Horizontally-opposed Piston Engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

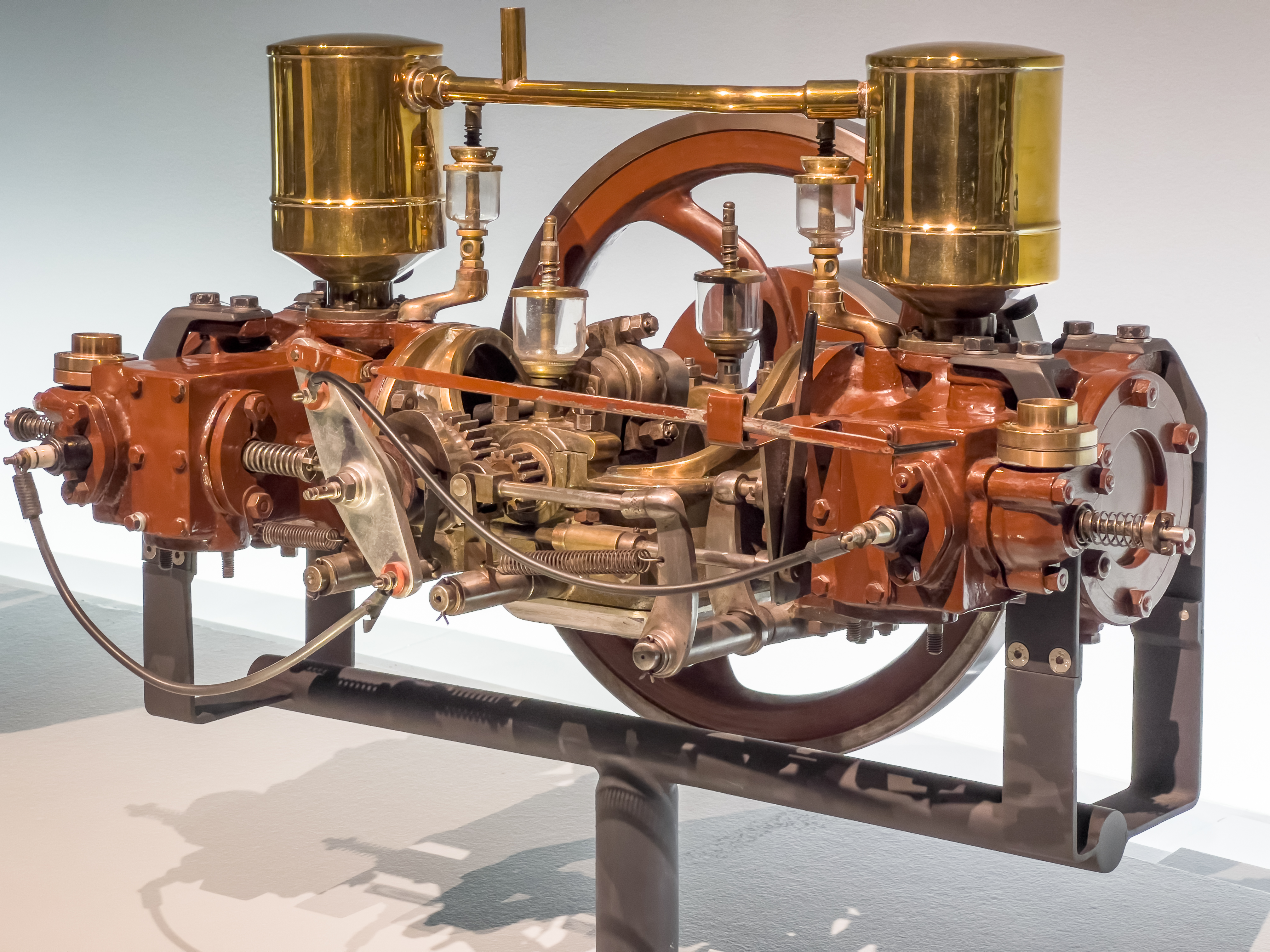 A flat engine is a
A flat engine is a
 Most flat engines use a "boxer" configuration, where each pair of opposing pistons move inwards and outwards at the same time, somewhat like boxing competitors punching their gloves together before a fight. Boxer engines have low vibration, being the only common configuration that has no unbalanced forces, regardless of the number of pairs of cylinders. Boxer engines therefore do not require either a
Most flat engines use a "boxer" configuration, where each pair of opposing pistons move inwards and outwards at the same time, somewhat like boxing competitors punching their gloves together before a fight. Boxer engines have low vibration, being the only common configuration that has no unbalanced forces, regardless of the number of pairs of cylinders. Boxer engines therefore do not require either a

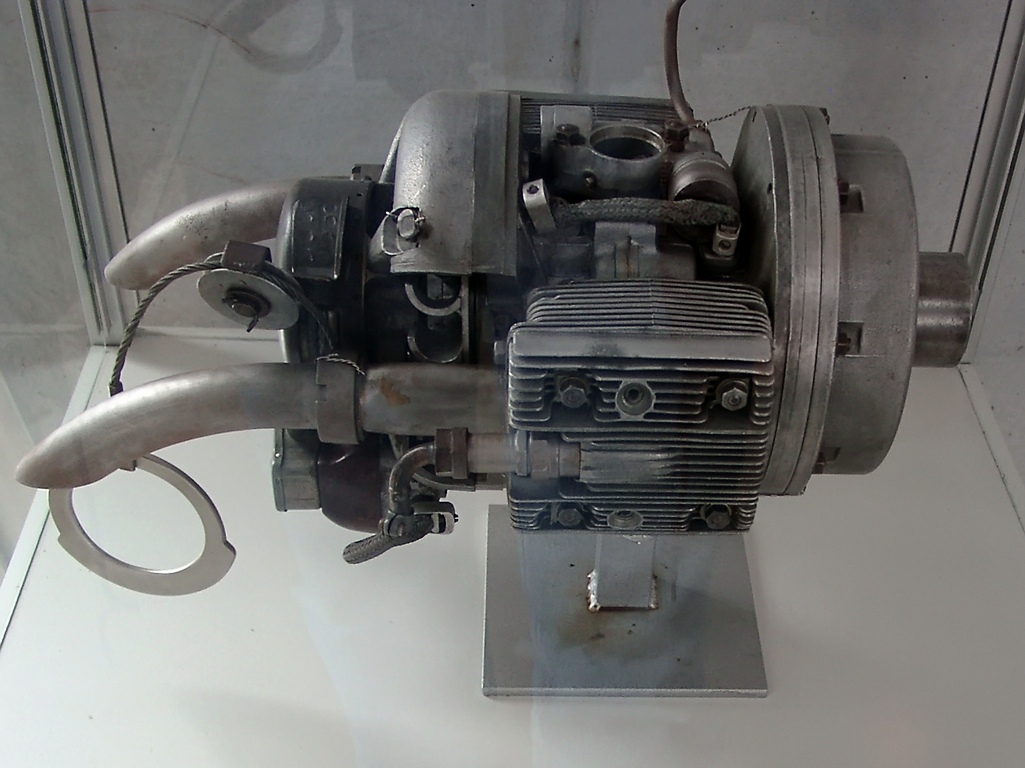 In 1902, the Pearse monoplane (which would later become one of the first aircraft to achieve flight) was powered by a flat-twin engine. Amongst the first commercially-produced aircraft to use a flat engine was the 1909 Santos-Dumont Demoiselle range of aeroplanes, which was powered by boxer-twin engines.
Several boxer-four engines have been produced specifically for light aircraft. A number of manufacturers produced boxer-six aircraft engines during the 1930s and 1940s.
During World War II, a boxer-twin engine called the "Riedel starter" was used as a starter motor/mechanical Auxiliary power unit#As mechanical "startup" APUs for jet engines, APU for the early German jet engines, such as the Junkers Jumo 004 and BMW 003. Designed by Norbert Riedel, these engines have a very Stroke ratio#Oversquare or short-stroke engine, oversquare stroke ratio of 2:1 so that they could fit within the intake diverter, directly forward of the turbine compressor.
In 1902, the Pearse monoplane (which would later become one of the first aircraft to achieve flight) was powered by a flat-twin engine. Amongst the first commercially-produced aircraft to use a flat engine was the 1909 Santos-Dumont Demoiselle range of aeroplanes, which was powered by boxer-twin engines.
Several boxer-four engines have been produced specifically for light aircraft. A number of manufacturers produced boxer-six aircraft engines during the 1930s and 1940s.
During World War II, a boxer-twin engine called the "Riedel starter" was used as a starter motor/mechanical Auxiliary power unit#As mechanical "startup" APUs for jet engines, APU for the early German jet engines, such as the Junkers Jumo 004 and BMW 003. Designed by Norbert Riedel, these engines have a very Stroke ratio#Oversquare or short-stroke engine, oversquare stroke ratio of 2:1 so that they could fit within the intake diverter, directly forward of the turbine compressor.

 A flat engine is a
A flat engine is a piston engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more Reciprocating motion, reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a Circular motion, rotating motion. This article ...
where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a reciprocating engine, piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating Shaft (mechanical engineering), shaft containing one or more crankpins, ...
. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine
An opposed-piston engine is a piston engine in which each cylinder (engine), cylinder has a piston at both ends, and no cylinder head. Petrol and diesel opposed-piston engines have been used mostly in large applications such as ships, military ...
design, whereby each cylinder has two pistons sharing a central combustion chamber.
The most common configuration of flat engines is the boxer engine
A flat engine is a Internal combustion engine#Reciprocating engines, piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct ...
configuration, in which the pistons of each opposed pair of cylinders move inwards and outwards at the same time. The other configuration is effectively a V engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder ...
with a 180-degree angle between the cylinder banks: in this configuration each pair of cylinders shares a single crankpin, so that as one piston moves inward, the other moves outward.
The first flat engine (Benz Contramotor) was built in 1897 by Karl Benz
Carl (or Karl) Friedrich Benz (; born Karl Friedrich Michael Vaillant; 25 November 1844 – 4 April 1929) was a German engine designer and automotive engineer. His Benz Patent-Motorwagen from 1885 is considered the first practical modern automo ...
. Flat engines have been used in aviation, motorcycle and automobile applications. They are now less common in cars than straight engine
The straight engine (also called inline engine) is a configuration of multi-cylinder piston engine where all of the cylinders are arranged in a single row, rather than radially or in two or more cylinder banks.
Design
A straight engine is eas ...
s (for engines with fewer than six cylinders) and V engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder ...
s (for engines with six or more cylinders). Flat engines are more common in aircraft, where straight engines are a rarity and V engines have almost vanished except in historical aircraft. They have even replaced radial engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating engine, reciprocating type internal combustion engine, internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinder (engine), cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. ...
s in many smaller installations.
Design
The advantages of flat engines are a short length, lowcentre of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. For a ...
and suitability for air cooling
Air cooling is a method of dissipating heat. It works by expanding the surface area or increasing the flow of air over the object to be cooled, or both. An example of the former is to add cooling fins to the surface of the object, either by maki ...
(due to the well-exposed, large-surface-area cylinders and cylinder heads, and their short length).
Compared with the more common straight engine
The straight engine (also called inline engine) is a configuration of multi-cylinder piston engine where all of the cylinders are arranged in a single row, rather than radially or in two or more cylinder banks.
Design
A straight engine is eas ...
s, flat engines have better primary balance
Engine balance refers to how the inertial forces produced by moving parts in an internal combustion engine or steam engine are neutralised with counterweights and balance shafts, to prevent unpleasant and potentially damaging vibration. The str ...
(resulting in less vibration); however, the disadvantages are increased width and the need to have two cylinder heads. Compared with V engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder ...
s – the most common layout for engines with six cylinders or more – flat engines again have a lower centre of mass, and, for six-cylinders, better primary balance; the disadvantage is again their being wider.
The most common usages of flat engines are:
* Flat-twin engine
A flat-twin engine is a two-cylinder internal combustion engine with the cylinders on opposite sides of the crankshaft. The most common type of flat-twin engine is the boxer-twin engine, where both pistons move inwards and outwards at the same ti ...
s are mostly used in motorcycles. Occasionally they have been used in light cars, aircraft and industrial applications, mostly up until the 1960s.
* Flat-four engine
A flat-four engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-four engine or boxer engine, is a four-cylinder piston engine with two banks of cylinders lying on opposite sides of a common crankshaft. The most common type of flat-four engine is the box ...
s are mostly used in cars (most notably in the earlier Volkswagen
Volkswagen (VW; )English: , . is a German automotive industry, automobile manufacturer based in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Established in 1937 by German Labour Front, The German Labour Front, it was revitalized into the global brand it ...
Types 1 to 4, and by Subaru
is the automaker, automobile manufacturing division of Japanese transportation conglomerate (company), conglomerate Subaru Corporation (formerly known as Fuji Heavy Industries), the Automotive industry#By manufacturer, twenty-first largest aut ...
in most of their models), and have occasionally been used in motorcycles. Their most common use is in smaller single-engine general-aviation aircraft, for which they are still manufactured and used to this day.
* Flat-six engine
A flat-six engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-six, is a six-cylinder piston engine with three cylinders on each side of a central crankshaft. The most common type of flat-six engine is the boxer-six engine, where each pair of opposed c ...
s are mostly used in aircraft and cars (particularly by the Porsche
Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, usually shortened to Porsche (; see below), is a German automobile manufacturer specializing in luxury, high-performance sports cars, SUVs and sedans, headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Th ...
911 sports car), and have occasionally been used in motorcycles.
* Flat-eight engine
A flat-eight engine, also called a horizontally-opposed eight, is an eight-cylinder piston engine with two banks of four inline cylinders, one on each side of a central crankshaft, 180° apart.
In a flat-eight engine, the connecting rods for corre ...
s have been used in several racing cars, mostly by Porsche in the 1960s.
* Flat-ten engine
A flat-ten engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-ten, is a ten-cylinder piston engine with five cylinders on each side of a central crankshaft.
There are no known flat-ten engines which reached production.
In the early 1960s, Chevrolet bui ...
s are not known to have reached production. A prototype road car engine was built by Chevrolet
Chevrolet ( ) is an American automobile division of the manufacturer General Motors (GM). In North America, Chevrolet produces and sells a wide range of vehicles, from subcompact automobiles to medium-duty commercial trucks. Due to the promi ...
in the 1960s.
* Flat-twelve engine
A flat-twelve engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-twelve, is a twelve-cylinder piston engine with six cylinders on each side of a central crankshaft.
Flat-twelve engines are less common than V12 engines, but they have been used in vari ...
s have been used in various racing cars, notably the Porsche 917K
The Porsche 917 is a sports prototype race car developed by German manufacturer Porsche to exploit the regulations regarding the construction of 5-litre sports cars. Powered by a Type 912 flat-12 engine which was progressively enlarged from 4 ...
, during the 1960s and 1970s, and in Ferrari
Ferrari S.p.A. (; ) is an Italian luxury sports car manufacturer based in Maranello. Founded in 1939 by Enzo Ferrari (1898–1988), the company built Auto Avio Costruzioni 815, its first car in 1940, adopted its current name in 1945, and be ...
road cars from 1973 to 1996. The Panhard EBR
The Panhard EBR (Panhard ''Engin Blindé de Reconnaissance'', French: Armored Reconnaissance Vehicle) is an armoured car designed by Panhard for the French Army and later used across the globe, notably by the French Army during the Algerian War ...
armoured car is one of the few military vehicles to have used such an engine.
* Flat-sixteen engine
A flat-sixteen engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-sixteen, is a sixteen-cylinder piston engine with eight cylinders on each side of a central crankshaft.
Flat-sixteen engines are less common than V16 engines, with only a couple of prot ...
s are not known to have reached production. Prototype racing car engines were built by Coventry
Coventry ( or rarely ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands county, in England, on the River Sherbourne. Coventry had been a large settlement for centurie ...
and Porsche in the 1960s and 1970s.
Boxer configuration
 Most flat engines use a "boxer" configuration, where each pair of opposing pistons move inwards and outwards at the same time, somewhat like boxing competitors punching their gloves together before a fight. Boxer engines have low vibration, being the only common configuration that has no unbalanced forces, regardless of the number of pairs of cylinders. Boxer engines therefore do not require either a
Most flat engines use a "boxer" configuration, where each pair of opposing pistons move inwards and outwards at the same time, somewhat like boxing competitors punching their gloves together before a fight. Boxer engines have low vibration, being the only common configuration that has no unbalanced forces, regardless of the number of pairs of cylinders. Boxer engines therefore do not require either a balance shaft
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in the opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force ...
or counterweights on the crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a reciprocating engine, piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating Shaft (mechanical engineering), shaft containing one or more crankpins, ...
to balance the weight of the reciprocating parts. However, a rocking couple
In physics, a couple or torque is a pair of forces that are equal in magnitude but opposite in their direction of action. A couple produce a pure rotational motion without any translational form.
Simple couple
The simplest kind of couple consi ...
is present, since each cylinder is slightly offset from the other member of its pair due to the distance between the crankpins along the crankshaft.
180-degree V engine
An alternative configuration for flat engines is as a 180-degreeV engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder ...
, which has been used on most twelve-cylinder flat engines. In this configuration, each pair of pistons shares a crankpin, this being simpler than the boxer configuration, where each piston has its own separate crankpin.
Aviation use

 In 1902, the Pearse monoplane (which would later become one of the first aircraft to achieve flight) was powered by a flat-twin engine. Amongst the first commercially-produced aircraft to use a flat engine was the 1909 Santos-Dumont Demoiselle range of aeroplanes, which was powered by boxer-twin engines.
Several boxer-four engines have been produced specifically for light aircraft. A number of manufacturers produced boxer-six aircraft engines during the 1930s and 1940s.
During World War II, a boxer-twin engine called the "Riedel starter" was used as a starter motor/mechanical Auxiliary power unit#As mechanical "startup" APUs for jet engines, APU for the early German jet engines, such as the Junkers Jumo 004 and BMW 003. Designed by Norbert Riedel, these engines have a very Stroke ratio#Oversquare or short-stroke engine, oversquare stroke ratio of 2:1 so that they could fit within the intake diverter, directly forward of the turbine compressor.
In 1902, the Pearse monoplane (which would later become one of the first aircraft to achieve flight) was powered by a flat-twin engine. Amongst the first commercially-produced aircraft to use a flat engine was the 1909 Santos-Dumont Demoiselle range of aeroplanes, which was powered by boxer-twin engines.
Several boxer-four engines have been produced specifically for light aircraft. A number of manufacturers produced boxer-six aircraft engines during the 1930s and 1940s.
During World War II, a boxer-twin engine called the "Riedel starter" was used as a starter motor/mechanical Auxiliary power unit#As mechanical "startup" APUs for jet engines, APU for the early German jet engines, such as the Junkers Jumo 004 and BMW 003. Designed by Norbert Riedel, these engines have a very Stroke ratio#Oversquare or short-stroke engine, oversquare stroke ratio of 2:1 so that they could fit within the intake diverter, directly forward of the turbine compressor.
Motorcycle use
Flat engines offer several advantages for motorcycles including a lowcentre of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. For a ...
, low vibration, suitability for shaft drive, and equal cooling of the cylinders (for air-cooled engines). The most common design of flat engine for motorcycles is the boxer-twin, beginning with the 1905 Fée flat-twin engine, manufactured by the Light Motors Company, which was the first production motorcycle engine. BMW Motorrad have a long history of boxer-twin motorcycles, beginning in 1923 with the BMW R32
Several motorcycles have been produced with flat-four engines, such as the 1938–1939 Zündapp, Zündapp K800 and the 1974–1987 Honda Gold Wing. In 1987, the Honda Gold Wing engine was upsized to a flat-six design.
Automotive use
When used in cars, advantages of flat engines are a lowcentre of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. For a ...
(which improves the handling of the car), short length, low vibration and suitability for air cooling (due to the well exposed, large surface area, cylinder heads and short length). However the larger width of flat engines (compared with the more common inline and V layouts) is a drawback, particularly when the engine is located between the steered wheels.
Flat engines were used by various automobile manufacturers – mostly with a boxer-four design – up until the late 1990s. Since then, only Porsche and Subaru have remained as significant manufacturers of flat engines.
Drivetrain layout
Due to the short length of flat engines, locating a flat engine outside of the car's wheelbase results in minimal overhang. Therefore, many cars with flat engines have used a rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout. Examples include the flat-twin BMW 600 (1957–1959) and BMW 700 (1959–1965); the flat-four Tatra 97 (1936–1939), Volkswagen Beetle (1938–2003) and Porsche 356 (1948–1965); and the flat-six Chevrolet Corvair (1959–1969), Porsche 911 (1963-present), and Tucker 48 (1947–1948). The opposite layout, front-engine, front-wheel-drive layout, front-engine front-wheel drive, was also common for cars with flat engines. Examples include the Citroën 2CV (1948–1990), Panhard Dyna X (1948–1954), Lancia Flavia (1961–1970), Citroën GS (1970–1986), Alfa Romeo Alfasud (1971–1989) and Subaru Leone (1971–1994). Subaru have been producing cars with a front-engine, four-wheel-drive layout powered by flat engines (mostly boxer-four engines) since 1971. Examples include the Subaru Leone (1971–1994), Subaru Legacy (1989-present) and Subaru Impreza (1992–present). The front half-shafts come out of a front differential that is part of the gearbox. A rear driveshaft connects the gearbox to the rear half-shafts. The traditional front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout is relatively uncommon for cars with flat engines, however some examples include the Toyota 86, Toyota 86 / Subaru BRZ (2012–present), Jowett Javelin (1947–1953), Glas Isar (1958–1965) and the Tatra 11 (1923–1927).History
The first flat engine was produced in 1897 by German engineerKarl Benz
Carl (or Karl) Friedrich Benz (; born Karl Friedrich Michael Vaillant; 25 November 1844 – 4 April 1929) was a German engine designer and automotive engineer. His Benz Patent-Motorwagen from 1885 is considered the first practical modern automo ...
. Called the ''kontra'' engine, it was a boxer-twin design. Early uses of flat engines in cars include the 1900 Lanchester Motor Company, Lanchester 8 hp Phaeton boxer-twin, the 1901 Wilson-Pilcher boxer-four, the 1904 Wilson-Pilcher ''18/24 HP'' boxer-six and the 1903 Ford Model A (1903–1904), Ford Model A, the 1904 Ford Model C and the 1905 Ford Model F.
In 1938, the Volkswagen Beetle (then called the "KdF-Wagen") was released with a rear-mounted flat-four engine. This Volkswagen air-cooled engine was produced for many years and also used in the Volkswagen Type 2 (Transporter, Kombi or Microbus), the Volkswagen Karmann Ghia sports car and the Volkswagen Type 3 compact car. A water-cooled version, known as the Volkswagen Wasserboxer engine, Wasserboxer, was introduced in 1982 and eventually replaced the air-cooled versions.
The majority of sports cars throughout Porsche's history are powered by flat engines, beginning with its first car; the 1948-1965 Porsche 356 used an air-cooled boxer-four engine. Also using boxer-four engines were the 1969-1976 Porsche 914, the 1965-1969 Porsche 912 and the 2016-present Porsche 982, Porsche Boxster/Cayman (982). The Porsche 911 (classic), Porsche 911 has exclusively used boxer-six engines from its introduction in 1964 until the present. In 1997, the Porsche 911 switched from being air-cooled to water-cooled.
Porsche flat-eight engines were used in various racing cars throughout the 1960s, such as the 1962 Porsche 804 Formula One car and the 1968-1971 Porsche 908 sports car. A flat-twelve engine was also produced by Porsche for the 1969-1973 Porsche 917 sports car.
Chevrolet
Chevrolet ( ) is an American automobile division of the manufacturer General Motors (GM). In North America, Chevrolet produces and sells a wide range of vehicles, from subcompact automobiles to medium-duty commercial trucks. Due to the promi ...
used a horizontally opposed air-cooled 6 cylinder engine in its Chevrolet Corvair, Corvair line during its entire production run from 1960 to 1969 in various applications and power ratings, including one of the first uses of a turbocharger in a mass-produced automobile.
The Subaru EA engine was introduced in 1966 and began Subaru
is the automaker, automobile manufacturing division of Japanese transportation conglomerate (company), conglomerate Subaru Corporation (formerly known as Fuji Heavy Industries), the Automotive industry#By manufacturer, twenty-first largest aut ...
's line of boxer-four engines that remain in production to this day. Most of Subaru's models are powered by a boxer-four engine in either naturally aspirated or turbocharged form. A print ad for the 1973 Subaru GL coupe referred to the engine as "quadrozontal". The company also produced boxer-six engines from 1988 to 1996 and 2001–2019. In 2008, the List of Subaru engines#Subaru EE engine (diesel), Subaru EE engine became the world's first passenger car diesel boxer engine. This engine is a turbocharged boxer-four with common rail fuel injection.
Ferrari used flat-twelve engines for various Formula One cars in the 1970s. A road car flat-twelve engine (using a 180-degree V12 configuration) was used for the 1973-1984 Ferrari Berlinetta Boxer, 1984-1996 Ferrari Testarossa and their derivatives.
Toyota uses the designation ''Toyota 4U-GSE'' for the boxer-four engine in the Toyota-badged versions of the Toyota 86, Toyota 86 / Subaru BRZ twins, although the engine is actually designed and built by Subaru as the Subaru FA engine#FA20, Subaru FA20 engine.
See also
* H engine *V engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder ...
* W engine
* X engine
* Radial engine
* History of the internal combustion engine
References
{{Authority control Flat engines, Engines by cylinder layout, Flat