Infratemporal Space on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The infratemporal space (also termed the infra-temporal space or the infra-temporal portion of the deep temporal space) is a fascial space of the head and neck (sometimes also termed 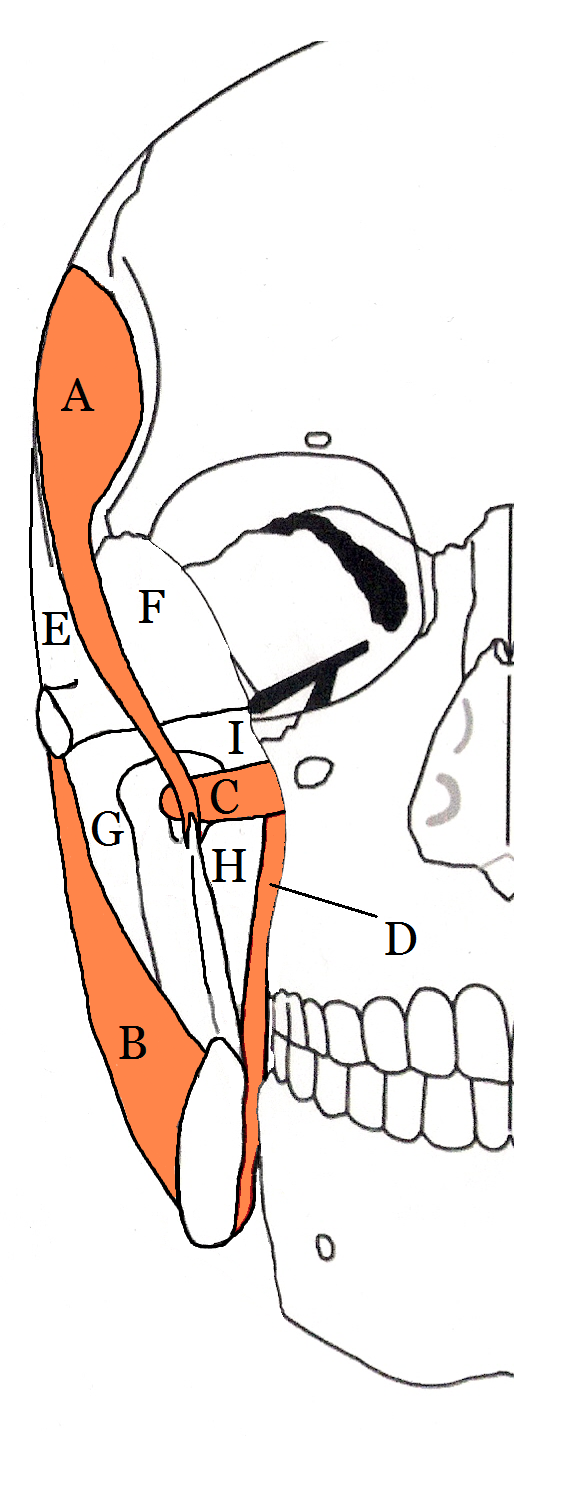
fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location.
...
l spaces or tissue spaces). It is a potential space
In anatomy, a potential space is a space between two adjacent structures that are normally pressed together (directly apposed). Many anatomic spaces are potential spaces, which means that they are potential rather than realized (with their realiz ...
in the side of the head, and is paired on either side. It is located posterior to the maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
, between the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bon ...
medially and by the base of skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, inferior area of the human skull, skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the Calvaria ...
superiorly. The term is derived from '' infra-'' meaning below and ''temporal'' which refers to the temporalis muscle
In anatomy, the temporalis muscle, also known as the temporal muscle, is one of the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is a broad, fan-shaped convergent muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic a ...
.
The infratemporal space is the inferior portion of the deep temporal space, which is one of the four compartments of the masticator space, along with the pterygomandibular space, the submasseteric space and the superficial temporal space. The deep temporal space is separated from the pterygomandibular space by the lateral pterygoid muscle
The lateral pterygoid muscle (or external pterygoid muscle) is a muscle of mastication. It has two heads. It lies superior to the medial pterygoid muscle. It is supplied by pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery, and the lateral pterygoid n ...
inferiorly and from the superficial temporal space by the temporalis muscle laterally. The deep temporal space and the superficial temporal space together make up the temporal spaces.

Location and structure
Anatomic boundaries
The boundaries of the infratemporal space are: * the greater wing of the sphenoid bone superiorly * the pterygomandibular space inferiorly * the infra-temporal surface of the maxilla anteriorly, * the lateral pterygoid plate, part of the lateral pterygoid muscle and lateral pharyngeal wall mediallyCommunications
The communications of the infratemporal space are: * the pterygomandibular space inferiorly, * the buccal space anteriorly and inferiorly, * to thecavernous sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The ...
via the pterygoid plexus of veins.
Contents
The contents of the infratemporal space are: * branches of themaxillary artery
The maxillary artery (eg, internal maxillary artery) supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible.
Structure
The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches ...
,
* the pterygoid venous plexus.
Clinical relevance
Infections of the infratemporal space are rare. They may be significant however, as it is possible for infection to spread via emissary veins from the pterygoid plexus to the cavernous sinus, which may result in cavernous sinus thrombosis, a rare but life-threatening condition. The signs and symptoms of an infratemporal space infection are swelling of the face in the region of the sigmoid notch, swelling of the mouth in the region of the maxillary tuberosity and marked trismus (difficulty opening the mouth), since some of themuscles of mastication
The four classical muscles of mastication elevate the mandible (closing the jaw) and move it forward/backward and laterally, facilitating biting and chewing. Other muscles are responsible for opening the jaw, namely the geniohyoid, mylohyoid, an ...
are restricted by the swelling. Treatment of an abscess of this space is usually by surgical incision and drainage
Incision and drainage (I&D), also known as clinical lancing, are minor surgical procedures to release pus or pressure built up under the skin, such as from an abscess, boil, or infected paranasal sinus. It is performed by treating the area wit ...
, with the incision being placed on the face (a small horizontal incision posterior to the junction of the temporal and frontal process of the zygomatic bone
In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (from ), also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone, situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forming part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit, of the temporal fos ...
. or both on the face and inside the mouth.
Odontogenic infection
The spread of odontogenic infections may sometimes involve the infratemporal space. The most likely causative tooth is the maxillary third molar (upperwisdom tooth
The third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is the most posterior of the three molars in each quadrant of the human dentition. The age at which wisdom teeth come through ( erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs between late teens a ...
).
References
{{Digestive tract Mouth Otorhinolaryngology Oral and maxillofacial surgery Fascial spaces of the head and neck