Integrated Urban Water Management on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
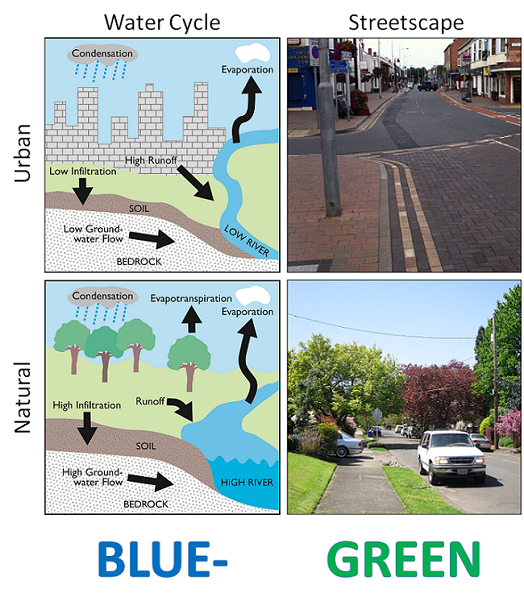 Integrated urban water management (IUWM) is the practice of managing
Integrated urban water management (IUWM) is the practice of managing
 Integrated urban water management (IUWM) is the practice of managing
Integrated urban water management (IUWM) is the practice of managing freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
, wastewater
Wastewater (or waste water) is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of do ...
, and storm water as components of a basin-wide management plan. It builds on existing water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Th ...
and sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
considerations within an urban settlement by incorporating urban water management within the scope of the entire river basin. IUWM is commonly seen as a strategy for achieving the goals of Water Sensitive Urban Design. IUWM seeks to change the impact of urban development
Urban means "related to a city". In that sense, the term may refer to:
* Urban area, geographical area distinct from rural areas
* Urban culture, the culture of towns and cities
Urban may also refer to:
General
* Urban (name), a list of peop ...
on the natural water cycle
The water cycle (or hydrologic cycle or hydrological cycle) is a biogeochemical cycle that involves the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth across different reservoirs. The mass of water on Earth remains fai ...
, based on the premise that by managing the urban water cycle as a whole; a more efficient use of resources can be achieved providing not only economic benefits but also improved social and environmental outcomes. One approach is to establish an inner, urban, water cycle loop through the implementation of reuse strategies. Developing this urban water cycle loop requires an understanding both of the natural, pre-development, water balance and the post-development water balance. Accounting for flows in the pre- and post-development systems is an important step toward limiting urban impacts on the natural water cycle.
IUWM within an urban water system can also be conducted by performance assessment of any new intervention strategies by developing a holistic approach which encompasses various system elements and criteria including sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): env ...
type ones in which integration of water system components including water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Th ...
, waste water
Wastewater (or waste water) is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of do ...
and storm water subsystems would be advantageous. Simulation of metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
type flows in urban water system can also be useful for analysing processes in urban water cycle of IUWM.
Components
Activities under the IUWM include the following: *Improvewater supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Th ...
and consumption efficiency
*Upgrade drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also calle ...
quality
Quality may refer to:
Concepts
*Quality (business), the ''non-inferiority'' or ''superiority'' of something
*Quality (philosophy), an attribute or a property
*Quality (physics), in response theory
*Energy quality, used in various science discipli ...
and wastewater treatment
Wastewater treatment is a process which removes and eliminates contaminants from wastewater. It thus converts it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once back in the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on ...
*Increase economic efficiency of services to sustain operations and investments for water, wastewater, and stormwater management
*Utilize alternative water source
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
s, including rain
Rain is a form of precipitation where water drop (liquid), droplets that have condensation, condensed from Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is res ...
water, and reclaimed and treated water
*Engage communities to reflect their needs and knowledge for water management
*Establish and implement policies and strategies to facilitate the above activities
*Support capacity development of personnel and institutions that are engaged in IUWM
According to Australia's Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency that is responsible for scientific research and its commercial and industrial applications.
CSIRO works with leading organisations arou ...
), IUWM requires the management of the urban water cycle in coordination with the hydrological water cycle which are significantly altered by urban landscapes and its correlation to increasing demand. Under natural conditions the water inputs at any point in the system are precipitation and overland flows; while the outputs are via surface flows, evapo-transpiration and groundwater recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs in ...
. The large volumes of piped water introduced with the change to an urban setting and the introduction of vast impervious areas strongly impact the water balance, increasing in-flows and dramatically altering the out-flow components.
Approaches
*TheAgenda 21
Agenda 21 is a non-binding action plan of the United Nations with regard to sustainable development. It is a product of the Earth Summit (UN Conference on Environment and Development) held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, in 1992. It is an action ag ...
(UN Department for Sustainable Development, 1992) has worked out the Dublin Principles for Integrated water resources management in more detail for urban areas. One of the objectives of Agenda 21 is to develop environmentally sound management of water resources for urban use.
*The Bellagio Statement formulated by the Environmental Sanitation Working Group of the Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council in 2000 include principals such as: Human dignity, quality of life, environmental security, an open stakeholder process, and many others.
*The UNEP 3 Step Strategic Approach developed in 2005 is based on the application of the "Cleaner Production approach" that has been successful in the industrial sector. The three steps are: Prevention, Treatment for reuse, and Planned discharge with stimulation of self-purification capacity.
*UNESCO's Institute for Water Education seeks to build on the progress made by the Bellagio Statement and UNEP's 3-step approach by developing the ''SWITCH'' approach to IUWM. Components include: the addition of a sustainability assessment, new methods of planning urban water systems, and modifications to planning and strategy development.
Examples
An example of IUWM is the Catskill/ Delaware water system that provides of water per day, including to all ofNew York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
. The IUWM process included an extensive stakeholder engagement
Stakeholder engagement is the process by which an organization involves people who may be affected by the decisions it makes or can influence the implementation of its decisions. They may support or oppose the decisions, be influential in the organ ...
process, whereby the needs of all parties were included into the final management plan. A partnership was created between New York City, the agricultural community, and the federal government. The case has become a model for successful IUWM.
Urban decision support systems
UrbanDecision Support System
A decision support system (DSS) is an information system that supports business or organizational decision-making activities. DSSs serve the management, operations and planning levels of an organization (usually mid and higher management) and ...
(UDSS) – is a data-driven urban water management system that uses sensors attached to water appliances in urban residences to collect data about water usage. The system was developed with a European Commission investment of 2.46 Million Euros to improve the water consumption behavior of households. Information about appliances and facilities such as dishwashers, showers, washing machines, taps – is wirelessly recorded and sent to the UDSS App on the user's mobile device. The UDSS is then able to analyze and show homeowners which appliances are using the most water, and which behavior or habits should be avoided in order to reduce the water usage.
Challenges
One of the most significant challenges for IUWM could be securing a consensus on the definition of IUWM and the implementation of stated objectives at operational stages of projects. In the developing world there is still a significant fraction of the population that has no access to proper water supply and sanitation. At the same time, population growth,urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
and industrialization
Industrialisation (British English, UK) American and British English spelling differences, or industrialization (American English, US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an i ...
continue to cause pollution and depletion of water sources. In the developed world, pollution of water sources is threatening the sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): env ...
of urban water systems. Climate change is likely to affect all urban centers, either with increasingly heavy storms or with prolonged droughts, or perhaps both. To address the challenges facing IUWM it is crucial to develop good approaches, so that policy development and planning are directed towards addressing these global change pressures, and to achieving truly sustainable urban water systems.
See also
* One Water (Management) * Integrated urban water management in Tegucigalpa * International trade and water *Water management in Greater Mexico City
Greater Mexico City (''Zona Metropolitana del Valle de México''), a metropolitan area with more than 19 million inhabitants including Mexico City, Mexico's capital (''Ciudad de México'', or CDMX) with about 9 million inhabitants, faces tremendous ...
* Water management in the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo
* Water security
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Integrated Urban Water Management Water resources management Sustainable urban planning