Hydrography Of The San Francisco Bay Area on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Hydrography of the San Francisco Bay Area is a complex network of watersheds, marshes, rivers, creeks, reservoirs, and bays predominantly draining into the
The Hydrography of the San Francisco Bay Area is a complex network of watersheds, marshes, rivers, creeks, reservoirs, and bays predominantly draining into the
 The Hydrography of the San Francisco Bay Area is a complex network of watersheds, marshes, rivers, creeks, reservoirs, and bays predominantly draining into the
The Hydrography of the San Francisco Bay Area is a complex network of watersheds, marshes, rivers, creeks, reservoirs, and bays predominantly draining into the San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay (Chochenyo language, Chochenyo: 'ommu) is a large tidal estuary in the United States, U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the cities of San Francisco, California, San ...
and Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
.
Bays
The largest bodies of water in the Bay Area are theSan Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay (Chochenyo language, Chochenyo: 'ommu) is a large tidal estuary in the United States, U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the cities of San Francisco, California, San ...
, San Pablo Bay
San Pablo Bay is a tidal estuary that forms the northern extension of the San Francisco Bay in the East Bay and North Bay regions of the San Francisco Bay Area in northern California.
Most of the Bay is shallow; however, there is a deep wate ...
, and Suisun Bay
Suisun Bay ( ; Wintun for "where the west wind blows") is a shallow tidal estuary (a northeastern extension of the San Francisco Bay) in Northern California. It lies at the confluence of the Sacramento River and San Joaquin River, forming the e ...
. The San Francisco Bay is one of the largest bays in the world. Many inlets on the edges of the three major bays are designated as bays in their own right, such as Richardson Bay
Richardson Bay (originally Richardson's Bay) is a shallow, ecology, ecologically rich arm of San Francisco Bay, managed under by the Richardson Bay Regional Agency, created under a joint powers agreement by the County of Marin, Town of Tiburon, C ...
, San Rafael Bay, Grizzly Bay, and San Leandro Bay.
Nearby bays along the Pacific Coast include Bodega Bay
Bodega Bay () is a shallow, rocky inlet of the Pacific Ocean on the coast of northern California in the United States. It is approximately across and is located approximately northwest of San Francisco and west of Santa Rosa, California, S ...
, Tomales Bay
Tomales Bay is a long, narrow inlet of the Pacific Ocean in Marin County in northern California in the United States.
Geography
Tomales Bay is approximately long and averages nearly wide, with relatively shallow depths averaging 18 ft, eff ...
, Drakes Bay
Drakes Bay ( Coast Miwok: ''Tamál-Húye'') is a bay along the Point Reyes National Seashore on the coast of northern California in the United States, approximately northwest of San Francisco at approximately 38 degrees north latitude. The ...
, Bolinas Bay, and Half Moon Bay
Half Moon Bay is a coastal city in San Mateo County, California, San Mateo County, California, United States, approximately south of San Francisco. Its population was 11,795 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Immediately north of Half Mo ...
.
Rivers
The largest rivers are theSacramento
Sacramento ( or ; ; ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of California and the seat of Sacramento County. Located at the confluence of the Sacramento and American Rivers in Northern California's Sacramento Valley, Sacramento's 2020 p ...
and San Joaquin Rivers, which drain into the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta and thence to Suisun Bay
Suisun Bay ( ; Wintun for "where the west wind blows") is a shallow tidal estuary (a northeastern extension of the San Francisco Bay) in Northern California. It lies at the confluence of the Sacramento River and San Joaquin River, forming the e ...
. Other major rivers of the North Bay are the Napa River
The Napa River is a river approximately long in the U.S. state of California. It drains a famous wine-growing region called the Napa Valley, in the mountains north of the San Francisco Bay. Milliken Creek and Mt. Veeder watersheds are a f ...
, the Petaluma River
The Petaluma River is a river in the California counties of Sonoma and Marin that becomes a tidal slough for most of its length. The headwaters are in the area southwest of Cotati. The flow is generally southward through Petaluma's old town, ...
, the Gualala River, and the Russian River; the former two drain into San Pablo Bay
San Pablo Bay is a tidal estuary that forms the northern extension of the San Francisco Bay in the East Bay and North Bay regions of the San Francisco Bay Area in northern California.
Most of the Bay is shallow; however, there is a deep wate ...
, the latter two into the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
.
In the South Bay, the Guadalupe River drains into San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay (Chochenyo language, Chochenyo: 'ommu) is a large tidal estuary in the United States, U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the cities of San Francisco, California, San ...
near Alviso.
Creeks
The Bay Area has a network ofstreams
A stream is a continuous body of surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long, large stream ...
that are generally called creeks, but sometimes called arroyos, due to the Spanish language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, gl ...
heritage evident in names such as Santa Rosa Creek and San Pablo Creek. Due to low rainfall in the summer months (May–October), many Bay Area creeks are intermittent, flowing above ground only during part of the year.
Political groups have been formed to preserve creeks or restore creeks which have been culverted for development. Baxter Creek in Contra Costa County
Contra Costa County (; ''Contra Costa'', Spanish language, Spanish for 'Opposite Coast') is a U.S. county, county located in the U.S. state of California, in the East Bay of the San Francisco Bay Area. As of the 2020 United States census, the ...
has been daylighted in various points along its piped route by Friends of Baxter Creek. Other organizations include Friends of Five Creeks, which monitors, restores, cleans and educates in relation to creeks flowing from the Berkeley Hills
The Berkeley Hills are a range of the Pacific Coast Ranges, and overlook the northeast side of the valley that encompasses San Francisco Bay. They were previously called the "Contra Costa Range/Hills" (from the original Spanish ''Sierra de la Co ...
to the Eastshore Estuary in the East Bay
The East Bay is the eastern region of the San Francisco Bay Area and includes cities along the eastern shores of San Francisco Bay and San Pablo Bay. The region has grown to include inland communities in Alameda and Contra Costa counties. Wi ...
.
Springs
The Bay Area has springs which are the source of most of the minor creeks in the East Bay hills such as Garrity Creek. In the North Bay there are hot springs which serve as further tourist attractions toWine Country
Wine Country is a region of California, in the northern San Francisco Bay Area, known worldwide as a premier wine-growing region. The region is famed for its wineries, its cuisine, Michelin star restaurants, boutique hotels, luxury resorts ...
tourists and spa goers.
Lakes
The Bay Area has many lakes, particularly if one includes artificial ones such asLake Berryessa
Lake Berryessa is the largest lake in Napa County, California, United States. This reservoir in the Vaca Mountains was formed following the construction of the Monticello Dam on Putah Creek in the 1950s. Since the early 1960s, this reservoir h ...
. Some are very small (such as Jewel Lake in Berkeley
Berkeley most often refers to:
*Berkeley, California, a city in the United States
**University of California, Berkeley, a public university in Berkeley, California
*George Berkeley (1685–1753), Anglo-Irish philosopher
Berkeley may also refer to ...
) and others are covered ( Summit Reservoir, for example). Lake Merced
Lake Merced () is a freshwater lake located on the West Side of San Francisco, in the southwest corner of the city. It is surrounded by three golf courses (the private Olympic Club and San Francisco Golf Club, and the public TPC Harding Park), as ...
and Lake Merritt
Lake Merritt is a lake located in a large tidal lagoon basin in the center of Oakland, California, just east of Downtown. It is named after Samuel Merritt, Oakland's mayor in 1867–1869, who had the lagoon dammed turning the varying tidal lag ...
are salt lakes; the former is drying up while the latter is a closed off estuarine cove.
Aquifers
Due to pollution of surface water, much of the area's potable water is located underground, for instance in the Mocho Subbasin of theLivermore Valley
The Livermore Valley, historically known as the Valle de San José (Valley of San José), is a valley in Alameda County, California, located in the East Bay region. The city of Livermore is located in the valley. The valley became known as "Liver ...
. As these aquifers get drawn down by pumping, there is increasing interest in ways to speed up the recharging of these resources.
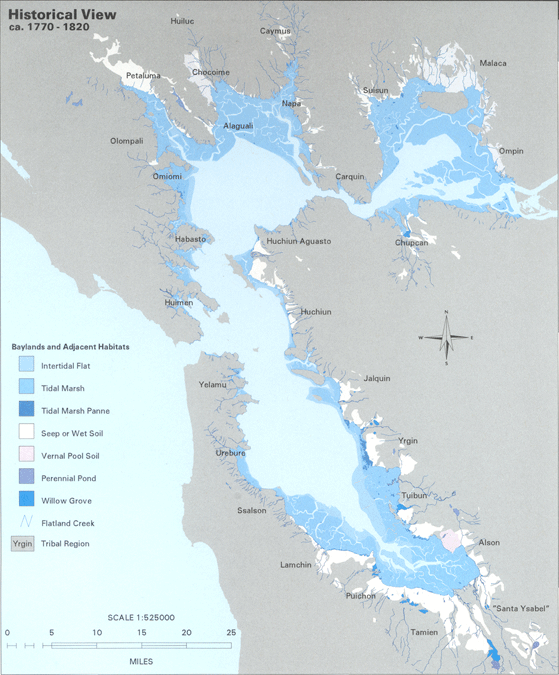
Wetlands
Prior to the introduction of European agricultural methods, the shores of San Francisco Bay consisted mostly of tidal marshes. Approximately 85% of those marshes have been lost or destroyed, but about 50 marshes and marsh fragments remain. In the Delta area, marshes were drained for farmland. In San Francisco, marshes were filled in for urban development. In the East Bay, portions were used as landfill. In the South Bay, huge tracts have served as commercialsalt evaporation pond
A salt evaporation pond is a shallow artificial salt pan designed to extract salts from sea water or other brines. The salt pans are shallow and expansive, allowing sunlight to penetrate and reach the seawater. Natural salt pans are formed thr ...
s. In the North Bay, the Napa Sonoma Marsh and Point Molate Marsh remain productive ecosystems. Some wetlands have been restored or protected from further development. Success stories include Eastshore State Park and Crissy Field
Crissy Field is a public recreation area on the northern shore of the San Francisco Peninsula in California, United States, located just east of the Golden Gate Bridge. It includes restored tidal marsh and beaches.
Crissy Field is a former Un ...
. Many native and recovered wetlands are preserved in the Don Edwards San Francisco Bay National Wildlife Refuge and the San Pablo Bay National Wildlife Refuge.
Wetlands also exist on the Pacific Coast (the Estero Americano, for instance) and in certain inland valleys: for example, the Laguna de Santa Rosa
The Laguna de Santa Rosa is a wetland complex that drains a watershed encompassing most of the Santa Rosa Plain in Sonoma County, California, United States.
The California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment has issued a safe ...
near Santa Rosa.
Transportation
The Bay Area is a large natural harbor. Around it have grown seaports and naval facilities. Active ports include the ports ofRichmond
Richmond most often refers to:
* Richmond, British Columbia, a city in Canada
* Richmond, California, a city in the United States
* Richmond, London, a town in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, England
* Richmond, North Yorkshire, a town ...
, Redwood City
Redwood City is a city on the San Francisco Peninsula in the Bay Area of Northern California, approximately south of San Francisco and northwest of San Jose. The city's population was 84,292 according to the 2020 census. The Port of Redwo ...
, San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
, and Oakland
Oakland is a city in the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area in the U.S. state of California. It is the county seat and most populous city in Alameda County, with a population of 440,646 in 2020. A major West Coast port, Oakland is ...
. Ships also traverse the bay heading to and from ports in Stockton and Sacramento
Sacramento ( or ; ; ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of California and the seat of Sacramento County. Located at the confluence of the Sacramento and American Rivers in Northern California's Sacramento Valley, Sacramento's 2020 p ...
. During World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
the region was the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
's major shipbuilding center for the Pacific. Former naval facilities include Point Molate Naval Fuel Depot, Alameda Point Naval Facility and Mare Island Naval Shipyard
The Mare Island Naval Shipyard (MINSY or MINS) was the first United States Navy base established on the Pacific Ocean and was in service 142 years from 1854 to 1996. It is located on Mare Island, northeast of San Francisco, in Vallejo, Califor ...
.
Many Bay Area cities have marinas, including Berkeley
Berkeley most often refers to:
*Berkeley, California, a city in the United States
**University of California, Berkeley, a public university in Berkeley, California
*George Berkeley (1685–1753), Anglo-Irish philosopher
Berkeley may also refer to ...
, Petaluma
Petaluma is a city in Sonoma County, California, United States, located in the North Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area. Its population was 59,776 according to the 2020 census.
Petaluma's name comes from the Miwok village named ''Péta ...
, and Redwood City
Redwood City is a city on the San Francisco Peninsula in the Bay Area of Northern California, approximately south of San Francisco and northwest of San Jose. The city's population was 84,292 according to the 2020 census. The Port of Redwo ...
.
There is also an extensive commuter ferry system, which is being expanded by the San Francisco Bay Water Transit Authority.
Oceanic harbors have been built at Bodega Bay
Bodega Bay () is a shallow, rocky inlet of the Pacific Ocean on the coast of northern California in the United States. It is approximately across and is located approximately northwest of San Francisco and west of Santa Rosa, California, S ...
and Half Moon Bay
Half Moon Bay is a coastal city in San Mateo County, California, San Mateo County, California, United States, approximately south of San Francisco. Its population was 11,795 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Immediately north of Half Mo ...
.
See also
* Ecology of the San Francisco Estuary * U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Bay ModelReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hydrography Of The San Francisco Bay AreaSan Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, commonly known as the Bay Area, is a List of regions of California, region of California surrounding and including San Francisco Bay, and anchored by the cities of Oakland, San Francisco, and San Jose, California, S ...
Geography of the San Francisco Bay Area
San Francisco Bay watershed
Water in California