Indian Civet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The large Indian civet (''Viverra zibetha'') is a
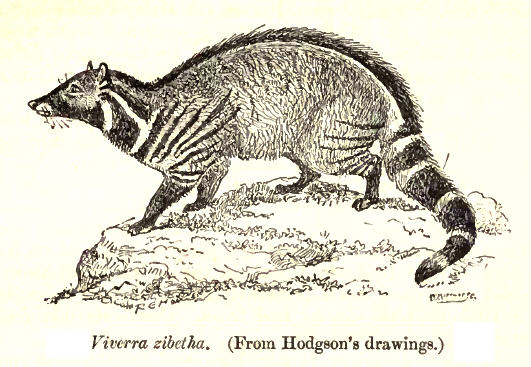
 The large Indian civet is grey or tawny and has a black spinal stripe running from behind the shoulders to the root of the tail. The front of the muzzle has a whitish patch emphasized by blackish behind on each side. The chin and fore throat are blackish. The sides and lower surface of the neck are banded with black stripes and white spaces in between. The tail has a variable number of complete black and white rings. Its
The large Indian civet is grey or tawny and has a black spinal stripe running from behind the shoulders to the root of the tail. The front of the muzzle has a whitish patch emphasized by blackish behind on each side. The chin and fore throat are blackish. The sides and lower surface of the neck are banded with black stripes and white spaces in between. The tail has a variable number of complete black and white rings. Its
 The large Indian civet is
The large Indian civet is
 ''Viverra zibetha'' was the
''Viverra zibetha'' was the
viverrid
Viverridae is a family (biology), family of small to medium-sized feliform mammals, comprising 14 genera with 33 species. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, in southern Europe, ...
native to South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
. It is listed as Least Concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been evaluated and categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as not being a focus of wildlife conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wil ...
on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological ...
. The global population is thought to be decreasing due to hunting and trapping driven by the demand for bushmeat
Bushmeat is meat from wildlife species that are Hunting, hunted for human consumption. Bushmeat represents a primary source of animal protein and a cash-earning commodity in poor and rural communities of humid tropical forest regions of the worl ...
.
Characteristics
 The large Indian civet is grey or tawny and has a black spinal stripe running from behind the shoulders to the root of the tail. The front of the muzzle has a whitish patch emphasized by blackish behind on each side. The chin and fore throat are blackish. The sides and lower surface of the neck are banded with black stripes and white spaces in between. The tail has a variable number of complete black and white rings. Its
The large Indian civet is grey or tawny and has a black spinal stripe running from behind the shoulders to the root of the tail. The front of the muzzle has a whitish patch emphasized by blackish behind on each side. The chin and fore throat are blackish. The sides and lower surface of the neck are banded with black stripes and white spaces in between. The tail has a variable number of complete black and white rings. Its claw
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes (mammals, reptiles, birds). Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or Arthro ...
s are retractable. The soles of the feet are hairy.
As indicated by its common name, this is a relatively large civet, almost certainly the largest of the ''Viverra
''Viverra'' is a mammalian genus that was first named and described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 as comprising several species including the large Indian civet (''V. zibetha''). The genus was subordinated to the viverrid family by John Edward Gray in ...
'' species and exceeded in size among the Viverridae family only by African civet
The African civet (''Civettictis civetta'') is a large viverrid native to sub-Saharan Africa, where it is considered common and widely distributed in woodlands and secondary forests. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008 ...
s and binturong
The binturong (''Arctictis binturong'') (, ), also known as the bearcat, is a viverridae, viverrid native to South Asia, South and Southeast Asia. It is uncommon in much of its range, and has been assessed as Vulnerable species, Vulnerable on th ...
s. Its head-and-body length ranges from with a long tail. The hind foot measures . Its weight ranges from . Some sources claim the species can weigh up to (though possibly attained in captivity).
Distribution and habitat
The large Indian civet ranges fromNepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, northeast India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , ...
, Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
to Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
, Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula is located in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area contains Peninsular Malaysia, Southern Tha ...
and Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
to Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
, Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
, Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
.
In Nepal, the large Indian civet was recorded up to in the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
.
In China, the wild large Indian civet population declined drastically by 94–99% since the 1950s following deforestation, due to hunting for the fur trade, use of its musk glands as medicine and for the perfume
Perfume (, ) is a mixture of fragrance, fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), Fixative (perfumery), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agre ...
industry. By the 1990s, it was largely confined to the north of Guangdong Province
) means "wide" or "vast", and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in AD 226. The name "''Guang''" ultimately came from Guangxin ( zh, labels=no, first=t, t= , s=广信), an outpost established in Han dynasty ...
in southern China, but has not been recorded in Hainan Island
Hainan is an island province and the southernmost province of China. It consists of the eponymous Hainan Island and various smaller islands in the South China Sea under the province's administration. The name literally means "South of the Sea ...
during surveys between 1998 and 2008.
Ecology and behaviour
 The large Indian civet is
The large Indian civet is solitary
Solitary is the state of being alone or in solitude. The term may refer to:
* ''Solitary'' (album), 2008 album by Don Dokken
* ''Solitary'' (2020 film), a British sci-fi thriller film
* ''Solitary'' (upcoming film), an American drama film
* "S ...
and nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatur ...
. It spends most of the time on the ground. It is an opportunistic hunter that preys on a wide variety of small animals.
Radio-tracked large Indian civets in Thailand had home ranges of .
Conservation
''Viverra zibetha'' is aprotected species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, invasiv ...
in Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
under the Wild Animals Protection Ordinance Cap 170, though it has not been recorded in a natural state in Hong Kong since the 1970s, and is considered extirpated
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.
Local extinctions mark a chan ...
.
Taxonomy
 ''Viverra zibetha'' was the
''Viverra zibetha'' was the scientific name
In Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin gramm ...
for the large Indian civet introduced by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
in 1758.
Several naturalists proposed species and subspecies in the 19th and 20th centuries, of which the following were recognised as valid subspecies by 2005:
* ''V. z. zibetha'' is the nominate subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics ( morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. ...
and occurs in Nepal and Northeast India
Northeast India, officially the North Eastern Region (NER), is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political Administrative divisions of India, administrative division of the country. It comprises eight States and ...
.
*''Viverra ashtoni'' described by Robert Swinhoe
Robert Swinhoe FRS (1 September 1836 – 28 October 1877) was an English diplomat and naturalist who worked as a Consul in Qing-era Taiwan (then known to Westerners as Formosa). He catalogued many Southeast Asian birds, and several, such as ...
in 1864 was a skin of an individual that was shot near the upper Min River in China's Fujian Province
Fujian is a province in southeastern China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou and its largest prefecture city by population is Qua ...
; occurs in China.
*''V. z. picta'' described by Robert Charles Wroughton Robert Charles Wroughton (15 August 1849, in Naseerabad – 15 May 1921) was an officer in the Indian Forest Service from 10 December 1871 to 1904. Trained in forestry in France, he joined the Indian Forest Service in the Bombay Presidency and ...
in 1915 was based on two skins from the vicinity of Hkamti by the upper Chindwin River
The Chindwin River (), also known as the Ningthi River (), is a river in Myanmar and is the largest tributary of the Irrawaddy River.
Sources
The Chindwin originates in the broad Hukawng Valley of Kachin State of Burma, roughly
, where the Tanai, ...
in Myanmar; occurs from Assam and northern Myanmar to Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to th ...
.
*''V. z. pruinosa'' also described by Wroughton in 1915 was a skin of an adult male large Indian civet from Myanmar's Tanintharyi Region
Tanintharyi Region (, ; Mon: or ; formerly Tenasserim Division and Tanintharyi Division) is a region of Myanmar, covering the long narrow southern part of the country on the northern Malay Peninsula, reaching to the Kra Isthmus. It borders ...
; occurs from southern Myanmar to Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia, historically known as Malaya and also known as West Malaysia or the Malaysian Peninsula, is the western part of Malaysia that comprises the southern part of the Malay Peninsula on Mainland Southeast Asia and the list of isla ...
.
*''V. z. hainana'' described by Ying-Xiang Wang and Xu in 1983 from Hainan Island.
References
External links
{{Taxonbar, from=Q757265 Mammals of Southeast Asia Mammals of Nepal Mammals of India Mammals of Bangladesh Fauna of Hong Kong Mammals described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Carnivorans of Malaysia Mammals of Singapore