Iazyges on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Iazyges () were an ancient
 In the 3rd century BC the Iazyges lived in modern-day south-eastern Ukraine along the northern shores of the
In the 3rd century BC the Iazyges lived in modern-day south-eastern Ukraine along the northern shores of the
 In the 2nd centuryBC, sometime before 179BC, the Iazyges began to migrate westward to the steppe near the Lower Dniester. This may have occurred because the
In the 2nd centuryBC, sometime before 179BC, the Iazyges began to migrate westward to the steppe near the Lower Dniester. This may have occurred because the
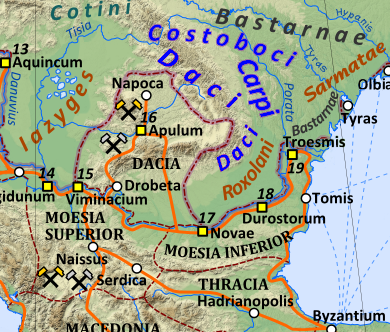 After the conquest of the Pannonian Basin, the Iazyges appear to have ruled over some measure of the remaining Germanic, Celtic, and Dacian populations, with the hilly areas north of modern-day Budapest retaining strong Germanic traditions, with a significant presence of Germanic burial traditions. Items of Celtic manufacturing appear up until the late 2nd centuryAD, in the northern area of the Carpathian Basin.
During the time of
After the conquest of the Pannonian Basin, the Iazyges appear to have ruled over some measure of the remaining Germanic, Celtic, and Dacian populations, with the hilly areas north of modern-day Budapest retaining strong Germanic traditions, with a significant presence of Germanic burial traditions. Items of Celtic manufacturing appear up until the late 2nd centuryAD, in the northern area of the Carpathian Basin.
During the time of
 In 169, the Iazyges, Quadi,
In 169, the Iazyges, Quadi,
 In late antiquity, historic accounts become much more diffuse and the Iazyges generally cease to be mentioned as a tribe. Beginning in the 4th century, most Roman authors cease to distinguish between the different Sarmatian tribes, and instead refer to all as Sarmatians. In the late 4th century, two Sarmatian peoples were mentioned—the Argaragantes and the Limigantes, who lived on opposite sides of the
In late antiquity, historic accounts become much more diffuse and the Iazyges generally cease to be mentioned as a tribe. Beginning in the 4th century, most Roman authors cease to distinguish between the different Sarmatian tribes, and instead refer to all as Sarmatians. In the late 4th century, two Sarmatian peoples were mentioned—the Argaragantes and the Limigantes, who lived on opposite sides of the
Copy at Google books (searching Metanastae)
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; ; Latin: ) were a large confederation of Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe from about the 5th century BCE to the 4t ...
tribe that traveled westward in 200BC from Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
to the steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
s of modern Ukraine. In , they moved into modern-day Hungary and Serbia near the Pannonian steppe between the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
and Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa (see below) is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. It was once called "the most Hungarian river" because it used to flow entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national bo ...
rivers, where they adopted a semi-sedentary lifestyle
Sedentary lifestyle is a Lifestyle (social sciences), lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and/or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while enga ...
.
In their early relationship with Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, the Iazyges were used as a buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between t ...
between the Romans and the Dacians; this relationship later developed into one of overlord and client state
A client state in the context of international relations is a State (polity), state that is economically, politically, and militarily subordinated to a more powerful controlling state. Alternative terms for a ''client state'' are satellite state, ...
, with the Iazyges being nominally sovereign subjects of Rome. Throughout this relationship, the Iazyges carried out raids on Roman land, which often caused punitive expedition
A punitive expedition is a military journey undertaken to punish a political entity or any group of people outside the borders of the punishing state or union. It is usually undertaken in response to perceived disobedient or morally wrong beha ...
s to be made against them.
Almost all of the major events of the Iazyges, such as the two Dacian Wars—in both of which the Iazyges fought, assisting Rome in stopping the Dacians' incursions into Roman conquered territory in the first war and defeating the Dacians in the second—are connected with war. Another such war is the Marcomannic War that occurred between 169 and 175, in which this time, Iazyges fought against Rome but were defeated by Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus ( ; ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 and a Stoicism, Stoic philosopher. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, the last of the rulers later known as the Five Good Emperors ...
and had severe penalties imposed on them.
Culture
Although the Iazyges werenomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
s before their migration to the Tisza plain, they became semi-sedentary once there, and lived in towns, although they migrated between these towns to allow their cattle to graze. Their language was a dialect of Old Iranian
The Iranian languages, also called the Iranic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian language ...
, which was quite different from most of the other Sarmatian dialects of Old Iranian. According to the Roman writer Gaius Valerius Flaccus, when an Iazyx became too old to fight in battle, they were killed by their sons or, according to Roman geographer Pomponius Mela
Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest known Roman geographer. He was born at the end of the 1st century BC in Tingentera (now Algeciras) and died AD 45.
His short work (''De situ orbis libri III.'') remained in use nea ...
, threw themselves from a rock.
Etymology
The Iazyges' name was Latinized as ' () or ', or sometimes as '. Their name was also occasionally spelled as ''Iazuges''. Several corruptions of their name, such as ', ', ', and ', existed. Other modern English forms of their name are ', ', ', and '. The root of the name may beProto-Iranian
Proto-Iranian or Proto-Iranic is the reconstructed proto-language of the Iranian languages branch of Indo-European language family and thus the ancestor of the Iranian languages such as Persian, Pashto, Sogdian, Zazaki, Ossetian, Mazandara ...
''*yaz-'', "to sacrifice", perhaps indicating a caste or tribe specializing in religious sacrifices.
According to Peter Edmund Laurent, a 19th-century French classical scholar, the Iazyges Metanastæ, a warlike Sarmatian race, which had migrated during the reign of the Roman Emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
, and therefore received the name of "Metanastæ", resided in the mountains west of the Theiss (Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa (see below) is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. It was once called "the most Hungarian river" because it used to flow entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national bo ...
) and east of the Gran () and Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
. The Greek Metanastæ () means "migrants". The united Scythians and Sarmatæ called themselves Iazyges, which Laurent connected with Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic ( ) is the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language and the oldest extant written Slavonic language attested in literary sources. It belongs to the South Slavic languages, South Slavic subgroup of the ...
(''językŭ'', "tongue, language, people").
Burial traditions
The graves made by the Iazyges were often rectangular or circular, although some were ovoid, hexagonal, or even octagonal. They were flat and were grouped like burials in modern cemeteries. Most of the graves' access openings face south, southeast, or southwest. The access openings are between and wide. The graves themselves are between and in diameter. After their migration to the Tisza plain, the Iazyges were in serious poverty. This is reflected in the poor furnishings found at burial sites, which are often filled with clay vessels, beads, and sometimes brooches. Iron daggers and swords were very rarely found in the burial site. Their brooches and arm-rings were of the La Tène type, showing the Dacians had a distinct influence on the Iazyges. Later tombs showed an increase in material wealth; tombs of the 2nd to early 4th centuries had weapons in them 86% of the time and armor in them 5% of the time. Iazygian tombs along the Roman border show a strong Roman influence.Diet
Before their migration into thePannonian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorpholog ...
, while still living north of Tyras, on the north-western coast of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, the geographer Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
states that their diet consisted largely of "honey, milk, and cheese". After their migration, the Iazyges were cattle breeders; they required salt to preserve their meat but there were no salt mines within their territory. According to Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history of ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
, the Iazyges received grain from the Romans.
The Iazyges used hanging, asymmetrical, barrel-shaped pots that had uneven weight distribution. The rope used to hang the pot was wrapped around the edges of the side collar; it is believed the rope was tied tightly to the pot, allowing it to spin in circles. Due to the spinning motion, there are several theories about the pot's uses. It is believed the small hanging pots were used to ferment alcohol using the seeds of touch-me-not balsam ('' Impatiens noli-tangere''), and larger hanging pots were used to churn butter and make cheese.
Military
The Iazyges wore heavy armor, such as sugarloaf helms, and scale armor made of iron, bronze, horn, orhorse hoof
A horse hoof is the lower extremity of each leg of a horse, the part that makes contact with the ground and carries the weight of the animal. It is both hard and flexible. It is a complex structure surrounding the distal Phalanx bones, phalanx o ...
, which was sewn onto a leather gown so the scales would partially overlap. They used long, two-handed lances called ; they wielded these from horses, which they barded. Their military was exclusively cavalry. They are believed to have used saddle blanket
The terms saddle blanket, saddle pad (or numnah), and saddle cloth refer to blankets, pads or fabrics inserted under a saddle. These are usually used to absorb sweat, cushion the saddle, and protect the horse's back. There are lighter types ...
s on their horses. Although it was originally Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
ish, it is believed the Iazyges used the , a trumpet-like wind instrument.
Religion
One of the Iazygian towns, Bormanon, is believed to have hadhot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a Spring (hydrology), spring produced by the emergence of Geothermal activity, geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow ...
s because settlement names starting with "Borm" were commonly used among European tribes to denote that the location had hot springs, which held religious importance for many Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
tribes. It is not known, however, whether the religious significance of the hot springs was passed on to the Iazyges with the concept itself. The Iazyges used horse-tails in their religious rituals.
Economy
When the Iazyges migrated to the plain between the Tisza and the Danube, their economy suffered severely. Many explanations have been offered for this, such as their trade with thePontic Steppe
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from n ...
and Black Sea being cut off and the absence of any mineable resources within their territory making their ability to trade negligible. Additionally, Rome proved more difficult to raid than the Iazyges' previous neighbors, largely due to Rome's well-organized army. The Iazyges had no large-scale organized production of goods for most of their history. As such, most of their trade goods were gained via small-scale raids upon neighboring peoples, although they did have some incidental horticulture. Several pottery workshops have been found in Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
, which was within the territory of the Iazyges, close to their border with Rome. These pottery workshops were built from the late 3rd century and have been found at Vršac–Crvenka, Grădinari–Selişte, Timişoara–Freidorf, Timişoara–Dragaşina, Hodoni, Pančevo
Pančevo (Serbian Cyrillic: Панчево, ; ; ; ; ) is a list of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the South Banat District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is located on the shores of rivers Timiș (ri ...
, Dolovo, and Izvin şi Jabuca.
The Iazyges' trade with the Pontic Steppe and Black Sea was extremely important to their economy; after the Marcomannic War, Marcus Aurelius offered them the concession of movement through Dacia to trade with the Roxolani
The Roxolani or Rhoxolāni ( , ; ) were a Sarmatian people documented between the 2nd century BC and the 4th century AD, first east of the Borysthenes (Dnieper) on the coast of Lake Maeotis (Sea of Azov), and later near the borders of Roman Daci ...
, which reconnected them with the Pontic Steppe trade network. This trade route lasted until 260, when the Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
took over Tyras and Olbia
Olbia (, ; ; ) is a city and communes of Italy, commune of 61,000 inhabitants in the Italy, Italian insular province of Sassari in northeastern Sardinia, Italy, in the historical region of Gallura. Called in the Roman age, Civita in the Middle ...
, cutting off both the Roxolani's and the Iazyges' trade with the Pontic Steppe. The Iazyges also traded with the Romans, although this trade was smaller in scale. While there are Roman bronze coins scattered along the entirety of the Roman Danubian Limes, the highest concentration of them appear in the Iazyges' territory.
Imports
Because the Iazyges had no organized production for most of their history, imported pottery finds are sparse. Some goods, such as bronze or silver vessels,amphorae
An amphora (; ; English ) is a type of container with a pointed bottom and characteristic shape and size which fit tightly (and therefore safely) against each other in storage rooms and packages, tied together with rope and delivered by land ...
, terracotta wares, and lamps are extremely rare or nonexistent. Some amphorae and lamps have been found in Iazygian territory, often near major river crossings near the border with Rome, but the location of the sites make it impossible to determine whether these goods are part of an Iazygain site, settlement, or cemetery; or merely the lost possessions of Roman soldiers stationed in or near the locations.
The most commonly found imported ware was ''Terra sigillata
Terra sigillata is a term with at least three distinct meanings: as a description of medieval medicinal earth; in archaeology, as a general term for some of the fine red ancient Roman pottery with glossy surface Slip (ceramics), slips made ...
''. At Iazygian cemeteries, a single complete ''terra sigillata'' vessel and a large number of fragments have been found in Banat. ''Terra sigillata
Terra sigillata is a term with at least three distinct meanings: as a description of medieval medicinal earth; in archaeology, as a general term for some of the fine red ancient Roman pottery with glossy surface Slip (ceramics), slips made ...
'' finds in Iazygian settlements are confusing in some cases; it can sometimes be impossible to determine the timeframe of the wares in relation to its area and thus impossible to determine whether the wares came to rest there during Roman times or after the Iazyges took control. Finds of ''terra sigillata'' of an uncertain age have been found in Deta, Kovačica–Čapaš, Kuvin, Banatska Palanka, Pančevo
Pančevo (Serbian Cyrillic: Панчево, ; ; ; ; ) is a list of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the South Banat District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is located on the shores of rivers Timiș (ri ...
, Vršac
Vršac ( sr-Cyrl, Вршац, ) is a city in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. As of 2022, the city urban area had a population of 31,946, while the city administrative area had 45,462 inhabitants. It is located in the geographical ...
, Zrenjanin–Batka, Dolovo, Delibata, Perlez, Aradac, Botoš, and Bočar. Finds of ''terra sigillata'' that have been confirmed to having been made the time of Iazygian possession but of uncertain date have been found in Timișoara–Cioreni, Hodoni, Iecea Mică, Timișoara–Freidorf, Satchinez, Criciova, Becicherecul Mic, and Foeni–Seliște. The only finds of ''terra sigillata'' whose time of origin is certain have been found in Timișoara–Freidorf, dated to the 3rd century AD. Amphorae fragments have been found in Timișoara–Cioreni, Iecea Mică, Timișoara–Freidorf, Satchinez, and Biled
Biled (; ) is a communes of Romania, commune in Timiș County, Romania. It is composed of a single village, Biled. It also included two other villages until 2004, when they were split off to form the commune of Șandra.
Administration
The curre ...
; all of these are confirmed to be of Iazygian origin but none of them have definite chronologies.
In Tibiscum, an important Roman and later Iazygian settlement, only a very low percent of pottery imports were imported during or after the 3rd century. The pottery imports consisted of ''terra sigillata'', amphorae, glazed pottery, and stamped white pottery. Only 7% of imported pottery was from the "late period" during or after the 3rd century, while the other 93% of finds were from the "early period", the 2nd century or earlier. Glazed pottery was almost nonexistent in Tibiscum; the only finds from the early period are a few fragments with Barbotine decorations and stamped with "''CRISPIN(us)''". The only finds from the late period are a handful of glazed bowl fragments that bore relief decorations on both the inside and the outside. The most common type of amphorae is the Dressel 24 similis; finds are from the time of rule of Hadrian to the late period. An amphora of type Carthage LRA 4 dated between the 3rd and 4th century AD has been found in Tibiscum-Iaz and an amphora of type Opaiţ 2 has been found in Tibiscum-Jupa.
Geography
Records of eight Iazygian towns have been documented; these are Uscenum, Bormanum, Abieta, Trissum, Parca, Candanum, Pessium, and Partiscum.Klaudios Ptolemaios. Handbuch der Geographie. Griechisch-Deutsch. Herausgegeben von Alfred Stückelberger und Gerd Graßhoff. Schwabe Verlag Basel. 2006, p. 310-311 There was also a settlement on Gellért Hill. Their capital was at Partiscum, the site of which roughly corresponds with that ofKecskemét
Kecskemét ( ) is a city with county rights in central Hungary. It is the List of cities and towns of Hungary, eighth-largest city in the country, and the county seat of Bács-Kiskun County, Bács-Kiskun.
Kecskemét lies halfway between the ca ...
, a city in modern-day Hungary. It is believed that a Roman road may have traversed the Iazyges' territory for about , connecting Aquincum
Aquincum (, ) was an ancient city, situated on the northeastern borders of the province of Pannonia within the Roman Empire. The ruins of the city can be found in Budapest, the capital city of Hungary. It is believed that Marcus Aurelius wrote ...
to Porolissum, and passing near the site of modern-day Albertirsa. This road then went on to connect with the Black Sea city states.
The area of plains between the Danube and Tisza rivers that was controlled by the Iazyges was similar in size to Italy and about long. The terrain was largely swampland dotted with a few small hills that was devoid of any mineable metals or minerals. This lack of resources and the problems the Romans would face trying to defend it may explain why the Romans never annexed it as a province but left it as a client-kingdom.
According to English cartographer Aaron Arrowsmith, the Iazyges Metanastæ lived east (sic) of the oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
Dacia separating it from oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
Pannonia and Germania. The Iazyges Metanastæ drove Dacians from Pannonia and Tibiscus River (today known as Timiș River).
History
Early history
 In the 3rd century BC the Iazyges lived in modern-day south-eastern Ukraine along the northern shores of the
In the 3rd century BC the Iazyges lived in modern-day south-eastern Ukraine along the northern shores of the Sea of Azov
The Sea of Azov is an inland Continental shelf#Shelf seas, shelf sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, and sometimes regarded as a northern extension of the Black Sea. The sea is bounded by Ru ...
, which the Ancient Greeks and Romans called the Lake of Maeotis. From there, the Iazyges—or at least some of them—moved west along the shores of the Black Sea into modern-day Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
and south-western Ukraine. It is possible the entirety of the Iazyges did not move west and that some of them stayed along the Sea of Azov, which would explain the occasional occurrence of the surname '; the Iazyges that possibly remained along the Sea of Azov, however, are never mentioned again.
Migration
 In the 2nd centuryBC, sometime before 179BC, the Iazyges began to migrate westward to the steppe near the Lower Dniester. This may have occurred because the
In the 2nd centuryBC, sometime before 179BC, the Iazyges began to migrate westward to the steppe near the Lower Dniester. This may have occurred because the Roxolani
The Roxolani or Rhoxolāni ( , ; ) were a Sarmatian people documented between the 2nd century BC and the 4th century AD, first east of the Borysthenes (Dnieper) on the coast of Lake Maeotis (Sea of Azov), and later near the borders of Roman Daci ...
, who were the Iazyges' eastern neighbors, were also migrating westward due to pressure from the Aorsi, which put pressure on the Iazyges and forced them to migrate westward as well.
The views of modern scholars as to how and when the Iazyges entered the Pannonian plain are divided. The main source of division is over the issue of if the Romans approved, or even ordered, the Iazyges to migrate, with both sides being subdivided into groups debating the timing of such a migration. Andreas Alföldi states that the Iazyges could not have been present to the north-east and east of the Pannonian Danube unless they had Roman approval. This viewpoint is supported by János Harmatta, who claims that the Iazyges were settled with both the approval and support of the Romans, so as to act as a buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between t ...
against the Dacians. András Mócsy suggests that Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus Augur, who was Roman consul in 26BC, may have been responsible for the settlement of the Iazyges as a buffer between Pannonia and Dacia. However, Mócsy also suggests that the Iazyges may have arrived gradually, such that they initially were not noticed by the Romans. John Wilkes
John Wilkes (17 October 1725 – 26 December 1797) was an English Radicalism (historical), radical journalist and politician, as well as a magistrate, essayist and soldier. He was first elected a Member of Parliament in 1757. In the Middlese ...
believes that the Iazyges reached the Pannonian plain either by the end of Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
's rule (14AD) or some time between 17 and 20AD. Constantin Daicoviciu
Constantin Daicoviciu (; February 22, 1898Brătescu, p. 591 – May 27, 1973) was a Romanian historian and archaeologist, professor at the University of Cluj, and titular member of the Romanian Academy.
He was born in Căvăran, at the time i ...
suggests that the Iazyges entered the area around 20AD, after the Romans called upon them to be a buffer state. Coriolan Opreanu supports the theory of the Iazyges being invited, or ordered, to occupy the Pannonian plain, also around 20AD. Gheorghe Bichir and Ion Horațiu Crișan support the theory that the Iazyges first began to enter the Pannonian plain in large numbers under Tiberius, around 20AD. The most prominent scholars that state the Iazyges were not brought in by the Romans, or later approved, are Doina Benea, Mark Ščukin, and Jenő Fitz. Doina Benea states that the Iazyges slowly infiltrated the Pannonian plain sometime in the first half of the 1st centuryAD, without Roman involvement. Jenő Fitz promotes the theory that the Iazyges arrived ''en masse'' around 50AD, although a gradual infiltration preceded it. Mark Ščukin states only that the Iazyges arrived by themselves sometime around 50AD. Andrea Vaday argued against the theory of a Roman approved or ordered migration, citing the lack of strategic reasoning, as the Dacians were not actively providing a threat to Rome during the 20–50AD period.
The occupation of the lands between the Danube and Tisza by the Iazyges was mentioned by Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
in his ''Naturalis Historia'' (77–79AD), in which he says that the Iazyges inhabited the basins and plains of the lands, while the forested and mountainous area largely retained a Dacian population, which was later pushed back to the Tisza by the Iazyges. Pliny's statements are corroborated by the earlier accounts of Seneca the Younger
Lucius Annaeus Seneca the Younger ( ; AD 65), usually known mononymously as Seneca, was a Stoicism, Stoic philosopher of Ancient Rome, a statesman, a dramatist, and in one work, a satirist, from the post-Augustan age of Latin literature.
Seneca ...
in his '' Quaestiones Naturales'' (61–64AD), where he uses the Iazyges to discuss the borders that separate the various peoples.
From 78 to 76BC, the Romans led an expedition to an area north of the Danube—then the Iazyges' territory—because the Iazyges had allied with Mithridates VI of Pontus
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator (; 135–63 BC) was the ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an effective, ambitious, and r ...
, with whom the Romans were at war. In 44BC King Burebista of Dacia died and his kingdom began to collapse. After this, the Iazyges began to take possession of the Pannonian Basin, the land between the Danube and Tisa rivers in modern-day south-central Hungary. Historians have posited this was done at the behest of the Romans, who sought to form a buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between t ...
between their provinces and the Dacians
The Dacians (; ; ) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area include ...
to protect the Roman province of Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It ...
. The Iazyges encountered the Basternae and Getae
The Getae or Getai ( or , also Getans) were a large nation who inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania, throughout much of Classical Antiquity. The main source of informa ...
along their migration path sometime around 20AD and turned southward to follow the coast of the Black Sea until they settled in the Danube Delta
The Danube Delta (, ; , ) is the second largest river delta in Europe, after the Volga Delta, and is the best preserved on the continent. Occurring where the Danube, Danube River empties into the Black Sea, most of the Danube Delta lies in Romania ...
. This move is attested by the large discrepancy in the location reported by Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
relative to that which was earlier given by Ovid
Publius Ovidius Naso (; 20 March 43 BC – AD 17/18), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a younger contemporary of Virgil and Horace, with whom he i ...
. Archeological finds suggest that while the Iazyges took hold of the northern plain between the Danube and the Tisa by around 50AD, they did not take control of the land south of the Partiscum-Lugio line until the late 1st or early 2nd century.
The effects of this migration have been observed in the ruins of burial sites left behind by the Iazyges; the standard grave goods made of gold being buried alongside a person were absent, as was the equipment of a warrior; this may have been because the Iazyges were no longer in contact with the Pontic Steppe and were cut off from all trade with them, which had previously been a vital part of their economy. Another problem with the Iazyges' new location was that it lacked both precious minerals and metals, such as iron, which could be turned into weapons. They found it was much more difficult to raid the Romans, who had organized armies around the area, as opposed to the disorganized armies of their previous neighbors. The cutting-off of trade with the Pontic Steppe meant they could no longer trade for gold for burial sites, assuming any of them could afford it. The only such goods they could find were the pottery and metals of the adjacent Dacian and Celtic peoples. Iron weapons would have been exceedingly rare, if the Iazyges even had them, and would likely have been passed down from father to son rather than buried because they could not have been replaced.
Post-migration
 After the conquest of the Pannonian Basin, the Iazyges appear to have ruled over some measure of the remaining Germanic, Celtic, and Dacian populations, with the hilly areas north of modern-day Budapest retaining strong Germanic traditions, with a significant presence of Germanic burial traditions. Items of Celtic manufacturing appear up until the late 2nd centuryAD, in the northern area of the Carpathian Basin.
During the time of
After the conquest of the Pannonian Basin, the Iazyges appear to have ruled over some measure of the remaining Germanic, Celtic, and Dacian populations, with the hilly areas north of modern-day Budapest retaining strong Germanic traditions, with a significant presence of Germanic burial traditions. Items of Celtic manufacturing appear up until the late 2nd centuryAD, in the northern area of the Carpathian Basin.
During the time of Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
, the Iazyges sent an embassy to Rome to request friendly relations. In a modern context, these "friendly relations" would be similar to a non-aggression pact
A non-aggression pact or neutrality pact is a treaty between two or more states/countries that includes a promise by the signatories not to engage in military action against each other. Such treaties may be described by other names, such as a t ...
. Around this time, some of the western parts of the land of the Iazyges were occupied, apparently without conflict, by the Quadi
The Quadi were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people during the Roman era, who were prominent in Greek and Roman records from about 20 AD to about 400 AD. By about 20 AD they had a kingdom centred in the area of present-day western Slovakia, north ...
, which scholar Nicholas Higham states "suggests long-term collaboration between hem
A hem in sewing is a garment finishing method, where the edge of a piece of cloth is folded and sewn to prevent unravelling of the fabric and to adjust the length of the piece in garments, such as at the end of the sleeve or the bottom of the ga ...
.
Later, during the reign of Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
, the Iazyges became one of many new client-tribes of Rome. Roman client states were treated according to the Roman tradition of patronage, exchanging rewards for service. The client king was called ''socius et amicus Romani Populi'' (ally and friend of the Roman People); the exact obligations and rewards of this relationship, however, are vague. Even after being made into a client state, the Iazyges conducted raids across their border with Rome, for example in 6AD and again in 16AD. In 20AD the Iazyges moved westward along the Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains ...
into the Pannonian Steppe, and settled in the steppes between the Danube and the Tisza river
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa (see below) is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. It was once called "the most Hungarian river" because it used to flow entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national bo ...
, taking absolute control of the territory from the Dacians. In 50AD, an Iazyges cavalry detachment assisted King Vannius, a Roman client-king of the Quadi, in his fight against the Suevi
file:1st century Germani.png, 300px, The approximate positions of some Germanic peoples reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 1st century. Suebian peoples in red, and other Irminones in purple.
The Suebi (also spelled Suavi, Suevi or Suebians ...
.
In the Year of Four Emperors, 69AD, the Iazyges gave their support to Vespasian
Vespasian (; ; 17 November AD 9 – 23 June 79) was Roman emperor from 69 to 79. The last emperor to reign in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolida ...
, who went on to become the sole emperor of Rome. The Iazyges also offered to guard the Roman border with the Dacians to free up troops for Vespasian's invasion of Italy; Vespasian refused, however, fearing they would attempt a takeover or defect. Vespasian required the chiefs of the Iazyges to serve in his army so they could not organize an attack on the undefended area around the Danube. Vespasian enjoyed support from the majority of the Germanic and Dacian tribes.
Domitian's campaign against Dacia was mostly unsuccessful; the Romans, however, won a minor skirmish that allowed him to claim it as a victory, even though he paid the King of Dacia, Decebalus
Decebalus (; ), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacians, Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a R ...
, an annual tribute of eight million sesterces in tribute to end the war. Domitian returned to Rome and received an ovation, but not a full triumph. Considering that Domitian had been given the title of Imperator
The title of ''imperator'' ( ) originally meant the rough equivalent of ''commander'' under the Roman Republic. Later, it became a part of the titulature of the Roman Emperors as their praenomen. The Roman emperors generally based their autho ...
—for military victories 22 times, this was markedly restrained, suggesting the populace—or at least the senate—was aware it had been a less-than-successful war, despite Domitian's claims otherwise. In 89AD, however, Domitian invaded the Iazyges along with the Quadi and Marcomanni. Few details of this war are known but it is recorded that the Romans were defeated, it is, however, known that Roman troops acted to repel simultaneous incursion by the Iazyges into Dacian lands.
In early 92AD the Iazyges, Roxolani, Dacians, and Suebi
file:1st century Germani.png, 300px, The approximate positions of some Germanic peoples reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 1st century. Suebian peoples in red, and other Irminones in purple.
The Suebi (also spelled Suavi, Suevi or Suebians ...
invaded the Roman province of Pannonia—modern-day Croatia, northern Serbia, and western Hungary. Emperor Domitian called upon the Quadi
The Quadi were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people during the Roman era, who were prominent in Greek and Roman records from about 20 AD to about 400 AD. By about 20 AD they had a kingdom centred in the area of present-day western Slovakia, north ...
and the Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people who lived close to the border of the Roman Empire, north of the River Danube, and are mentioned in Roman records from approximately 60 BC until about 400 AD. They were one of the most important members of th ...
to supply troops to the war. Both client-tribes refused to supply troops so Rome declared war upon them as well. In May 92AD, the Iazyges annihilated the Roman Legio XXI Rapax
Legio XXI Rapax ("Predator, Twenty-First Legion") was a Roman legion, legion of the Imperial Roman army. The symbol of the legion is thought to have been a Capricorn (astrology), capricorn.
History
Foundation
It was founded in 31 BC by the ...
in battle. Domitian, however, is said to have secured victory in this war by January of the next year. It is believed, based upon a rare Aureus coin showing an Iazyx with a Roman standard kneeling, with the caption of "''Signis a Sarmatis Resitvtis''", that the standard is taken from the annihilated Legio XXI Rapax was returned to Rome at the end of the war. Although the accounts of the Roman-Iazyges wars of 89 and 92AD are both muddled, it has been shown they are separate wars and not a continuation of the same war. The threat presented by the Iazyges and neighbouring people to the Roman provinces was significant enough that Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
travelled across the Mid and Lower Danube in late 98 to early 99, where he inspected existing fortification and initiated the construction of more forts and roads.
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
, a Roman Historian, records in his book ''Germania
Germania ( ; ), also more specifically called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman provinces of Germania Inferior and Germania Superio ...
'', which was written in 98AD, that the Osi tribes paid tribute to both the Iazyges and the Quadi, although the exact date this relationship began is unknown.
During the Flavian dynasty
The Flavian dynasty, lasting from 69 to 96 CE, was the second dynastic line of emperors to rule the Roman Empire following the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Julio-Claudians, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian and his two sons, Titus and Domitian. Th ...
, the princes of the Iazyges were trained in the Roman army, officially as an honor but in reality serving as a hostage, because the kings held absolute power over the Iazyges. There were offers from the princes of the Iazyges to supply troops but these were denied because of the fear they might revolt or desert in a war.
Dacian wars
An alliance between the Iazyges and the Dacians led the Romans to focus more on the Danube than the Rhine. This is shown by the placement of the Roman legions; during the time of Augustus's rule there were eight legions stationed along the Rhine, four stationed inMainz
Mainz (; #Names and etymology, see below) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, and with around 223,000 inhabitants, it is List of cities in Germany by population, Germany's 35th-largest city. It lies in ...
, and another four in Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
. Within a hundred years of Augustus' rule, however, Roman military resources had become centered along the Danube rather than the Rhine, with nine legions stationed along the Danube and only one at the Rhine. By the time of Marcus Aurelius, however, twelve legions were stationed along the Danube. The Romans also built a series of forts along the entire right bank of the Danube—from Germany to the Black Sea—and in the provinces of Rhaetia
Raetia or Rhaetia ( , ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west wit ...
, Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, R ...
, and Pannonia the legions constructed bridge-head forts. Later, this system was expanded to the lower Danube with the key castra of Poetovio, Brigetio, and Carnuntum
Carnuntum ( according to Ptolemy) was a Roman legionary fortress () and headquarters of the Roman navy, Pannonian fleet from 50 AD. After the 1st century, it was capital of the Pannonia Superior province. It also became a large city of app ...
. The Classis Pannonica and Classis Flavia Moesica were deployed to the right and lower Danube, respectively; they, however, had to overcome the mass of whirlpools and cataracts of the Iron Gates.
First Dacian War
Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
, with the assistance of the Iazyges, led his legions into Dacia against King Decebalus, in the year 101. In order to cross the Danube with such a large army, Apollodorus of Damascus, the Romans' chief architect, created a bridge through the Iron Gates by cantilevering it from the sheer face of the Iron Gates. From this he created a great bridge with sixty piers that spanned the Danube. Trajan used this to strike deep within Dacia, forcing the king, Decebalus, to surrender and become a client king.
Second Dacian War
As soon as Trajan returned to Rome, however, Decebalus began to lead raids into Roman territory and also attacked the Iazyges, who were still a client-tribe of Rome. Trajan concluded that he had made a mistake in allowing Decebalus to remain so powerful. In 106AD, Trajan again invaded Dacia, with 11 legions, and, again with the assistance of the Iazyges—who were the only barbarian tribe that aided the Romans in this war— and the only barbarian tribe in the Danube region which did not ally with Dacia. The Iazyges were the only tribe to aid Rome in both Dacian Wars, pushed rapidly into Dacia. Decebalus chose to commit suicide rather than be captured, knowing that he would be paraded in a triumph before being executed. In 113AD Trajan annexed Dacia as a new Roman province, the first Roman province to the east of the Danube. Trajan, however, did not incorporate the steppe between the Tisza river and the Transylvanian mountains into the province of Dacia but left it for the Iazyges. Back in Rome, Trajan was given a triumph lasting 123 days, with lavish gladiatorial games and chariot races. The wealth coming from the gold mines of Dacia funded these lavish public events and the construction of Trajan's Column, which was designed and constructed by Apollodorus of Damascus; it was tall and had 23 spiral bands filled with 2,500 figures, giving a full depiction of the Dacian war. Ancient sources say 500,000 slaves were taken in the war but moderns sources believe it was probably closer to 100,000 slaves.After the Dacian Wars
Ownership of the region ofOltenia
Oltenia (), also called Lesser Wallachia in antiquated versions – with the alternative Latin names , , and between 1718 and 1739 – is a historical province and geographical region of Romania in western Wallachia. It is situated between the Da ...
became a source of dispute between the Iazyges and the Roman empire. The Iazyges had originally occupied the area before the Dacians seized it; it was taken during the Second Dacian War by Trajan, who was determined to constitute Dacia as a province. The land offered a more direct connection between Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
and the new Roman lands in Dacia, which may be the reason Trajan was determined to keep it. The dispute led to war in 107–108, where the future emperor Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia '' ...
, then governor of Pannonia Inferior, defeated them. The exact terms of the peace treaty are not known, but it is believed the Romans kept Oltenia in exchange for some form of concession, likely involving a one-time tribute payment. The Iazyges also took possession of Banat around this time, which may have been part of the treaty.
In 117, the Iazyges and the Roxolani invaded Lower Pannonia and Lower Moesia, respectively. The war was probably brought on by difficulties in visiting and trading with each other because Dacia lay between them. The Dacian provincial governor Gaius Julius Quadratus Bassus was killed in the invasion. The Roxolani surrendered first, so it is likely the Romans exiled and then replaced their client king with one of their choosing. The Iazyges then concluded peace with Rome. The Iazyges and other Sarmatians invaded Roman Dacia in 123, likely for the same reason as the previous war; they were not allowed to visit and trade with each other. Marcius Turbo stationed 1,000 legionaries in the towns Potaissa and Porolissum, which the Romans probably used as the invasion point into Rivulus Dominarum. Marcius Turbo succeeded in defeating the Iazyges; the terms of the peace and the date, however, are not known.
Marcomannic Wars
 In 169, the Iazyges, Quadi,
In 169, the Iazyges, Quadi, Suebi
file:1st century Germani.png, 300px, The approximate positions of some Germanic peoples reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 1st century. Suebian peoples in red, and other Irminones in purple.
The Suebi (also spelled Suavi, Suevi or Suebians ...
, and Marcomanni once again invaded Roman territory. The Iazyges led an invasion into Alburnum in an attempt to seize its gold mines. The exact motives for and directions of the Iazyges' war efforts are not known. Marcus Claudius Fronto, who was a general during the Parthian wars and then the governor of both Dacia and Upper Moesia, held them back for some time but was killed in battle in 170. The Quadi surrendered in 172, the first tribe to do so; the known terms of the peace are that Marcus Aurelius installed a client-king Furtius on their throne and the Quadi were denied access to the Roman markets along the Roman Limes, limes. The Marcomanni accepted a similar peace but the name of their client-king is not known.
In 173, the Quadi rebelled and overthrew Furtius and replaced him with Ariogaesus, who wanted to enter into negotiations with Marcus. Marcus refused to negotiate because the success of the Marcomannic wars was in no danger. At that point the Iazyges had not yet been defeated by Rome. having not acted, Marcus Aurelius appears to have been unconcerned, but when the Iazyges attacked across the frozen Danube in late 173 and early 174, Marcus redirected his attention to them. Trade restrictions on the Marcomanni were also partially lifted at that time; they were allowed to visit the Roman markets at certain times of certain days. In an attempt to force Marcus to negotiate, Ariogaesus began to support the Iazyges. Marcus Aurelius put out a bounty on him, offering 1,000 aurei for his capture and delivery to Rome or 500 aurei for his severed head. After this, the Romans captured Ariogaesus but rather than executing him, Marcus Aurelius sent him into exile.
In the winter of 173, the Iazyges launched a raid across the frozen Danube but the Romans were ready for pursuit and followed them back to the Danube. Knowing the Roman legionaries were not trained to fight on ice, and that their own horses had been trained to do so without slipping, the Iazyges prepared an ambush, planning to attack and scatter the Romans as they tried to cross the frozen river. The Roman army, however, formed a solid square and dug into the ice with their shields so they would not slip. When the Iazyges could not break the Roman lines, the Romans counter-attacked, pulling the Iazyges off of their horses by grabbing their spears, clothing, and shields. Soon both armies were in disarray after slipping on the ice and the battle was reduced to many brawls between the two sides, which the Romans won. After this battle the Iazyges—and presumably the Sarmatians in general—were declared the primary enemy of Rome.
The Iazyges surrendered to the Romans in March or early April of 175. Their prince Banadaspus had attempted peace in early 174 but the offer was refused and Banadaspus was deposed by the Iazyges and replaced with Zanticus. The terms of the peace treaty were harsh; the Iazyges were required to provide 8,000 men as auxiliaries and release 100,000 Romans they had taken hostage, and were forbidden from living within ten Roman miles (roughly of the Danube. Marcus had intended to impose even harsher terms; it is said by Cassius Dio that he wanted to entirely exterminate the Iazyges but was distracted by the rebellion of Avidius Cassius. During this peace deal, Marcus Aurelius broke from the Roman custom of Emperors sending details of peace treaties to the Roman Senate; this is the only instance in which Marcus Aurelius is recorded to have broken this tradition. Of the 8,000 auxiliaries, 5,500 of them were sent to Britannia to serve with the Legio VI Victrix, suggesting that the situation there was serious; it is likely the British tribes, seeing the Romans being preoccupied with war in Germania and Dacia, had decided to rebel. All of the evidence suggests the Iazyges' horsemen were an impressive success. The 5,500 troops sent to Britain were not allowed to return home, even after their 20-year term of service had ended. After Marcus Aurelius had beaten the Iazyges; he took the title of ''Sarmaticus'' in accordance with the Roman military decorations and punishments#Victory titles, Roman practice of victory titles.
After the Marcomannic Wars
In 177, the Iazyges, the Buri tribe, Buri, and other Germanic tribes invaded Roman territory again. It is said that in 178, Marcus Aurelius took the bloody spear from the Temple of Bellona, Rome, Temple of Bellona and hurled it into the land of the Iazyges. In 179, the Iazyges and the Buri were defeated, and the Iazyges accepted peace with Rome. The peace treaty placed additional restrictions on the Iazyges but also included some concessions. They could not settle on any of the islands of the Danube and could not keep boats on the Danube. They were, however, permitted to visit and trade with the Roxolani throughout the Dacian Province with the knowledge and approval of its governor, and they could trade in the Roman markets at certain times on certain days. In 179, the Iazyges and the Buri joined Rome in their war against the Quadi and the Marcomanni after they secured assurances that Rome would prosecute the war to the end and not quickly make a peace deal. As part of a treaty made in 183, Commodus forbade the Quadi and the Marcomanni from waging war against the Iazyges, the Buri, or the Vandals, suggesting that at this time all three tribes were loyal client-tribes of Rome. In 214, however, Caracalla led an invasion into the Iazyges' territory. In 236, the Iazyges invaded Rome but were defeated by Emperor Maximinus Thrax, who took the title Sarmaticus Maximus following his victory. The Iazyges, Marcomanni, and Quadi raided Pannonia together in 248, and again in 254. It is suggested the reason for the large increase in the amount of Iazyx raids against Rome was that the Goths led successful raids, which emboldened the Iazyges and other tribes. In 260, the Goths took the cities of Tyras andOlbia
Olbia (, ; ; ) is a city and communes of Italy, commune of 61,000 inhabitants in the Italy, Italian insular province of Sassari in northeastern Sardinia, Italy, in the historical region of Gallura. Called in the Roman age, Civita in the Middle ...
, again cutting off the Iazyges' trade with the Pontic Steppe and the Black Sea. From 282 to 283, Emperor Carus lead a successful campaign against the Iazyges.
The Iazyges and Carpi (people), Carpi raided Roman territory in 293, and Diocletian responded by declaring war. From 294 to 295, Diocletian waged war upon them and won. As a result of the war, some of the Carpi were transported into Roman territory so they could be controlled. From 296 to 298, Galerius successfully campaigned against the Iazyges. In 358, the Iazyges were at war with Rome. In 375, Emperor Valentinian I, Valentinian had a stroke in Brigetio while meeting with envoys from the Iazyges. Around the time of the Gothic migration, which led the Iazyges to be surrounded on their northern and eastern borders by Gothic tribes, and most intensely during the reign of Constantine the Great, Constantine I, a series of earthworks known as the Devil's Dykes (Ördögárok) was built around the Iazygian territory, possibly with a degree of Roman involvement. Higham suggests that the Iazyges became more heavily tied to the Romans during this period, with strong cultural influence.
Late history and legacy
 In late antiquity, historic accounts become much more diffuse and the Iazyges generally cease to be mentioned as a tribe. Beginning in the 4th century, most Roman authors cease to distinguish between the different Sarmatian tribes, and instead refer to all as Sarmatians. In the late 4th century, two Sarmatian peoples were mentioned—the Argaragantes and the Limigantes, who lived on opposite sides of the
In late antiquity, historic accounts become much more diffuse and the Iazyges generally cease to be mentioned as a tribe. Beginning in the 4th century, most Roman authors cease to distinguish between the different Sarmatian tribes, and instead refer to all as Sarmatians. In the late 4th century, two Sarmatian peoples were mentioned—the Argaragantes and the Limigantes, who lived on opposite sides of the Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa (see below) is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. It was once called "the most Hungarian river" because it used to flow entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national bo ...
river. One theory is that these two tribes were formed when the Roxolani conquered the Iazyges, after which the Iazyges became the Limigantes and the Roxolani became the Argaragantes. Another theory is that a group of Early Slavs, Slavic tribesmen who gradually migrated into the area were subservient to the Iazyges; the Iazyges became known as the Argaragantes and the Slavs were the Limigantes. Yet another theory holds that the Roxolani were integrated into the Iazyges. Regardless of which is true, in the 5th century both tribes were conquered by the Goths and, by the time of Attila, they were absorbed into the Huns.
Foreign relations
The Roman Empire
The Iazyges often harassed the Roman Empire after their arrival in the Pannonian Basin, but they never rose to become a true threat. During the 1st century, Rome used diplomacy to secure their northern borders, especially on the Danube, by way of befriending the tribes, and by sowing distrust amongst the tribes against each other. Rome defended their Danubian border not just by way of repelling raids, but also by levying diplomatic influence against the tribes and launching punitive expeditions. The combination of diplomatic influence and swift punitive expeditions allowed the Romans to force the various tribes, including the Iazyges, into becoming client states of the Roman Empire. Even after the Romans abandoned Dacia, they consistently projected their power north of the Danube against the Sarmatian tribes, especially during the reigns of Constantine the Great, Constantine, Constantius II, and Valentinian I, Valentinian. To this end, Constantine constructed a permanent bridge across the middle Danube in order to improve logistics for campaigns against the Goths and Sarmatians. Another key part of the relationship between the Roman Empire and the Sarmatian tribes was the settling of tribes in Roman lands, with emperors often accepting refugees from the Sarmatian tribes into nearby Roman territory. When the Huns arrived in the Russian steppes and conquered the tribes that were there, they often lacked the martial ability to force the newly conquered tribes to stay, leading to tribes like the Greuthungi, Vandals, Alans, andGoths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
migrating and settling within the Roman Empire rather than remaining subjects of the Huns. The Roman Empire benefited from accepting these refugee tribes, and thus continued to allow them to settle, even after treaties were made with Hunnic leaders such as Rugila and Attila that stipulated that the Roman Empire would reject all refugee tribes, with rival or subject tribes of the Huns being warmly received by Roman leaders in the Balkans.
Archeology
Around the time of Trajan, the Romans established routes between Dacia and Pannonia, with evidence of Roman goods appearing in Iazygian land occurring around 100AD, largely centered near important river crossings. Additionally, a small number of Roman inscriptions and buildings were made during this period, which scholar Nicholas Higham states suggests either a high degree of Romanization or the presence of diplomatic or military posts within Iazygian territory. Roman goods were widespread in the second and early third centuryAD, especially near Aquincum, the capital of Roman Pannonia Inferior, and the area east to the Tizsa valley.Roxolani
The Iazyges also had a strong relationship with theRoxolani
The Roxolani or Rhoxolāni ( , ; ) were a Sarmatian people documented between the 2nd century BC and the 4th century AD, first east of the Borysthenes (Dnieper) on the coast of Lake Maeotis (Sea of Azov), and later near the borders of Roman Daci ...
, another Sarmatian tribe, both economically and diplomatically. During the second Dacian War, where the Iazyges supported the Romans, while the Roxolani supported the Dacians, the Iazyges and Roxolani remained neutral to each other. After the Roman annexation of Dacia, the two tribes were effectively isolated from each other, until the 179 peace concession from Emperor Marcus Aurelius which permitted the Iazyges and Roxolani to travel through Dacia, subject to the approval of the governor. Because of the new concession allowing them to trade with the Roxolani they could, for the first time in several centuries, trade indirectly with the Pontic Steppe and the Black Sea. It is believed the Iazyges traveled through Small Wallachia until they reached the Wallachian Plain, but there is little archeological evidence to prove this. Cypraea shells began to appear in this area in the last quarter of the 2nd century.
Quadi
The scholar Higham suggests that there was some degree of "long-term collaboration" between the Iazyges and theQuadi
The Quadi were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people during the Roman era, who were prominent in Greek and Roman records from about 20 AD to about 400 AD. By about 20 AD they had a kingdom centred in the area of present-day western Slovakia, north ...
, noting that they were allied in the late 2nd centuryAD, and that the Iazyges ceded the western portions of their land to them shortly after arriving in the Pannonian Basin, apparently without conflict.
List of princes
* Gesander (prince), Gesander ?? * Banadaspus: ?174AD * Zanticus (prince), Zanticus: 174AD? * Benga (prince), Benga and Babaï (prince), Babaï: co-rulers in 470471ADSee also
* Jasz people * Gothic Wars * Pannonian AvarsNotes
References
Sources
Primary sources
* Ammianus Marcellinus in ''Res Gestae'' (22.30) *Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history of ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
in ''Roman History'' (67.5, 68.10, 69.15–22, 71.7–17, 72, 73.2)
* Eutropius (historian), Eutropius in ''Eutropii Breviarium'' (7.23, 8.3)
* Gaius Valerius Flaccus, Flaccus in ''Argonautica'' (173–180)
* Gaius Valerius Flaccus in ''Argonautica'' (6.323−339, 7.123, 7.288)
* Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
in ''Natural History (Pliny), Natural History'' (4.80−81)
* Ptolemy in ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'' (3.5–8)
* Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
in ''Geography'' (2.5, 7.2−3, 11.2–5)
* Suetonius in ''De vita Caesarum'' (12.6)
* Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
in ''The History'' (1.79, 2.80−81, 3.5), ''The Annals'' (12.29–30), and Agricola (book), ''Agricola'' (41)
* John Xiphilinus (historian), Xiphilinus in ''Epitome of Dio'' (250.17–251.22, 259–260)
Modern sources
Books
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Copy at Google books (searching Metanastae)
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Websites
* * *Further reading
* Bennett, Julian (1997). ''Trajan: Optimus Princeps''. Bloomington, IN: Indianapolis University Press. . * Birley, Anthony (1987). ''Marcus Aurelius: A Biography''. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. . * . * Christian, David (1999). ''A History of Russia, Mongolia and Central Asia'', Vol. 1. Blackwell. . * * Kerr, William George (1995). ''A Chronological Study of the Marcomannic Wars of Marcus Aurelius''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. . * Gyula Kristó, Kristó, Gyula (1998). ''Magyarország története – 895–1301'' [''The History of Hungary – From 895 to 1301'']. Budapest: Osiris. . * Macartney, C. A. (1962). ''Hungary: A Short History''. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. . * Peck, Harry Thurston (1898). ''Harpers Dictionary of Classical Antiquities''. New York: Harper and Brothers. . * Strayer, Joseph R., editor in chief (1987). ''A Dictionary of the Middle Ages''. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. .External links
* {{Commons category inline, Iazyges Ancient tribes in Dacia Ancient tribes in Hungary Ancient tribes in Serbia Historical Iranian peoples Iranian nomads Roman buffer states Roman Dacia Sarmatian tribes Serbia in the Roman era