Hugh Reeves on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hugh Quentin Alleyne Reeves (1909 – 25 October 1955) was a British inventor and engineer. He was one of the most productive and creative engineers attached to 
 Reeves was born at Seaford
Reeves was born at Seaford
Station IX
Station IX (formerly known as the Inter-Services Research Bureau) was a secret British Special Operations Executive factory making special weapons and equipment during World War II.
The small Welbike paratrooper's motorcycle and the Welrod assa ...
the SOE research station during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.

 Reeves was born at Seaford
Reeves was born at Seaford Sussex
Sussex (Help:IPA/English, /ˈsʌsɪks/; from the Old English ''Sūþseaxe''; lit. 'South Saxons'; 'Sussex') is an area within South East England that was historically a kingdom of Sussex, kingdom and, later, a Historic counties of England, ...
. His first prep school was West Downs School
West Downs School, Romsey Road, Winchester, Hampshire, was an English independent preparatory school, which was established in 1897 and closed in 1988.
History Founding
The school was founded by Lionel Helbert (1870–1919), with help from hi ...
at Winchester
Winchester (, ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs N ...
but he transferred to St Cyprian's School
St Cyprian's School was an English preparatory school for boys, which operated in the early 20th century in Eastbourne, East Sussex. Like other preparatory schools, its purpose was to train pupils to do well enough in the examinations (usual ...
, Eastbourne
Eastbourne () is a town and seaside resort in East Sussex, on the south coast of England, east of Brighton and south of London. It is also a non-metropolitan district, local government district with Borough status in the United Kingdom, bor ...
. He then went to Harrow
Harrow may refer to:
Places
* Harrow, Victoria, Australia
* Harrow, Ontario, Canada
* The Harrow, County Wexford, a village in Ireland
* London Borough of Harrow, England
* Harrow, London, a town in London
* Harrow (UK Parliament constituency)
* ...
and Sidney Sussex College, Cambridge
Sidney Sussex College (historically known as "Sussex College" and today referred to informally as "Sidney") is a Colleges of the University of Cambridge, constituent college of the University of Cambridge in England. The College was founded in 1 ...
.
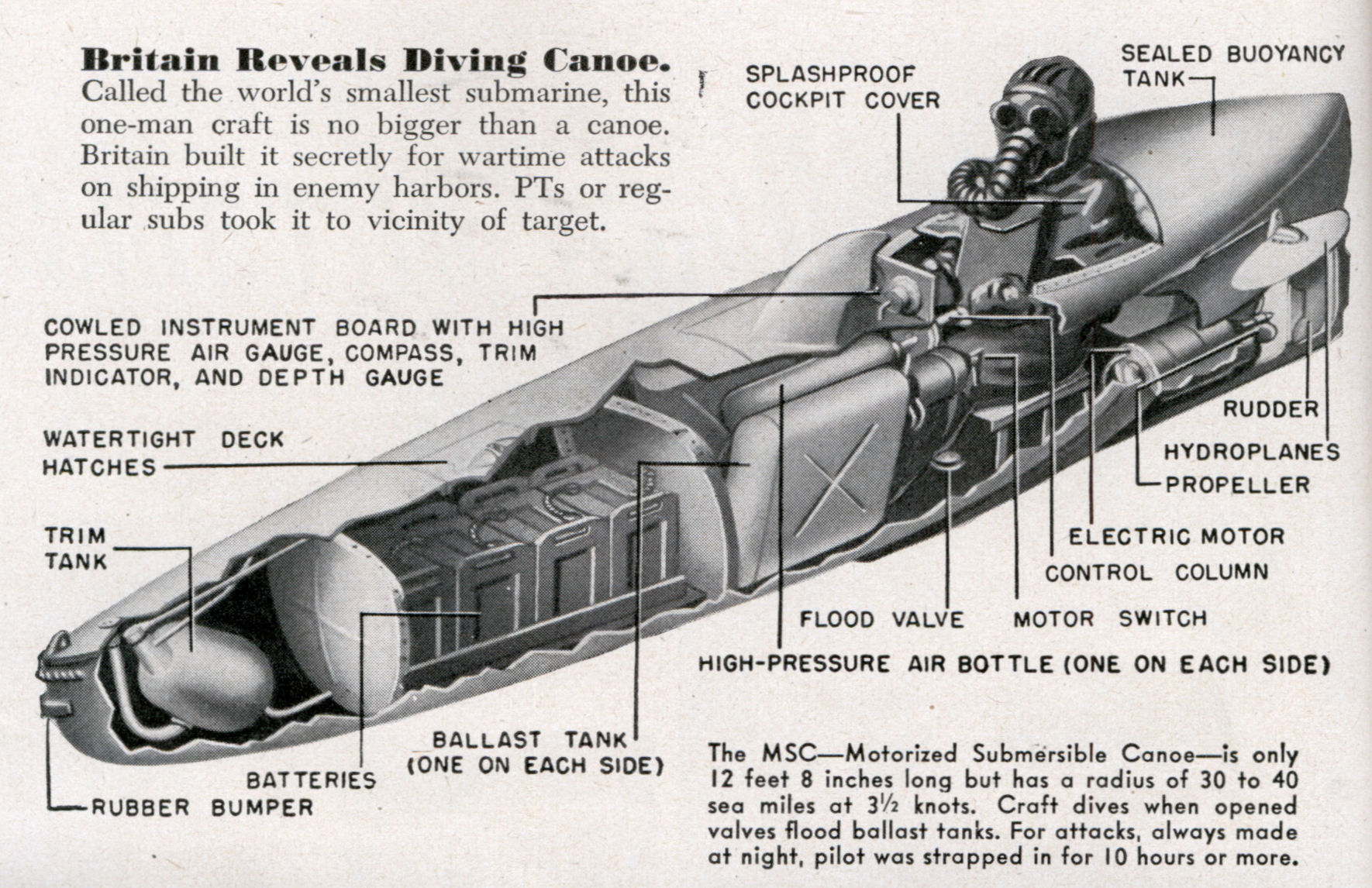
During World War II Major Reeves was attached to Station IX, where he invented both the Welrod and the sleeve gun (similar to the Welrod, though single shot and intended to be concealed up a sleeve), as well as designing the Motorised Submersible Canoe
The Motorised Submersible Canoe (MSC), nicknamed Sleeping Beauty, was an underwater vehicle built by the British Special Operations Executive (SOE) during the Second World War. It was designed to enable a single frogman to sabotage enemy ships, ...
. He was also, among others, behind the silencer for the Sten gun
The STEN (or Sten gun) is a British submachine gun chambered in 9×19mm which was used extensively by British and Commonwealth forces throughout World War II and during the Korean War. The Sten paired a simple design with a low production co ...
, fluorescent night sights, the Welgun and the Welbum propulsion system. This was made clear in a document that was produced at the end of the war to ensure that the correct people were credited for their inventions.
Reeves continued inventing after the war with patents for ''Improvements in Diving Equipment'' in 1950 and ''Wheel holding chocks for Aircraft'' in 1955.
Death
Reeves was involved in a project to reduce noise in jet engines. While carrying out tests at RAF Bitteswell on a Hawker Hunter F.5 fitted with a Sapphire engine, he was suddenly drawn into the intake of the silencer and was killed.References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Reeves, H Q A 1909 births 1955 deaths People educated at Harrow School People educated at St Cyprian's School Alumni of Sidney Sussex College, Cambridge 20th-century British inventors Victims of aviation accidents or incidents in England Victims of aviation accidents or incidents in 1955