Induced Polarization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Induced polarization (IP) is a geophysical imaging technique used to identify the electrical chargeability of subsurface materials, such as ore.
The polarization effect was originally discovered by Conrad Schlumberger when measuring the resistivity of rock.
The survey method is similar to electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), in that an
Example IP equipment and image results Geophysical imaging
electric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
is transmitted into the subsurface through two electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
s, and voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
is monitored through two other electrodes.
Induced polarization is a geophysical method used extensively in mineral exploration and mining operations. Resistivity and IP methods are often applied on the ground surface using multiple four-electrode sites. In an IP survey (and when making resistivity measurements), capacitive properties of the subsurface materials are determined as well. As a result, IP surveys provide additional information about the spatial variation in lithology and grain-surface chemistry.
The IP survey can be made in time-domain and frequency-domain mode:
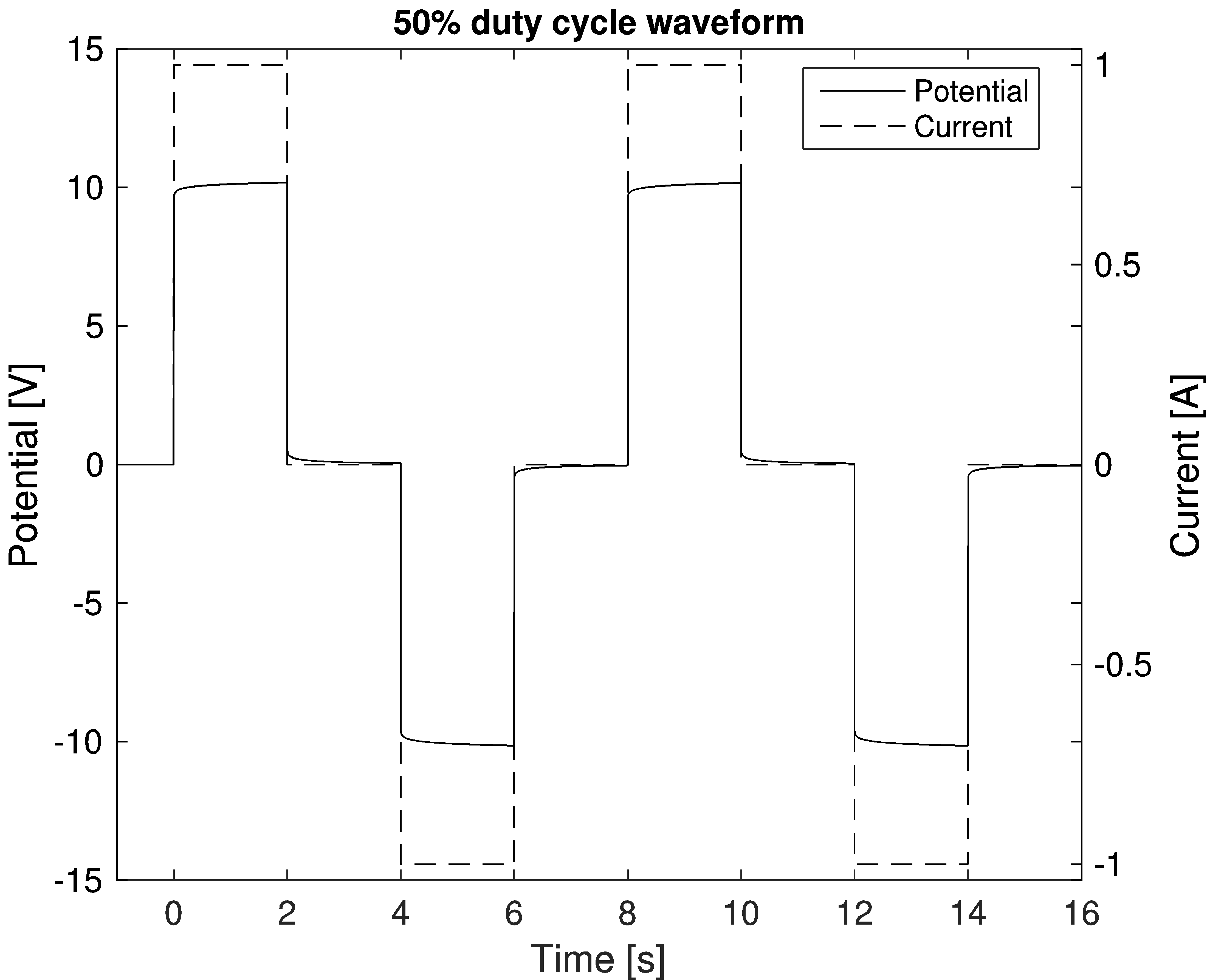
In the '' time-domain induced polarization'' method, the voltage response is observed as a function of time after the injected current is switched off or on.
In the '' frequency-domain induced polarization'' mode, an alternating current is injected into the ground with variable frequencies. Voltage phase-shifts are measured to evaluate the impedance spectrum at different injection frequencies — this is commonly referred to as spectral IP.
The IP method is one of the most widely used techniques in mineral exploration and in the mining industry. Additionally, IP has applications in hydrogeophysical surveying, environmental investigations and geotechnical engineering projects.
Measurement methods
Time domain

Time-domain
In mathematics and signal processing, the time domain is a representation of how a signal, function, or data set varies with time. It is used for the analysis of function (mathematics), mathematical functions, physical signal (information theory), ...
IP methods measure the resulting voltage following a change in the injected current. The time domain IP potential response can be evaluated by considering the mean value on the resulting voltage, known as integral
In mathematics, an integral is the continuous analog of a Summation, sum, which is used to calculate area, areas, volume, volumes, and their generalizations. Integration, the process of computing an integral, is one of the two fundamental oper ...
chargeability or by evaluating the spectral information and considering the shape of the potential response (i.e. describing the response with a Cole-Cole model).
Frequency domain
Frequency-domain IP methods usesalternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
s (AC) to induce electric charges in the subsurface, and the apparent resistivity is measured at different AC frequencies.
See also
* DC impedance spectroscopy * AC impedance spectroscopy * Electrical resistivity measurement of concrete * Geophysical imagingReferences
Further reading
* {{cite book , author-last1=Kearey , author-first1=Philip , author-first2=Michael , author-last2=Brooks , title=An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration , date=1991 , edition=2 , publisher= Blackwell Science , isbn=978-0-632-02923-5External links
Example IP equipment and image results Geophysical imaging