Intergalactic star on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An intergalactic star, also known as an intracluster star or a rogue star, is a
An intergalactic star, also known as an intracluster star or a rogue star, is a

 The way these stars arise is still a mystery, but several scientifically credible
The way these stars arise is still a mystery, but several scientifically credible
 An intergalactic star, also known as an intracluster star or a rogue star, is a
An intergalactic star, also known as an intracluster star or a rogue star, is a star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
not gravitationally bound to any galaxy
A galaxy is a Physical system, system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar medium, interstellar gas, cosmic dust, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek ' (), literally 'milky', ...
. Although a source of much discussion in the scientific community during the late 1990s, intergalactic stars are now generally thought to have originated in galaxies, like other stars, before being expelled as the result of either galaxies colliding or of a multiple-star system traveling too close to a supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions, of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical ...
, which are found at the center of many galaxies.
Collectively, intergalactic stars are referred to as the intracluster stellar population, or IC population for short, in the scientific literature.
Discovery
The hypothesis that stars exist only in galaxies was disproven in January 1997 with the discovery of intergalactic stars. The first to be discovered were in theVirgo Cluster
The Virgo Cluster is a cluster of galaxies whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly (16.5 ± 0.1 Mpc) away in the Virgo constellation. Comprising approximately 1,300 (and possibly up to 2,000) member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the larger ...
of galaxies, where some one trillion are now surmised to exist.
Formation

 The way these stars arise is still a mystery, but several scientifically credible
The way these stars arise is still a mystery, but several scientifically credible hypotheses
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific method, scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educ ...
have been suggested and published by astrophysicists.
The most common hypothesis is that the collision of two or more galaxies can toss some stars out into the vast empty regions of intergalactic space. Although stars normally reside within galaxies, they can be expelled by gravitational forces when galaxies collide. It is commonly believed that intergalactic stars may primarily have originated from extremely small galaxies, since it is easier for stars to escape a smaller galaxy's gravitational pull, than that of a large galaxy. However, when large galaxies collide, some of the gravitational disturbances might also expel stars. Published in August 2015, a study of supernovae in intergalactic space suggested that the progenitor stars had been expelled from their host galaxies during a galactic collision between two giant ellipticals, as their supermassive black hole centres merged.
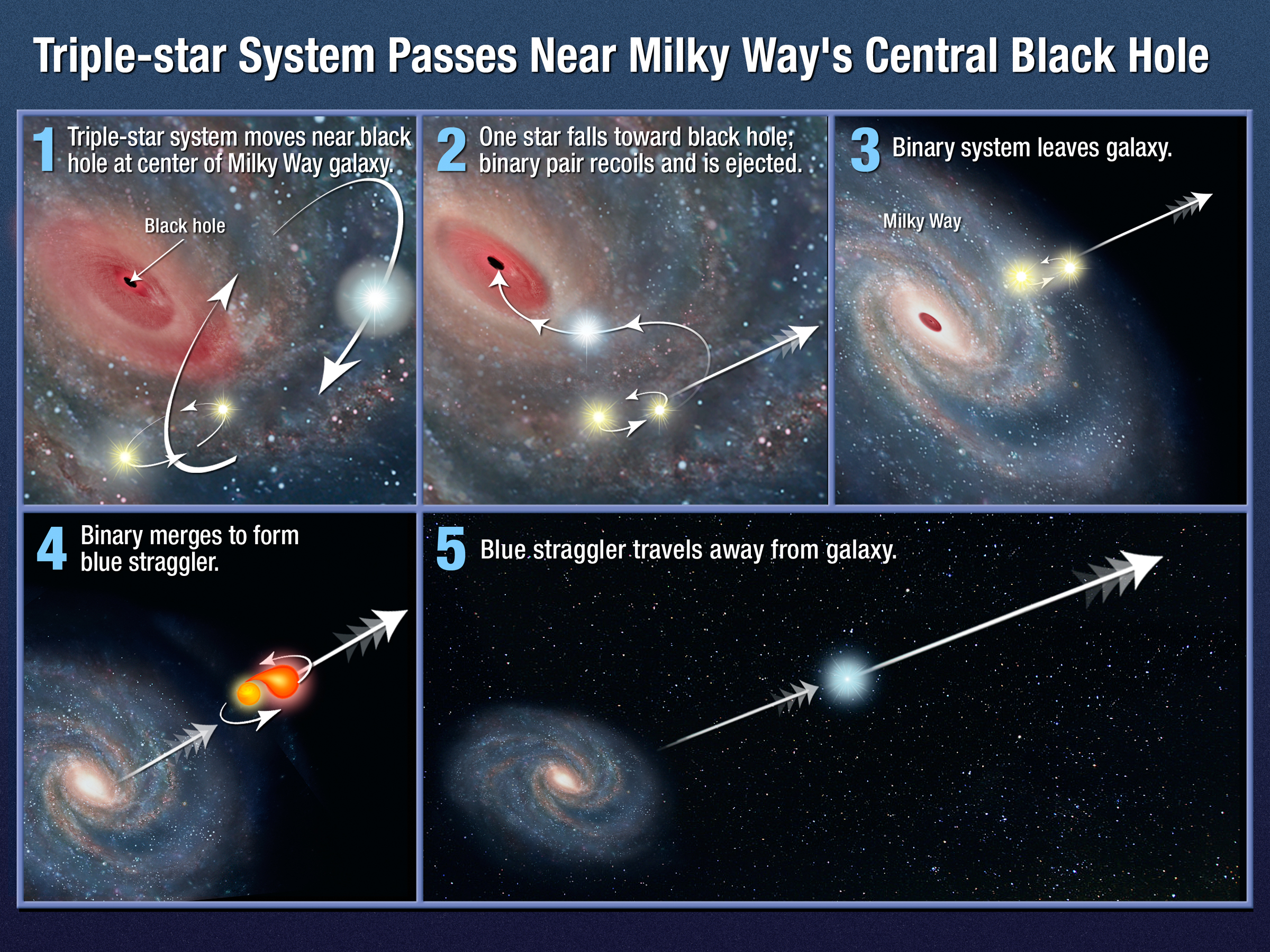
Another hypothesis, that is not mutually exclusive to the galactic collisions hypothesis, is that intergalactic stars were ejected from their galaxy
A galaxy is a Physical system, system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar medium, interstellar gas, cosmic dust, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek ' (), literally 'milky', ...
of origin by a close encounter with the supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions, of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical ...
in the galaxy center, should there be one. In such a scenario, it is likely that the intergalactic star(s) was originally part of a multiple star system where the other stars were pulled into the supermassive black hole and the soon-to-be intergalactic star was accelerated and ejected away at very high speeds. Such an event could theoretically accelerate a star to such high speeds that it becomes a hypervelocity star, thereby escaping the gravitational well of the entire galaxy. In this respect, model calculations (from 1988) predict the supermassive black hole in the center of our Milky Way galaxy to expel one star every 100,000 years on average.
Observation history
In January 1997, theHubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
discovered a large number of intergalactic stars in the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. Another study, published later in January 1997, confirmed that astronomers had discovered a group of intergalactic planetary nebulae
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionization, ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated to pla ...
in the Fornax Cluster
The Fornax Cluster is a cluster of galaxies lying at a distance of 19 megaparsecs (62 million light-years). It has an estimated mass of solar masses, making it the second richest galaxy cluster within 100 million light-years, after the consider ...
of galaxies in 1992 and 1993.
In 2005, at the Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Warren Brown and his team attempted to measure the speeds of hypervelocity stars by using the Doppler Technique, by which light is observed for the similar changes that occur in sound when an object is moving away or toward something. But the speeds found are only estimated minimums, as in reality their speeds may be larger than the speeds found by the researchers. "One of the newfound exiles is moving in the direction of the constellation Ursa Major at about 1.25 million mph with respect to the galaxy. It is 240,000 light-years away. The other is headed toward the constellation Cancer, outbound at 1.43 million miles per hour and 180,000 light-years away."
In the late 2000s, a diffuse glow from the intergalactic medium, but of unknown origin, was discovered. In 2012, it was suggested and shown that it might originate from intergalactic stars. Subsequent observations and studies have elaborated on the issue and described the diffuse extragalactic background radiation in more detail.
Some Vanderbilt astronomers report that they have identified more than 675 stars at the edge of the Milky Way, between the Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy and is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way. It was originally named the Andromeda Nebula and is cataloged as Messier 31, M31, and NGC 224. Andromeda has a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isop ...
and the Milky Way. They argue that these stars are hypervelocity (intergalactic) stars that were ejected from the Milky Way's Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a ...
. These stars are red giants with a high metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the Abundance of the chemical elements, abundance of Chemical element, elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal currently detectable (i.e. non-Dark matter, dark) matt ...
(a measure of the proportion of chemical elements other than hydrogen and helium within a star) indicating an inner galactic origin, since stars outside the disks of galaxies tend to have low metallicity and are older.
Some recently discovered supernovae have been confirmed to have exploded hundreds of thousands of light-years from the nearest star or galaxy. Most intergalactic star candidates found in the neighborhood of the Milky Way seem not to have an origin in the Galactic Center but in the Milky Way disk or elsewhere.
Mass
In 2005, the Spitzer Space Telescope revealed a hitherto unknown infrared component in the background from the cosmos. Since then, several other anisotropies at other wavelengths including blue and x-ray have been detected with other space telescopes and they are now collectively described as the diffuse extragalactic background radiation. Several explanations have been discussed by scientists, but in 2012, it was suggested and shown how for the first time this diffuse radiation might originate from intergalactic stars. If that is the case, they might collectively comprise as much mass as that found in the galaxies. A population of such magnitude was at one point thought to explain the photon underproduction crisis, and may explain a significant part of thedark matter
In astronomy, dark matter is an invisible and hypothetical form of matter that does not interact with light or other electromagnetic radiation. Dark matter is implied by gravity, gravitational effects that cannot be explained by general relat ...
problem.
Known locations
The first intergalactic stars were discovered in the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. These stars are notable for their isolation, residing approximately 300,000 light-years away from the nearest galaxy. Despite the difficulty in determining their exact mass, it is estimated that intergalactic stars constitute around 10 percent of the mass of theVirgo cluster
The Virgo Cluster is a cluster of galaxies whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly (16.5 ± 0.1 Mpc) away in the Virgo constellation. Comprising approximately 1,300 (and possibly up to 2,000) member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the larger ...
, potentially outweighing any of its 2,500 galaxies
In 2012, astronomers identified approximately 675 rogue stars at the edge of the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
, towards the Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy and is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way. It was originally named the Andromeda Nebula and is cataloged as Messier 31, M31, and NGC 224. Andromeda has a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isop ...
. These stars were likely ejected from the Milky Way's core by interactions with the central supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions, of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical ...
. The study led by Kelly Holley-Bockelmann and Lauren Palladino from Vanderbilt University
Vanderbilt University (informally Vandy or VU) is a private university, private research university in Nashville, Tennessee, United States. Founded in 1873, it was named in honor of shipping and railroad magnate Cornelius Vanderbilt, who provide ...
highlighted the unusual red coloration and high velocities of these stars, indicating their dramatic journey from the galactic center.
See also
* * * * *, or interstellar planet * *References
Sources
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Intergalactic Star Extragalactic astronomy Star types