InflateSail August on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
InflateSail was a 3U CubeSat launched on PSLV C38 on 23 June 2017 into a 505 km polar

Sun-synchronous orbit
A Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), also called a heliosynchronous orbit, is a nearly polar orbit around a planet, in which the satellite passes over any given point of the planet's surface at the same local mean solar time. More technically, it is ...
. It carried a 1 m long inflatable rigidizable mast, and a 10 m2 drag-deorbiting sail. Its primary aim was to demonstrate the effectiveness of drag based deorbiting from low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an geocentric orbit, orbit around Earth with a orbital period, period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial object ...
(LEO). Built by Surrey Space Centre of the University of Surrey
The University of Surrey is a public research university in Guildford, Surrey, England. The university received its Royal Charter, royal charter in 1966, along with a Plate glass university, number of other institutions following recommendations ...
, it was one of the Technology Demonstrator CubeSats for the QB50 mission. An identical drag sail payload was planned to be included on the RemoveDEBRIS demonstrator.
Inflatable mast
The inflatable mast was deployed first to distance the sail from the main body of the satellite. The inflatable skin was a 3-ply, 45 μm thick metal-polymer laminate which used the same strain rigidization process as the Echo 2 balloon. The inflation gas was stored in two cool gas generators (CGGs). The inflation gas was vented almost immediately after the deployment and rigidization process. Fully folded, the inflatable was just over in height.Sail structure
The 10 m2 sail was made up of four quadrants of 12 μm thick polyethylene naphthalate, supported by four bistable carbon fiber tape-springs. The structure was similar in format to both NanoSail-D2 and LightSail 2. The deployment of the sail was driven by a brushless DC motor.Spacecraft
InflateSail included an avionics suite to support the deployable sail payload. The spacecraft was powered by a GOMSpace power system and returned attitude data from the Stellenbosch/Surrey Attitude Determination and Control System. Communications with ground were executed through the TRXVU Transceiver procured from ISIS, using the UHF band to transmit and the VHF to receive. Beacon data containing spacecraft parameters were transmitted at 60s intervals at 436.060MHz 1200bd BPSK.
Launch
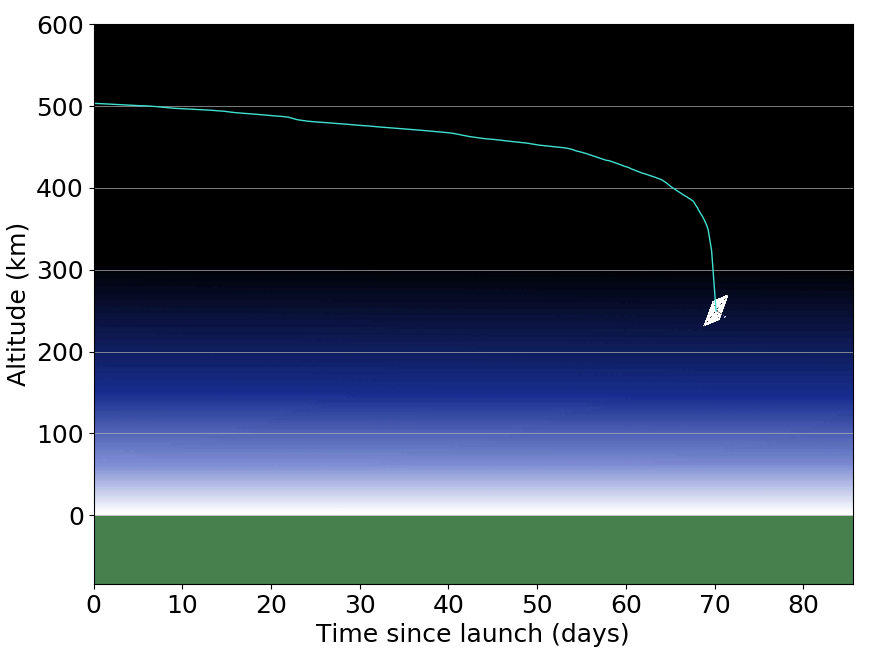
InflateSail was launched on board the PSLV-C38 as one of 31 passenger satellites. InflateSail was one of 8 QB50 satellites on this launch. PSLV-C38 lifted off at 09:29 (IST)/03:59 (UTC) on 23 June 2017 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in India. InflateSail was ejected into a 518x494km orbit approximately 20 minutes after lift off.Altitude loss
InflateSail successfully deployed its sail approximately one hour after ejection from the launch vehicle and was the first European sail successfully deployed in space. InflateSail rapidly lost altitude and decayed on 3 September 2017 after 72 days in orbit.
References
{{Orbital launches in 2017 CubeSats Spacecraft launched in 2017