Homebrew (video games) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Homebrew, when applied to
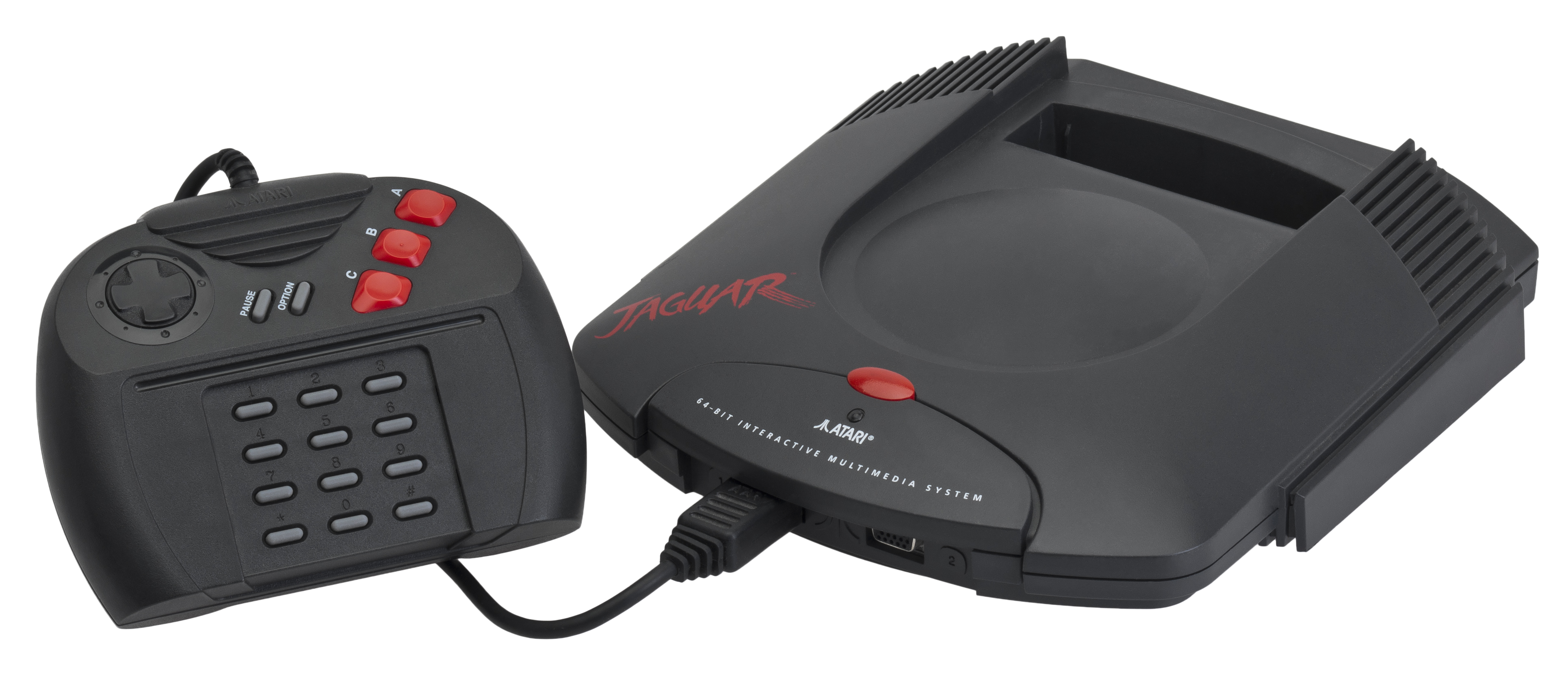
 The first hobbyist-developed Atari Jaguar game was released in 1995: a version of ''
The first hobbyist-developed Atari Jaguar game was released in 1995: a version of ''
In 2012, Ukrainian developer KRIKzz would develop their own device for the Nintendo 64, the EverDrive 64, which is also utilized for homebrew development. The N64Brew community has hosted game jam development competitions in 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023, and 2024. These competitions focused on creating games for the system (rather than demos, compared to the '98 and '99 competitions). These competitions also held interviews with the judges and developers behind the games they worked on. Notable judges for the competitions were former Nintendo 64 developers, such as Allan Findlay, David Doak, Neil Voss, and Giles Goddard. In August 2020, a
The 16-bit top-down shooter Xeno Crisis has received a version for the Nintendo 64, released on physical cartridge in April 2023.
Swiss
is an “all-in-one homebrew utility”, including a file browser, and the ability to force software to use different video modes that aren't officially supported, such as progressive scan or 16:9 widescreen. Th
Game Boy Interface
is a homebrew software frontend for the Game Boy Player peripheral, and is often used for capturing high-quality footage from Game Boy, Game Boy Color, and Game Boy Advance games. The 16-bit top-down shooter '' Xeno Crisis'' has received a version for the GameCube, released on physical optical disc.
 The
The
 Since the release of the Nintendo DS, a great deal of hacking has occurred involving the DS's fully rewritable firmware, Wi-Fi connection, game cards that allow SD storage, and software use. There are now many emulators for the DS, as well as the NES, SNES, Sega Master System, Sega Mega Drive, Neo-Geo Pocket, Neo-Geo MVS (arcade), and older handheld consoles like the Game Boy Color.
There are a number of cards which either have built-in flash memory, or a slot which can accept SD, or MicroSD (like the DSTT, R4, AceKard and ez-flash V/Vi) cards. These cards typically enable DS console gamers to use their console to play MP3s and videos, and other non-gaming functions traditionally reserved for separate devices.
In South Korea, many video game consumers exploit illegal copies of video games, including for the Nintendo DS. In 2007, 500,000 copies of DS games were sold, while the sales of the DS hardware units was 800,000.
Another modification device called Action Replay, manufactured by the company Datel, is a device which allows the user to input cheat codes that allows it to hack games, granting the player infinite
Since the release of the Nintendo DS, a great deal of hacking has occurred involving the DS's fully rewritable firmware, Wi-Fi connection, game cards that allow SD storage, and software use. There are now many emulators for the DS, as well as the NES, SNES, Sega Master System, Sega Mega Drive, Neo-Geo Pocket, Neo-Geo MVS (arcade), and older handheld consoles like the Game Boy Color.
There are a number of cards which either have built-in flash memory, or a slot which can accept SD, or MicroSD (like the DSTT, R4, AceKard and ez-flash V/Vi) cards. These cards typically enable DS console gamers to use their console to play MP3s and videos, and other non-gaming functions traditionally reserved for separate devices.
In South Korea, many video game consumers exploit illegal copies of video games, including for the Nintendo DS. In 2007, 500,000 copies of DS games were sold, while the sales of the DS hardware units was 800,000.
Another modification device called Action Replay, manufactured by the company Datel, is a device which allows the user to input cheat codes that allows it to hack games, granting the player infinite
 In advance of the Wii's release, WiiCade was the first site to host Adobe Flash homebrew games specifically designed for the Wii and its remote, which could be played without any exploits using the Wii's Opera (web browser), Opera web browser. The Wii Opera software development kit lets developers make their own games for the Wii via JavaScript.
The Wii was hacked via a custom serial interface in December 2007. The goal of most Wii exploits today is to install The Homebrew Channel, a custom channel that lets users run homebrew software on the console. Its first full release was in December 2008; earlier that year, Team Twiizers (now known as fail0verflow) released an exploit called the Twilight Hack which uses a malformed save file (Buffer overflow) to load an Executable and Linkable Format, ELF file (boot.elf) into memory (if present in the root directory of the SD card), which will then install The Homebrew Channel via unsigned code. Though Nintendo has successfully patched various older exploits to install The Homebrew Channel, many exploits to run the channel on current firmware exist. Note that only exploits that use disc games are compatible with installing The Homebrew Channel on the vWii (virtual Wii) mode on a Wii U (with the exception of "wuphax", an exploit that installs the channel via Wii U-specific system permission exploits). The console's controller was also a popular target for modification.
, there are many other exploits that can hack the Wii for homebrew aside from the Twilight Hack, allowing the installation of The Homebrew Channel from supported games and on specific system software revisions. This includes exploits such as (but not limited to) Smash Stack (using an exploit found within the game's stage editor in NTSC releases of ''Super Smash Bros. Brawl''), BannerBomb (using a malformed Channel; patched in firmware version 4.3), LetterBomb (using the Wii's Wii system software#Wii Message Board, Messaging Board), WilBrand (alternative to Letterbomb that supports firmware versions 3.0 to 4.3), FlashHax (using the Internet Channel), str2hax (using a DNS exploit in the Wii's EULA), BlueBomb (using Bluetooth), and ModMii (an exploit for PC users).
Note that most of these exploits above requires the use of an SD card, since they expect the ELF loader file (boot.elf) to be present on the root of the medium. However, both FlashHax and str2hax (and even BlueBomb for that matter) do not require the use of an SD card in order to exploit the Wii as they can download the ELF loader file directly off the internet (depending on the console model) if the SD card itself or the ELF loader file on the SD card is not present. BlueBomb also allowed for the Wii Mini to become hackable for the first time, which was a hardware revision of the Wii that was deemed "unhackable" by many users prior to the release of the exploit, mainly due to the lack of an SD card slot and internet connectivity on the Wii Mini.
In advance of the Wii's release, WiiCade was the first site to host Adobe Flash homebrew games specifically designed for the Wii and its remote, which could be played without any exploits using the Wii's Opera (web browser), Opera web browser. The Wii Opera software development kit lets developers make their own games for the Wii via JavaScript.
The Wii was hacked via a custom serial interface in December 2007. The goal of most Wii exploits today is to install The Homebrew Channel, a custom channel that lets users run homebrew software on the console. Its first full release was in December 2008; earlier that year, Team Twiizers (now known as fail0verflow) released an exploit called the Twilight Hack which uses a malformed save file (Buffer overflow) to load an Executable and Linkable Format, ELF file (boot.elf) into memory (if present in the root directory of the SD card), which will then install The Homebrew Channel via unsigned code. Though Nintendo has successfully patched various older exploits to install The Homebrew Channel, many exploits to run the channel on current firmware exist. Note that only exploits that use disc games are compatible with installing The Homebrew Channel on the vWii (virtual Wii) mode on a Wii U (with the exception of "wuphax", an exploit that installs the channel via Wii U-specific system permission exploits). The console's controller was also a popular target for modification.
, there are many other exploits that can hack the Wii for homebrew aside from the Twilight Hack, allowing the installation of The Homebrew Channel from supported games and on specific system software revisions. This includes exploits such as (but not limited to) Smash Stack (using an exploit found within the game's stage editor in NTSC releases of ''Super Smash Bros. Brawl''), BannerBomb (using a malformed Channel; patched in firmware version 4.3), LetterBomb (using the Wii's Wii system software#Wii Message Board, Messaging Board), WilBrand (alternative to Letterbomb that supports firmware versions 3.0 to 4.3), FlashHax (using the Internet Channel), str2hax (using a DNS exploit in the Wii's EULA), BlueBomb (using Bluetooth), and ModMii (an exploit for PC users).
Note that most of these exploits above requires the use of an SD card, since they expect the ELF loader file (boot.elf) to be present on the root of the medium. However, both FlashHax and str2hax (and even BlueBomb for that matter) do not require the use of an SD card in order to exploit the Wii as they can download the ELF loader file directly off the internet (depending on the console model) if the SD card itself or the ELF loader file on the SD card is not present. BlueBomb also allowed for the Wii Mini to become hackable for the first time, which was a hardware revision of the Wii that was deemed "unhackable" by many users prior to the release of the exploit, mainly due to the lack of an SD card slot and internet connectivity on the Wii Mini.
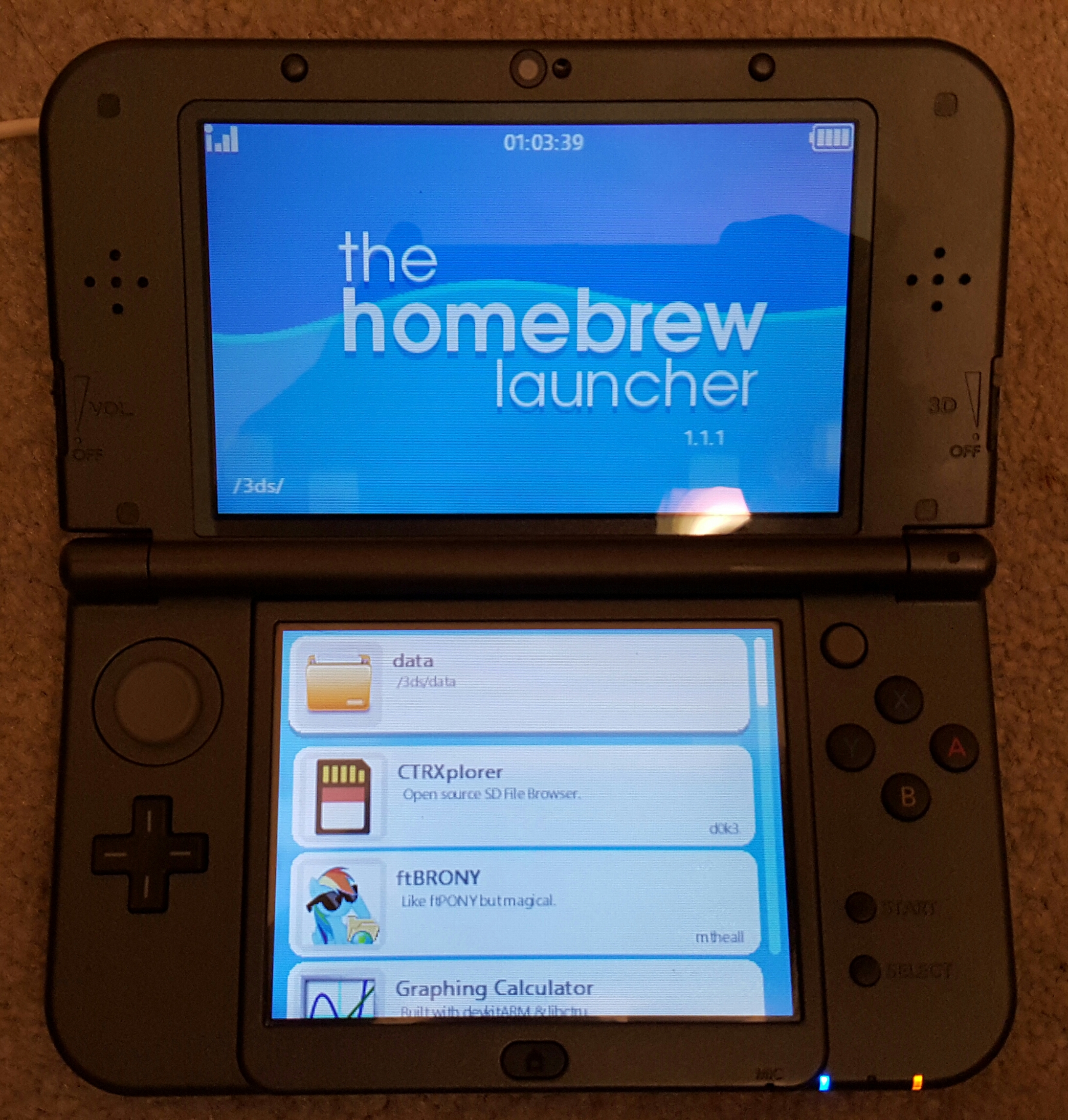 The first public homebrew exploit for the Nintendo 3DS, ninjhax, originally called ssspwn, allowed the user to scan a QR Code to exploit the game Cubic Ninja. Other ways to run The Homebrew Launcher have been discovered since then, including freakyhax, an exploit in the Deluxe edition of Freakyforms: Your Creations, Alive!; Doodlebomb, an exploit in the 1.1.1 and older versions of Swapdoodle; browserhax, broswerhax-xl, SSloth browser, and super-skaterhax (all of which used the 3DS' Internet Browser (Nintendo 3DS), Internet Browser with the latter exclusive to New 3DS models); soundhax, using the Nintendo 3DS Sound app; pichaxx, using Pokémon Picross; unSAFE_MODE, which injects a corrupted WiFi profile into the SAFE_MODE firmware; kartdlphax and Kartminer7, both using Mario Kart 7; MSET9, which utilizes an exploit in the System Settings application; ntrboot, using an NDS/DSi flash cart; and smashbroshax, a New 3DS exclusive exploit for Super Smash Bros. for Nintendo 3DS and Wii U, Super Smash Bros. for Nintendo 3DS.
The majority of system updates that have "Further improvements to overall system stability and other minor adjustments have been made to enhance the user experience" in their changelog are simply to patch Homebrew Launcher (userland) exploits. Those that require a specific version of a game or application are often patched in these updates by adding exploited application versions to the "IsTitleAllowed" blacklist, which prevents outdated applications on the list from launching and forces users to update those applications to the latest version to launch the application. For example, notehax only works on outdated versions of Flipnote Studio 3D. In the 11.6.0-39 system update, all regions of Flipnote Studio version <=1.0.1 in USA, <=1.2.0 in EUR, and <=1.3.1 in JPN were blocked from launching the application, patching the exploit on current firmware.
Unsigned software can be launched from the SD card without having to install custom firmware on the device by using an exploit to run The Homebrew Launcher. The Homebrew Launcher itself can be launched on system versions 9.0-11.16 on any 3DS system. However, without installing custom firmware, the user will need to run the exploit each time they want to access The Homebrew Launcher.
To directly install custom software onto the 3DS home menu, custom firmware is needed. There are several custom firmware releases available, the most popular being Luma3DS. Requirements to install custom firmware involve using various exploits to run a boot ROM exploit called boot9strap, which executes custom code before boot ROM lockout. In December 2020, an exploit was released that used an oversight in DSiWare, which can run custom code from the DSiWare menu in the 3DS settings app to install the 3DS hacks.
Many of the software homebrew exploits that were used to install custom firmware have been blocked in system version 11.17.0-50 (which released in May 2023). Despite this, other methods to exploit the 3DS for homebrew, such as the aforementioned MSET9 for all 3DS models and ntrboot as a fallback for the aforementioned exploit, are still available.
The first public homebrew exploit for the Nintendo 3DS, ninjhax, originally called ssspwn, allowed the user to scan a QR Code to exploit the game Cubic Ninja. Other ways to run The Homebrew Launcher have been discovered since then, including freakyhax, an exploit in the Deluxe edition of Freakyforms: Your Creations, Alive!; Doodlebomb, an exploit in the 1.1.1 and older versions of Swapdoodle; browserhax, broswerhax-xl, SSloth browser, and super-skaterhax (all of which used the 3DS' Internet Browser (Nintendo 3DS), Internet Browser with the latter exclusive to New 3DS models); soundhax, using the Nintendo 3DS Sound app; pichaxx, using Pokémon Picross; unSAFE_MODE, which injects a corrupted WiFi profile into the SAFE_MODE firmware; kartdlphax and Kartminer7, both using Mario Kart 7; MSET9, which utilizes an exploit in the System Settings application; ntrboot, using an NDS/DSi flash cart; and smashbroshax, a New 3DS exclusive exploit for Super Smash Bros. for Nintendo 3DS and Wii U, Super Smash Bros. for Nintendo 3DS.
The majority of system updates that have "Further improvements to overall system stability and other minor adjustments have been made to enhance the user experience" in their changelog are simply to patch Homebrew Launcher (userland) exploits. Those that require a specific version of a game or application are often patched in these updates by adding exploited application versions to the "IsTitleAllowed" blacklist, which prevents outdated applications on the list from launching and forces users to update those applications to the latest version to launch the application. For example, notehax only works on outdated versions of Flipnote Studio 3D. In the 11.6.0-39 system update, all regions of Flipnote Studio version <=1.0.1 in USA, <=1.2.0 in EUR, and <=1.3.1 in JPN were blocked from launching the application, patching the exploit on current firmware.
Unsigned software can be launched from the SD card without having to install custom firmware on the device by using an exploit to run The Homebrew Launcher. The Homebrew Launcher itself can be launched on system versions 9.0-11.16 on any 3DS system. However, without installing custom firmware, the user will need to run the exploit each time they want to access The Homebrew Launcher.
To directly install custom software onto the 3DS home menu, custom firmware is needed. There are several custom firmware releases available, the most popular being Luma3DS. Requirements to install custom firmware involve using various exploits to run a boot ROM exploit called boot9strap, which executes custom code before boot ROM lockout. In December 2020, an exploit was released that used an oversight in DSiWare, which can run custom code from the DSiWare menu in the 3DS settings app to install the 3DS hacks.
Many of the software homebrew exploits that were used to install custom firmware have been blocked in system version 11.17.0-50 (which released in May 2023). Despite this, other methods to exploit the 3DS for homebrew, such as the aforementioned MSET9 for all 3DS models and ntrboot as a fallback for the aforementioned exploit, are still available.
 In 2016, an exploit (computer security), exploit for the PlayStation Vita was released named "HENkaku". This exploit used a bug found on the 3.60 system firmware, allowing users to run unsigned software. It was installed by visiting a website and clicking on the install button on the PlayStation Vita web browser. This had to be done every time the user turned the system on, and was patched in firmware version 3.61. However, in 2018, computer science student TheFloW (Andy Nguyen) found a kernel bug in firmware versions 3.65, 3.67, and 3.68 that allowed unsigned code to be run. Eventually, he developed an exploit called "h-encore" which allowed one to install the HENkaku hack on later PS Vita versions. The kernel bug was patched in firmware version 3.69, but the user space, userland bug still works. Because HENkaku needs to be reinstalled every time the device is turned on again, an optional flasher program named ensō can be used alongside HENkaku to flash it into the system, making the plugin stay permanently even after shutdown and reboot, until uninstalled through the ensō installer.
On February 13, 2019, TheFloW released a downgrader tool that can downgrade any Vita console to an older firmware down to its factory firmware.
On December 26, 2022, TheFloW released HENlo, a WebKit-based exploit chain for developers and security researchers on his GitHub page; a working implementation of the exploit which can be used on all Vita firmware versions was released by SKGleba.
In 2016, an exploit (computer security), exploit for the PlayStation Vita was released named "HENkaku". This exploit used a bug found on the 3.60 system firmware, allowing users to run unsigned software. It was installed by visiting a website and clicking on the install button on the PlayStation Vita web browser. This had to be done every time the user turned the system on, and was patched in firmware version 3.61. However, in 2018, computer science student TheFloW (Andy Nguyen) found a kernel bug in firmware versions 3.65, 3.67, and 3.68 that allowed unsigned code to be run. Eventually, he developed an exploit called "h-encore" which allowed one to install the HENkaku hack on later PS Vita versions. The kernel bug was patched in firmware version 3.69, but the user space, userland bug still works. Because HENkaku needs to be reinstalled every time the device is turned on again, an optional flasher program named ensō can be used alongside HENkaku to flash it into the system, making the plugin stay permanently even after shutdown and reboot, until uninstalled through the ensō installer.
On February 13, 2019, TheFloW released a downgrader tool that can downgrade any Vita console to an older firmware down to its factory firmware.
On December 26, 2022, TheFloW released HENlo, a WebKit-based exploit chain for developers and security researchers on his GitHub page; a working implementation of the exploit which can be used on all Vita firmware versions was released by SKGleba.
fortheusers.org
These hosted applications can be downloaded directly on the Wii U using The Homebrew App Store app in the repository. The Wii U's built-in Wii sandbox environment (often nicknamed vWii or Wii Mode) is capable of running Wii homebrew, such as The Homebrew Channel. However, due to changes made to the Wii operating system that runs in vWii mode, previous exploits that utilized the Wii Menu to load the HackMii Installer, such as Letterbomb, do not work. The only way to hack the vWii without using one of the exploit games is by using Wii U homebrew applications, such as wuphax or Compat Installer. The operating system changes also prevent some homebrew applications from functioning properly, requiring developers to create alternate versions to run on vWii.
Retro Video Gamer - publisher of Homebrew Heroes book
SSEGA Sega Genesis Homebrew section
SEGA retro video games
gbadev.org
Skeetendo
VGB
Main Page
- N64Brew Wiki, which provides accurate documentation of the Nintendo 64, its peripherals, and related software.
Awesome N64 Development
- A maintained list of N64 development resources, toolchains, and N64 homebrew-related programs.
Libdragon
- Official website for the Nintendo 64 opensource SDK, known as LibDragon. {{DEFAULTSORT:Homebrew (Video Games) Custom firmware Homebrew software, Video game development Dedicated consoles
video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
s, refers to software produced by hobbyists for proprietary video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
s which are not intended to be user-programmable. The official documentation is often only available to licensed developers, and these systems may use storage formats that make distribution difficult, such as ROM cartridges or encrypted CD-ROMs. Many consoles have hardware restrictions to prevent unauthorized development.
Development can use unofficial, community maintained toolchain
A toolchain is a set of software development tools used to build and otherwise develop software. Often, the tools are executed sequentially and form a pipeline such that the output of one tool is the input for the next. Sometimes the term is us ...
s or official development kits such as Net Yaroze
The is a Game development kit, development kit for the PlayStation (console), PlayStation video game console. It was a promotion by Sony Computer Entertainment to computer programming hobbyists which launched in June 1996 in Japan and in 1997 in ...
, Linux for PlayStation 2, or Microsoft XNA
Microsoft XNA (a recursive acronym for XNA's not acronymed) is a freeware set of tools with a Managed code, managed Runtime system, runtime environment that Microsoft Gaming developed to facilitate video game game development, development. XNA is ...
. Targets for homebrew games are typically those which are no longer commercially relevant or produced, and with simpler graphics and/or computational abilities, such as the Atari 2600
The Atari 2600 is a home video game console developed and produced by Atari, Inc. Released in September 1977 as the Atari Video Computer System (Atari VCS), it popularized microprocessor-based hardware and games stored on swappable ROM cartridg ...
, Nintendo Entertainment System
The Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) is an 8-bit home video game console developed and marketed by Nintendo. It was first released in Japan on 15 July 1983 as the and was later released as the redesigned NES in several test markets in the ...
, Wii, Nintendo 3DS
The is a foldable dual-screen handheld game console produced by Nintendo. Announced in March 2010 as the successor to the Nintendo DS, the console was released originally on February 26, 2011 and went through various revisions in its lifetime, ...
, Wii U
The Wii U ( ) is a home video game console developed by Nintendo as the successor to the Wii. Released in late 2012, it is the first eighth-generation video game console and competed with Microsoft's Xbox One and Sony's PlayStation 4.
The W ...
, Genesis, Dreamcast
The is the final home video game console manufactured by Sega. It was released in Japan on November 27, 1998, in North America on September 9, 1999 and in Europe on October 14, 1999. It was the first sixth-generation video game console, prec ...
, Game Boy Advance
The (GBA) is a 32-bit handheld game console, manufactured by Nintendo, which was released in Japan on March 21, 2001, and to international markets that June. It was later released in mainland China in 2004, under the name iQue Game Boy Advanc ...
, PlayStation
is a video gaming brand owned and produced by Sony Interactive Entertainment (SIE), a division of Japanese conglomerate Sony. Its flagship products consists of a series of home video game consoles produced under the brand; it also consists ...
, and PlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Interactive Entertainment, Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October, in Europe on 24 Novembe ...
.
Several groups within the homebrew community have created unofficial games and software for consoles, as well as circumventing the hardware and software restrictions imposed on them to allow for the use of homebrew.
Development
New games for older systems are typically developed usingemulator
In computing, an emulator is Computer hardware, hardware or software that enables one computer system (called the ''host'') to behave like another computer system (called the ''guest''). An emulator typically enables the host system to run sof ...
s. Development for newer systems usually involves actual hardware, given the lack of accurate emulator
In computing, an emulator is Computer hardware, hardware or software that enables one computer system (called the ''host'') to behave like another computer system (called the ''guest''). An emulator typically enables the host system to run sof ...
s. However, efforts have been made to use actual console hardware for many older systems. Atari 2600
The Atari 2600 is a home video game console developed and produced by Atari, Inc. Released in September 1977 as the Atari Video Computer System (Atari VCS), it popularized microprocessor-based hardware and games stored on swappable ROM cartridg ...
programmers may burn an EEPROM
EEPROM or E2PROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) is a type of non-volatile memory. It is used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or as a separate chip d ...
to plug into a custom cartridge board or use audio transfer via the Starpath Supercharger. Game Boy Advance
The (GBA) is a 32-bit handheld game console, manufactured by Nintendo, which was released in Japan on March 21, 2001, and to international markets that June. It was later released in mainland China in 2004, under the name iQue Game Boy Advanc ...
developers have several ways to use GBA flash cartridges in this regard.
First generation consoles
Odyssey
In 2009, ''Odball'' became the first game for theMagnavox Odyssey
The Magnavox Odyssey is the first commercial home video game console. The hardware was designed by a small team led by Ralph H. Baer at Sanders Associates, while Magnavox completed development and released it in the United States in September ...
since 1973. It was produced by Robert Vinciguerra who has since written several other Odyssey games. On July 11, 2011, ''Dodgeball'' was published by Chris Read.
Second generation consoles

Atari 2600
Channel F
A handful of games have been programmed for the Fairchild Channel F, the first console to use ROM cartridges. The first known release is Sean Riddle's clone of '' Lights Out'' which included instructions on how to modify the SABA#20 Chess game into a Multi-Cartridge. There is also a version of ''Tetris'' and in 2008 "Videocart 27: ''Pac-Man''" became the first full production game for the system since it was discontinued.Third/Fourth generation consoles
NES / Famicom
Several compilers are available for theNintendo Entertainment System
The Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) is an 8-bit home video game console developed and marketed by Nintendo. It was first released in Japan on 15 July 1983 as the and was later released as the redesigned NES in several test markets in the ...
, but like the Atari 2600, most development is done in 6502 assembly language. One impediment to NES homebrew development is the relative difficulty involved with producing physical cartridges, although third-party flash carts do exist, making homebrew possible on original NES hardware.
In April 2023 NESFab, a new programming language for the NES, was released. The programming language is based upon C# and C++ making the development of software for the system relatively fast and efficient. Its release consequently witnessed the increment of homebrew games for the NES, amongst them being Mosh-Lift by Morphcat Games and Ballooney by Nikusoft.
Several varieties of custom processors are used within NES cartridges to expand system capabilities; most are difficult to replicate except by scavenging old cartridges unless the mapper in question was commonly used and thus cloned a lot, as is the case with the MMC3, or is simply consisted of discrete logic. One of the unofficial games that supports parallax scrolling and the MMC5 chip is ''Street Fighter II: Nostalgic Edition'', which is a port of '' Street Fighter II: The World Warrior'' developed by Parisoft.
While the original Famicom and its clones can play unlicensed games, the 10NES hardware lock-out mechanism of the original model NES complicates the production of physical cartridges. The 10NES chip can be permanently disabled by performing a minor change to the hardware. The redesigned NES (also known as the New-Style NES or the New Famicom) lacks the 10NES chip.
Genesis / Mega Drive
TheSega Genesis
The Sega Genesis, known as the outside North America, is a 16-bit Fourth generation of video game consoles, fourth generation home video game console developed and sold by Sega. It was Sega's third console and the successor to the Master Sys ...
has no physical lockout mechanism (instead relying on software encoding), making it easier to release software for the system. '' Pier Solar and the Great Architects'', '' Paprium'', and a port of ''Teenage Queen'' are examples of games that were released as physical cartridges. Other games include ''Sacred Line Genesis'', ''Coffee Crisis'', and ''Frog Feast'' for the Genesis and ''Mighty Mighty Missile'' for the Sega CD
The Sega CD, known as in most regions outside North America and Brazil, is a CD-ROM accessory and format for the Sega Genesis produced by Sega as part of the fourth generation of video game consoles. Originally released in November 1991, it ca ...
.
The 2018 game '' Tanglewood'' was notable in that it was developed using original Sega Genesis development hardware.
TurboGrafx-16 / PC Engine
TheTurboGrafx-16
The TurboGrafx-16, known in Japan as the , is a home video game console developed by Hudson Soft and manufactured by NEC. It was released in Japan in 1987 and in North America in 1989. The first console of the fourth generation of video game con ...
/PC Engine
The TurboGrafx-16, known in Japan as the , is a home video game console developed by Hudson Soft and manufactured by NEC. It was released in Japan in 1987 and in North America in 1989. The first console of the fourth generation, it launched ...
has a comparatively small homebrew scene. The first homebrew title was MindRec's ''Implode'' in 2002, a few years after the system's last official release ('' Dead of the Brain I & II'' for the PC Engine in 1999). The title was released on CD-ROM. Two years later, MindRec released ''Meteor Blaster DX'' on CD-R. Their official word on the change of CD format was that they were unable to be pressed to CD-ROM proper due to the glass mastering software suddenly unable to handle the unorthodox style of CD structure that the system expects. Five years later, Aetherbyte Studios released ''Insanity'', a '' Berzerk'' clone, on pressed CD-ROMs, quelling the notion of unpressable CDs. Aetherbyte later went on to prototype and produce a new HuCard
The (Known as the TurboChip in regions where the PC Engine was marketed as the TurboGrafx-16) is a ROM cartridge in the form of a card, designed by Hudson Soft for NEC's PC Engine and PC Engine SuperGrafx video game consoles, which were or ...
design called "''AbCARD''", which was fully compatible with the console. Aetherbyte celebrated the 30th Anniversary of the PC Engine since its release in 1987.
There is one C compiler for the console known as HuC, however it has not been officially updated since 2005. The MagicKit assembler is generally considered the de facto assembler for the console, and comes included with HuC. Additional libraries for HuC/MagicKit include Squirrel, a sound engine developed by Aetherbyte Studios, and the SGX/ACD library, developed by Tomatheous, that gives the developer easy access to the SuperGrafx
The , also known as simply the SuperGrafx, is a fourth-generation home video game console manufactured by NEC Home Electronics and released in Japan in 1989. It is the successor system to the PC Engine, released two years prior. Originally kn ...
video hardware as well as the Arcade Card.
The cc65 C compiler is compatible with the console, although there is no development library supported for it.
There are a few original TurboGrafx CD games being made such as ''FX Unit Yuki: The Henshin Engine'' and a port of ''Mysterious Song'' in 2012. In 2025, Special Ninja Squad's demo was released for the system, coming out on HuCard format.
SNES / Super Famicom
Bung Enterprises released the Game Doctor SF hardware series. It allows users to copy games and run new games on SNES hardware. ROMs can be converted into the Game Doctor SF format and put onto a 3 1/2" floppy. Games as large as twelvemegabits
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communication. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as ...
can be put on floppy disks formatted to 1.6 megabytes. An alternative device is the Super Flash, by Tototek, which allows multiple games to be burned onto a flash memory chip in a cartridge. This allows games as large as 48 megabits. The system can also program compatibility with a C compiler. The language program interest growth from French fans, porting Konami’s ''Asterix
''Asterix'' ( or , "Asterix the Gauls, Gaul"; also known as ''Asterix and Obelix'' in some adaptations or ''The Adventures of Asterix'') is a Franco-Belgian comics, French comic album book series, series about a Gaulish village which, thanks ...
'' beat ‘em up.
The run and gun game ''Alisha's Adventure'' used original Super Famicom development hardware. WaterMelon's action role-playing game codenamed ''ProjectN'' is a brand-new homebrew game for the SNES that is currently in development. ''Dottie -dreads nought-'' has been released for the 2021 SNESdev Game Jam, among ''Supercooked'' in 2022.
Neo-Geo MVS, AES, and CD
The Neo-Geo Home Cart and Arcade Systems can be tough candidates for homebrew development. Neo-Geo AES (Advanced Entertainment System) and MVS (Multi-Video System) cartridges have two separate boards: one for video, and one for sound. If programming a cartridge for the system were to occur, it would involve replacing the old ROM chips with one's newly programmed ones as the cartridges are in a sense, Arcade boards. NGDevTeam, who have released '' Fast Striker'' and '' Gunlord'', simply printed out their own board and soldered their own ROM chips onto it; this, however, can cause the Universe Bios logo to look corrupted if a custom BIOS were to be programmed. Programming for the Neo-Geo CD, however, is easier than programming for cartridges. The CDs themselves can actually contain both sound and video respectively. Depending on the Megabit count for a game program, load times will vary. A CD game with low Megabit counts will load only one time, whereas a CD game with higher megabit counts could load in between scenes, or rounds. As of 2014, other full games have been scheduled for release in physical form, such as ''Neo Xyx''. Razoola, programmer of the Neo-Geo Universe Bios, was working in January 23rd, 2019 on a "Skeleton Game Driver" that supports two players. This ROM is meant to remedy the corrupted Universe Bios Screens, as well as work with an unmodified/stock Neo-Geo MVS or AES. '' Razion'' is an example of an original Neo Geo game ported over to modern consoles, in this case the Nintendo Switch.Game Boy
There are many toolkits and utilities available to program homebrew on the Game Boy. ROM hacks of games on the handheld are available for the system. There are also unofficial ports and demakes of games from other home consoles and handhelds made for the Game Boy, some examples are a demake of the PlayStation game '' Castlevania: Symphony of the Night'', a port of the infamous Philips CD-i game '' Zelda’s Adventure'', and a port of '' Stunt Race FX''.Lynx
Very soon after the release of the Lynx was the first homebrew devkit release which was later named BLL (as it was done by the same developers as BJL for the Atari Jaguar). At the beginning, game development on BLL used 65C02 assembly much like on the Atari ST, but soon cc65 support was added. In the recent years, the homebrew scene developed a number of new games.Fifth generation consoles
Jaguar
 The first hobbyist-developed Atari Jaguar game was released in 1995: a version of ''
The first hobbyist-developed Atari Jaguar game was released in 1995: a version of ''Tetris
''Tetris'' () is a puzzle video game created in 1985 by Alexey Pajitnov, a Soviet software engineer. In ''Tetris'', falling tetromino shapes must be neatly sorted into a pile; once a horizontal line of the game board is filled in, it disa ...
'' called ''JSTetris''. It was written using a Jaguar with a custom BIOS and a homebrew development kit named BJL running on Atari ST. After purchasing all the intellectual property assets of Atari Corporation
Atari Corporation was an American manufacturer of Home computer, home computers and Video game console, video game consoles. It was founded by Jack Tramiel on May 17, 1984, as Tramel Technology, Ltd., but then took on the Atari name less than ...
from JTS in 1998, Hasbro Interactive, on May 14, 1999, announced that they have released all rights to the Jaguar, declaring the console an open platform. Following the announcement, a few developers and publishers, such as AtariAge, B&C Computervisions, Piko Interactive
Piko Interactive LLC is an American video game publisher based in San Antonio, Texas. Founded in early 2013 by Eli Galindo, the company focuses on physical re-releases of games from older video game consoles and digitally released ports to newer ...
, Songbird Productions, Telegames
Telegames, Inc. is an American video game company based in Mabank, Texas, with a sister operation based in England.
Telegames was known for supporting not just modern game systems but also classic game systems, after they had been abandoned by ...
, and Video61, have released both previously unfinished games from the Jaguar's past as well as several brand new games.
Since emulation of the console is still limited, coding uses a real console through either the Skunkboard development cartridge, using a BJL modified Jaguar, or the official Alpine Development Kit. The commercial game '' BattleSphere Gold'', also contains the JUGS (Jaguar Unmodified Game Server) aid to development.
Games are released in either cartridge, CD–or both–formats. Most developers have published their works either online on forums or in cartridge via independent publishers. Since both systems do not have regional locking, all of the titles are region free. Some of the earliest CD releases were not encrypted, requiring either B&C's Jaguar CD Bypass Cartridge or Reboot's Jagtopia (Freeboot) program burned into a CD in order to run unencrypted CD games, but Curt Vendel of Atari Museum released the binaries and encryption keys for both the cartridge and CD format, making it possible to run games without the need of development hardware. A cracked BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
of the Jaguar D can be soldered inside the system.
There are also ST-to-Jaguar conversions, which involves porting titles from the Atari ST
Atari ST is a line of personal computers from Atari Corporation and the successor to the company's Atari 8-bit computers, 8-bit computers. The initial model, the Atari 520ST, had limited release in April–June 1985, and was widely available i ...
to the Jaguar, which may include some enhancements. While they can be downloaded for free, select titles were sold on August 3, 2016 and others, as of date, are being licensed and sold in festivals dedicated to the system such as E-JagFest, JagFest, or online via AtariAge.
PC-FX
There is only one Homebrew development kit known for the PC-FX, which is based on theGNU Compiler Collection
The GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) is a collection of compilers from the GNU Project that support various programming languages, Computer architecture, hardware architectures, and operating systems. The Free Software Foundation (FSF) distributes ...
version 2.95.1. The Mednafen author began work on a library for the compiler called pcfxlib but it was discontinued due to lack of interest until trap15 started development of a new library called liberis. The toolchain is designed for a Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
environment, although it can also be used with cygwin
Cygwin ( ) is a free and open-source Unix-like environment and command-line interface (CLI) for Microsoft Windows. The project also provides a software repository containing open-source packages. Cygwin allows source code for Unix-like operati ...
. To date, no Homebrew titles for the PC-FX have been released, although Aetherbyte Studios and Eponasoft have both expressed interest in developing new software for the console.
PlayStation
Making games on the PlayStation is possible with any model of the system through the use of a modchip or the double 'Swap Trick'. There is also a softmod/save game exploit called "tonyhax". Requirements consist of a PC, SDK, and a 'Comms Link' device to upload and download files to and from the console. Another way of starting homebrew on the PlayStation is 'UniROM', which is a Softmod. UniROM works by being installed onto a cheat-device, which is connected via the parallel-port (on old consoles) and allows loading of custom code via burned CDs and the serial port. Homebrew was originally promoted by Sony with theNet Yaroze
The is a Game development kit, development kit for the PlayStation (console), PlayStation video game console. It was a promotion by Sony Computer Entertainment to computer programming hobbyists which launched in June 1996 in Japan and in 1997 in ...
, which had a large scene for quite some time. However, the official Net Yaroze site was shut down in mid-2009, and Sony stopped supporting the system as well as the users who still owned the console.
Saturn
All models of theSega Saturn
The is a home video game console developed by Sega and released on November 22, 1994, in Japan, May 11, 1995, in North America, and July 8, 1995, in Europe. Part of the fifth generation of video game consoles, it is the successor to the succes ...
can be used for hobbyist development. Modchips for the Saturn Model 1 have been scarce for some time, as it seems that no one has produced any new modchips in years. As such, the only two options left are to either perform the swap trick or extensively modify a Saturn Model 2 modchip.
Running homebrew on the Model 2 can be accomplished by bridging two points on the modchip, soldering a wire from the modchip to the Saturn power supply, and inserting it where the CD-ROM ribbon cable inserts. The swap trick is more difficult to pull off on this Model due to the lack of an access light.
Another method is what is known as the "PseudoSaturn" unlocking method. It is a program created by CyberWarrior2000 that abuses the "Pro Action Replay" cartridge's firmware. It unlocks region, frequency, and CD protection of most Saturn models. Either a modded Saturn or a swap trick is required to run the installer, which loads the code in the FlashROM of the cartridge. Afterwards, the cartridge unlocks everything and most software can be run, from backups to homebrews. There is also now a new engine for development called the Jo-Engine created by Johannes Fetz to allow easy development of 2D games. This engine is currently able to compile 2D games without the Sega Graphic Libraries (SGL). Another engine by XL2, called the Z-Treme engine, led to the creation of a fully 3D Sonic the Hedgehog
is a video game series and media franchise created by the Japanese developers Yuji Naka, Naoto Ohshima, and Hirokazu Yasuhara for Sega. The franchise follows Sonic the Hedgehog (character), Sonic, an anthropomorphic blue hedgehog who battle ...
game called Sonic Z-Treme. Z-Treme uses Sega Basic Libraries (SBL) and Sega Graphic Libraries (SGL).
Virtual Boy
Nintendo's Virtual Boy has no region lock, but it wasn't until the flash carts FlashBoy and FlashBoy+ were released that the homebrew scene began to grow. Two previously unreleased games, '' Bound High!'' and ''Niko-Chan Battle'' (the Japanese version of '' Faceball'') have been released. In 2015, a dedicated fan ported Konami’s cyberpunkpoint-and-click
Point and click are one of the actions of a computer user moving a pointer to a certain location on a screen (''pointing'') and then pressing a button on a mouse or other pointing device (''click''). An example of point and click is in hypermedi ...
'' Snatcher'' over to the Virtual Boy platform. ''Red Square'', a Yume Nikki fan game was created in six weeks for the 2019 Dream Diary Jam.
Nintendo 64
TheNintendo 64
The (N64) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Nintendo. It was released in Japan on June 23, 1996, in North America on September 29, 1996, and in Europe and Australia on March 1, 1997. As the successor to the Super Nintendo E ...
Homebrew scene began, and started off small, in January 1997, after the release of the DoctorV64, by Bung, during which many hobbyist developers utilized the use of a DoctorV64 for playback of their game or demo code, while also programming and utilizing their own written tools and programs for development, usually for Windows 95, or Linux.
Nintendo 64 homebrew demo scene competitions, known as "''Presence Of Mind''" were held, in which entrants utilized the DoctorV64, were hosted by the now-defunct N64 Homebrew Development website, Dextrose.com, in December 1997, leading into 1998, and 1999.
A ''Presence Of Mind'' competition was due to happen in 2000, but with the waning popularity of the console by this time, did not occur.
Between the years 2001 and 2005, homebrew development for the console stalled.
A new flashcart for the system, titled the NeoMyth Flashcart, was announced in May 2006.
Jennifer Taylor started work on the opensource SDK known as ''LibDragon'' in May 2009, for developers to utilize a non-proprietary SDK for homebrew game and program development on the Nintendo 64.
In April 2010, another new developer-friendly device for running custom programs and code, known as the 64Drive, would begin to be developed by Marshall H.In 2012, Ukrainian developer KRIKzz would develop their own device for the Nintendo 64, the EverDrive 64, which is also utilized for homebrew development. The N64Brew community has hosted game jam development competitions in 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023, and 2024. These competitions focused on creating games for the system (rather than demos, compared to the '98 and '99 competitions). These competitions also held interviews with the judges and developers behind the games they worked on. Notable judges for the competitions were former Nintendo 64 developers, such as Allan Findlay, David Doak, Neil Voss, and Giles Goddard. In August 2020, a
wiki
A wiki ( ) is a form of hypertext publication on the internet which is collaboratively edited and managed by its audience directly through a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages that can either be edited by the public or l ...
dedicated to providing accurate documentation of the Nintendo 64, its peripherals, and related software was created by the Nintendo 64 homebrew community.
There have also been a number of other game emulator
In computing, an emulator is Computer hardware, hardware or software that enables one computer system (called the ''host'') to behave like another computer system (called the ''guest''). An emulator typically enables the host system to run sof ...
s developed for the Nintendo 64, notably a Nintendo Entertainment System, Super Nintendo, Neo Geo, Game Boy and Game Boy Color
The (GBC or CGB) is an 8-bit handheld game console developed by Nintendo. It was released in Japan on October 21, 1998, and to international markets that November. Compared to the original Game Boy, the Game Boy Color features a color TFT scre ...
and a ScummVM emulator, among others.
In 2025, active development for the console and programs for the console is back in full swing. There are roughly 6,000 active members within the Nintendo 64 Homebrew community.The 16-bit top-down shooter Xeno Crisis has received a version for the Nintendo 64, released on physical cartridge in April 2023.
Sixth generation consoles
Dreamcast
Despite its short commercial lifespan of less than two years in North America, theDreamcast
The is the final home video game console manufactured by Sega. It was released in Japan on November 27, 1998, in North America on September 9, 1999 and in Europe on October 14, 1999. It was the first sixth-generation video game console, prec ...
benefits from an active homebrew scene even ten years after its discontinuation. Due to a flaw in the Dreamcast’s BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
, which was intended for use with MIL-CD's, the console can run software from a CD-R
CD-R (Compact disc-recordable) is a digital media, digital optical disc data storage device, storage format. A CD-R disc is a compact disc that can only be Write once read many, written once and read arbitrarily many times.
CD-R discs (CD-Rs) ...
without the use of a modchip. Sega responded to this by removing MIL-CD support from the BIOS on all Dreamcast consoles manufactured from November 2000 onwards.
The console is especially notable for its commercial homebrew scene. One notable project was the Bleemcast! emulator, which was a series of bootdisks made to play PlayStation
is a video gaming brand owned and produced by Sony Interactive Entertainment (SIE), a division of Japanese conglomerate Sony. Its flagship products consists of a series of home video game consoles produced under the brand; it also consists ...
games on the system, featuring visual enhancements over the original console. Newer independent releases include '' Last Hope'', released by RedSpotGames, and '' DUX'', both Shoot 'em up
Shoot 'em ups (also known as shmups or STGs) are a Video game genre, subgenre of action games. There is no consensus as to which design elements compose a shoot 'em up; some restrict the definition to games featuring spacecraft and certain typ ...
style games. These releases were written using the KallistiOS development system. A port of the freeware high-level development language Fenix and BennuGD is available for use in game development; many DIV Games Studio games have been ported and others were originally written for the system.
PlayStation 2
Early versions of thePlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Interactive Entertainment, Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October, in Europe on 24 Novembe ...
have a buffer overflow bug in the part of the BIOS that handles PS1 game compatibility; hackers found a way to turn this into a loophole called the PS2 Independence Exploit (released in August 2003), allowing the use of homebrew software. Other options for homebrew development would be the use of a modchip or the utilization of a PS2 hard drive and an HD Loader. In Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and Australia, the PS2 came with a free Yabasic interpreter on the bundled demo disc for some time. This allows simple programs to be created for the PS2 by the end-user. This was included in a failed attempt to circumvent a UK tax by defining the console as a "computer" if it contained certain software. A port of the NetBSD
NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was fork (software development), forked. It continues to ...
project and BlackRhino GNU/Linux, an alternative Debian
Debian () is a free and open-source software, free and open source Linux distribution, developed by the Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock in August 1993. Debian is one of the oldest operating systems based on the Linux kerne ...
-based distribution, are also available for the PS2.
Sony released an official Linux-based operating system for the PS2 in 2002, with the contents of the kit including a keyboard, mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
, Network Adaptor and HDD. The North American versions were discontinued in 2003 after the kits quickly went out of stock not too long afterwards, however the European version was still available for quite some time. The kit boots by installing a proprietary interface (the run-time environment) from a region-encoded DVD, meaning that the North American and European kits would only work with PS2 systems from their respective regions.
A more recent development called Free McBoot or FMCB (first released in May 2008) allows homebrew programs to be launched without a trigger disc required by the older exploit (Independence Exploit). This also allows the use of homebrew on unmodded systems without a functional disc drive. However, installation of the exploit to each individual memory card requires either an already exploited/modded system in order to launch the installer, or a boot image that can load an app to boot into Executable and Linkable Format
In computing, the Executable and Linkable FormatTool Interface Standard (TIS) Portable Formats SpecificationVersion 1.1'' (October 1993) (ELF, formerly named Extensible Linking Format) is a common standard file format for executable files, obje ...
(ELF) binaries (a Network Adaptor with a hard drive is also required). The installation is keyed to the Memory Card and will only be usable on the same version consoles that it was originally installed on, unless a Multi-Install is performed. The only drawback to this exploit is that it needs to be installed/compiled on each individual memory card. Simply copying from one memory card to another will not work. This exploit does not work on the latest slimline PS2s manufactured since late 2008 (the later SCPH-9000x models with BIOS 2.30 and newer), but will work on all models prior to that. The newest versions of Free McBoot (version 1.90 and newer) also have the ability to install and boot from both Sony and non-Sony HDDs when using an original "fat" model PS2 and network adapter. This support is called Free HDBoot or FHDB. With a few minor issues, it is now possible to play games entirely from the HDD, without the need to use the optical disc drive nor a physical memory card. Free McBoot is also notable for allowing the user to copy PS1/PS2 save files from a Memory Card to a USB drive, a functionality normally only possible with tools such as DexDrive.
After installing an exploit, unsigned executables (in ELF format) may be launched from a Memory Card or a USB drive. Such programs include emulators, media players, hard drive management tools, and PC-based or NAS-based file shares. Using homebrew programs (e.g. 'SMS Media Player') it is possible to listen to various audio file formats ( MP3, OMA, Ogg Vorbis
Vorbis is a free and open-source software project headed by the Xiph.Org Foundation. The project produces an audio coding format and software reference encoder/decoder (codec) for lossy audio compression, libvorbis. Vorbis is most common ...
, AAC, FLAC
FLAC (; Free Lossless Audio Codec) is an audio coding format for lossless compression of digital audio, developed by the Xiph.Org Foundation, and is also the name of the free software project producing the FLAC tools, the reference software ...
, AC3), and watch various video formats (DivX
DIVX (Digital Video Express) is a discontinued digital video format. Created in part by Circuit City, it was an unsuccessful attempt to create an alternative to video rental in the United States. The format's poor reception from consumers resu ...
/ XviD, MPEG1, MPEG2
MPEG-2 (a.k.a. H.222/H.262 as was defined by the ITU) is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods ...
, MPEG4-ASP in AVI Container) using the console. Games can also be played on any device connected to the console (i.e. external USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
/FireWire
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony a ...
/ thumb drive/hard disk drive (FAT32
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers and was the default file system for the MS-DOS and Windows 9x operating systems. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on ...
only), the internal hard disk on early revision consoles, network shares ( Windows Network or PS2 host: protocol), and even optical CD-R(W)/DVD±R(W) discs (modded systems or patched discs)). A number of homebrew emulators of older computer and gaming systems have also been developed for the PS2.
GameCube
Homebrew development on the NintendoGameCube
The is a PowerPC-based home video game console developed and marketed by Nintendo. It was released in Japan on September 14, 2001, in North America on November 18, 2001, in Europe on May 3, 2002, and in Australia on May 17, 2002. It is the suc ...
tended to be difficult, since it uses a proprietary MiniDVD-based drive and media as opposed to the standard DVD drives of the PS2 and Xbox for piracy protection. Also, its connectivity is limited, as it does not feature a USB port or an HDD port like the PlayStation 2.
The barrier to burning Nintendo GameCube discs with a consumer DVD burner is the Burst Cutting Area, a "barcode" in the innermost ring of the disc, an area inaccessible to most burners and writeable only by very expensive disc pressing machines. For a long time the only way to run homebrew software on Nintendo GameCube was through a patching-system exploit of '' Phantasy Star Online Episode I & II'', requiring users to find the game and a Broadband Adapter. Both of these are difficult to find because a follow-up has been released (under the name '' Phantasy Star Online Episode I & II Plus'') and thus the original PSO was rarely sold after then, and because the Broadband Adapter was not often carried in stores due to the Nintendo GameCube's very limited selection of online games.
As of August 2019, the most common method is to use an Action Replay in conjunction with an SD card adapter inserted into the memory card slot, allowing the user to run homebrew from the SD card, or over Ethernet. Another method involves using a modchip to allow the GameCube to run homebrew from a MiniDVD-R via the disc drive. Another method uses a save game exploit which involves transferring modified game save files to a GameCube memory card that triggers arbitrary code execution when loaded by an official game, allowing custom software to be run from a memory card, SD card, or other media. As the Nintendo GameCube's case does not fit a full-size DVD-R, third party replacement cases are available.
Homebrew software for the Nintendo GameCube mainly consist of emulators for other systems, as well as several popular homebrew utilitiesSwiss
is an “all-in-one homebrew utility”, including a file browser, and the ability to force software to use different video modes that aren't officially supported, such as progressive scan or 16:9 widescreen. Th
Game Boy Interface
is a homebrew software frontend for the Game Boy Player peripheral, and is often used for capturing high-quality footage from Game Boy, Game Boy Color, and Game Boy Advance games. The 16-bit top-down shooter '' Xeno Crisis'' has received a version for the GameCube, released on physical optical disc.
Xbox
 The
The Xbox
Xbox is a video gaming brand that consists of four main home video game console lines, as well as application software, applications (games), the streaming media, streaming service Xbox Cloud Gaming, and online services such as the Xbox networ ...
console uses several measures, including cryptographically signed code to obfuscate firmware. The primary method of executing homebrew code required installing a mod chip which could be flashed with a modified Microsoft BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
. This BIOS allowed the system to boot unsigned executables (XBEs) and control several hardware variables, such as region coding and video mode. With the leak of Microsoft's official development kit ( XDK), homebrew coders were able to write replacement Xbox GUIs (known as dashboards), games and applications for the Xbox.
A softmod
A softmod (short for software modification) is a method of using software to modify the intended behavior of hardware, such as computer hardware, or video game consoles in a way that can overcome restrictions of the firmware, or install custom f ...
, which uses a commercial game such as '' 007: Agent Under Fire'', '' Mech Assault'', or '' Splinter Cell'', had been created to execute a persistent softmod installer without modification of the hardware. This method utilizes modified font and sound files to cause the Xbox to cause a stack buffer overflow
In software, a stack buffer overflow or stack buffer overrun occurs when a program writes to a memory address on the program's call stack outside of the intended data structure, which is usually a fixed-length buffer.
Stack buffer overflow bugs ...
and load a homebrew dashboard. Once in this condition, the Xbox is able to execute homebrew games and applications upon boot up.
Due to the Xbox using standard PC libraries, writing homebrew games is relatively easy and the vast majority of libraries available for a PC programmer are available to an Xbox homebrew programmer.
One of the more common type of homebrew games for the Xbox are ports of PC games whose source has been publicly released or leaked. Many classic PC games have been released for Xbox, but most are created with the XDK which limits their availability. The only places to find these ports are through IRC
IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is a text-based chat system for instant messaging. IRC is designed for group communication in discussion forums, called '' channels'', but also allows one-on-one communication via private messages as well as chat ...
or peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of Node ...
browsers.
The Xbox system is also very adept at running emulators ported from the PC given its high processing power. It is able to emulate systems up to the previous generation, including the Nintendo 64
The (N64) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Nintendo. It was released in Japan on June 23, 1996, in North America on September 29, 1996, and in Europe and Australia on March 1, 1997. As the successor to the Super Nintendo E ...
and the PlayStation
is a video gaming brand owned and produced by Sony Interactive Entertainment (SIE), a division of Japanese conglomerate Sony. Its flagship products consists of a series of home video game consoles produced under the brand; it also consists ...
. For this reason, many different emulators have been created for or ported to the Xbox.
Game Boy Advance
Homebrew development for theGame Boy Advance
The (GBA) is a 32-bit handheld game console, manufactured by Nintendo, which was released in Japan on March 21, 2001, and to international markets that June. It was later released in mainland China in 2004, under the name iQue Game Boy Advanc ...
has been popular due to the availability of C compilers and ready-made, high-quality code libraries, as well as debugging features for several Game Boy Advance emulators like VisualBoyAdvance-M, mGBA, NO$GBA, and Mesen.
Adding to the popularity of homebrew for the GBA is the immense Pokémon ROM hacking
ROM hacking is the process of Modding, modifying a ROM image, ROM image or ROM file to alter the contents contained within, usually of a video game to alter the game's graphics, dialogue, Level (video games), levels, gameplay, and/or other elemen ...
community and the wide availability of Flash ROM cartridges and cartridge writers for the system, as well as nostalgia for the system overall (of which the latter also applies to all other retro game systems in general regardless of the generation and brand).
Seventh generation consoles
PlayStation Portable
Nintendo DS
health
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, p ...
, power-ups, access to any part of the game, infinite in game currency, the ability to walk through walls, and various other abilities depending on the game and code used.
Photographer Steve Chapman, looking for other ways to continue his photography work with smaller equipment, created DS-DSLR, an application that allowed him to control his camera without his bulky laptop. When his camera was connected to the DS through the GBA cartridge slot, DS-DSLR allowed him to execute many tasks, including controlled bracketing, custom interval shots, and timed long exposures. DS-DSLR even had a noise-activated shutter control which was activated when the DS mic detected noise.
With the DSi, it too has some homebrew exploits, some of which use DSiWare apps such as Flipnote Studio (aka ugopwn), sudokuhax, using a game called Sudoku by EA Games, grtpwn, exidiahax, fieldrunhax, 4swordhax, UNO*hax, and an exploit using Petit Computer called petit-compwner. There is also systemflaaw, which uses the DSi-exclusive game System Flaw.
A user by the name of shutterbug2000 on GBAtemp has released two DSi exploits, one being called Memory Pit, an exploit using the DSi Camera app, and the other known as the Flipnote Lenny exploit (aka ugopwn), using Flipnote Studio.
Xbox 360
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
has released a version of its proprietary Software Development Kit (SDK) for free, to would-be homebrew programmers. This SDK, called XNA Game Studio, is a free version of the SDK available to professional development companies and college students. However, to create Xbox 360 games one must pay for a premium membership to the XNA Creators Club. Once the games are verified, the games written with XNA Studio can be made available for 80, 240, or 400 Microsoft Points to all Xbox 360
The Xbox 360 is a home video game console developed by Microsoft. As the successor to the Xbox (console), original Xbox, it is the second console in the Xbox#Consoles, Xbox series. It was officially unveiled on MTV on May 12, 2005, with detail ...
owners (through Xbox Live). This allows creators of homebrew content access to their target audience of Xbox 360 owners. This content is available under the Indie Games section of the New Xbox Experience.
On March 20, 2007, it was announced that a hack using the previously discovered hypervisor vulnerability in the Xbox 360 kernel versions 4532 and 4548 had been developed to allow users to run XeLL, a Linux bootloader. The initial hack was beyond the average user and required an Xbox serial cable to be installed and a flashed DVD Drive firmware. Felix Domke, the programmer behind XeLL, has since announced a live bootable Linux CD suitable for novice users, with the capabilities to be installed to the SATA hard drive of the Xbox 360. Despite the availability of such a distribution, the Xbox 360 still isn't considered a popular platform for homebrew development, given the dependence of the exploit on the DVD-ROM being able to load a burnt DVD game, a modified version of the game ''Peter Jackson's King Kong, King Kong'', and two older kernel revisions of the console itself. A group independent of Microsoft was working on the means to run homebrew code, as part of the Free60 project.
''Note: The hypervisor vulnerability in the Xbox 360 kernel versions 4532 and 4548 was addressed by Microsoft with the release of the NXE system and dashboard update in 2008.''
Homebrew was since re-enabled on any Xbox 360 with dash 2.0.7371.0 or lower via an exploit referred to as the JTAG / SMC hack but was promptly patched again by Microsoft with the 2.0.8495.0 update.
Homebrew has now become available on most Xbox 360 consoles due to the Reset Glitch Hack. It works on all current dashboards up to the latest revision. Because the Reset Glitch Hack required a modchip, soldering skills are a necessity when attempting to use this exploit. This exploit was patched in the late Winchester revisions of the Xbox 360 E variant with mitigations in the hardware.
In recent years, a new software-based exploit called Bad Update was introduced, which allows the ability to run homebrew without the need of a modchip nor directly modifying the console's hardware (as what was previously done with the (still popular) Reset Glitch Hack), albeit with some limitations. It works on all Xbox 360 consoles up to the latest revision. Since Bad Update relies on winning race conditions with a 33% success rate (and each attempt taking between 10 and 20 minutes), hardware-based solutions such as the aforementioned Reset Glitch Hack are still preferred by many users. Currently, this exploit is the only way to allow homebrew to work on the late Winchester revisions of the console, which patched the RGH exploit.
PlayStation 3
The PlayStation 3 was designed to run other operating systems from day one. Very soon after launch, the first users managed to install Fedora Core 5 onto the PlayStation 3 via the 'Install Other OS' option in the PlayStation 3's XMB (Xross Media Bar), which also allows configuring the PlayStation 3 to boot into the other OS installed by default. So far, several Linux flavors have been successfully installed to the PlayStation 3, such as Fedora (operating system), Fedora Core 5, Fedora Core 6, Gentoo Linux, Gentoo, Ubuntu (operating system), Ubuntu and Yellow Dog Linux (YDL). The latter comes installed with the Cell SDK by default, allowing programmers a low cost entry into Cell programming. See also: Linux for PlayStation 3 Originally, graphics support was limited to framebuffer access only (no access to the PlayStation 3's graphics chip RSX), yet some access to the RSX 'Reality Synthesizer', RSX graphics processor was achieved (but Sony blocked this with firmware release 2.10). As of firmware release 3.21, consumers are no longer able to access the 'Other OS' due to Sony removing the facility from the software in an update. Sony said this was in response to several 'security concerns'. Homebrew developers do have access to the Cell microprocessor, including 6 of its 7 active Synergistic Processing Elements (SPEs). The Game OS resides under a hypervisor and prevents users from taking full control of the PlayStation 3's hardware. This is a security measure which helps Sony feel secure enough to allow users to install other operating systems on the PS3. The Sixaxis controller has also been exposed to Linux and Windows, but no driver seems to have been successfully created yet that exposes its accelerometer functionality, except for Motioninjoy. However other drivers have successfully used it as a controller for gaming and other applications. In May 2008, a vulnerability was found in the PlayStation 3 allowing users to install a partial debug firmware on a regular console. However, the debug functionality is disabled, so neither homebrew applications nor backup games can be run yet. Another exploit was found on August 14, 2008, allowing users to boot some backup games from the PlayStation 3's Hard disk drive, HDD, although the exact instructions on how to do this were not released at that time. However, a different person posted instructions 10 days later, which explained the exploit. On January 6, 2009, a hacking ring known as the "''Sh4d0ws''" leaked the jig files needed to launch the PlayStation 3 into service mode. Although the PlayStation 3 can be triggered into service mode, it is not yet of any use because the files needed to make changes to the console have not been leaked. On August 31, 2010, PSGroove, an exploit for the PS3 through the USB port, was released and made open source. This exploit works on all of the PS3 models released up until then. A guide for the creation of the PSGroove is available through several online sources. George Hotz, better known under his nickname "geohot", appeared on ''Attack of the Show!, Attack of the Show'' because he released the PlayStation 3's encryption keys, therefore any homebrew or custom firmware can be signed. Once signed, homebrew can be natively run. It would be difficult for Sony to fix this because it would most likely require a voluntary recall and the most expensive parts would have to be replaced. In 2011, Sony, with help from law firm Kilpatrick Stockton, sued Hotz and associates of the group fail0verflow for their jailbreaking activities. Charges included violating the Digital Millennium Copyright Act, DMCA, Computer Fraud and Abuse Act, CFAA, Contributory liability, copyright law, and California Comprehensive Computer Data Access and Fraud Act, California's CCDAFA, and for breach of contract (related to the PlayStation Network Terms of service, User Agreement), tortious interference, misappropriation, and trespass.Wii
 In advance of the Wii's release, WiiCade was the first site to host Adobe Flash homebrew games specifically designed for the Wii and its remote, which could be played without any exploits using the Wii's Opera (web browser), Opera web browser. The Wii Opera software development kit lets developers make their own games for the Wii via JavaScript.
The Wii was hacked via a custom serial interface in December 2007. The goal of most Wii exploits today is to install The Homebrew Channel, a custom channel that lets users run homebrew software on the console. Its first full release was in December 2008; earlier that year, Team Twiizers (now known as fail0verflow) released an exploit called the Twilight Hack which uses a malformed save file (Buffer overflow) to load an Executable and Linkable Format, ELF file (boot.elf) into memory (if present in the root directory of the SD card), which will then install The Homebrew Channel via unsigned code. Though Nintendo has successfully patched various older exploits to install The Homebrew Channel, many exploits to run the channel on current firmware exist. Note that only exploits that use disc games are compatible with installing The Homebrew Channel on the vWii (virtual Wii) mode on a Wii U (with the exception of "wuphax", an exploit that installs the channel via Wii U-specific system permission exploits). The console's controller was also a popular target for modification.
, there are many other exploits that can hack the Wii for homebrew aside from the Twilight Hack, allowing the installation of The Homebrew Channel from supported games and on specific system software revisions. This includes exploits such as (but not limited to) Smash Stack (using an exploit found within the game's stage editor in NTSC releases of ''Super Smash Bros. Brawl''), BannerBomb (using a malformed Channel; patched in firmware version 4.3), LetterBomb (using the Wii's Wii system software#Wii Message Board, Messaging Board), WilBrand (alternative to Letterbomb that supports firmware versions 3.0 to 4.3), FlashHax (using the Internet Channel), str2hax (using a DNS exploit in the Wii's EULA), BlueBomb (using Bluetooth), and ModMii (an exploit for PC users).
Note that most of these exploits above requires the use of an SD card, since they expect the ELF loader file (boot.elf) to be present on the root of the medium. However, both FlashHax and str2hax (and even BlueBomb for that matter) do not require the use of an SD card in order to exploit the Wii as they can download the ELF loader file directly off the internet (depending on the console model) if the SD card itself or the ELF loader file on the SD card is not present. BlueBomb also allowed for the Wii Mini to become hackable for the first time, which was a hardware revision of the Wii that was deemed "unhackable" by many users prior to the release of the exploit, mainly due to the lack of an SD card slot and internet connectivity on the Wii Mini.
In advance of the Wii's release, WiiCade was the first site to host Adobe Flash homebrew games specifically designed for the Wii and its remote, which could be played without any exploits using the Wii's Opera (web browser), Opera web browser. The Wii Opera software development kit lets developers make their own games for the Wii via JavaScript.
The Wii was hacked via a custom serial interface in December 2007. The goal of most Wii exploits today is to install The Homebrew Channel, a custom channel that lets users run homebrew software on the console. Its first full release was in December 2008; earlier that year, Team Twiizers (now known as fail0verflow) released an exploit called the Twilight Hack which uses a malformed save file (Buffer overflow) to load an Executable and Linkable Format, ELF file (boot.elf) into memory (if present in the root directory of the SD card), which will then install The Homebrew Channel via unsigned code. Though Nintendo has successfully patched various older exploits to install The Homebrew Channel, many exploits to run the channel on current firmware exist. Note that only exploits that use disc games are compatible with installing The Homebrew Channel on the vWii (virtual Wii) mode on a Wii U (with the exception of "wuphax", an exploit that installs the channel via Wii U-specific system permission exploits). The console's controller was also a popular target for modification.
, there are many other exploits that can hack the Wii for homebrew aside from the Twilight Hack, allowing the installation of The Homebrew Channel from supported games and on specific system software revisions. This includes exploits such as (but not limited to) Smash Stack (using an exploit found within the game's stage editor in NTSC releases of ''Super Smash Bros. Brawl''), BannerBomb (using a malformed Channel; patched in firmware version 4.3), LetterBomb (using the Wii's Wii system software#Wii Message Board, Messaging Board), WilBrand (alternative to Letterbomb that supports firmware versions 3.0 to 4.3), FlashHax (using the Internet Channel), str2hax (using a DNS exploit in the Wii's EULA), BlueBomb (using Bluetooth), and ModMii (an exploit for PC users).
Note that most of these exploits above requires the use of an SD card, since they expect the ELF loader file (boot.elf) to be present on the root of the medium. However, both FlashHax and str2hax (and even BlueBomb for that matter) do not require the use of an SD card in order to exploit the Wii as they can download the ELF loader file directly off the internet (depending on the console model) if the SD card itself or the ELF loader file on the SD card is not present. BlueBomb also allowed for the Wii Mini to become hackable for the first time, which was a hardware revision of the Wii that was deemed "unhackable" by many users prior to the release of the exploit, mainly due to the lack of an SD card slot and internet connectivity on the Wii Mini.
Eighth/Ninth generation consoles
3DS
 The first public homebrew exploit for the Nintendo 3DS, ninjhax, originally called ssspwn, allowed the user to scan a QR Code to exploit the game Cubic Ninja. Other ways to run The Homebrew Launcher have been discovered since then, including freakyhax, an exploit in the Deluxe edition of Freakyforms: Your Creations, Alive!; Doodlebomb, an exploit in the 1.1.1 and older versions of Swapdoodle; browserhax, broswerhax-xl, SSloth browser, and super-skaterhax (all of which used the 3DS' Internet Browser (Nintendo 3DS), Internet Browser with the latter exclusive to New 3DS models); soundhax, using the Nintendo 3DS Sound app; pichaxx, using Pokémon Picross; unSAFE_MODE, which injects a corrupted WiFi profile into the SAFE_MODE firmware; kartdlphax and Kartminer7, both using Mario Kart 7; MSET9, which utilizes an exploit in the System Settings application; ntrboot, using an NDS/DSi flash cart; and smashbroshax, a New 3DS exclusive exploit for Super Smash Bros. for Nintendo 3DS and Wii U, Super Smash Bros. for Nintendo 3DS.
The majority of system updates that have "Further improvements to overall system stability and other minor adjustments have been made to enhance the user experience" in their changelog are simply to patch Homebrew Launcher (userland) exploits. Those that require a specific version of a game or application are often patched in these updates by adding exploited application versions to the "IsTitleAllowed" blacklist, which prevents outdated applications on the list from launching and forces users to update those applications to the latest version to launch the application. For example, notehax only works on outdated versions of Flipnote Studio 3D. In the 11.6.0-39 system update, all regions of Flipnote Studio version <=1.0.1 in USA, <=1.2.0 in EUR, and <=1.3.1 in JPN were blocked from launching the application, patching the exploit on current firmware.
Unsigned software can be launched from the SD card without having to install custom firmware on the device by using an exploit to run The Homebrew Launcher. The Homebrew Launcher itself can be launched on system versions 9.0-11.16 on any 3DS system. However, without installing custom firmware, the user will need to run the exploit each time they want to access The Homebrew Launcher.
To directly install custom software onto the 3DS home menu, custom firmware is needed. There are several custom firmware releases available, the most popular being Luma3DS. Requirements to install custom firmware involve using various exploits to run a boot ROM exploit called boot9strap, which executes custom code before boot ROM lockout. In December 2020, an exploit was released that used an oversight in DSiWare, which can run custom code from the DSiWare menu in the 3DS settings app to install the 3DS hacks.
Many of the software homebrew exploits that were used to install custom firmware have been blocked in system version 11.17.0-50 (which released in May 2023). Despite this, other methods to exploit the 3DS for homebrew, such as the aforementioned MSET9 for all 3DS models and ntrboot as a fallback for the aforementioned exploit, are still available.
The first public homebrew exploit for the Nintendo 3DS, ninjhax, originally called ssspwn, allowed the user to scan a QR Code to exploit the game Cubic Ninja. Other ways to run The Homebrew Launcher have been discovered since then, including freakyhax, an exploit in the Deluxe edition of Freakyforms: Your Creations, Alive!; Doodlebomb, an exploit in the 1.1.1 and older versions of Swapdoodle; browserhax, broswerhax-xl, SSloth browser, and super-skaterhax (all of which used the 3DS' Internet Browser (Nintendo 3DS), Internet Browser with the latter exclusive to New 3DS models); soundhax, using the Nintendo 3DS Sound app; pichaxx, using Pokémon Picross; unSAFE_MODE, which injects a corrupted WiFi profile into the SAFE_MODE firmware; kartdlphax and Kartminer7, both using Mario Kart 7; MSET9, which utilizes an exploit in the System Settings application; ntrboot, using an NDS/DSi flash cart; and smashbroshax, a New 3DS exclusive exploit for Super Smash Bros. for Nintendo 3DS and Wii U, Super Smash Bros. for Nintendo 3DS.
The majority of system updates that have "Further improvements to overall system stability and other minor adjustments have been made to enhance the user experience" in their changelog are simply to patch Homebrew Launcher (userland) exploits. Those that require a specific version of a game or application are often patched in these updates by adding exploited application versions to the "IsTitleAllowed" blacklist, which prevents outdated applications on the list from launching and forces users to update those applications to the latest version to launch the application. For example, notehax only works on outdated versions of Flipnote Studio 3D. In the 11.6.0-39 system update, all regions of Flipnote Studio version <=1.0.1 in USA, <=1.2.0 in EUR, and <=1.3.1 in JPN were blocked from launching the application, patching the exploit on current firmware.
Unsigned software can be launched from the SD card without having to install custom firmware on the device by using an exploit to run The Homebrew Launcher. The Homebrew Launcher itself can be launched on system versions 9.0-11.16 on any 3DS system. However, without installing custom firmware, the user will need to run the exploit each time they want to access The Homebrew Launcher.
To directly install custom software onto the 3DS home menu, custom firmware is needed. There are several custom firmware releases available, the most popular being Luma3DS. Requirements to install custom firmware involve using various exploits to run a boot ROM exploit called boot9strap, which executes custom code before boot ROM lockout. In December 2020, an exploit was released that used an oversight in DSiWare, which can run custom code from the DSiWare menu in the 3DS settings app to install the 3DS hacks.
Many of the software homebrew exploits that were used to install custom firmware have been blocked in system version 11.17.0-50 (which released in May 2023). Despite this, other methods to exploit the 3DS for homebrew, such as the aforementioned MSET9 for all 3DS models and ntrboot as a fallback for the aforementioned exploit, are still available.
PlayStation 4
In 2015, an exploit (computer security), exploit for the PlayStation 4 was released for firmware 1.76 and below which grants kernel access. The userland exploit was WebKit via the PS4 Web Browser. This opened the door for unsigned code on the system and a homebrew community began to emerge. Over time, further exploits have been found that grant kernel level modifications to the system. The firmware versions for these are 4.05, 4.74, 5.05/5.07, 6.72, 7.02, 7.55, 9.00 and up to 11.00 using the PPPwn exploit developed by TheFlow. Most of these use the PS4 Web Browser as the entry point, but the PPPwn exploit uses a vulnerability found in the Playstation 4 network settings and a computer to send payloads. Homebrew on the PS4 includes being able to boot the PS4 into a Linux distribution, although this is not permanent and the console will revert to Orbis OS on reboot. Some payloads can patch games on the fly, such as 60 FPS for games that were never given official patches, character mods, and removal of intros and cutscenes. These patches can even work on physical retail discs inserted into the console; they are done at runtime in RAM and such leave the physical disc data intact.PlayStation Vita
 In 2016, an exploit (computer security), exploit for the PlayStation Vita was released named "HENkaku". This exploit used a bug found on the 3.60 system firmware, allowing users to run unsigned software. It was installed by visiting a website and clicking on the install button on the PlayStation Vita web browser. This had to be done every time the user turned the system on, and was patched in firmware version 3.61. However, in 2018, computer science student TheFloW (Andy Nguyen) found a kernel bug in firmware versions 3.65, 3.67, and 3.68 that allowed unsigned code to be run. Eventually, he developed an exploit called "h-encore" which allowed one to install the HENkaku hack on later PS Vita versions. The kernel bug was patched in firmware version 3.69, but the user space, userland bug still works. Because HENkaku needs to be reinstalled every time the device is turned on again, an optional flasher program named ensō can be used alongside HENkaku to flash it into the system, making the plugin stay permanently even after shutdown and reboot, until uninstalled through the ensō installer.
On February 13, 2019, TheFloW released a downgrader tool that can downgrade any Vita console to an older firmware down to its factory firmware.
On December 26, 2022, TheFloW released HENlo, a WebKit-based exploit chain for developers and security researchers on his GitHub page; a working implementation of the exploit which can be used on all Vita firmware versions was released by SKGleba.
In 2016, an exploit (computer security), exploit for the PlayStation Vita was released named "HENkaku". This exploit used a bug found on the 3.60 system firmware, allowing users to run unsigned software. It was installed by visiting a website and clicking on the install button on the PlayStation Vita web browser. This had to be done every time the user turned the system on, and was patched in firmware version 3.61. However, in 2018, computer science student TheFloW (Andy Nguyen) found a kernel bug in firmware versions 3.65, 3.67, and 3.68 that allowed unsigned code to be run. Eventually, he developed an exploit called "h-encore" which allowed one to install the HENkaku hack on later PS Vita versions. The kernel bug was patched in firmware version 3.69, but the user space, userland bug still works. Because HENkaku needs to be reinstalled every time the device is turned on again, an optional flasher program named ensō can be used alongside HENkaku to flash it into the system, making the plugin stay permanently even after shutdown and reboot, until uninstalled through the ensō installer.
On February 13, 2019, TheFloW released a downgrader tool that can downgrade any Vita console to an older firmware down to its factory firmware.
On December 26, 2022, TheFloW released HENlo, a WebKit-based exploit chain for developers and security researchers on his GitHub page; a working implementation of the exploit which can be used on all Vita firmware versions was released by SKGleba.
Wii U
The most common way to execute code on the Wii U for 5.5.6 and below is through vulnerabilities in the Wii U's built-in web browser. Websites specifically made to exploit these vulnerabilities usually use them to run the Homebrew Launcher from the user's SD card, allowing for other unsigned programs to be run. The Homebrew Launcher could also be used to run or install custom firmware, such as Mocha or Haxchi. Haxchi could optionally be enabled on boot using Coldboot Haxchi, a modified version of Haxchi that runs the Virtual Console game it is installed to on boot. In January 2022, Tiramisu and the EnvironmentLoader were released. EnvironmentLoader allows custom firmware, such as Tiramisu, to be automatically loaded on boot, similar to Coldboot Haxchi. However, it uses the system's built-in Health and Safety Information app to run the exploit instead of a Virtual Console game. This removes the requirement to purchase a compatible Virtual Console game and reduces the risk of Brick (electronics), bricking the console. Later in September 2022 the first public beta for the Aroma environment was released. Aroma used the same exploit that allowed EnvironmentLoader to run Tiramisu, enabling easy migration between the two. Aroma also introduced Modules, a new Plugin System, and a new Homebrew app format, in the form of .wuhb files. In addition, Aroma dropped support of .elf-based homebrew applications, including the Homebrew Launcher, in favor of Launching Homebrew from the Wii U Menu directly using .wuhb and .rpx files. Many homebrew applications that run via the Homebrew Launcher (or Wii U Menu on Aroma) have been collected and hosted ofortheusers.org
These hosted applications can be downloaded directly on the Wii U using The Homebrew App Store app in the repository. The Wii U's built-in Wii sandbox environment (often nicknamed vWii or Wii Mode) is capable of running Wii homebrew, such as The Homebrew Channel. However, due to changes made to the Wii operating system that runs in vWii mode, previous exploits that utilized the Wii Menu to load the HackMii Installer, such as Letterbomb, do not work. The only way to hack the vWii without using one of the exploit games is by using Wii U homebrew applications, such as wuphax or Compat Installer. The operating system changes also prevent some homebrew applications from functioning properly, requiring developers to create alternate versions to run on vWii.
Nintendo Switch
The Nintendo Switch was first exploited by a team called ReSwitched. On March 14, 2017, about 11 days after the console's release, the team released their exploit to the public. This exploit was called PegaSwitch. It did not allow true homebrew to run on the system at the time, but it did let developers look for other security bugs in the system. Later that year on October 1, ReSwitched announced new exploits and tools that allowed homebrew developers to start working on homebrew programs for the system before they could be launched. At the 34th Chaos Communication Congress, hackers Plutoo, Derrek, and Naehrwert announced a kernel exploit for the system (which they explicitly said they would not release it to the public) and said that a homebrew launcher was coming soon. Currently, the Nintendo Switch has both a homebrew launcher and custom firmware. Access to a Japanese copy of ''Puyo Puyo Tetris'' is needed to install CFW on version 1.0.0. The ability to install homebrew on the Nintendo Switch is also dependent on the version of the console. As consoles that were released after June 2018 with version 4.1.0 shipped have their boot ROMs patched against the full control TrustZone exploit that would allowed for homebrew to be installed, it is currently not possible to install homebrew to the HAC-001(-01) revision of the Nintendo Switch, the Nintendo Switch Lite, and the Nintendo Switch – OLED Model without the purchase and installation of a specialized modchip which replicates the vulnerability of the Tegra X1 chip.Xbox One, Series X, and Series S
The Xbox One and Xbox Series X and Series S, Series X/S have a Dev Mode which, though intended to be used for retail game development, can be used to run unsigned homebrew software. It can be enabled on any retail Xbox console. Dev Mode disables retail games and software while enabled. Homebrew software can be developed as Universal Windows Platform applications, allowing many programs designed to run on desktop editions of Windows 10 to run on the console including console emulators. In order to activate developer mode, one has to first register for an app developer account, which has a fee of $19.PlayStation 5
The PlayStation 5 is capable of running unsigned code on lower firmwares. A userland, kernel (and optionally hypervisor) exploit chain is required to be able to load homebrew on the PS5. As of April 2024, firmware 3.00 to 4.51 is exploitable using an IPv6 kernel exploit that was originally patched on the PS4 but later resurfaced on the PS5. This exploit chain does not contain a hypervisor exploit, although a payload was created that works as a partial bypass to defeat enough security to run homebrew, dubbed libhijacker. Homebrew on the PS5 consists of unofficial 60/120 FPS patches for backwards-compatible PS4 games and cheats, as well as adjusting the console’s fan speeds.See also
*Fangame *Hacking of consumer electronics *Mod (video gaming) * Modchip *ROM hacking
ROM hacking is the process of Modding, modifying a ROM image, ROM image or ROM file to alter the contents contained within, usually of a video game to alter the game's graphics, dialogue, Level (video games), levels, gameplay, and/or other elemen ...
*Privilege escalation#Jailbreaking, Jailbreaking
*Softmod
References
External links
Retro Video Gamer - publisher of Homebrew Heroes book
SSEGA Sega Genesis Homebrew section
SEGA retro video games
gbadev.org
Skeetendo
VGB
Main Page
- N64Brew Wiki, which provides accurate documentation of the Nintendo 64, its peripherals, and related software.
Awesome N64 Development
- A maintained list of N64 development resources, toolchains, and N64 homebrew-related programs.
Libdragon
- Official website for the Nintendo 64 opensource SDK, known as LibDragon. {{DEFAULTSORT:Homebrew (Video Games) Custom firmware Homebrew software, Video game development Dedicated consoles