included works contracts within the scope of services, and provided for the abolition of restrictions on the freedom to provide services in respect of public works contracts.
The Court of Justice has held that secondary education
Secondary education is the education level following primary education and preceding tertiary education.
Level 2 or ''lower secondary education'' (less commonly ''junior secondary education'') is considered the second and final phase of basic e ...
falls outside the scope of article 56, because usually the state funds it, though higher education does not. Health care generally counts as a service. In '' Geraets-Smits v Stichting Ziekenfonds'' Mrs Geraets-Smits claimed she should be reimbursed by Dutch social insurance for the costs of receiving treatment in Germany. The Dutch health authorities regarded the treatment as unnecessary, so she argued this restricted the freedom (of the German health clinic) to provide services. Several governments submitted that hospital services should not be regarded as economic, and should not fall within article 56. But the Court of Justice held that health care was a "service" even though the government (rather than the service recipient) paid for the service. National authorities could be justified in refusing to reimburse patients for medical services abroad if the health care received at home was without undue delay, and it followed "international medical science" on which treatments counted as normal and necessary. The Court requires that the individual circumstances of a patient justify waiting lists, and this is also true in the context of the UK's National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern ...
. Aside from public services, another sensitive field of services are those classified as illegal. '' Josemans v Burgemeester van Maastricht'' held that the Netherlands' regulation of cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae that is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from the continent of Asia. However, the number of species is disputed, with as many as three species be ...
consumption, including the prohibitions by some municipalities on tourists (but not Dutch nationals) going to coffee shops, fell outside article 56 altogether. The Court of Justice reasoned that narcotic drugs were controlled in all member states, and so this differed from other cases where prostitution or other quasi-legal activity was subject to restriction.
If an activity does fall within article 56, a restriction can be justified under article 52 or over-riding requirements developed by the Court of Justice. In '' Alpine Investments BV v Minister van Financiën'' a business that sold commodities
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that specifically has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
Th ...
futures (with Merrill Lynch
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, doing business as Merrill, and previously branded Merrill Lynch, is an American investment management and wealth management division of Bank of America. Along with BofA Securities, the investm ...
and another banking firm) attempted to challenge a Dutch law prohibiting cold calling customers. The Court of Justice held the Dutch prohibition pursued a legitimate aim to prevent "undesirable developments in securities trading" including protecting the consumer from aggressive sales tactics, thus maintaining confidence in the Dutch markets. In '' Omega Spielhallen GmbH v Bonn'' a "laserdrome" business was banned by the Bonn
Bonn () is a federal city in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located on the banks of the Rhine. With a population exceeding 300,000, it lies about south-southeast of Cologne, in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region. This ...
council. It bought fake laser gun services from a UK firm called Pulsar Ltd, but residents had protested against "playing at killing" entertainment. The Court of Justice held that the German constitutional value of human dignity, which underpinned the ban, did count as a justified restriction on the freedom to provide services. In '' Liga Portuguesa de Futebol v Santa Casa da Misericórdia de Lisboa'' the Court of Justice also held that the state monopoly on gambling, and a penalty for a Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
firm that had sold internet gambling services, was justified to prevent fraud and gambling where people's views were highly divergent. The ban was proportionate as this was an appropriate and necessary way to tackle the serious problems of fraud that arise over the internet. In the Services Directive a group of justifications were codified in article 16 that the case law has developed.
Digital Single Market
 In May 2015 the Juncker Commission announced a plan to reverse the fragmentation of internet shopping and other online services by establishing a Single Digital Market that would cover digital services and goods from e-commerce to parcel delivery rates, uniform telecoms and copyright rules.
In May 2015 the Juncker Commission announced a plan to reverse the fragmentation of internet shopping and other online services by establishing a Single Digital Market that would cover digital services and goods from e-commerce to parcel delivery rates, uniform telecoms and copyright rules.
People
The free movement of people means EU citizens can move freely between member states for whatever reason (or without any reason) and may reside in any member state they choose if they are not an undue burden on the social welfare system or public safety in their chosen member state. This required reduction of administrative formalities and greater recognition of professional qualifications of other states. Fostering the free movement of people has been a major goal of European integration since the 1950s. Broadly defined, this freedom enables citizens of one Member State to travel to another, to reside and to work there (permanently or temporarily). The idea behind EU legislation in this field is that citizens from other member states should be treated equally to domestic citizens and should not be discriminated against. The main provision on the freedom of movement of persons is Article 45 of the TFEU, which prohibits restrictions on the basis of nationality.Free movement of workers
Since its foundation, the Treaties sought to enable people to pursue their life goals in any country through free movement. Reflecting the economic nature of the project, the European Community originally focused upon free movement of workers: as a " factor of production". However, from the 1970s, this focus shifted towards developing a more "social" Europe.'' Defrenne v Sabena (No 2)'' (1976Case 43/75
0/ref> Free movement was increasingly based on "
citizenship
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationalit ...
", so that people had rights to empower them to become economically and socially active, rather than economic activity being a precondition for rights. This means the basic "worker" rights in TFEU article 45 function as a specific expression of the general rights of citizens in TFEU articles 18 to 21. According to the Court of Justice, a "worker" is anybody who is economically active, which includes everyone in an employment relationship, "under the direction of another person" for "remuneration". A job, however, need not be paid in money for someone to be protected as a worker. For example, in ''Steymann v Staatssecretaris van Justitie
''Udo Steymann v Staatssecretaris van Justitie '' (1988Case 196/87is a European Union law case, concerning the free movement of workers in the European Union.
Facts
Udo Steymann was a German plumber working in the Netherlands. He joined the Raj ...
'', a German man claimed the right to residence in the Netherlands, while he volunteered plumbing and household duties in the Bhagwan community, which provided for everyone's material needs irrespective of their contributions. The Court of Justice held that Mr Steymann was entitled to stay, so long as there was at least an "indirect quid pro quo" for the work he did. Having "worker" status means protection against all forms of discrimination by governments, and employers, in access to employment, tax, and social security
Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance ...
rights. By contrast a citizen, who is "any person having the nationality of a Member State" ( TFEU article 20(1)), has rights to seek work, vote in local and European elections, but more restricted rights to claim social security
Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance ...
. In practice, free movement has become politically contentious as nationalist political parties appear to have utilised concerns about immigrants taking jobs and benefits.
 The Free Movement of Workers Regulation articles 1 to 7 set out the main provisions on equal treatment of workers. First, articles 1 to 4 generally require that workers can take up employment, conclude contracts, and not suffer discrimination compared to nationals of the member state. In a famous case, the '' Belgian Football Association v Bosman'', a Belgian footballer named Jean-Marc Bosman claimed that he should be able to transfer from R.F.C. de Liège to USL Dunkerque when his contract finished, regardless of whether Dunkerque could afford to pay Liège the habitual transfer fees. The Court of Justice held "the transfer rules constitute an obstacle to free movement" and were unlawful unless they could be justified in the public interest, but this was unlikely. In '' Groener v Minister for Education'' the Court of Justice accepted that a requirement to speak Gaelic to teach in a
The Free Movement of Workers Regulation articles 1 to 7 set out the main provisions on equal treatment of workers. First, articles 1 to 4 generally require that workers can take up employment, conclude contracts, and not suffer discrimination compared to nationals of the member state. In a famous case, the '' Belgian Football Association v Bosman'', a Belgian footballer named Jean-Marc Bosman claimed that he should be able to transfer from R.F.C. de Liège to USL Dunkerque when his contract finished, regardless of whether Dunkerque could afford to pay Liège the habitual transfer fees. The Court of Justice held "the transfer rules constitute an obstacle to free movement" and were unlawful unless they could be justified in the public interest, but this was unlikely. In '' Groener v Minister for Education'' the Court of Justice accepted that a requirement to speak Gaelic to teach in a Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
design college could be justified as part of the public policy of promoting the Irish language, but only if the measure was not disproportionate. By contrast in ''Angonese v Cassa di Risparmio di Bolzano SpA
''Roman Angonese v Cassa di Risparmio di Bolzano S.p.A.'' (2000) C-281/98 is an EU law case, concerning the free movement of workers in the European Union.
Facts
A bank in Bolzano, where Italian and German are spoken, required a certificate of ...
'' a bank in Bolzano
Bolzano ( ; ; or ) is the capital city of South Tyrol (officially the province of Bolzano), Northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third largest in historical Tyrol. The ...
, Italy, was not allowed to require Mr Angonese to have a bilingual certificate that could only be obtained in Bolzano. The Court of Justice, giving "horizontal" direct effect to TFEU article 45, reasoned that people from other countries would have little chance of acquiring the certificate, and because it was "impossible to submit proof of the required linguistic knowledge by any other means", the measure was disproportionate. Second, article 7(2) requires equal treatment in respect of tax. In '' Finanzamt Köln Altstadt v Schumacker'' the Court of Justice held that it contravened TFEU art 45 to deny tax benefits (e.g. for married couples, and social insurance expense deductions) to a man who worked in Germany, but was resident in Belgium when other German residents got the benefits. By contrast in '' Weigel v Finanzlandesdirektion für Vorarlberg'' the Court of Justice rejected Mr Weigel's claim that a re-registration charge upon bringing his car to Austria violated his right to free movement. Although the tax was "likely to have a negative bearing on the decision of migrant workers to exercise their right to freedom of movement", because the charge applied equally to Austrians, in absence of EU legislation on the matter it had to be regarded as justified. Third, people must receive equal treatment regarding "social advantages", although the Court has approved residential qualifying periods. In '' Hendrix v Employee Insurance Institute'' the Court of Justice held that a Dutch national was not entitled to continue receiving incapacity benefits when he moved to Belgium, because the benefit was "closely linked to the socio-economic situation" of the Netherlands. Conversely, in '' Geven v Land Nordrhein-Westfalen'' the Court of Justice held that a Dutch woman living in the Netherlands, but working between 3 and 14 hours a week in Germany, did not have a right to receive German child benefits, even though the wife of a man who worked full-time in Germany but was resident in Austria could. The general justifications for limiting free movement in TFEU article 45(3) are "public policy, public security or public health", and there is also a general exception in article 45(4) for "employment in the public service".
For workers not citizens of the union but employed in one member state with a work permit, there is not the same freedom of movement within the Union. They need to apply for a new work permit if wanting to work in a different state. A facilitation mechanism for this process is the Van Der Elst visa which gives easier rules should a non-EU worker already in one EU state need to be sent to another, for the same employer, because of a service contract that the employer made with a customer in that other state.
Free movement of citizens
Beyond the right of free movement to work, the EU has increasingly sought to guarantee rights of citizens, and rights simply by being a human being. But although the Court of Justice stated that 'Citizenship is destined to be the fundamental status of nationals of the Member States', political debate remains on who should have access to public services and welfare systems funded by taxation. In 2008, just 8 million people from 500 million EU citizens (1.7 per cent) had in fact exercised rights of free movement, the vast majority of them workers. According to TFEU article 20, citizenship of the EU derives from nationality of a member state. Article 21 confers general rights to free movement in the EU and to reside freely within limits set by legislation. This applies for citizens and their immediate family members. This triggers four main groups of rights: (1) to enter, depart and return, without undue restrictions, (2) to reside, without becoming an unreasonable burden on social assistance, (3) to vote in local and European elections, and (4) the right to equal treatment with nationals of the host state, but for social assistance only after 3 months of residence.passport
A passport is an official travel document issued by a government that certifies a person's identity and nationality for international travel. A passport allows its bearer to enter and temporarily reside in a foreign country, access local aid ...
or national identity card. Article 5 gives every citizen a right of entry, subject to national border controls. Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) encompasses European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their common borders. As an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) policy of the European Union (EU), it ...
countries (of which Ireland is not included) have abolished the need to show travel documents, and police searches at borders, altogether. These reflect the general principle of free movement in TFEU article 21. Second, article 6 allows every citizen to stay three months in another member state, whether economically active or not. Article 7 allows stays over three months with evidence of "sufficient resources... not to become a burden on the social assistance system". Articles 16 and 17 give a right to permanent residence after 5 years without conditions. Third, TEU article 10(3) requires the right to vote in the local constituencies for the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
wherever a citizen lives.
child support
Child support (or child maintenance) is an ongoing, periodic payment made by a parent for the financial benefit of a child (state or parent, caregiver, guardian) following the end of a marriage or other similar relationship. Child maintenance is ...
, without the need for a residence permit, because Germans did not need one. In '' Trojani v Centre public d’aide sociale de Bruxelles'', a French man who lived in Belgium for two years was entitled to the "minimex" allowance from the state for a minimum living wage. In '' Grzelczyk v Centre Public d’Aide Sociale d’Ottignes-Louvain-la-Neuve'' a French student, who had lived in Belgium for three years, was entitled to receive the "minimex" income support for his fourth year of study. Similarly, in '' R (Bidar) v London Borough of Ealing'' the Court of Justice held that it was lawful to require a French UCL economics student to have lived in the UK for three years before receiving a student loan, but not that he had to have additional "settled status". Similarly, in '' Commission v Austria'', Austria was not entitled to restrict its university places to Austrian students to avoid "structural, staffing and financial problems" if (mainly German) foreign students applied, unless it proved there was an actual problem. However, in '' Dano v Jobcenter Leipzig'', the Court of Justice held that the German government was entitled to deny child support
Child support (or child maintenance) is an ongoing, periodic payment made by a parent for the financial benefit of a child (state or parent, caregiver, guardian) following the end of a marriage or other similar relationship. Child maintenance is ...
to a Romanian mother who had lived in Germany for 3 years, but had never worked. Because she lived in Germany for over 3 months, but under 5 years, she had to show evidence of "sufficient resources", since the Court reasoned the right to equal treatment in article 24 within that time depended on lawful residence under article 7.
Schengen Area
Within theSchengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) encompasses European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their common borders. As an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) policy of the European Union (EU), it ...
, 25 of the EU member states (excluding Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, and Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
) and the four EFTA members (Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
, Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, and Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
) have abolished physical barriers across the single market by eliminating border controls. In 2015, limited controls were temporarily re-imposed at some internal borders in response to the migrant crisis.
Public sector procurement of goods and services
Public procurement
Government procurement or public procurement is the purchase of goods, works (construction) or services by the state, such as by a government agency or a state-owned enterprise. In 2019, public procurement accounted for approximately 12% of GDP ...
legislation and guidance based on "a set of basic standards for the award of public contracts which are derived directly from the rules and principles of the EC Treaty", relating to the four freedoms, require equal treatment, non-discrimination, mutual recognition, proportionality and transparency to be maintained when purchasing goods and services for EU public sector bodies.
Integration of non-EU states
Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
, Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
, and Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
through the agreement on the European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Asso ...
(EEA) and to Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
through sectoral bilateral and multilateral agreements. The exceptions, where these EFTA states are not bound by EU law, are:
*the common agricultural policy and the common fisheries policy (although the EEA agreement contains provisions on trade in agricultural and fishery produce);
*the customs union;
*the common trade policy;
*the common foreign and security policy;
*the field of justice and home affairs (although each EFTA country is part of the Schengen area); and
*the economic and monetary union (EMU).
Switzerland
Switzerland, a member of EFTA but not of the EEA, participates in the single market with a number of exceptions, as defined by the Switzerland–European Union relations.Western Balkans
Stabilisation and Association Agreement
In talks with countries that have expressed a wish to join the European Union, the EU typically concludes European Union Association Agreement, Association Agreements in exchange for commitments to political, economic, trade, or human rights ref ...
states have a "comprehensive framework in place to move closer to the EU and to prepare for heir
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Offi ...
future participation in the Single Market".
Turkey
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
has participated in the European Union–Turkey Customs Union since 1995, which enables it to participate in the free movement of goods (but not of agriculture or services, nor people) with the EU.
Georgia, Moldova, and Ukraine
Through the agreement of the Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area (DCFTA), the three post-Soviet countries ofGeorgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
were given access to the "four freedoms" of the EU single market: free movement of goods, services, capital, and people. Movement of people however, is in form of visa free regime for short stay travel, while movement of workers remains within the remit of the EU Member States
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often de ...
.The EU-Ukraine Association Agreement and Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area What's it all about?European External Action Service
The European External Action Service (EEAS) is the diplomatic service in charge of executing all Foreign relations of the European Union, international relations of the European Union. The EEAS is led by the Vice-President of the European Co ...
. . The DCFTA is an "example of the integration of a Non- EEA-Member into the EU Single Market".EU-Ukraine Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade AreaEuropean External Action Service
The European External Action Service (EEAS) is the diplomatic service in charge of executing all Foreign relations of the European Union, international relations of the European Union. The EEAS is led by the Vice-President of the European Co ...
. .
Northern Ireland
TheUnited Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
left the European Union at the end of January 2020 and left the single market in December 2020. Under the terms of the Northern Ireland Protocol of the Brexit withdrawal agreement
The Brexit withdrawal agreement, officially titled Agreement on the withdrawal of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland from the European Union and the European Atomic Energy Community, is a treaty between the European Uni ...
, Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
remains aligned to the European single market in a limited way to maintain an open border on the island of Ireland. This includes legislation on sanitary and phytosanitary standards for veterinary controls, rules on agricultural production/marketing, VAT and excise in respect of goods, and state aid rules. It also introduces some controls on the flow of goods to Northern Ireland from Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
.
Under the terms of the Protocol, the Northern Ireland Assembly
The Northern Ireland Assembly (; ), often referred to by the metonym ''Stormont'', is the devolved unicameral legislature of Northern Ireland. It has power to legislate in a wide range of areas that are not explicitly reserved to the Parliam ...
has the power by a simple majority to continue or terminate the protocol arrangements. In the event that consent to continue is not given, the arrangements would cease to apply after two years. The Joint Committee would make alternative proposals to the UK and EU to avoid a hard border on the island of Ireland.
Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Akrotiri and Dhekelia (), officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA), is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory made of two non-contiguous areas on the island of Geography of Cyprus, Cyprus. The area ...
, the British Sovereign Base Areas, located on the island of Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, are integral parts of the EU Customs Union, allowing goods to move freely.
Further developments
Since 2015, the European Commission has been aiming to build a single market for energy. and for the defence industry. On 2 May 2017, the European Commission announced a package of measures intended to enhance the functioning of the single market within the EU: *a single digital gateway based on an upgraded Your Europe portal, offering enhanced access to information, assistance services and online procedures throughout the EU *Single Market Information Tool (a proposed regulation under which the commission could require EU businesses to provide information in relation to the internal market and related areas where there is a suspicion that businesses are blocking the operation of the single market rules) * SOLVIT Action Plan (aiming to reinforce and improve the functioning of the existing SOLVIT network).New Hanseatic League
The New Hanseatic League is a political grouping of economically like-minded northern European states, established in February 2018, that is pushing for a more developed European single market, particularly in the services sector.See also
*Law of the European Union
European Union law is a system of Supranational union, supranational Law, laws operating within the 27 member states of the European Union (EU). It has grown over time since the 1952 founding of the European Coal and Steel Community, to promote ...
* Community preference
* Union State
The Union State is a supranational union consisting of Belarus and Russia, with the stated aim of deepening the relationship between the two states through integration in economic and defence policy. Originally, the Union State aimed to crea ...
, a similar free movement zone for Russian and Belarusian citizens
Notes
References
;Books * * * * ;Articles * * * * * *External links
European Union: internal market
{{Authority control Economic integration European Union law