Inflatable Boat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 An inflatable boat is a lightweight
An inflatable boat is a lightweight

 There are ancient carved images of animal skins filled with air being used as one-man floats to cross rivers. These floats were inflated by mouth.
The discovery of the process to vulcanize rubber was made by Charles Goodyear in 1838, and was granted a US patent in 1844. Vulcanization stabilized the rubber, making it durable and flexible. In late 1843, Thomas Hancock filed for a UK patent, which was also granted in 1844, after the
There are ancient carved images of animal skins filled with air being used as one-man floats to cross rivers. These floats were inflated by mouth.
The discovery of the process to vulcanize rubber was made by Charles Goodyear in 1838, and was granted a US patent in 1844. Vulcanization stabilized the rubber, making it durable and flexible. In late 1843, Thomas Hancock filed for a UK patent, which was also granted in 1844, after the 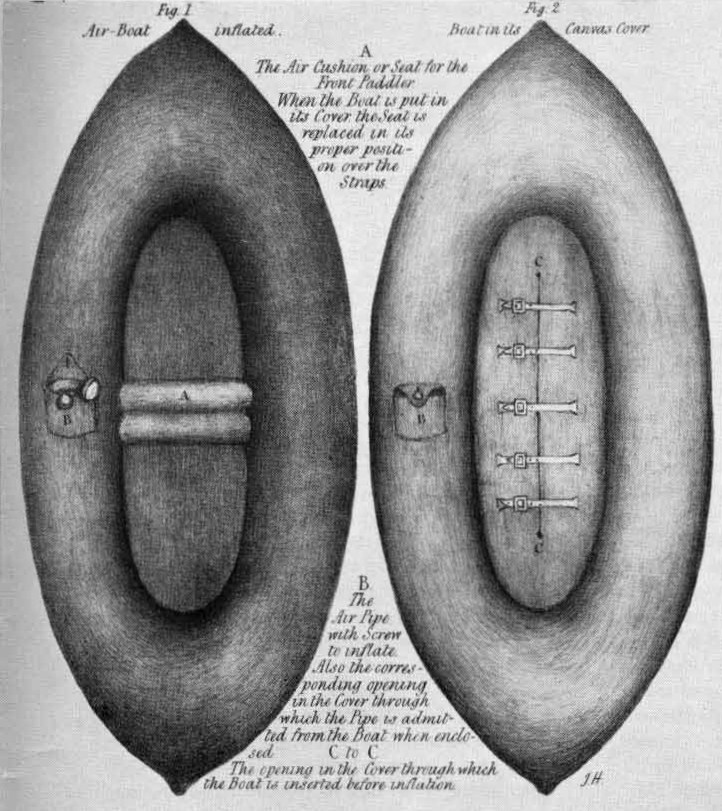 In 1844–1845, British naval officer Lieutenant Peter Halkett developed two types of inflatable boats intended for use by Arctic explorers. Both were made of rubber-impregnated " Mackintosh cloth." In the Halkett boat, the "boat cloak" served as a waterproof poncho or cloak until inflated, when it became a one-man boat. A special pocket held bellows for inflation, and a blade to turn a walking stick into a paddle. A special umbrella could double as a sail. Halkett later developed a two-man boat carried in a knapsack. When inflated, it could carry two men paddling on either side, and when deflated it served as a waterproof blanket for camping on wet ground. The Admiralty was sceptical about potential uses for Halkett's designs; on 8 May 1845, Lord Herbert, First Secretary to the Admiralty, wrote to Halkett that "My Lords are of an opinion that your invention is extremely clever and ingenious, and that it might be useful in Exploring and Surveying Expeditions, but they do not consider that it would be made applicable for general purposes in the Naval Service".
The Admiralty saw no use for Halkett's designs in general naval service, but explorers liked this larger design. John Franklin bought one for the ill-fated 1845 expedition, in which the entire expedition party of 129 men and two ships vanished.
In his explorations along the
In 1844–1845, British naval officer Lieutenant Peter Halkett developed two types of inflatable boats intended for use by Arctic explorers. Both were made of rubber-impregnated " Mackintosh cloth." In the Halkett boat, the "boat cloak" served as a waterproof poncho or cloak until inflated, when it became a one-man boat. A special pocket held bellows for inflation, and a blade to turn a walking stick into a paddle. A special umbrella could double as a sail. Halkett later developed a two-man boat carried in a knapsack. When inflated, it could carry two men paddling on either side, and when deflated it served as a waterproof blanket for camping on wet ground. The Admiralty was sceptical about potential uses for Halkett's designs; on 8 May 1845, Lord Herbert, First Secretary to the Admiralty, wrote to Halkett that "My Lords are of an opinion that your invention is extremely clever and ingenious, and that it might be useful in Exploring and Surveying Expeditions, but they do not consider that it would be made applicable for general purposes in the Naval Service".
The Admiralty saw no use for Halkett's designs in general naval service, but explorers liked this larger design. John Franklin bought one for the ill-fated 1845 expedition, in which the entire expedition party of 129 men and two ships vanished.
In his explorations along the  In 1866, four men crossed the Atlantic Ocean from New York to Britain on a three-tube raft called ''Nonpareil''.
From 1900 to 1910, the development of rubber manufacturing enabled attempts at producing circular rubber inflatable boats, similar to modern coracles. These were only usable as rafts, and could only be propelled by paddling. In addition, they tended to crack at seams and folds due to the imperfect manufacturing process of the rubber.
In 1866, four men crossed the Atlantic Ocean from New York to Britain on a three-tube raft called ''Nonpareil''.
From 1900 to 1910, the development of rubber manufacturing enabled attempts at producing circular rubber inflatable boats, similar to modern coracles. These were only usable as rafts, and could only be propelled by paddling. In addition, they tended to crack at seams and folds due to the imperfect manufacturing process of the rubber.
 Inflatable liferafts were also used successfully to save crews of aircraft that ditched in the sea; bombing, naval and anti-submarine aircraft flying long distances over water being much more common from the start of WWII. In the 1950s, the French Navy officer and biologist Alain Bombard was the first to combine the outboard engine, a rigid floor and a boat shaped inflatable. The former
Inflatable liferafts were also used successfully to save crews of aircraft that ditched in the sea; bombing, naval and anti-submarine aircraft flying long distances over water being much more common from the start of WWII. In the 1950s, the French Navy officer and biologist Alain Bombard was the first to combine the outboard engine, a rigid floor and a boat shaped inflatable. The former
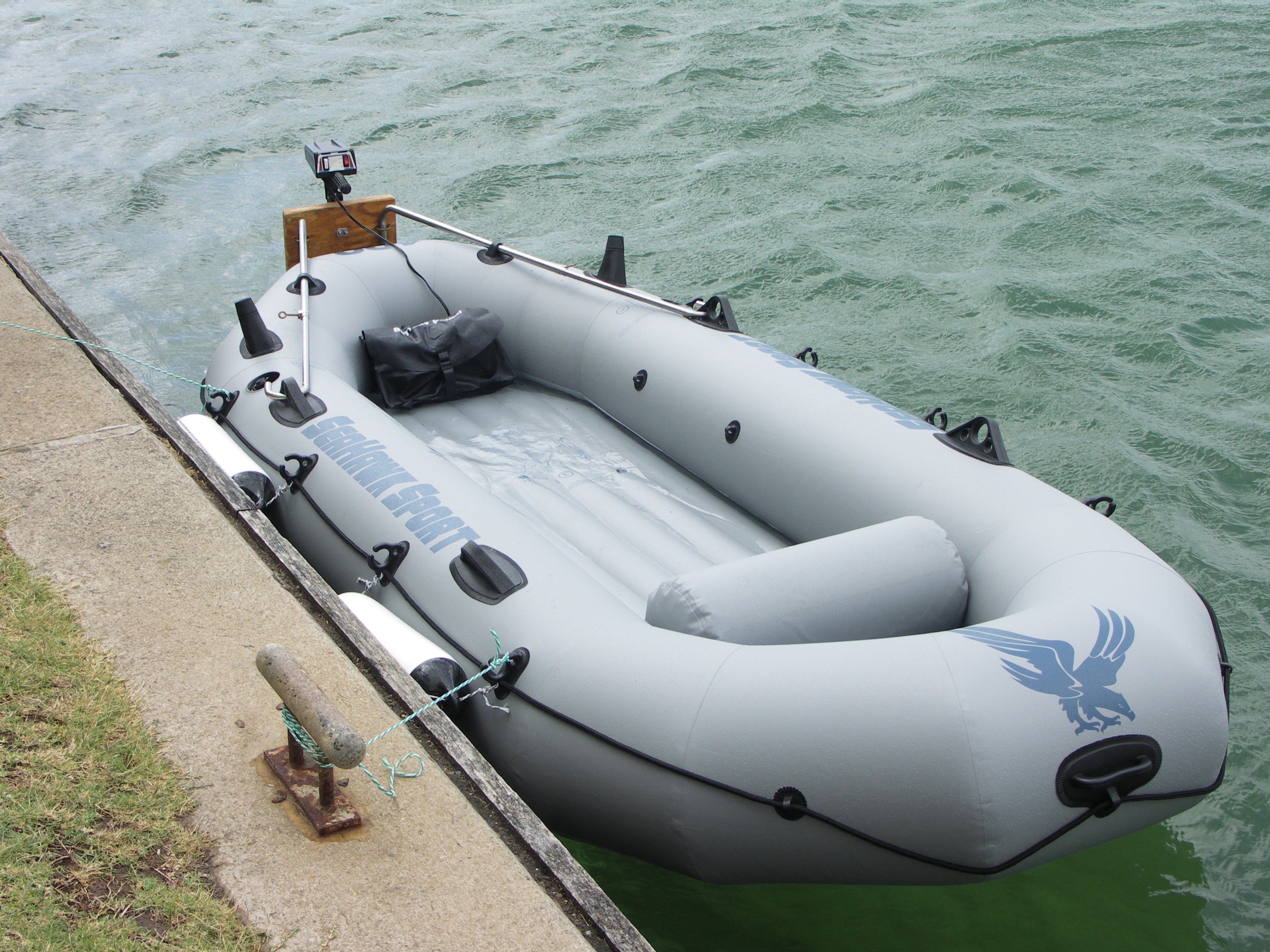 Contemporary inflatable boats are manufactured using supported fabric. They are made of rubberized synthetic fabrics, PVC and
Contemporary inflatable boats are manufactured using supported fabric. They are made of rubberized synthetic fabrics, PVC and
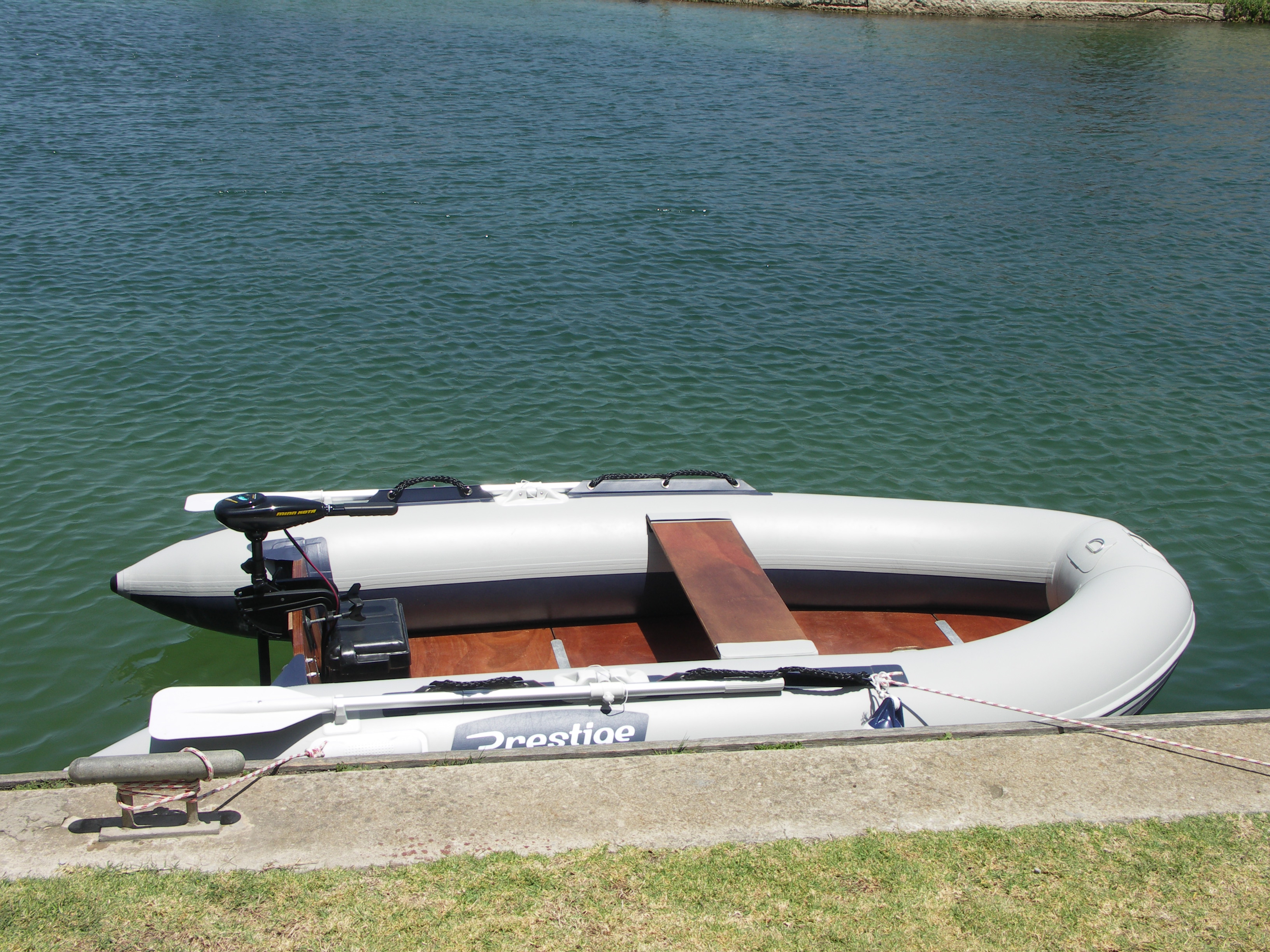
 The modern rigid inflatable boat (RIB) is a development of the inflatable boat, which has a rigid floor and solid hull. The external shape of the hull lets it cut through waves more easily giving a more comfortable ride when traveling fast in rough conditions. The structure of the hull is capable of supporting a more powerful transom mounted outboard engine or even an inboard engine.
The modern rigid inflatable boat (RIB) is a development of the inflatable boat, which has a rigid floor and solid hull. The external shape of the hull lets it cut through waves more easily giving a more comfortable ride when traveling fast in rough conditions. The structure of the hull is capable of supporting a more powerful transom mounted outboard engine or even an inboard engine.
 Inflatables are commonly between long and are propelled by outboard motors of . Due to their speed, portability, and weight, inflatable boats are used in diverse roles:
Inflatable and rigid-hulled inflatable boats are often used for short
Inflatables are commonly between long and are propelled by outboard motors of . Due to their speed, portability, and weight, inflatable boats are used in diverse roles:
Inflatable and rigid-hulled inflatable boats are often used for short
 An inflatable boat can be transported in various ways:
Deflated and Packed: The most significant advantage of inflatable boats is their ability to be deflated, folded, and packed into a compact size. Once deflated, they can be stored in a carry bag and transported in the trunk of a car or the bed of a truck.
On a Trailer: If the inflatable boat is larger or if it has a hard bottom (like a
An inflatable boat can be transported in various ways:
Deflated and Packed: The most significant advantage of inflatable boats is their ability to be deflated, folded, and packed into a compact size. Once deflated, they can be stored in a carry bag and transported in the trunk of a car or the bed of a truck.
On a Trailer: If the inflatable boat is larger or if it has a hard bottom (like a

boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size or capacity, its shape, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically used on inland waterways s ...
constructed with its sides and bow made of flexible tubes containing pressurised gas. For smaller boats, the floor and hull are often flexible, while for boats longer than , the floor typically consists of three to five rigid plywood or aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
sheets fixed between the tubes, but not joined rigidly together. Often the transom is rigid, providing a location and structure for mounting an outboard motor.
Some inflatable boats can be disassembled and packed into a small volume, so that they can be easily stored and transported. The boat, when inflated, is kept rigid cross-ways by a foldable removable thwart. This feature makes these boats suitable for liferafts for larger boats or aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, i ...
, and for travel or recreational purposes.
History
Early attempts

 There are ancient carved images of animal skins filled with air being used as one-man floats to cross rivers. These floats were inflated by mouth.
The discovery of the process to vulcanize rubber was made by Charles Goodyear in 1838, and was granted a US patent in 1844. Vulcanization stabilized the rubber, making it durable and flexible. In late 1843, Thomas Hancock filed for a UK patent, which was also granted in 1844, after the
There are ancient carved images of animal skins filled with air being used as one-man floats to cross rivers. These floats were inflated by mouth.
The discovery of the process to vulcanize rubber was made by Charles Goodyear in 1838, and was granted a US patent in 1844. Vulcanization stabilized the rubber, making it durable and flexible. In late 1843, Thomas Hancock filed for a UK patent, which was also granted in 1844, after the Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company
The Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company is an American multinational tire manufacturer headquartered in Akron, Ohio. Goodyear manufactures tires for passenger vehicles, aviation, commercial trucks, military and police vehicles, motorcycles, recreati ...
patent had been granted. In 1852, while traveling in England, Charles Goodyear discovered that Thomas Hancock's company was producing vulcanized rubber and sued. Thomas Hancock had been shown a sample of Goodyear's rubber in 1842, but had not been told the process that made it—and Hancock said he had developed his process independently. The last of the suits were settled in 1855. Shortly thereafter, several people expanded on experimentation of rubber coated fabrics.
In 1839 the Duke of Wellington tested the first inflatable pontoons. In 1840, the English scientist Thomas Hancock designed inflatable craft using his new methods of rubber vulcanization and described his achievements in ''The Origin and Progress of India Rubber Manufacture in England'' published a few years later.
 In 1844–1845, British naval officer Lieutenant Peter Halkett developed two types of inflatable boats intended for use by Arctic explorers. Both were made of rubber-impregnated " Mackintosh cloth." In the Halkett boat, the "boat cloak" served as a waterproof poncho or cloak until inflated, when it became a one-man boat. A special pocket held bellows for inflation, and a blade to turn a walking stick into a paddle. A special umbrella could double as a sail. Halkett later developed a two-man boat carried in a knapsack. When inflated, it could carry two men paddling on either side, and when deflated it served as a waterproof blanket for camping on wet ground. The Admiralty was sceptical about potential uses for Halkett's designs; on 8 May 1845, Lord Herbert, First Secretary to the Admiralty, wrote to Halkett that "My Lords are of an opinion that your invention is extremely clever and ingenious, and that it might be useful in Exploring and Surveying Expeditions, but they do not consider that it would be made applicable for general purposes in the Naval Service".
The Admiralty saw no use for Halkett's designs in general naval service, but explorers liked this larger design. John Franklin bought one for the ill-fated 1845 expedition, in which the entire expedition party of 129 men and two ships vanished.
In his explorations along the
In 1844–1845, British naval officer Lieutenant Peter Halkett developed two types of inflatable boats intended for use by Arctic explorers. Both were made of rubber-impregnated " Mackintosh cloth." In the Halkett boat, the "boat cloak" served as a waterproof poncho or cloak until inflated, when it became a one-man boat. A special pocket held bellows for inflation, and a blade to turn a walking stick into a paddle. A special umbrella could double as a sail. Halkett later developed a two-man boat carried in a knapsack. When inflated, it could carry two men paddling on either side, and when deflated it served as a waterproof blanket for camping on wet ground. The Admiralty was sceptical about potential uses for Halkett's designs; on 8 May 1845, Lord Herbert, First Secretary to the Admiralty, wrote to Halkett that "My Lords are of an opinion that your invention is extremely clever and ingenious, and that it might be useful in Exploring and Surveying Expeditions, but they do not consider that it would be made applicable for general purposes in the Naval Service".
The Admiralty saw no use for Halkett's designs in general naval service, but explorers liked this larger design. John Franklin bought one for the ill-fated 1845 expedition, in which the entire expedition party of 129 men and two ships vanished.
In his explorations along the Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and Westward Expansion Trails, emigrant trail in North America that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon Territory. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail crossed what ...
, and the tributaries and forks of the Platte River in 1842 and 1843, John C. Frémont recorded what may have been the first use of an inflatable rubber boat for travel down rivers and rapids in the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
. In his account of the expedition he described his boat:
Among the useful things which formed a portion of our equipage, was an India-rubber boat, 18 feet long, made somewhat in the form of a bark canoe of the northern lakes. The sides were formed by two airtight cylinders, eighteen inches in diameter, connected with others forming the bow and stern. To lessen the danger of accidents to the boat, these were divided into four different compartments, and the interior was sufficiently large to contain five or six persons, and a considerable weight of baggage.In 1848, General George Cullum, the US Army Corps of Engineers, introduced a rubber coated fabric inflatable bridge pontoon, which was used in the Mexican–American War and later on to a limited extent during the American Civil War.
 In 1866, four men crossed the Atlantic Ocean from New York to Britain on a three-tube raft called ''Nonpareil''.
From 1900 to 1910, the development of rubber manufacturing enabled attempts at producing circular rubber inflatable boats, similar to modern coracles. These were only usable as rafts, and could only be propelled by paddling. In addition, they tended to crack at seams and folds due to the imperfect manufacturing process of the rubber.
In 1866, four men crossed the Atlantic Ocean from New York to Britain on a three-tube raft called ''Nonpareil''.
From 1900 to 1910, the development of rubber manufacturing enabled attempts at producing circular rubber inflatable boats, similar to modern coracles. These were only usable as rafts, and could only be propelled by paddling. In addition, they tended to crack at seams and folds due to the imperfect manufacturing process of the rubber.
Modern inflatable boat
In the early 20th century, independent production of inflatable boats began with the airship manufacturing company RFD in England and the Zodiac company in France. This was brought about by the development of rubber-coated fabrics for theairship
An airship, dirigible balloon or dirigible is a type of aerostat (lighter-than-air) aircraft that can navigate through the air flying powered aircraft, under its own power. Aerostats use buoyancy from a lifting gas that is less dense than the ...
industry.
Reginald Foster Dagnall, English designer and founder of RFD, switched in 1919 to the development of inflatable boats, using the coated fabric from hydrogen airships. The Air Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force and civil aviation that existed from 1918 to 1964. It was under the political authority of the ...
was impressed with trials of his boat on a lake near Guildford
Guildford () is a town in west Surrey, England, around south-west of central London. As of the 2011 census, the town has a population of about 77,000 and is the seat of the wider Borough of Guildford, which had around inhabitants in . The nam ...
and began to give his firm contracts for the production of life-saving equipment.
Meanwhile, in France a similar pattern emerged. The airship company Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
began to develop inflatable rubber boats, and in 1934, invented the inflatable kayak
]
A kayak is a small, narrow human-powered watercraft typically propelled by means of a long, double-bladed paddle. The word ''kayak'' originates from the Inuktitut word '' qajaq'' (). In British English, the kayak is also considered to be ...
and catamaran
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hull (watercraft), hulls of equal size. The wide distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts stability through resistance to rolling and overturning; no ballast is requi ...
. These led to the modern Zodiac inflatable boat. The company became Zodiac Nautic in 2015.
Development continued after World War II with the discovery of new synthetic materials, such as neoprene and new adhesives, which allowed the boats to become sturdier and less prone to damage.
World War II
Submarine warfare in theBattle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allies of World War II, ...
led to casualties among warships and merchant ships. In the military, inflatable boats were used to transport torpedoes and other cargo. They also helped troops land in shallow water, and their compact size made overland transport possible. The US had two standard boats the LCRL and LCRS.
The Marine Raiders were originally trained to carry out raids and landings from Landing Craft Rubber Large (LCRL) inflatable boats carried by high speed transports. In August 1942 the submarines and carried elements of the 2nd Raider Battalion who carried out the Makin Island raid from LCRL inflatable boats. Invasions of the Battle of Arawe by the 112th Cavalry Regiment and parts of the Battle of Tarawa involved amphibious landings in inflatable boats against heavy enemy resistance.
One of the models, the Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
brand inflatable boat, became popular with the military, and contributed significantly to the rise of the civilian inflatable boat industry in Europe and in the United States. After World War II, governments sold surplus inflatable boats to the public.
Post-war inflatables
 Inflatable liferafts were also used successfully to save crews of aircraft that ditched in the sea; bombing, naval and anti-submarine aircraft flying long distances over water being much more common from the start of WWII. In the 1950s, the French Navy officer and biologist Alain Bombard was the first to combine the outboard engine, a rigid floor and a boat shaped inflatable. The former
Inflatable liferafts were also used successfully to save crews of aircraft that ditched in the sea; bombing, naval and anti-submarine aircraft flying long distances over water being much more common from the start of WWII. In the 1950s, the French Navy officer and biologist Alain Bombard was the first to combine the outboard engine, a rigid floor and a boat shaped inflatable. The former airplane
An airplane (American English), or aeroplane (Commonwealth English), informally plane, is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, Propeller (aircraft), propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a vari ...
-manufacturer Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
built that boat and a friend of Bombard, the diver Jacques-Yves Cousteau
Jacques-Yves Cousteau, (, also , ; 11 June 191025 June 1997) was a French naval officer, oceanographer, filmmaker and author. He co-invented the first successful open-circuit self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA), called the A ...
began to use it, after Bombard sailed across the Atlantic Ocean with his inflatable in 1952. Cousteau was convinced by the shallow draught and good performance of this type of boat and used it as tenders on his expeditions.
The inflatable boat was so successful that Zodiac lacked the manufacturing capacity to satisfy demand. In the early 1960s, Zodiac licensed production to a dozen companies in other countries. In the 1960s, the British company Humber was the first to build Zodiac brand inflatable boats in the United Kingdom.
Some inflatables have inflated keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element of a watercraft, important for stability. On some sailboats, it may have a fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose as well. The keel laying, laying of the keel is often ...
s whose V-shape help the hull move through waves reducing the slamming effect caused by the flat hull landing back on the water surface after passing over the top of a wave at speed.
Types
 Contemporary inflatable boats are manufactured using supported fabric. They are made of rubberized synthetic fabrics, PVC and
Contemporary inflatable boats are manufactured using supported fabric. They are made of rubberized synthetic fabrics, PVC and polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) is a class of polymers composed of organic chemistry, organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term ...
, providing light-weight and airtight sponsons. Depending on fabric choice, the fabric panels are assembled using either hot or cold manufacturing processes. Different styles of one-way valves are used to add or remove air, and some brands include inter-communicating valves that reduce the effect of a puncture.
Inflatable boats with transoms have an inflatable keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element of a watercraft, important for stability. On some sailboats, it may have a fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose as well. The keel laying, laying of the keel is often ...
that creates a slight V-bottom along the line of the hull to improve the hull's seakeeping
Seakeeping ability or seaworthiness is a measure of how well-suited a watercraft is to conditions when underway. A ship or boat which has good seakeeping ability is said to be very seaworthy and is able to operate effectively even in high sea stat ...
and directional stability. These vessels are very light, so if powered with an engine, it is best to put weight in the bow area to keep the bow from rising while the boat is going up on plane.
People increasingly use inflatables for personal recreational use on lakes, rivers, and oceans—and for white water rafting
Rafting and whitewater rafting are recreational outdoor activities which use an inflatable raft to navigate a river or other body of water. This is often done on whitewater or different degrees of rough water. Dealing with risk is often a ...
and kayaking
Kayaking is the use of a kayak for moving over water. It is distinguished from canoeing by the sitting position of the paddler and the number of blades on the paddle. A kayak is a low-to-the-water, canoe-like boat in which the paddler sits fac ...
, and for scuba divers to reach dive sites. Users can deflate, fold, and store fabric bottom inflatable boats in compact bags, making them ideal for limited storage and quick, easy access.
Sail rigs are available for inflatable dinghies, kayaks, and catamarans. In keeping with the portability of the inflatable hull, sail attachments fold or disassemble to fit in a compact bundle. Leeboard
A leeboard is a form of pivoting keel
used largely by sailboats, very often in lieu of a fixed keel. Typically mounted in pairs on each side of a hull, leeboards function much like a centreboard, allowing shallow-draft craft to ply waters ...
s on the sides perform the same function as a centerboard, so users can tack these boats into the wind.
Rigid inflatable boat
Soft inflatable boat
A soft inflatable boat (SIB) lacks the solid hull of a RIB and often has a removable slatted floor, so the boat can be deflated and transported in a car or other vehicle. Such boats have a lowdraft
Draft, the draft, or draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a v ...
and are therefore useful for traveling across shallow water and beaching in places without landing facilities.
Some SIBs have a rigid transom that can support an outboard engine. Inflatable boats with transoms have an inflatable keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element of a watercraft, important for stability. On some sailboats, it may have a fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose as well. The keel laying, laying of the keel is often ...
that creates a slight V-bottom along the line of the hull to improve the hull's seakeeping
Seakeeping ability or seaworthiness is a measure of how well-suited a watercraft is to conditions when underway. A ship or boat which has good seakeeping ability is said to be very seaworthy and is able to operate effectively even in high sea stat ...
and directional stability. These vessels are very light, so if powered with an engine, it is best to put weight in the bow area to keep the bow from rising while the boat is going up on plane.
Soft inflatable boats are available with several floor choices:
* Roll up slat floor
* Hard floor made of fiberglass, aluminum or wood panels
* Ribbed air floor (on inflatable rafts)
* High pressure air floor
Uses
scuba diving
Scuba diving is a Diving mode, mode of underwater diving whereby divers use Scuba set, breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface breathing gas supply, and therefore has a limited but variable endurance. The word ''scub ...
excursions.
The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea publishes recommended regulations for inflatable boats used in rescue operations. Some life rafts also contain additional inflatable sections to ensure that the raft self-rights in heavy seas.
Inflatable life rafts have also been used since the 1930s on military aircraft that operate over water.
These boats are often used by special-operations units of the armed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a ...
of several nations, for such purposes as landing on beaches
A beach is a landform alongside a body of water which consists of loose particles. The particles composing a beach are typically made from Rock (geology), rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle beach, shingle, pebbles, etc., or biological s ...
. Because inflatable craft can be stored compactly they can also be transported on midget submarine
A midget submarine is any submarine under 150 tons, typically operated by a crew of one or two but sometimes up to six or nine, with little or no on-board living accommodation. They normally work with mother ships, from which they are launched an ...
s such as those operated by the Advanced SEAL Delivery System. They have also been used by other forces without government sponsorship, such as guerrillas and pirates.
Lifeguard
A lifeguard is a rescuer who supervises the safety and rescue of swimmers, surfers, and other water sports participants such as in a swimming pool, water park, beach, spa, river and lake. Lifeguards are trained in swimming and Cardiopulmonary ...
s use inflatable boats or jet skis to reduce the time to reach a swimmer in distress. Inflatables are also used in conjunction with larger rescue craft, such as the Y class lifeboat used with the Tamar and Severn class lifeboats.
They are used in a number of sporting events and for recreational purposes, such as whitewater rafting, inflatable rescue boat racing, water skiing and fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
.
Transportation
 An inflatable boat can be transported in various ways:
Deflated and Packed: The most significant advantage of inflatable boats is their ability to be deflated, folded, and packed into a compact size. Once deflated, they can be stored in a carry bag and transported in the trunk of a car or the bed of a truck.
On a Trailer: If the inflatable boat is larger or if it has a hard bottom (like a
An inflatable boat can be transported in various ways:
Deflated and Packed: The most significant advantage of inflatable boats is their ability to be deflated, folded, and packed into a compact size. Once deflated, they can be stored in a carry bag and transported in the trunk of a car or the bed of a truck.
On a Trailer: If the inflatable boat is larger or if it has a hard bottom (like a RIB
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs () are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ...
), it might be more convenient to transport it on a trailer. This is especially useful if the boat has an outboard motor attached.
On Roof Racks: Some individuals use roof racks on their vehicles
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velomobiles), animal-powered tr ...
to transport inflatable boats. The boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size or capacity, its shape, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically used on inland waterways s ...
is either deflated and packed or partially inflated and secured on top of the car.
Using a Boat Dolly: For short distances, like moving the boat from a parking area to the water’s edge, a boat dolly or hand cart can be useful. These are especially handy for heavier inflatables or those with motors.
See also
* Inflatable kayaks *List of inflatable manufactured goods
This is a non-comprehensive list of inflatable manufactured goods, as no such list could ever completely contain all items that regularly change. An inflatable is an object that can typically be inflated with a gas, including air, hydrogen, heliu ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Inflatable Boat Inflatable boats Lifeboats Military boats Inflatable manufactured goods