Hsaing Waing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The ''hsaing waing'' ( my, ဆိုင်းဝိုင်း, ; also spelt ''saing waing''), commonly dubbed the Burmese traditional orchestra (မြန်မာ့ဆိုင်း), is a traditional Burmese folk musical ensemble that accompanies numerous forms of rituals, performances, and ceremonies in modern-day Myanmar (Burma).
''Hsaing waing'' musicians use a hemitonic and anhemitonic scale similar to the one used by Indonesian gamelan musicians. The ensemble's principal instruments, including the ''pat waing'', ''kyi waing'', and ''hne'', each play variations on a single melody ( heterophony).
The ''hsaing waing'' ( my, ဆိုင်းဝိုင်း, ; also spelt ''saing waing''), commonly dubbed the Burmese traditional orchestra (မြန်မာ့ဆိုင်း), is a traditional Burmese folk musical ensemble that accompanies numerous forms of rituals, performances, and ceremonies in modern-day Myanmar (Burma).
''Hsaing waing'' musicians use a hemitonic and anhemitonic scale similar to the one used by Indonesian gamelan musicians. The ensemble's principal instruments, including the ''pat waing'', ''kyi waing'', and ''hne'', each play variations on a single melody ( heterophony).
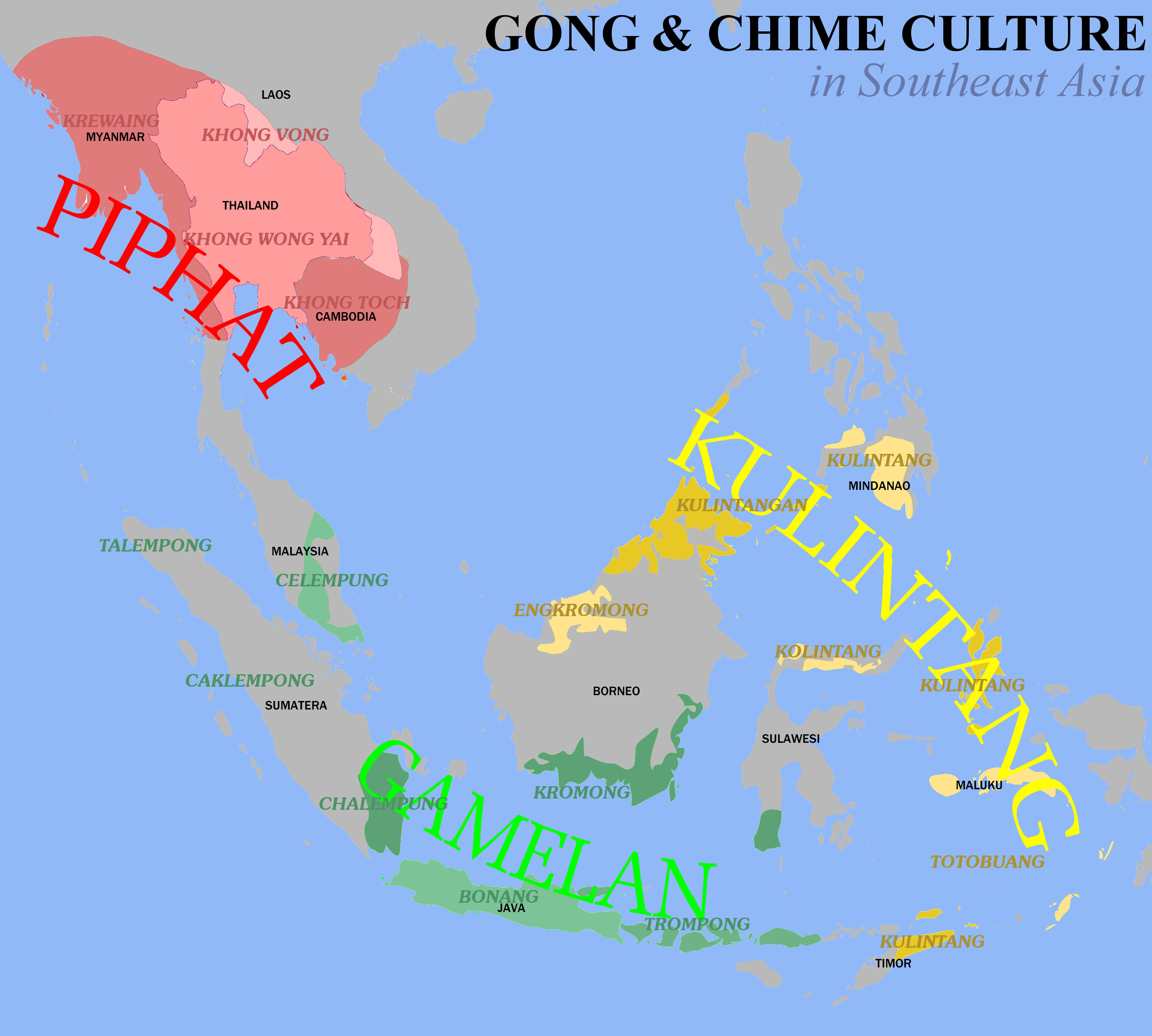 The ''hsaing waing'' is the product of indigenous musical traditions, enriched with contact with a diverse array of musical traditions in neighboring Southeast Asian societies. The ''hsaing waing'' ensemble's principal instrument, a drum circle called '' pat waing'', continues to use Indian drum-tuning methods, and is considered the last remaining vestige of Indian instrumentation in Southeast Asia. Similar gong and chime ensembles are found in neighboring Thailand and Laos, where it is called '' piphat'', and in Cambodia, where it is called '' pinpeat''. However, these ensembles do not employ the use of a ''pat waing''.
The ''hsaing waing'' is the product of indigenous musical traditions, enriched with contact with a diverse array of musical traditions in neighboring Southeast Asian societies. The ''hsaing waing'' ensemble's principal instrument, a drum circle called '' pat waing'', continues to use Indian drum-tuning methods, and is considered the last remaining vestige of Indian instrumentation in Southeast Asia. Similar gong and chime ensembles are found in neighboring Thailand and Laos, where it is called '' piphat'', and in Cambodia, where it is called '' pinpeat''. However, these ensembles do not employ the use of a ''pat waing''.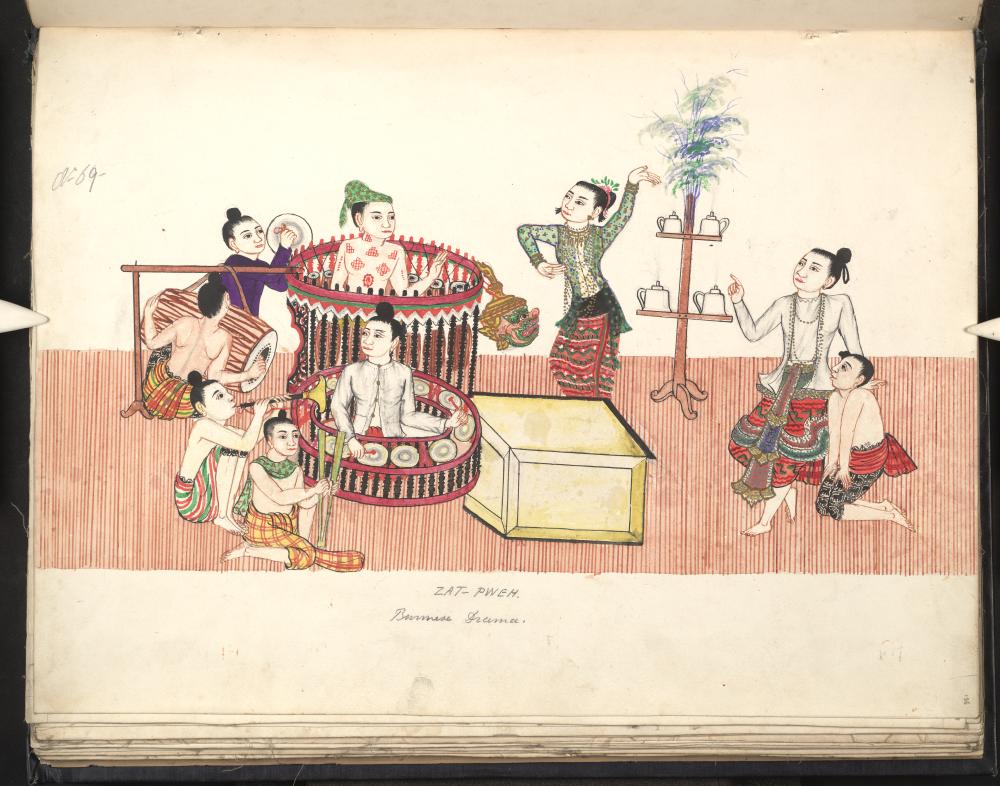 The earliest pictorial evidence of the ''hsaing waing'' ensemble dates to the 1600s, coinciding with the Burmese invasion of the
The earliest pictorial evidence of the ''hsaing waing'' ensemble dates to the 1600s, coinciding with the Burmese invasion of the
 The ''hsaing waing'' ensemble includes a variety of percussion and wind instruments, including various gongs and drums:
*'' Pat waing'' (ပတ်ဝိုင်း) ''or pat lon'' (ပတ်လုံး) - a set of 18 to 21 drums in a circle with a range of more than 3 octaves
*''Kyi waing'' (ကြေးဝိုင်း) - small bronze gongs in a circular frame
*''Maung hsaing'' (မောင်းဆိုင်း) - a gong chime made of larger bronze gongs in a rectangular frame
*''Wa letkhot'' (ဝါးလက်ခုပ်, ) - wooden clappers
*''Hne'' (နှဲ) - double reed oboe
*''Si'' (စည်း) - bell
*''Wa'' (ဝါး) - clapper
*''Si to'' (စည်းတို)
*''Lingwin'' (လင်းကွင်း) - cymbals
*''Sakhun'' (စခွန့်) - a double-headed drum on a stand
*''Chauk lon pat'' (ခြောက်လုံးပတ်, ) - a set of eight tuned drums
*''Pat ma gyi'' (ပတ်မကြီး) - a big drum suspended from a pole frame depicting a mythical '' pyinsarupa''
*''Min pauk'' (မင်းပေါက်, ) - entryway made in the panels, forming the framework of a drum-circle
For more formal and classical performances, the ensemble may be accompanied by the '' saung gauk,'' the Burmese harp, the '' pattala'', a Burmese xylophone, or the
The ''hsaing waing'' ensemble includes a variety of percussion and wind instruments, including various gongs and drums:
*'' Pat waing'' (ပတ်ဝိုင်း) ''or pat lon'' (ပတ်လုံး) - a set of 18 to 21 drums in a circle with a range of more than 3 octaves
*''Kyi waing'' (ကြေးဝိုင်း) - small bronze gongs in a circular frame
*''Maung hsaing'' (မောင်းဆိုင်း) - a gong chime made of larger bronze gongs in a rectangular frame
*''Wa letkhot'' (ဝါးလက်ခုပ်, ) - wooden clappers
*''Hne'' (နှဲ) - double reed oboe
*''Si'' (စည်း) - bell
*''Wa'' (ဝါး) - clapper
*''Si to'' (စည်းတို)
*''Lingwin'' (လင်းကွင်း) - cymbals
*''Sakhun'' (စခွန့်) - a double-headed drum on a stand
*''Chauk lon pat'' (ခြောက်လုံးပတ်, ) - a set of eight tuned drums
*''Pat ma gyi'' (ပတ်မကြီး) - a big drum suspended from a pole frame depicting a mythical '' pyinsarupa''
*''Min pauk'' (မင်းပေါက်, ) - entryway made in the panels, forming the framework of a drum-circle
For more formal and classical performances, the ensemble may be accompanied by the '' saung gauk,'' the Burmese harp, the '' pattala'', a Burmese xylophone, or the
 The ''hsaing waing'' ( my, ဆိုင်းဝိုင်း, ; also spelt ''saing waing''), commonly dubbed the Burmese traditional orchestra (မြန်မာ့ဆိုင်း), is a traditional Burmese folk musical ensemble that accompanies numerous forms of rituals, performances, and ceremonies in modern-day Myanmar (Burma).
''Hsaing waing'' musicians use a hemitonic and anhemitonic scale similar to the one used by Indonesian gamelan musicians. The ensemble's principal instruments, including the ''pat waing'', ''kyi waing'', and ''hne'', each play variations on a single melody ( heterophony).
The ''hsaing waing'' ( my, ဆိုင်းဝိုင်း, ; also spelt ''saing waing''), commonly dubbed the Burmese traditional orchestra (မြန်မာ့ဆိုင်း), is a traditional Burmese folk musical ensemble that accompanies numerous forms of rituals, performances, and ceremonies in modern-day Myanmar (Burma).
''Hsaing waing'' musicians use a hemitonic and anhemitonic scale similar to the one used by Indonesian gamelan musicians. The ensemble's principal instruments, including the ''pat waing'', ''kyi waing'', and ''hne'', each play variations on a single melody ( heterophony).
Origins
 The ''hsaing waing'' is the product of indigenous musical traditions, enriched with contact with a diverse array of musical traditions in neighboring Southeast Asian societies. The ''hsaing waing'' ensemble's principal instrument, a drum circle called '' pat waing'', continues to use Indian drum-tuning methods, and is considered the last remaining vestige of Indian instrumentation in Southeast Asia. Similar gong and chime ensembles are found in neighboring Thailand and Laos, where it is called '' piphat'', and in Cambodia, where it is called '' pinpeat''. However, these ensembles do not employ the use of a ''pat waing''.
The ''hsaing waing'' is the product of indigenous musical traditions, enriched with contact with a diverse array of musical traditions in neighboring Southeast Asian societies. The ''hsaing waing'' ensemble's principal instrument, a drum circle called '' pat waing'', continues to use Indian drum-tuning methods, and is considered the last remaining vestige of Indian instrumentation in Southeast Asia. Similar gong and chime ensembles are found in neighboring Thailand and Laos, where it is called '' piphat'', and in Cambodia, where it is called '' pinpeat''. However, these ensembles do not employ the use of a ''pat waing''. The earliest pictorial evidence of the ''hsaing waing'' ensemble dates to the 1600s, coinciding with the Burmese invasion of the
The earliest pictorial evidence of the ''hsaing waing'' ensemble dates to the 1600s, coinciding with the Burmese invasion of the Ayutthaya Kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom (; th, อยุธยา, , IAST: or , ) was a Siamese kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. The Ayutthaya Kingdom is consi ...
, which may have introduced additional instruments, principally a gong chime called ''kyi waing''. However, the Burmese ''hsaing waing'' differs greatly in its diversity of instruments and musical style from Thai ensembles. Many of the ''hsaing waing'' instruments are shared instead with the an ensemble of Mon origin, the Thai '' piphat mon'' ensemble, indicating shared origins.
During the British colonial era, Sein Beda
Sein Beda ( my, စိန်ဗေဒါ; also spelt Sein Baydar; 10 November 1882 – 8 October 1942) was a prominent Burmese classical musician based in Mandalay, Burma (now Myanmar).
Career
Sein Beda was known for his expertise in the hsa ...
, a prominent musician, introduced various innovations to the ensemble, including decorating ensemble stands with traditional Burmese motifs and glass mosaic, introducing a jazz band to the ensemble, creating spotlights, and introducing musician uniforms.
Instrumentation
 The ''hsaing waing'' ensemble includes a variety of percussion and wind instruments, including various gongs and drums:
*'' Pat waing'' (ပတ်ဝိုင်း) ''or pat lon'' (ပတ်လုံး) - a set of 18 to 21 drums in a circle with a range of more than 3 octaves
*''Kyi waing'' (ကြေးဝိုင်း) - small bronze gongs in a circular frame
*''Maung hsaing'' (မောင်းဆိုင်း) - a gong chime made of larger bronze gongs in a rectangular frame
*''Wa letkhot'' (ဝါးလက်ခုပ်, ) - wooden clappers
*''Hne'' (နှဲ) - double reed oboe
*''Si'' (စည်း) - bell
*''Wa'' (ဝါး) - clapper
*''Si to'' (စည်းတို)
*''Lingwin'' (လင်းကွင်း) - cymbals
*''Sakhun'' (စခွန့်) - a double-headed drum on a stand
*''Chauk lon pat'' (ခြောက်လုံးပတ်, ) - a set of eight tuned drums
*''Pat ma gyi'' (ပတ်မကြီး) - a big drum suspended from a pole frame depicting a mythical '' pyinsarupa''
*''Min pauk'' (မင်းပေါက်, ) - entryway made in the panels, forming the framework of a drum-circle
For more formal and classical performances, the ensemble may be accompanied by the '' saung gauk,'' the Burmese harp, the '' pattala'', a Burmese xylophone, or the
The ''hsaing waing'' ensemble includes a variety of percussion and wind instruments, including various gongs and drums:
*'' Pat waing'' (ပတ်ဝိုင်း) ''or pat lon'' (ပတ်လုံး) - a set of 18 to 21 drums in a circle with a range of more than 3 octaves
*''Kyi waing'' (ကြေးဝိုင်း) - small bronze gongs in a circular frame
*''Maung hsaing'' (မောင်းဆိုင်း) - a gong chime made of larger bronze gongs in a rectangular frame
*''Wa letkhot'' (ဝါးလက်ခုပ်, ) - wooden clappers
*''Hne'' (နှဲ) - double reed oboe
*''Si'' (စည်း) - bell
*''Wa'' (ဝါး) - clapper
*''Si to'' (စည်းတို)
*''Lingwin'' (လင်းကွင်း) - cymbals
*''Sakhun'' (စခွန့်) - a double-headed drum on a stand
*''Chauk lon pat'' (ခြောက်လုံးပတ်, ) - a set of eight tuned drums
*''Pat ma gyi'' (ပတ်မကြီး) - a big drum suspended from a pole frame depicting a mythical '' pyinsarupa''
*''Min pauk'' (မင်းပေါက်, ) - entryway made in the panels, forming the framework of a drum-circle
For more formal and classical performances, the ensemble may be accompanied by the '' saung gauk,'' the Burmese harp, the '' pattala'', a Burmese xylophone, or the piano
The piano is a stringed keyboard instrument in which the strings are struck by wooden hammers that are coated with a softer material (modern hammers are covered with dense wool felt; some early pianos used leather). It is played using a musica ...
and violin
The violin, sometimes known as a ''fiddle'', is a wooden chordophone (string instrument) in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in the family in regular ...
, both of which were introduced during the colonial era. The Mon version of the ''hsaing waing'' ensemble also includes a crescent-shaped brass gong chime called '' la gyan hsaing'' in Burmese.
Types
Music from the ''hsaing waing'' ensemble accompanies singing, dancing, and dialogues in all types of theatrical performances. Burmese scholarship recognizes 5 main types of ''hsaing waing'' ensembles: #''Bala hsaing (''ဗလာဆိုင်း) - performed at celebratory occasions such as weddings, Buddhist ordainment rituals ('' shinbyu''), ear-piercing ceremonies, funerals, lethwei competitions, and pagoda commemorations #''Zat hsaing (''ဇာတ်ဆိုင်း) - accompanies traditional dramatic theatre and play performances #''Yokthe hsaing'' (ရုပ်သေးဆိုင်း) - accompanies classical marionette (puppetry) shows #''Nat hsaing'' (နတ်ဆိုင်း) - accompanies spirit propitiation rituals #''Anyeint
Anyeint (; ; my, အငြိမ့်; also spelt a-nyeint) is a traditional Burmese entertainment form that combines dance with instrumental music, song, and comedy routines, in theatrical performances.Seekins, Donald M. (2006) "Anyeint (Any ...
hsaing'' (အငြိမ့်ဆိုင်း) - accompanies traditional ''anyeint'' performances
The distinct repertoire of recognizable tunes accompanies of each of these types of ''hsaing waing'' ensembles.
Musical styles
Music of the ''hsaing waing'' is characterized by dynamic, lively and sudden contrasts and shifts in rhythm, melody and tempo. The melody typically follows a regular meter of 4 to 8 beats. ''Anyeint
Anyeint (; ; my, အငြိမ့်; also spelt a-nyeint) is a traditional Burmese entertainment form that combines dance with instrumental music, song, and comedy routines, in theatrical performances.Seekins, Donald M. (2006) "Anyeint (Any ...
'' dance performances, as well as nat gadaw and marionette
A marionette (; french: marionnette, ) is a puppet controlled from above using wires or strings depending on regional variations. A marionette's puppeteer is called a marionettist. Marionettes are operated with the puppeteer hidden or reveale ...
puppet performances, are accompanied by the music of the ''hsaing waing'', with the sudden shifts in musical rhythm reflected in the dancer's changing poses. The melody is shaped by tones; a complex system of pitches, principal and auxiliary tones, and melodic phrase terminals (cadential formulas), ornaments, and the vocal lines are associated with particular modes, which are context-driven (depending on environment and stage situations) and express varying emotions. The gong instrumentation provide repetitive motifs (see ostinato
In music, an ostinato (; derived from Italian word for ''stubborn'', compare English ''obstinate'') is a motif or phrase that persistently repeats in the same musical voice, frequently in the same pitch. Well-known ostinato-based pieces include ...
) during the course of a performance.
By contrast, classical singing of the Mahāgīta tradition derived from royal chamber music, which is characterized by a quieter and more restrained musical style, is accompanied by either a classical ensemble or a single ''saung gauk''.
See also
* Myanmar National Symphony Orchestra * Pinpeat * PiphatReferences
{{reflist Burmese music Burmese culture