Inferior Meatus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
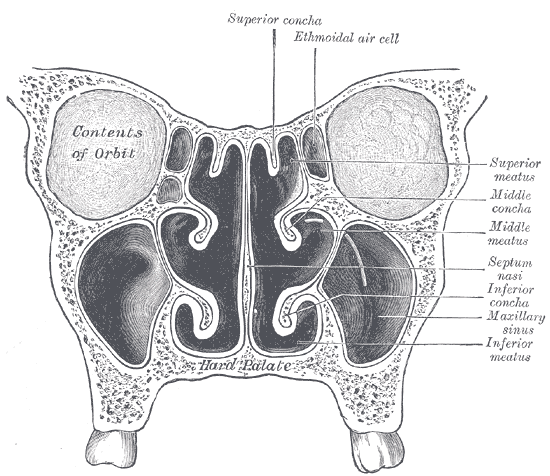 The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior
The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior
anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatus
In anatomy, a meatus (, , : meatus or meatuses)Entry "meatus" in Merriam-Webster Onlin ...
es (passages) through the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
s nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nas ...
: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferior'').
The nasal meatuses are the spaces beneath each of the corresponding nasal conchae. In the case where a fourth, supreme nasal concha is present, there is a fourth supreme nasal meatus.
Structure
 The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior
The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cell
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinuses entail a number of small ...
s. Above and at the back of the superior concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess which the sphenoidal sinus
The sphenoid sinus is a paired paranasal sinus in the Body of sphenoid bone, body of the sphenoid bone. It is one pair of the four paired paranasal sinuses.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 64 T ...
opens into. The superior meatus occupies the middle third of the nasal cavity’s lateral wall.
The middle meatus is the middle-sized and located nasal opening, lying underneath the middle concha and above the inferior concha where the meatus extends along its length. On it is a curved fissure, the hiatus semilunaris
The semilunar hiatus (eg, hiatus semilunaris) is a crescent-shaped/semicircular/ curved slit/groove upon the lateral wall of the nasal cavity at the middle nasal meatus just inferior to the ethmoidal bulla. It is the location of the openings for ...
, limited below by the edge of the uncinate process of the ethmoid
In the ethmoid bone, a sickle shaped projection, the uncinate process, projects posteroinferiorly from the ethmoid labyrinth.
Between the posterior edge of this process and the anterior surface of the ethmoid bulla, there is a two-dimensional sp ...
and above by an elevation named the bulla ethmoidalis
The ethmoid bulla (or ethmoidal bulla) is a rounded elevation upon the lateral wall of the middle nasal meatus (nasal cavity inferior to the middle nasal concha) produced by one or more of the underlying middle ethmoidal air cells (which open i ...
; the middle ethmoidal cells
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinuses entail a number of smal ...
are contained within this bulla and open on or near to it.
Through the hiatus semilunaris the meatus communicates with a curved passage termed the infundibulum An infundibulum (Latin for ''funnel''; plural, ''infundibula'') is a funnel-shaped cavity or organ.
Anatomy
* Brain: the pituitary stalk, also known as the ''infundibulum'' and ''infundibular stalk'', is the connection between the hypothalamus an ...
, which communicates in front with the anterior ethmoidal cells and in rather more than fifty percent of skulls is continued upward as the frontonasal duct into the frontal air-sinus; when this continuity fails, the frontonasal duct opens directly into the anterior part of the meatus.
Below the bulla ethmoidalis and hidden by the uncinate process of the ethmoid is the opening of the maxillary sinus
The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus (or antrum of Nathaniel Highmore (surgeon), Highmore) is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, located in the maxilla. It drains into the middle meatus of the noseHuman Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 209- ...
(ostium maxillare); an accessory opening is frequently present above the posterior part of the inferior nasal concha.
The inferior meatus is the largest of the three. It lies below the inferior concha and above the nasal cavity. It extends most of the length of the nasal cavity’s lateral wall. It is broader in the front than at the back, and presents anteriorly the lower orifice of the nasolacrimal canal
The nasolacrimal duct (also called the tear duct) carries tears from the lacrimal sac of the eye into the nasal cavity. The duct begins in the eye socket between the maxillary and lacrimal bones, from where it passes downwards and backwards. The o ...
.
References
External links
* * — Coronal section {{Authority controlmeatus
In anatomy, a meatus (, , : meatus or meatuses)Entry "meatus" in Merriam-Webster Onlin ...
Otorhinolaryngology