Industrial America on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Manufacturing jobs helped build out the U.S. middle class following
Manufacturing jobs helped build out the U.S. middle class following
 Between 1980 and 1985, U.S. manufacturing was impacted negatively as Japanese productivity rose at a rapid rate, leading to a fall of 12% in Japanese products, and the increase in U.S. interest rates that led to the appreciation of the U.S. dollar. This was the opposite policy from that which a rise in Japanese productivity would have dictated, and the US policy action made Japanese products 30% cheaper than American until 1986. The US machine tool sector never recovered from this body blow. Between 1983 and 2005, U.S. exports grew by 340%, with exports of manufactured goods increasing by 407% over this period.
In 1983, the primary export commodities of the U.S. was transportation equipment, computer and electronic products, agricultural products, machinery (except electrical), chemicals, and food and kindred products. Together these commodities totaled 69 percent of total U.S. exports. By 2005, the primary export commodities were largely the same: computer and electronic products, transportation equipment, chemicals, machinery (except electrical), miscellaneous manufactured commodities, and agricultural products. Together these commodities accounted for 69 percent of total U.S. merchandise exports.
Between 1983 and 2005, exports of computer and electronic products grew by 493%, overtaking transportation as the leading export commodity, which grew by 410%. Though agricultural products exports grew by 26% during this period, its share of overall merchandise exports fell from 12% in 1983 to 4% in 2005.
In 1983, the top trading partners for U.S. exports were
Between 1980 and 1985, U.S. manufacturing was impacted negatively as Japanese productivity rose at a rapid rate, leading to a fall of 12% in Japanese products, and the increase in U.S. interest rates that led to the appreciation of the U.S. dollar. This was the opposite policy from that which a rise in Japanese productivity would have dictated, and the US policy action made Japanese products 30% cheaper than American until 1986. The US machine tool sector never recovered from this body blow. Between 1983 and 2005, U.S. exports grew by 340%, with exports of manufactured goods increasing by 407% over this period.
In 1983, the primary export commodities of the U.S. was transportation equipment, computer and electronic products, agricultural products, machinery (except electrical), chemicals, and food and kindred products. Together these commodities totaled 69 percent of total U.S. exports. By 2005, the primary export commodities were largely the same: computer and electronic products, transportation equipment, chemicals, machinery (except electrical), miscellaneous manufactured commodities, and agricultural products. Together these commodities accounted for 69 percent of total U.S. merchandise exports.
Between 1983 and 2005, exports of computer and electronic products grew by 493%, overtaking transportation as the leading export commodity, which grew by 410%. Though agricultural products exports grew by 26% during this period, its share of overall merchandise exports fell from 12% in 1983 to 4% in 2005.
In 1983, the top trading partners for U.S. exports were
 The
The
Manufacturing Sector Council
2018. * U.S. Chamber of Commerce * Working: People Talk About What They Do All Day and How They Feel About What They Do – American workers on their jobs in the 1970s *
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
is a vital economic sector
One classical breakdown of economic activity distinguishes three sectors:
* Primary: involves the retrieval and production of raw materials, such as corn, coal, wood or iron. Miners, farmers and fishermen are all workers in the primary sect ...
in the United States of America
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguo ...
. The United States is the world's second-largest manufacturer after the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
with a record high real output in 2021 of $2.5 trillion.
As of December 2016, the U.S. manufacturing industry employed 12.35 million people. A year later, in December 2017, U.S. manufacturing employment grew by 207,000, or 1.7%, employees. Though still a large part of the US economy, in Q1 2018 manufacturing contributed less to GDP than the 'Finance, insurance, real estate, rental, and leasing' sector, the 'Government' sector, or 'Professional and business services' sector.
Manufacturing output recovered from the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of market decline in economies around the world that occurred from late 2007 to mid-2009.
, reaching an all-time high in 2021, but manufacturing employment has been declining since the 1990s, giving rise to what is known as a "jobless recovery," which made job creation or preservation in the manufacturing sector an important topic in the 2016 United States presidential election
United States presidential election, Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 8, 2016. The Republican Party (United States), Republican ticket of businessman Donald Trump and Indiana Governor, Indiana governor Mike P ...
.
Employment
 Manufacturing jobs helped build out the U.S. middle class following
Manufacturing jobs helped build out the U.S. middle class following World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, as the U.S. established pro-labor policies and faced limited global competition. Between 1980 and 1985, and then again 2001 to 2009, there were precipitous declines in US manufacturing jobs; it is estimated that 1/3 of U.S. manufacturing jobs vanished in the eight years between 2001 and 2009, and few have returned, the worst period for U.S. manufacturing since the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
.
Since 1979, the number of U.S. manufacturing employment has been declining, especially the sharp decline in 2001 and 2007. The way in which employment in the U.S. manufacturing industry has fallen provides a series of potential policy responses including insights into how the industry is changing, and unemployment.
There are several possible explanations for the decline. Bill Lazonick argues that legalization of companies buying their own shares of stock in 1982 has led to sustained stock market bubbles that distorted investment away from physical plant. Others point to automation or developments outside the United States, such as the rise of China, globalized free trade, and supply chain innovation. These have arguably resulted in the off-shoring of thousands of U.S. manufacturing facilities and millions of manufacturing jobs to lower-wage countries. Meanwhile, technological innovation has increased productivity significantly, meaning that manufacturing output in the United States has increased by 80% since the 1980s, despite large job losses in the manufacturing sector during that same period.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the government of the United States, U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics, labor economics and ...
(BLS) forecast in October 2017 that manufacturing employment would fall from 12.3 million in 2016 to 11.6 million in 2026, a decline of 736,000 employees over a decade. As a share of employment, manufacturing was estimated to fall from 7.9% of the total U.S. economy in 2016 to 6.9% of it in 2026, continuing a long-term downward trend.
The U.S. manufacturing industry employed 12.4 million people in March 2017, generating output (nominal GDP) of $2.2 trillion in Q3 2016, with real GDP of $1.9 trillion in 2009 dollars. The share of persons employed in manufacturing relative to total employment has steadily declined since the 1960s. Employment growth in industries such as construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
, finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Admin ...
, insurance
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to protect ...
and real estate, and services industries played a significant role in reducing manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
's overall share of U.S. employment. In 1990, services surpassed manufacturing as the largest contributor to overall private industry production, and then the finance, insurance and real estate sector surpassed manufacturing in 1991.
Since the entry of China into the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland that regulates and facilitates international trade. Governments use the organization to establish, revise, and enforce the rules that g ...
in December 2001, the decline in manufacturing jobs has accelerated. The U.S. goods trade deficit (imports greater than exports) with China was approximately $350 billion in 2016. However it is possible that the import of goods from China is a result rather than a cause. The US stock market also ended a sustained fourteen year bubble in 2001, and the ensuing job loss pushed a significant portion of US population below the poverty line.
''The Economist'' reported in January 2017 that manufacturing historically created good paying jobs for workers without a college education, particularly for men. The jobs paid well enough so that women did not have to work when they had young children. Unions were strong and owners did not want to risk strikes in their factories due to large capital investments and significant on the job training. Such jobs are much less available in the post-2001 era in the U.S. though they remain available in Germany, Switzerland and Japan, leading to calls to bring those jobs back from overseas, establish protectionism, and reduce immigration. Making it illegal for companies to purchase shares of their own stock has not yet gained traction as a remedy for the diversion of operating profits away from reinvestment in equipment and people. Manufacturing continues to evolve, due to factors such as information technology, supply chain innovations such as containerization
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers (also called shipping containers, or International Organization for Standardization, ISO containers). Containerization, also referred as container stuf ...
, companies un-bundling tasks that used to be in one location or business, reduced barriers to trade, and competition from low-cost developing countries such as China and Mexico. Competition from high wage nations such as Germany is also increasing.
History
 Between 1980 and 1985, U.S. manufacturing was impacted negatively as Japanese productivity rose at a rapid rate, leading to a fall of 12% in Japanese products, and the increase in U.S. interest rates that led to the appreciation of the U.S. dollar. This was the opposite policy from that which a rise in Japanese productivity would have dictated, and the US policy action made Japanese products 30% cheaper than American until 1986. The US machine tool sector never recovered from this body blow. Between 1983 and 2005, U.S. exports grew by 340%, with exports of manufactured goods increasing by 407% over this period.
In 1983, the primary export commodities of the U.S. was transportation equipment, computer and electronic products, agricultural products, machinery (except electrical), chemicals, and food and kindred products. Together these commodities totaled 69 percent of total U.S. exports. By 2005, the primary export commodities were largely the same: computer and electronic products, transportation equipment, chemicals, machinery (except electrical), miscellaneous manufactured commodities, and agricultural products. Together these commodities accounted for 69 percent of total U.S. merchandise exports.
Between 1983 and 2005, exports of computer and electronic products grew by 493%, overtaking transportation as the leading export commodity, which grew by 410%. Though agricultural products exports grew by 26% during this period, its share of overall merchandise exports fell from 12% in 1983 to 4% in 2005.
In 1983, the top trading partners for U.S. exports were
Between 1980 and 1985, U.S. manufacturing was impacted negatively as Japanese productivity rose at a rapid rate, leading to a fall of 12% in Japanese products, and the increase in U.S. interest rates that led to the appreciation of the U.S. dollar. This was the opposite policy from that which a rise in Japanese productivity would have dictated, and the US policy action made Japanese products 30% cheaper than American until 1986. The US machine tool sector never recovered from this body blow. Between 1983 and 2005, U.S. exports grew by 340%, with exports of manufactured goods increasing by 407% over this period.
In 1983, the primary export commodities of the U.S. was transportation equipment, computer and electronic products, agricultural products, machinery (except electrical), chemicals, and food and kindred products. Together these commodities totaled 69 percent of total U.S. exports. By 2005, the primary export commodities were largely the same: computer and electronic products, transportation equipment, chemicals, machinery (except electrical), miscellaneous manufactured commodities, and agricultural products. Together these commodities accounted for 69 percent of total U.S. merchandise exports.
Between 1983 and 2005, exports of computer and electronic products grew by 493%, overtaking transportation as the leading export commodity, which grew by 410%. Though agricultural products exports grew by 26% during this period, its share of overall merchandise exports fell from 12% in 1983 to 4% in 2005.
In 1983, the top trading partners for U.S. exports were Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
(21% of total merchandise exports), Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
(11%), United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
(5%), Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
(4%), Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
(4%), the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
(4%), Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
(3%), France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
(3%), South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
(3%), and Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
and Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
(2%).
In 2005, the top markets for U.S. exports were Canada (24%), Mexico (13%), Japan (6%), China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
(5%), United Kingdom (4%), Germany (4%), South Korea (3%), the Netherlands (3%), France (2%), and Taiwan (2%). Between 1983 and 2005, exports to Mexico increased by 1,228%, allowing it to replace Japan as the second-largest market for U.S. exports.
In the first quarter of 2010, overall U.S. merchandise exports increased by 20 percent compared to the first quarter of 2009, with manufactured goods exports increasing by 20 percent. As in 2009, the highest export commodities were transportation equipment, computer and electronic products, chemicals, machinery (except electrical), agricultural products, and miscellaneous manufactured commodities.
In the first quarter of 2010, the primary markets for U.S. merchandise exports were Canada, Mexico, China, Japan, the United Kingdom, Germany, South Korea, Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, the Netherlands, and Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
. With the exception of the Netherlands, exports to all of these countries increased in the first quarter of 2010, compared to the same quarter in 2009. Notably, exports to Canada increased by 22 percent, Mexico by 28 percent, and China by 47 percent over this period. Exports to the two NAFTA
The North American Free Trade Agreement (, TLCAN; , ALÉNA), referred to colloquially in the Anglosphere as NAFTA, ( ) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that created a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The ...
partners accounted for nearly one-third (32%) of U.S. merchandise trade in the first quarter of 2010.
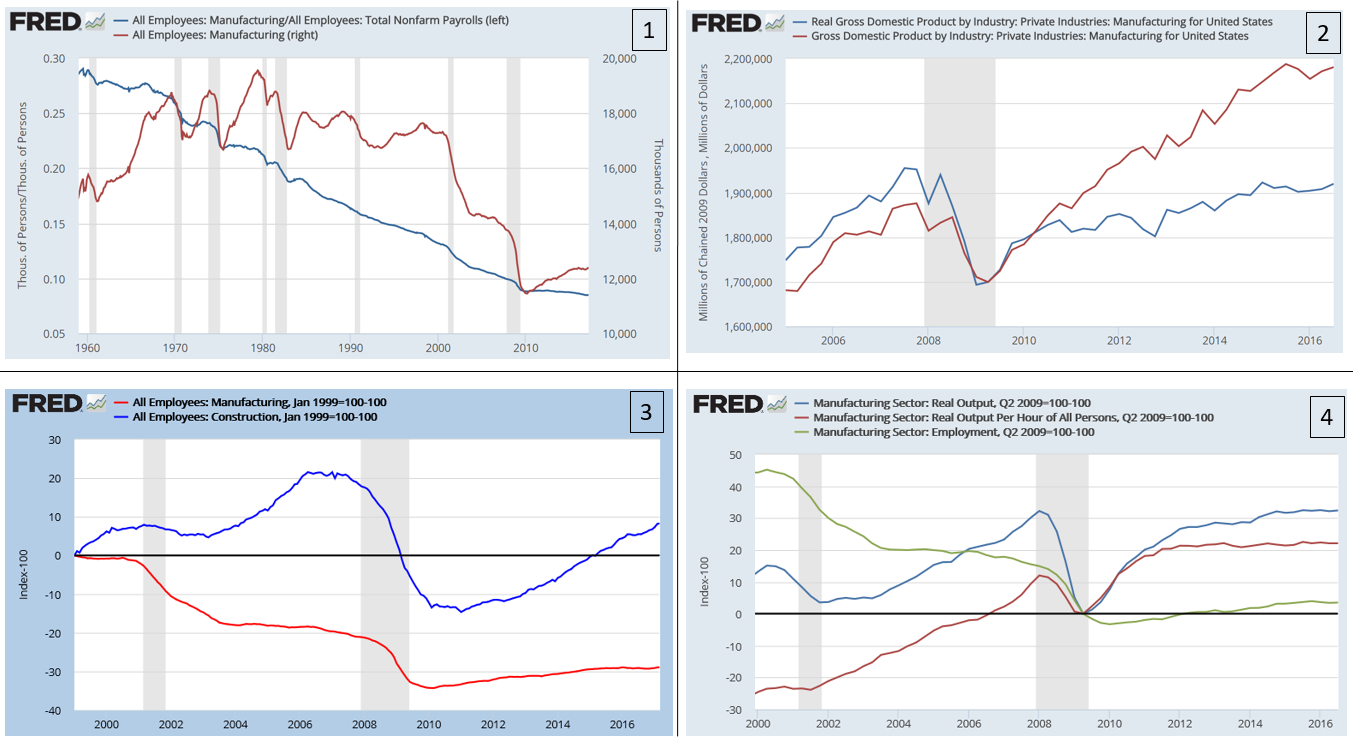
The panel chart in this section includes four diagrams describing manufacturing labor, output, and productivity historical trends through 2016:
*Figure 1-Job measures: The blue line (left axis) is the ratio of manufacturing jobs to the total number of non-farm payroll jobs. It has declined since the 1960s as manufacturing jobs fell and services expanded. The red line (right axis) is the number of manufacturing jobs (000s), which had fallen by nearly one-third since the late 1990s.
*Figure 2-Output measures: Real (inflation adjusted) GDP (blue line) and nominal GDP (red line) from the manufacturing sector. While both rose from the trough due to the Great Recession, the real GDP had yet to regain its pre-crisis (2007) level as of 2016.
*Figure 3-Job measures, indexed: The red line shows the percent change in manufacturing jobs, measured relative to the 1999 as the starting point. The blue line shows construction jobs. Both were below pre-crisis levels in 2016.
*Figure 4-Productivity measures, indexed: Measured from the end of the recession (June 2009), employment (green line) is up about 5%, but real output is up over 30%, indicating a significant gain in productivity (i.e., output per labor hour).
Forecast
 The
The Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the government of the United States, U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics, labor economics and ...
projected in October 2017 that:
*10.5 of the 11.5 million net jobs created (90%) over the 2016–2026 period would be in services. The service jobs growth rate would be about 0.8%. However, the goods producing sector, which includes manufacturing, would only add 219,000 jobs over that period, growing at a rate of 0.1%.
*Manufacturing employment would fall from 12.3 million in 2016 to 11.6 million in 2026, a decline of 736,000. As a share of employment, manufacturing would fall from 7.9% in 2016 to 6.9% in 2026.
*Employment in production occupations (a subset of manufacturing) was expected to fall from 9.4 million in 2016 to 9.0 million in 2026 (a 4% decline), falling from 6.0% of employment to 5.4%.
*According to the Semiconductor Industries Association, by the end of 2022, the chip industry has committed almost $200 billion to build and expand 40 plants in 16 states, creating 40,000 future jobs. According to the Natural Resources Defense Council, a similar amount has been promised to US factories making electric cars and batteries.
Trade policy
U.S. manufacturing employment has declined steadily as a share of total employment, from around 28% in 1960 to 8% in March 2017. Manufacturing employment has fallen from 17.2 million persons in December 2000 to 12.4 million in March 2017, a decline of about 5.7 million or about one-third even as the U.S.population ballooned from 220 million to 330 million in the same time frame. An estimated 1–2 million of the job losses in manufacturing 1999–2011 were due to competition with China (the China shock), which entered theWorld Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland that regulates and facilitates international trade. Governments use the organization to establish, revise, and enforce the rules that g ...
in December 2001. The Economic Policy Institute
The Economic Policy Institute (EPI) is a 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) non-profit think tank based in Washington, D.C., that carries out economic research and analyzes the economic impact of policies and proposals. Affiliated with the Labor un ...
estimated that the trade deficit with China cost about 2.7 million jobs between 2001 and 2011, including manufacturing and other industries.
While U.S. manufacturing employment is down, output was near a record level in 2017 in real GDP terms, indicating productivity (output per worker) has also improved significantly. This is likely due to automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
, global supply chains, process improvements, and other technology changes.
Economist Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman ( ; born February 28, 1953) is an American New Keynesian economics, New Keynesian economist who is the Distinguished Professor of Economics at the CUNY Graduate Center, Graduate Center of the City University of New York. He ...
argued in December 2016 that "America's shift away from manufacturing doesn't have much to do with trade, and even less to do with trade policy." He also cited the work of other economists indicating that the declines in manufacturing employment from 1999 to 2011 due to trade policy generally and trade with China specifically were "less than a fifth of the absolute loss of manufacturing jobs over the period" but that the effects were significant for regions directly impacted by those losses.
The Biden administration's 2023 Trade Policy Agenda focused on strengthening domestic industries and minimizing reliance on foreign supply chains. The CHIPS and Science Act
The CHIPS and Science Act is a U.S. federal statute enacted by the 117th United States Congress and signed into law by President Joe Biden on August 9, 2022. The act authorizes roughly $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and ...
allocated nearly $53 billion to support semiconductor manufacturing in the U.S. The U.S. Department of Commerce proposed for 16 new semiconductor manufacturing facilities, which would shift the U.S. into a position of resiliency against foreign manufacturers.
Modern overview
TheUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
is the world's second largest manufacturer (after China) with a record high real output in Q1 2018 of $2.00 trillion (i.e., adjusted for inflation in 2009 Dollars) about one percent above the 2007 peak before the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of market decline in economies around the world that occurred from late 2007 to mid-2009.
of $1.95 trillion. The U.S. manufacturing industry employed 12.35 million people in December 2016 and 12.56 million in December 2017, an increase of 207,000 or 1.7%.
Historically, manufacturing has provided relatively well-paid blue-collar
A blue-collar worker is a person who performs manual labor or skilled trades. Blue-collar work may involve skilled or unskilled labor. The type of work may involve manufacturing, retail, warehousing, mining, carpentry, electrical work, custodia ...
jobs, although this has been affected by globalization and automation.
Manufacturing continues to evolve, due to factors such as information technology, supply chain innovations such as containerization
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers (also called shipping containers, or International Organization for Standardization, ISO containers). Containerization, also referred as container stuf ...
, companies un-bundling tasks that used to be in one location or business, reduced barriers to trade, and competition from low-cost developing countries such as China and Mexico.
Manufacturing is conducted among globally distributed supply chains, with various stages of production conducted in different countries. For example, automotive parts may be manufactured in the U.S., shipped to Mexico for assembly, then sent back to the U.S. In some cases, the components of the final product cross the border multiple times. An estimated 40% of the value of U.S. imports from Mexico is from content produced in the U.S.; this figure is 25% for Canada but only 4% for China. This "production sharing" is an indication of the integrated nature of the supply chains between the U.S., Mexico and Canada in the NAFTA region.
Trade balance
During 2016, the U.S. exported $1,051 billion in manufactured goods and imported $1,920 billion, a manufacturing goods deficit of $868 billion. The largest exports were transportation equipment ($252B), Chemicals ($174B), Computers and Electronic Products ($116B) and "Machinery-Except Electrical" ($109B).Industries
As of 2019, durable and nondurable goods manufacturing account for $3.1t and $3t of gross output of GDP, respectively. However, 2023 research from McKinsey states that GDP numbers don't accurately capture manufacturing's economic impact. In its findings, while manufacturing accounted for 11 percent of US GDP and 8 percent of direct employment, it drove 20 percent of capital investment, 30 percent of productivity growth, 60 percent of the country's exports, and garnered 70 percent of business research and development funding.International comparison
TheCongressional Research Service
The Congressional Research Service (CRS) is a public policy research institute of the United States Congress. Operating within the Library of Congress, it works primarily and directly for members of Congress and their committees and staff on a ...
reported in January 2017 that:
*"The United States' share of global manufacturing activity declined from 28% in 2002, following the end of the 2001 U.S. recession, to 16.5% in 2011. Since then, the U.S. share has risen to 18.6%, the largest share since 2009. These estimates are based on the value of each country's manufacturing in U.S. dollars; part of the decline in the U.S. share was due to a 23% decline in the value of the dollar between 2002 and 2011, and part of the rise since 2011 is attributable to a stronger dollar.
*China displaced the United States as the largest manufacturing country in 2010. Again, part of China's rise by this measure has been due to the appreciation of its currency, the renminbi, against the U.S. dollar. The reported size of China's manufacturing sector decreased slightly in 2015 due to currency adjustments.
*Manufacturing output, measured in each country's local currency adjusted for inflation, has been growing more slowly in the United States than in China, South Korea, Germany, and Mexico, but more rapidly than in most European countries and Canada.
*Employment in manufacturing has fallen in most major manufacturing countries over the past quarter-century. In the United States, manufacturing employment since 1990 has declined in line with the changes in Western Europe and Japan, although the timing of the decline has differed from country to country.
*U.S. manufacturers spend far more on research and development (R&D) than those in any other country, but manufacturers' R&D spending is rising more rapidly in several other countries.
*Manufacturers in many countries appear to be spending increasing amounts on R&D, relative to their value added. U.S. manufacturers spend approximately 11% of value added on R&D, an increase of more than three percentage points since 2002. A large proportion of U.S. manufacturers' R&D takes place in high technology sectors, such as pharmaceutical, electronics, and aircraft manufacturing, whereas in most other countries the largest share of R&D occurs in medium-technology sectors such as automotive and machinery manufacturing."
See also
*Economy of the United States
The United States has a highly developed mixed economy. It is the world's largest economy by nominal GDP and second largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). As of 2025, it has the world's seventh highest nominal GDP per capita and ninth ...
* National Network for Manufacturing Innovation
*National Occupational Research Agenda
The National Occupational Research Agenda (NORA) is a partnership program developed by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). The program was founded in 1996 to provide a framework for research collaborations among univ ...
Manufacturing Sector Council
2018. * U.S. Chamber of Commerce * Working: People Talk About What They Do All Day and How They Feel About What They Do – American workers on their jobs in the 1970s *
Made in USA
A Made in USA mark is a country of origin label affixed to American-made products that indicates the product is "all or virtually all" domestically produced, manufactured and assembled in the United States. The label is regulated by the Federal ...
Further reading
*References
{{North America topic , Manufacturing inManufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...