Indre By on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Indre By ( English: ), also known as Copenhagen Center or K or Downtown Copenhagen, is an administrative district (''bydel'') in central
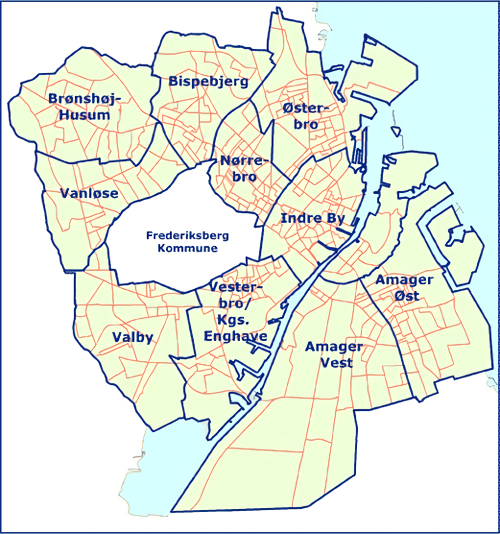 This district is the historic, geographic and political heart of present-day Copenhagen, and reflects the history of Denmark. Its boundaries pretty much reflect the entire cityãs extent during the reign of King Christian IV (1588-1648).
At the time it was a fortified city and its borders were made of
This district is the historic, geographic and political heart of present-day Copenhagen, and reflects the history of Denmark. Its boundaries pretty much reflect the entire cityãs extent during the reign of King Christian IV (1588-1648).
At the time it was a fortified city and its borders were made of
 * Amalienborg Palace
* Bû¡rsen, The Stock Exchange
* Christiansborg Palace located on
* Amalienborg Palace
* Bû¡rsen, The Stock Exchange
* Christiansborg Palace located on
City of Copenhagenãs statistical office
Photos from around Copenhagen City
{{Copenhagen Copenhagen city districts
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from MalmûÑ, Sweden, by the ...
, the capital of Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
. It covers an area of , has a population of 26,223, and a population density of 5,638 per km2.
Neighboring city districts are as follows:
* to the east and south east is Christianshavn, separated from the Inner City by the Inner Harbour (''Inderhavnen'') and Copenhagen Harbour (''Kû¡benhavns Havn'')
* to the north is Indre ûsterbro
* to the west is Indre Nû¡rrebro and Frederiksberg municipality, which is not a part of Copenhagen municipality but rather an enclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is so ...
surrounded by the municipality, with both being separated from the Indre By along the "lakes" (Skt. Jû¡rgens Lake, Peblinge Lake, and Sortedams Lake)
* to the southwest is Vesterbro
* to the south is Vestamager, separated from the Inner City by the South Harbour (''Sydhavnen'')
The Indre By district
 This district is the historic, geographic and political heart of present-day Copenhagen, and reflects the history of Denmark. Its boundaries pretty much reflect the entire cityãs extent during the reign of King Christian IV (1588-1648).
At the time it was a fortified city and its borders were made of
This district is the historic, geographic and political heart of present-day Copenhagen, and reflects the history of Denmark. Its boundaries pretty much reflect the entire cityãs extent during the reign of King Christian IV (1588-1648).
At the time it was a fortified city and its borders were made of defensive wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications such as curtain walls with t ...
s with moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch dug around a castle, fortification, building, or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. Moats can be dry or filled with water. In some places, moats evolved into more extensive water d ...
s. To ensure water for the moats there was a series of dams.
Entry and exit to the city was through the town's four gates: Vesterport (" Western Gate") near the current RûËdhuspladsen (''City Hall Square''), Nû¡rreport (" Northern Gate") near the current Nû¡rreport station
The fortifications of Copenhagen underwent a comprehensive modernization and expansion in the 17th century. The project was commenced and was largely the masterplan of Christian IV in the early 17th century but was continued and completed by his s ...
, ûsterport (" Eastern Gate") by the current ûsterport station, and Amagerport (" Amager Gate", i.e. functionally the Southern Gate) between Christianshavn and the island of Amager
Amager ( ), located in the ûresund, is Denmark's most densely populated island, with more than 216,000 inhabitants (January 2022). The protected natural area of ''Naturpark Amager'' (including Kalvebod FûÎlled) makes up more than one-third of the ...
. The gates were dismantled in 1856. The locations are now commemorated with milestone
A milestone is a numbered marker placed on a route such as a road, railway, railway line, canal or border, boundary. They can indicate the distance to towns, cities, and other places or landmarks like Mileage sign, mileage signs; or they c ...
s erected on the spot.
Additionally artificial lakes were constructed as part of Christian IV's large building project. These still exist to this day, and are simply referred to as the "lakes" (Skt. Jû¡rgens Lake, Peblinge Lake, and Sortedams Lake). The area beyond the lakes, now heavily populated city districts, was then used primarily for grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to free range (roam around) and consume wild vegetations in order to feed conversion ratio, convert the otherwise indigestible (by human diges ...
. It was prohibited to build beyond these original city limits so that the fortificationãs cannons could have clear shot and so that the enemy could not find any hiding areas. The line that marked this "no build" zone was called the Demarcation Line (''Demarkationslinien'') The line was moved further out as the shooting range of canons improved, and was not abolished until after the cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
epidemic of 1853.
The fortification system was sold to Copenhagen municipality in 1869 and largely dismantled the year after. Evidence of the walls can be found in the street names outlining the central part of the city. From Kastellet at the northeast point of the district runs ''ûster Voldgade'' ("Eastern Wall Street") to the southwest. The street changes names near Nû¡rreport Train Station and continues as ''Nû¡rre Voldgade'' ("Northern Wall Street"). ''Vester Voldgade'' ("Western Wall Street") starts at ûrsteds Park and runs southeast until it reaches the water of Copenhagen Harbour (''Kû¡benhavns Havn''). The fortification system continues on the other side of the water in the Christianshavn city district.
A ring of parks (''fûÎstningsringen'', English "fortification ring") has been erected outside where the walls once stood, and remnants of the bastion
A bastion is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the ...
s, ravelins and moats can be seen in ûstre AnlûÎg park, the Botanical Gardens, ûrsted Park and Tivoli Gardens.
In the central historic district of Copenhagen, eclectic architecture prevails.
This area features not only cultural landmarks but also numerous business premises, providing the opportunity to work and enjoy art simultaneously. Among such buildings are the neat and presentable building on Ny Kongensgade 15, built in 1880 by master carpenter P. Hansen and Bredgade 38 is a historic building built in 1801 by architect Andreas Gallander. Despite being carefully guarded, they still offer modern working spaces, allowing professionals to immerse themselves in a rich historical ambiance while conducting their daily business.
History
Copenhagen was founded around year 1000 by Sweyn I Forkbeard and his sonCanute the Great
Cnut ( ; ; ã 12 November 1035), also known as Canute and with the epithet the Great, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norway from 1028 until his death in 1035. The three kingdoms united under Cnut's rul ...
.
It was only a fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
village
A village is a human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban v ...
until the middle of the 12th century when ''Havn'' ("Harbour"), as the town was then called, assumed increasing importance in the Danish kingdom. Around 1160 King Waldemar the Great gave control of Copenhagen to Absalon, Bishop of Roskilde. Whereas other cities in the Danish realm were under the governance of the king, Havn or ''Kû¡bmannehavn'' (Merchants' Harbour) as it comes to be known, was given to the Bishop of Roskilde. Bishop Absalon built his fortified "Castle at Havn" in 1167 on a little island outside the harbour itself, the remains of which can still be seen under present day Christiansborg Palace. The castle stood 200 years.
The Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
erected cathedrals in Roskilde
Roskilde ( , ) is a city west of Copenhagen on the Danish island of Zealand. With a population of 53,354 (), the city is a business and educational centre for the region and the 10th largest city in Denmark. It is governed by the administrative ...
(Roskilde Cathedral
Roskilde Cathedral (), in the city of Roskilde on the island of Zealand (Denmark), Zealand (''SjûÎlland'') in eastern Denmark, is a cathedral of the Lutheranism, Lutheran Church of Denmark.
The cathedral is one of the most important churches in D ...
) and in Lund
Lund (, ;"Lund"
(US) and ) is a city in the provinces of Sweden, province of Scania, southern Swed ...
( Lund Cathedral), in what is now (US) and ) is a city in the provinces of Sweden, province of Scania, southern Swed ...
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, which laid the basis for further development in those regional centres, and as Havn was midway between the two cities, it was centrally located for traffic and trading.
In the years that follow, the town grew tenfold in size. The excellent harbour
A harbor (American English), or harbour (Commonwealth English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences), is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be Mooring, moored. The t ...
encouraged Copenhagen's growth until it became an important centre of commerce (hence its name). Churches and abbeys were founded. Kû¡bmannehavn's economy blossomed due to the income from an enormous herring fishery trade, which provided large parts of Catholic Europe with salted herring for Lent
Lent (, 'Fortieth') is the solemn Christianity, Christian religious moveable feast#Lent, observance in the liturgical year in preparation for Easter. It echoes the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring Temptation of Christ, t ...
.
In 1254, it received its charter as a city under Bishop Jakob Erlandsen.
Copenhagen was located at the most important approach to the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
and the rich North German trading towns of the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
, providing Copenhagen with power and wealth, but also threatening its very existence. It was repeatedly attacked by Wend pirates and the Hanseatic League.
Time and again the town was besieged and laid waste by the Hanseatic League. In 1369 they tore down the castle, but a new castleãCopenhagen Castle was built in its place. At the same time the Danish king was also attempting to take Copenhagen back from the bishop. The crown succeeded in 1416, when King Erik of Pomerania took control of the town. Thenceforth Copenhagen belonged to the Danish Crown.
Despite centuries of power struggles and warring the town grew increasingly rich. Copenhageners did a brisk trade with friend and foe alike. Foreign merchants came to the town. Craft guilds were established and the University of Copenhagen
The University of Copenhagen (, KU) is a public university, public research university in Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark. Founded in 1479, the University of Copenhagen is the second-oldest university in Scandinavia, after Uppsala University.
...
was founded.
By the time of Christian IV's coronation in 1596, Copenhagen had become rich and powerful. The new king decided to make the town the economic, military, religious, and cultural centre for the whole of the Nordic region. The king established the first trading companies with sole rights to trade with lands overseas. In order to restrict imports, factories were set up so that the country could manufacture as many goods as possible on its own.
Christian IV expanded Copenhagen by adding two new districts: Nyboder ("New Booths") for the large numbers of navy personnel and the merchants' new district and Christianshavn ("Christian's Harbour"), which is modelled after Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
. A modern fortification with earthworks and bastions was built to surround the whole of the extended town. Gradually, however, it paralleled the town limits, and for the next 200 years or so traffic entering and leaving Copenhagen had to pass through Copenhagen's four narrow town gates.
Apart from the new earthworks, Christian IV commissioned German and Dutch architects and craftsmen to construct magnificent edifices designed to enhance his prestige. To this very day those buildings make their mark on the cityscape of Copenhagen.
By the time of Christian IV's death in 1648, Copenhagen had become Denmark's principal fortification and naval port, and the town formed a framework for the administration of the Danish kingdom and as a centre of trade in Northern Europe.
In the 1840s there was pressure placed on the military to dismantle the ring of fortifications in the inner city, and the military sold the land to Copenhagen municipality, which took ownership in October 1869. Dismantling began and discussions raged as to what to do with the land. Part of the land was used for parks and green areas.
Dismantling the fortifications and moving the capital areaãs defenses further out from the city also allowed the city to expand, opening up the development of many of the other city districts in todayãs Copenhagen.
Attractions
 * Amalienborg Palace
* Bû¡rsen, The Stock Exchange
* Christiansborg Palace located on
* Amalienborg Palace
* Bû¡rsen, The Stock Exchange
* Christiansborg Palace located on Slotsholmen
Slotsholmen (English language, English: The Castle Islet) is an island in the harbour of Copenhagen, Denmark, and part of Copenhagen Indre By, Inner City. The name is taken from the successive castles and palaces located on the island since Absal ...
* Copenhagen Botanical Garden
* Copenhagen City Hall (''RûËdhuset'')
* Christiania
* Frederiksstaden
Frederiksstaden is a district in Copenhagen, Denmark. Constructed during the reign of Frederick V of Denmark, Frederick V in the second half of the 18th century, it is considered to be one of the most important rococo complexes in Europe and was in ...
* Copenhagen Central Station
Copenhagen Central Station (, ; abbreviated ''Kû¡benhavn H'', colloquially usually referred to as ''HovedbanegûËrden'' or simply ''Hovedbanen'') is the Central station, main railway station in Copenhagen, Denmark, and the largest railway station ...
(''HovedbanegûËrd'')
* Gefion Fountain
* The Hirschsprung Collection (''Den Hirschsprungske samling'')
* Kastellet
* Kongens Have ("The King's Park")
* National Art Museum (''Statens Museum for Kunst'')
* National Museum of Denmark
The National Museum of Denmark (Nationalmuseet) in Copenhagen is Denmark, Denmark's largest museum of cultural history, comprising the histories of Danish and foreign cultures, alike. The museum's main building is located a short distance from S ...
* Nyboder
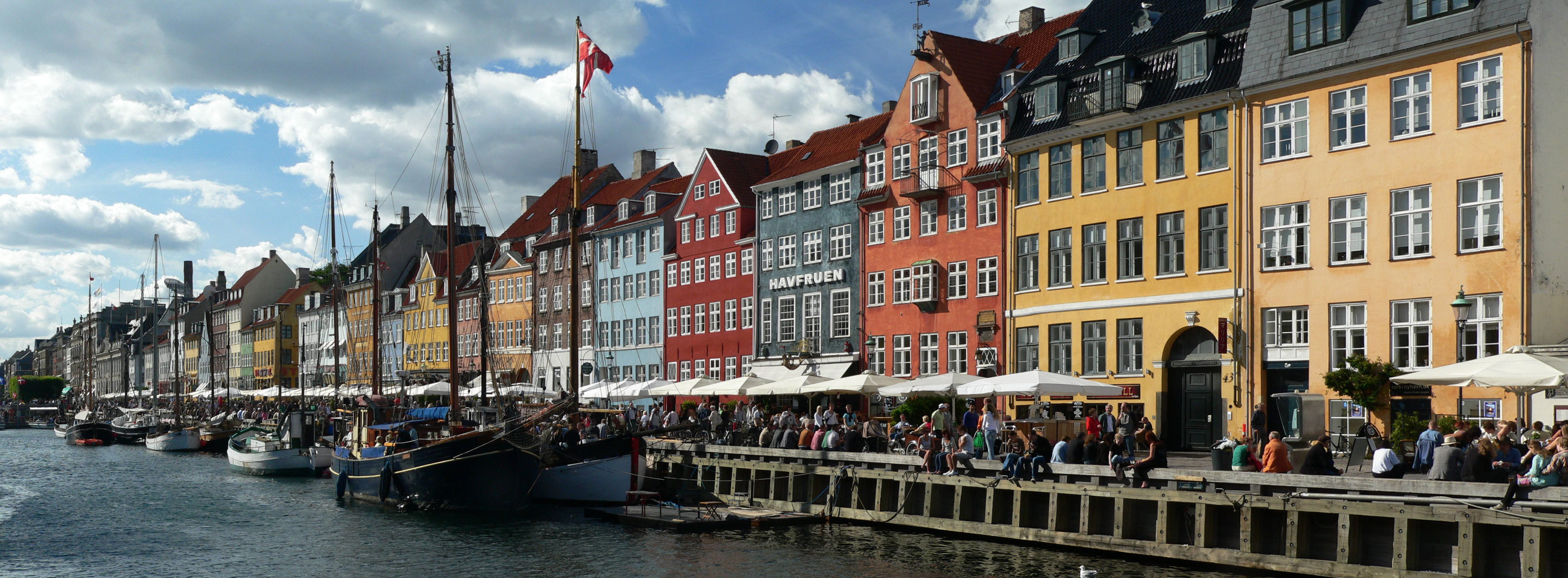
* Nyhavn
* Rosenborg Castle
Rosenborg Castle () is a renaissance castle in Copenhagen, Denmark. The castle was originally built as a country summerhouse in 1606 and is an example of Christian IV's many architectural projects. It was built in the Dutch Renaissance style, t ...
* Royal Danish Theatre
The Royal Danish Theatre (RDT, Danish: ') is both the national Danish performing arts institution and a name used to refer to its old purpose-built venue from 1874 located on Kongens Nytorv in Copenhagen. The theatre was founded in 1748, first s ...
* RundetûËrn, the Round Tower
* Strû¡get
* The Little Mermaid
* University of Copenhagen
The University of Copenhagen (, KU) is a public university, public research university in Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark. Founded in 1479, the University of Copenhagen is the second-oldest university in Scandinavia, after Uppsala University.
...
* ûstre AnlûÎg
ûstre AnlûÎg is a public park in Copenhagen. Once it was a part of the old Fortifications of Copenhagen, city fortifications. The park was designed by landscape architect H.A. Flindt who also designed ûrstedsparken and University of Copenhagen ...
("The Eastern Fortification") park
* GrûËbrû¡dretorv
* Gammel Strand
External links
City of Copenhagenãs statistical office
Photos from around Copenhagen City
{{Copenhagen Copenhagen city districts