Intensive Margin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Within economics, margin is a concept used to describe the current level of consumption or production of a
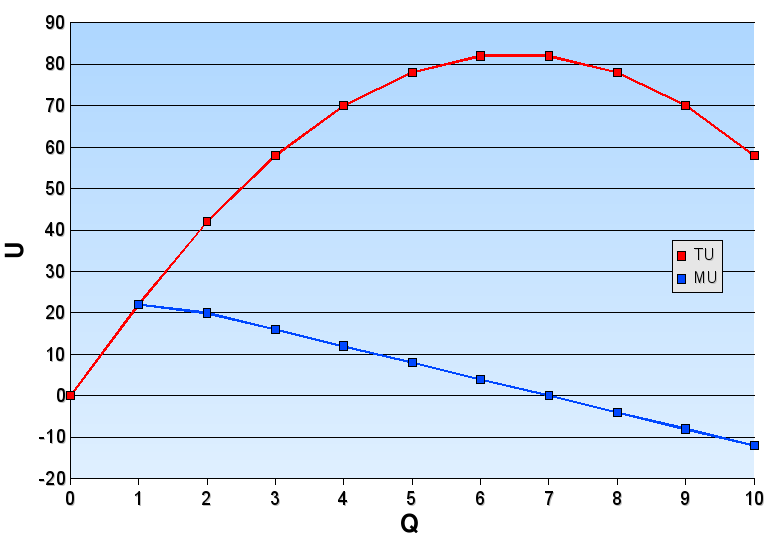 Marginal utility describes the added satisfaction or benefits a consumer will obtain by purchasing an additional product or service. The marginal utility can be positive, negative or zero. A negative marginal utility states that the user gains dissatisfaction from an additional unit, whilst a marginal utility of zero states that no satisfaction is gained from the additional unit.Gans, J., King, S., & Mankiw, G. (2011). Principles of microeconomics (pp. 65–94). Cengage Learning Australia.
Within marginal utility, the
Marginal utility describes the added satisfaction or benefits a consumer will obtain by purchasing an additional product or service. The marginal utility can be positive, negative or zero. A negative marginal utility states that the user gains dissatisfaction from an additional unit, whilst a marginal utility of zero states that no satisfaction is gained from the additional unit.Gans, J., King, S., & Mankiw, G. (2011). Principles of microeconomics (pp. 65–94). Cengage Learning Australia.
Within marginal utility, the

 The
The
 In defining circumstances where both suppliers and buyers are price takers, therefore allowing the demand and supply functions to not influence one another, marginalism and neoclassical economics can define models of
In defining circumstances where both suppliers and buyers are price takers, therefore allowing the demand and supply functions to not influence one another, marginalism and neoclassical economics can define models of
 In the instance of a company holding a monopoly over a particular market, the company now acts as
In the instance of a company holding a monopoly over a particular market, the company now acts as
good
In most contexts, the concept of good denotes the conduct that should be preferred when posed with a choice between possible actions. Good is generally considered to be the opposite of evil. The specific meaning and etymology of the term and its ...
or service
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a ...
.Marginalism Definition. Investopedia. (2022). Retrieved 12 April 2022, from https://www.investopedia.com/terms/m/marginalism.asp. Margin also encompasses various concepts within economics, denoted as marginal concepts In economics, marginal concepts are associated with a ''specific change'' in the quantity used of a good or service, as opposed to some notion of the over-all significance of that class of good or service, or of some total quantity thereof.{{citat ...
, which are used to explain the specific change in the quantity of goods and services produced and consumed. These concepts are central to the economic theory of marginalism
Marginalism is a theory of economics that attempts to explain the discrepancy in the value of goods and services by reference to their secondary, or marginal, utility. It states that the reason why the price of diamonds is higher than that of wa ...
. This is a theory that states that economic decisions are made in reference to incremental units at the margin,Reading: Marginal Utility , Microeconomics. Courses.lumenlearning.com. (2022). Retrieved 12 April 2022, from https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-microeconomics/chapter/marginal-utility/. and it further suggests that the decision on whether an individual or entity will obtain additional units of a good or service depends on the marginal utility
Marginal utility, in mainstream economics, describes the change in ''utility'' (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. Marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. Negative marginal utilit ...
of the product.Stiglitz, J. (2000). The Contributions of the Economics of Information to Twentieth Century Economics. The Quarterly Journal Of Economics, 115(4), 1441–1478. https://doi.org/10.1162/003355300555015.
These marginal concepts are used to theorise various market behaviours and form the basis of price theory. It is a central idea within microeconomics
Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and Theory of the firm, firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarcity, scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. M ...
and is used to predict the demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a goods, good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. In economics "demand" for a commodity is not the same thing as "desire" for it. It refers to both the desi ...
and supply of goods and services within an economy.
Marginal concepts
Marginal cost
Marginal cost
In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is increased, i.e. the cost of producing additional quantity. In some contexts, it refers to an increment of one unit of output, and in others it ...
is the change in monetary cost associated with an increase in the quantity of production of a certain good or service. It is measured in dollars per unit, and includes all the variable costs that alter depending on the level of production. Marginal cost differs from average cost as it solely provides the additional cost of one unit, rather than the average cost of each unit.
The marginal cost function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-orie ...
is the slope of the total cost function. Thus, given a continuous and differentiable
In mathematics, a differentiable function of one real variable is a function whose derivative exists at each point in its domain. In other words, the graph of a differentiable function has a non- vertical tangent line at each interior point in ...
cost function, the marginal cost function is the derivative of the cost function with respect to the quantity produced.Nguyen, B., & Wait, A. (2016). Essentials of microeconomics (pp. 1–185). Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group.
Marginal utility
 Marginal utility describes the added satisfaction or benefits a consumer will obtain by purchasing an additional product or service. The marginal utility can be positive, negative or zero. A negative marginal utility states that the user gains dissatisfaction from an additional unit, whilst a marginal utility of zero states that no satisfaction is gained from the additional unit.Gans, J., King, S., & Mankiw, G. (2011). Principles of microeconomics (pp. 65–94). Cengage Learning Australia.
Within marginal utility, the
Marginal utility describes the added satisfaction or benefits a consumer will obtain by purchasing an additional product or service. The marginal utility can be positive, negative or zero. A negative marginal utility states that the user gains dissatisfaction from an additional unit, whilst a marginal utility of zero states that no satisfaction is gained from the additional unit.Gans, J., King, S., & Mankiw, G. (2011). Principles of microeconomics (pp. 65–94). Cengage Learning Australia.
Within marginal utility, the law of diminishing marginal utility
Marginal utility, in mainstream economics, describes the change in ''utility'' (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. Marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. Negative marginal utilit ...
describes that the benefit to a consumer of an additional unit is inversely related to the number of current units, demonstrating that the added benefit of each new unit is less than the unit prior.
An example of this could be demonstrated by a family buying dinner. The 1st plate of food would have a greater marginal utility than the 30th plate of food, as the families hunger would be reduced and they would thus obtain less value from it.
Marginal rate of substitution
The marginal rate of substitution is the least favourable rate an individual or entity would exchange a good or service for another good or service.Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS) Definition. Investopedia. (2022). Retrieved 7 April 2022, from https://www.investopedia.com/terms/m/marginal_rate_substitution.asp The marginal rate of substitution is associated with the value an individual or entity places on each unit, and would only trade if it provides a positive net value, whereby the value of the good or service obtained is greater than the one given away. The marginal rate of substitution is calculated between two goods placed on theindifference curve
In economics, an indifference curve connects points on a graph representing different quantities of two goods, points between which a consumer is ''indifferent''. That is, any combinations of two products indicated by the curve will provide the c ...
, displaying the utility of each good. The slope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a Line (mathematics), line is a number that describes the direction (geometry), direction of the line on a plane (geometry), plane. Often denoted by the letter ''m'', slope is calculated as the ratio of t ...
of the utility curve represents the quantity of goods one would be satisfied in substituting for one another. There are however difficulties in quantifying the utility of different goods and services in comparison to one another, provide a critique of this framework.
Marginal product
In the theory of marginality, the marginal product of an input is the extra output obtained by adding one unit to a specific input.Blair, R., & Saygin, P. (2020). Uncertainty and the marginal revenue product–wage gap. Managerial And Decision Economics, 42(3), 564–569. https://doi.org/10.1002/mde.3254 This assumes all the other factors contributing to the output remain constant. For example, the marginal product of labour would be the added production when increasing a unit of labour, such as hours worked. Marginality states that theoretically, the wage rate would equal the marginal product of labour. If the wage rate is below the marginal product of labour, profit-maximising businesses would continue to hire more employees until themarginal product
In economics and in particular neoclassical economics, the marginal product or marginal physical productivity of an input (factor of production) is the change in output resulting from employing one more unit of a particular input (for instance, t ...
reduces to the wage rate according to the law of diminishing return. Moreover, this theory can be applied to working capital
Working capital (WC) is a financial metric which represents operating liquidity available to a business, organisation, or other entity, including governmental entities. Along with fixed assets such as plant and equipment, working capital is consi ...
, where businesses will employ more capital when the rate of interest
In finance and economics, interest is payment from a debtor or deposit-taking financial institution to a lender or depositor of an amount above repayment of the principal sum (that is, the amount borrowed), at a particular rate. It is distinct ...
on the capital is less than the marginal product. The value of the final product can thus be considered as a contribution of the various inputs and values derived by each.
Margin squeeze
Margin squeeze is a pricing strategy implemented by vertically integrated companies who are the dominant provider of an input.Gaudin, G., & Mantzari, D. (2016).Margin squeeze: An above-cost predatory pricing approach. Journal Of Competition Law And Economics, 12(1), 151–179. https://doi.org/10.1093/joclec/nhv042 It is used to narrow the margin between the wholesale price of the input it controls and the downstream retail price to render other retailers unprofitable. It hence squeezes the margin of a good or service. This squeezing of the margin can either be executed by increasing theprice
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation expected, required, or given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, especially when the product is a service rather than a ph ...
for the upstream product, decreasing the price of the downstream product or performing both simultaneously.
This strategy is viewed as an anti-competitive strategy and under anti-trust policies is prohibited in most competitive markets. The European courts considered that a margin squeeze constitutes specific and independent abuse
Abuse is the act of improper usage or treatment of a person or thing, often to unfairly or improperly gain benefit. Abuse can come in many forms, such as: physical or verbal maltreatment, injury, assault, violation, rape, unjust practices, ...
, and the US supreme court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over Stat ...
deemed that it falls under the existing abuse of refusal to deal or predation. The European courts stated that the strategy "does not allow even an equally efficient competitor to trade profitably in the downstream market on a lasting basis", and is hence viewed as an illegal strategy.Julien, B., Rey, P., & Saavedra, C. (2014). The Economics of Margin Squeeze. Idei.fr. Retrieved 23 May 2022, from http://idei.fr/sites/default/files/medias/doc/by/jullien/Margin_Squeeze_Policy_Paper_revised_March_2014.pdf.
Applications within Price theory

Supply
In bothneoclassical economics
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption, and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a go ...
and marginalism
Marginalism is a theory of economics that attempts to explain the discrepancy in the value of goods and services by reference to their secondary, or marginal, utility. It states that the reason why the price of diamonds is higher than that of wa ...
, supply curves are given by the marginal cost curve. The marginal cost curve is the marginal cost of an additional unit at each given quantity. The law of diminishing returns states the marginal cost of an additional unit of production for an organisation or business increases as the quantity produced increases. Consequently, the marginal cost curve is an increasing function for large quantities of supply.
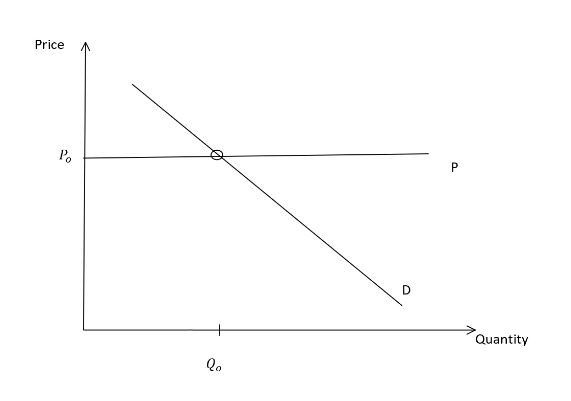
Given a price set by a competitive market
In economics, competition is a scenario where different economic firmsThis article follows the general economic convention of referring to all actors as firms; examples in include individuals and brands or divisions within the same (legal) fir ...
, a company will produce a product if the selling price is greater than the production cost of the unit.Perloff, J. (2021). Microeconomics (pp. 33–96). Pearson Education, Limited. The company will consequently produce products until the marginal cost of an additional unit is greater than the sale price.
Demand
 The
The demand curve
A demand curve is a graph depicting the inverse demand function, a relationship between the price of a certain commodity (the ''y''-axis) and the quantity of that commodity that is demanded at that price (the ''x''-axis). Demand curves can be us ...
within economics is founded within marginalism in terms of marginal utility. Marginal utility states that a buyer will attribute some level of benefit to an additional unit of consumption, and given the concept of diminishing marginal utility, the marginal utility
Marginal utility, in mainstream economics, describes the change in ''utility'' (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. Marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. Negative marginal utilit ...
of each new product will decrease as the overall quantity increases. Due to this, the demand curve will decrease as the quantity of goods increases.
Price theory states that the consumer will be willing to purchase an additional unit of a product if the marginal utility is greater than the cost of the good, as it provides a net benefit to the consumer. Given the marginal utility gradually decreases, the consumer will purchase additional units of a good or service until the marginal benefit of an additional unit is equal to the price of the unit as set by the market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
*Marketing, the act of sat ...
, shown by the intersection of the demand and cost functions.TURVEY, R. (2022). DEMAND AND SUPPLY (pp. 74–91). ROUTLEDGE.
An increase in price would consequently decrease demand for the individual as it would shift the cost curve
In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. In a free market economy, productively efficient firms optimize their production process by minimizing cost consistent with each possible ...
up, and intersect the marginal utility curve at a point to the left of the original intersection, decreasing the quantity demanded. Since the demand of the market is the demand of all consumers combined, the market demand also follows this principle.
Market behaviour
Perfectly competitive environment
perfect competition
In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. In Economic model, theoret ...
. However, it does not provide an accurate depiction in an imperfect environment. Within a perfectly competitive environment, marginalism is used within the principles of demand and supply to show that the intersection of the curves would be the market equilibrium.
This is the case as a company will only produce while the price is greater or equal to the marginal cost, given by the supply curve, and the consumer will only buy the good if the demand at that quantity is greater than the cost. The intersection point is consequently equilibrium as it is the price and quantity where a goods supply would equal its demand. Any natural deviation from this equilibrium would be naturally resolved within a competitive environment and return to this state.
Monopoly
 In the instance of a company holding a monopoly over a particular market, the company now acts as
In the instance of a company holding a monopoly over a particular market, the company now acts as price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation expected, required, or given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, especially when the product is a service rather than a ph ...
makers rather than price takers, and will regulate the quantity supplied and price sold to maximise profit
Profit may refer to:
Business and law
* Profit (accounting), the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market
* Profit (economics), normal profit and economic profit
* Profit (real property), a nonpossessory inter ...
s. In an environment where they can not enact price discrimination, monopolistic companies will theoretically use the concept of marginalism to maximise profit.
Given a demand curve, a company's total revenue is equal to the product of the demand curve and quantity supplied. The marginal revenue curve can then be calculated as the derivative
In mathematics, the derivative is a fundamental tool that quantifies the sensitivity to change of a function's output with respect to its input. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is t ...
of the total revenue curve with respect to the quantity produced. This provides the additional revenue
In accounting, revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of product (business), goods and services related to the primary operations of a business.
Commercial revenue may also be referred to as sales or as turnover. Some compan ...
of each unit sold.
Given monopolistic companies act as price makers, and control the quantity supplied, they will produce at a quantity that allows them to maximise their profit.
Therefore they will produce until the marginal cost curve is greater than the marginal revenue curve, as any products sold after will incur a decrease from the maximum profit, and the price will be set by the demand function at that given quantity.Greenlaw, S., & Shapiro, D. (2022). How a Profit-Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output and Price. Opentextbc.ca. Retrieved 8 May 2022, from https://opentextbc.ca/principlesofeconomics2eopenstax/chapter/how-a-profit-maximizing-monopoly-chooses-output-and-price/
Criticisms
There are several critiques of the theory of marginal utility. A majorcritique
Critique is a method of disciplined, systematic study of a written or oral discourse. Although critique is frequently understood as fault finding and negative judgment, Rodolphe Gasché (2007''The honor of thinking: critique, theory, philosophy ...
is that the theory ignores how an individual's valuation of a good or service may be dependent on their reference point and personal circumstances and they may not act as ‘rationale’.Critiques of Expected Utility Theory. Princeton.edu. (2009). Retrieved 8 May 2022, from https://www.princeton.edu/~dixitak/Teaching/EconomicsOfUncertainty/Slides&Notes/Notes10.pdf. Psychologists have suggested that people's perceptions and judgements are influenced by their reference position. This is demonstrated by Richard Thaler’s endowment effect experiment, whereby individuals were sold small objects and then offered an option for the item to be bought back from them. He found that people would only sell the product at a premium, demonstrating that the value of the good was higher when viewed as something that could be lost compared to something that could be acquired. John List however performed a similar experiment with trading cards
A trading card (or collectible card) is a small card, usually made out of paperboard or thick paper, which usually contains an image of a certain person, place or thing (fictional or real) and a short description of the picture, along with other t ...
and found these subjects were less influenced by endowment. His research suggested that traders learnt from prior experiences and make decisions based on long term value, rather than the emotions associated with the loss of the good. Moreover, findings suggest that benefits and costs are processed in different parts of the brain and thus may not be perfectly correlated.
The uncertainty over how much marginal utility
Marginal utility, in mainstream economics, describes the change in ''utility'' (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. Marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. Negative marginal utilit ...
an individual will give to a certain good or service and its dependence on their individual reference point and context makes it difficult to quantify each individual's marginal utility for a certain product. However, marginal utility theory
Marginal utility, in mainstream economics, describes the change in ''utility'' (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. Marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. Negative marginal utilit ...
assumes this deviation to be non-existent and the consumer to be perfectly rational
Rationality is the quality of being guided by or based on reason. In this regard, a person acts rationally if they have a good reason for what they do, or a belief is rational if it is based on strong evidence. This quality can apply to an ...
and uniform. Therefore, there is no certainty that people will act as theorised and they are expected to deviate, limiting this theory.
Another key limitation of margin is how marginal change is measured. Quantifying the marginal utility
Marginal utility, in mainstream economics, describes the change in ''utility'' (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. Marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. Negative marginal utilit ...
of certain products and services such as food may be difficult as utility is a subjective value and thus individuals may struggle to associate a numerical value to it.
The theory also assumes the marginal utility of money to be constant, however, this is not true in practice as the value of each additional dollar decreases as the overall quantity of money increases. Thus the marginal utility of money can be considered non-uniform in practice. For example, gaining $1 after having only $2 is worth more than gaining $1 after having $2,000,000.
Alternate theories
Labour theory of value
The labour theory of value is an economic theory that states that the value of a good or service is quantified by the ‘socially necessary labour’ required to produce it. The theory is often associated withMarxian economics
Marxian economics, or the Marxian school of economics, is a heterodox school of political economic thought. Its foundations can be traced back to Karl Marx's critique of political economy. However, unlike critics of political economy, Marxian ...
and is central to his theory that centres on how capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
exploits the working class.
This theory values a good or service based on the duration and intensity of labour required to produce it. The theory also encompasses the means of production
In political philosophy, the means of production refers to the generally necessary assets and resources that enable a society to engage in production. While the exact resources encompassed in the term may vary, it is widely agreed to include the ...
, referring to the tools
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates ...
, materials, power and other means required to produce the goods or services that are a result of prior labour. In its simplest form, the final value of a product is equal to the sum of the value of labour time( average skill and productivity) and the value of the means of production, also known as constant capital
Constant or The Constant may refer to:
Mathematics
* Constant (mathematics), a non-varying value
* Mathematical constant, a special number that arises naturally in mathematics, such as or
Other concepts
* Control variable or scientific co ...
.
Diamond-water paradox
The labour theory of value was used to explain the Diamond-Water paradox as proposed byAdam Smith
Adam Smith (baptised 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the field of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as the "father of economics"——— or ...
. It asserts that although diamonds
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of electricity, and insol ...
had minimal practical value compared to water back in the 19th century, the value demanded by diamonds exceeds the value of water, a resource which was essential to life and had many applications. Smith used this to support the labour theory of value, suggesting that value associated with diamonds was reflective of the labour required to obtain them, compared to water, a more readily available resource. He argued that this supports how the cost of a good is determined by its labour cost compared to use value.Smith, A. (1998). An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations. Electric Book Co.
Marginalism advocates however argued that Smith misunderstood marginalism fundamentally. They claimed that the marginal usefulness can only be attributed as a specific quantity, rather than categorically. For most individuals, water is sufficiently abundant, therefore the value of an additional loss or gain of a gallon of water would be very minor, whereas the rarity of diamonds means the gain or loss of one diamond would be more significant. The first gallon
The gallon is a unit of volume in British imperial units and United States customary units.
The imperial gallon (imp gal) is defined as , and is or was used in the United Kingdom and its former colonies, including Ireland, Canada, Australia ...
of water an individual has access to would have more value than the first diamond, however, each subsequent gallon would have reduced value, to the point where the first diamond would have more value than the nth gallon. The notion is a result of diminishing marginal utility
Marginal utility, in mainstream economics, describes the change in ''utility'' (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. Marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. Negative marginal utilit ...
.
See also
*Marginalism
Marginalism is a theory of economics that attempts to explain the discrepancy in the value of goods and services by reference to their secondary, or marginal, utility. It states that the reason why the price of diamonds is higher than that of wa ...
* Marginal utility
Marginal utility, in mainstream economics, describes the change in ''utility'' (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. Marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. Negative marginal utilit ...
* Labor theory of value
The labor theory of value (LTV) is a theory of value that argues that the exchange value of a good or service is determined by the total amount of " socially necessary labor" required to produce it. The contrasting system is typically known as ...
* Monopoly
References
{{Authority controlMargin
Margin may refer to:
Physical or graphical edges
*Margin (typography), the white space that surrounds the content of a page
* Continental margin, the zone of the ocean floor that separates the thin oceanic crust from thick continental crust
*Leaf ...