Hitachi HD44780 LCD Controller on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller is an alphanumeric
The Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller is an alphanumeric
 The Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller is limited to monochrome text displays and is often used in copiers,
The Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller is limited to monochrome text displays and is often used in copiers,
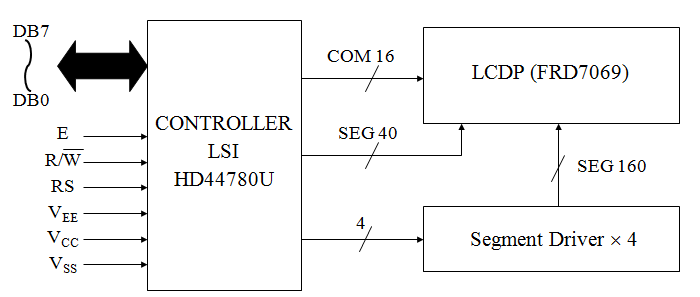
 Character LCDs use a 16-contact interface, commonly using pins or card edge connections on 0.1 inch (2.54 mm) centers. Those without backlights may have only 14 pins, omitting the two pins powering the light. This interface was designed to be easily hooked up to the
Character LCDs use a 16-contact interface, commonly using pins or card edge connections on 0.1 inch (2.54 mm) centers. Those without backlights may have only 14 pins, omitting the two pins powering the light. This interface was designed to be easily hooked up to the
 The Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller is an alphanumeric
The Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller is an alphanumeric dot matrix
A dot matrix is a 2-dimensional patterned Array data structure, array, used to represent characters, symbols and images. Most types of modern technology use dot matrices for display of information, including mobile phones, televisions, and pri ...
liquid crystal display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other Electro-optic modulator, electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers to display information. Liq ...
(LCD) controller developed by Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
in the 1980s. The character set of the controller includes ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
characters, Japanese Kana characters, and some symbols in two 40 character lines. Using an extension driver, the device can display up to 80 characters. Numerous third-party displays are compatible with its 16-pin interface and instruction set, making it a popular and cheap LCD driver.
Architecture
 The Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller is limited to monochrome text displays and is often used in copiers,
The Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller is limited to monochrome text displays and is often used in copiers, fax machine
Fax (short for facsimile), sometimes called telecopying or telefax (short for telefacsimile), is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material (both text and images), normally to a telephone number connected to a printer or other out ...
s, laser printer
Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a Electric charge, negatively charged cylinder call ...
s, industrial test equipment, and networking equipment, such as routers and storage devices.
Compatible LCD screens are manufactured in several standard configurations. Common sizes are one row of eight characters (8×1), and 16×2, 20×2 and 20×4 formats. Larger custom sizes are made with 32, 40 and 80 characters and with 1, 2, 4 or 8 lines. The most commonly manufactured larger configuration is 40×4 characters, which requires two individually addressable HD44780 controllers with expansion chips as a single HD44780 chip can only address up to 80 characters.
Character LCDs may have a backlight
A backlight is a form of illumination used in liquid-crystal displays (LCDs) that provides light from the back or side of a display panel. LCDs do not produce light on their own, so they require illumination—either from available light, ambie ...
, which may be LED, fluorescent, or electroluminescent. The nominal operating voltage for LED backlights is 5V at full brightness, with dimming at lower voltages dependent on the details such as LED color. Non-LED backlights often require higher voltages.
Interface
 Character LCDs use a 16-contact interface, commonly using pins or card edge connections on 0.1 inch (2.54 mm) centers. Those without backlights may have only 14 pins, omitting the two pins powering the light. This interface was designed to be easily hooked up to the
Character LCDs use a 16-contact interface, commonly using pins or card edge connections on 0.1 inch (2.54 mm) centers. Those without backlights may have only 14 pins, omitting the two pins powering the light. This interface was designed to be easily hooked up to the Intel MCS-51
The Intel MCS-51 (commonly termed 8051) is a single-chip microcontroller (MCU) series developed by Intel in 1980 for use in embedded systems. The architect of the Intel MCS-51 instruction set was John H. Wharton.. Intel's original versions w ...
XRAM interface, using only two address pins, which allowed displaying text on LCD using simple MOVX commands, offering a cost effective option for adding text display to devices.
The predominant pinout is as follows (exceptions exist):
Notes:
* Vee (also V0): This is an analog input, typically connected to a potentiometer. The user must be able to control this voltage independent of all other adjustments, in order to optimise visibility of the display that varies i. a. with temperature and, in some cases, height above the sea level. With a wrong adjustment, the display will seem to malfunction.
* R/: In most applications, reading from the HD44780 is not necessary. In that case, this pin can be permanently connected to ground and no processor pins need to be allocated to control it.
Mode selection
In 8-bit mode, all transfers happen in one cycle of the enable pin (E) with all 8 bits on the data bus and the RS and R/ pins stable. In 4-bit mode, data are transferred as pairs of 4-bit "nibble
In computing, a nibble, or spelled nybble to match byte, is a unit of information that is an aggregation of four- bits; half of a byte/ octet. The unit is alternatively called nyble, nybl, half-byte or tetrade. In networking or telecommuni ...
s" on the upper data pins, D7–D4, with two enable pulses and the RS and R/ pins stable. The four most significant bits (7–4) must be written first, followed by the four least significant bits (3–0). The high/low sequence must be completed each time or the controller will not properly receive further commands.
Selecting 4-bit or 8-bit mode requires careful selection of commands. There are two primary considerations. First, with D3–D0 unconnected, these lines will always appear high (binary 1111) to the HD44780 since there are internal pull-up MOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
s. Second, the LCD may initially be in one of three states:
* State 1: 8-bit mode
* State 2: 4-bit mode, waiting for the first set of 4 bits
* State 3: 4-bit mode, waiting for the second set of 4 bits
State 3 may occur, for example, if a prior control was aborted after sending only the first 4 bits of a command while the HD44780 was in 4-bit mode.
The following algorithm ensures that the LCD is in the desired mode:
The same command is sent three times, Function Set with 8-bit interface D7–D4 = binary 0011, the lower four bits are "don't care", using single enable pulses. If the controller is in 4-bit mode, the lower four bits are ignored so they cannot be sent until the interface is in a known size configuration.
Starting in state 1 (8-bit configuration):
* Send Function Set command. Command will be executed, set 8-bit mode.
* Send Function Set command. Command will be executed, set 8-bit mode.
* Send Function Set command. Command will be executed, set 8-bit mode.
Starting in state 2 (4-bit configuration, waiting for first 4-bit transfer):
* Send Function Set command. First 4 bits received.
* Send Function Set command. Last 4 bits, command accepted, set 8-bit mode.
* Send Function Set command. Command will be executed, set 8-bit mode.
Starting in state 3 (4-bit configuration, waiting for last 4-bit transfer):
* Send Function Set command. Last 4 bits, unknown command executed.
* Send Function Set command. In 8-bit mode command will be executed, otherwise first 4 bits received.
* Send Function Set command. 8-bit command will be executed or last 4 bits of previous command; set 8-bit mode.
In all three starting cases, the bus interface is now in 8-bit mode, 1 line, 5×8 characters. If a different configuration 8-bit mode is desired, an 8-bit bus Function Set command should be sent to set the full parameters. If 4-bit mode is desired, binary 0010 should be sent on D7–D4 with a single enable pulse. Now the controller will be in 4-bit mode and a full 4-bit bus Function Set command sequence (two enables with command bits 7–4 and 3–0 on subsequent cycles) will complete the configuration of the Function Set register.
Instruction set
The HD44780 instruction set is shown below: DDRAM is Display Data RAM and CGRAM is Character Generator RAM. The DDRAM is 80 bytes (40 per row) addressed with a gap between the two rows. The first row is addresses 0 to 39 decimal or 0 to 27 hex. The second row is addresses 64 to 103 decimal or 40 to 67 hex. The CGRAM is read/write memory used to encode up to 8 characters in the character generator. It consists of 64 fields at addresses 0 to 3F hex. Each field is 5 bits mapping to a row of pixels of each character. Each 8 fields in the CGRAM are used for each character. The lower 3 bits of the character codes from 0–7 and 8–15 select the groups of 8 fields in the CGRAM memory. Reading and writing to the DDRAM is done by setting the RS input high during bus transfers. The DDRAM must also be selected by using the Set DDRAM address command which selects the DDRAM for access and also sets the starting address for DDRAM access. Likewise reading and writing to the CGRAM is done by setting the RS input high during bus transfers. The CGRAM must also be selected by the Set CGRAM address command which selects the CGRAM for access and also sets the starting address for CGRAM access. The execution times listed in this table are based on an oscillator frequency of 270 kHz. The data sheet indicates that for a resistor of 91 kΩ at VCC=5 V the oscillator can vary between 190 kHz and 350 kHz resulting in wait times of 52.6 μs and 28.6 μs instead of 37 μs. If a display with the recommended 91 kΩ resistor is powered from 3.3 volts the oscillator will run much slower. If the busy bit is not used and instructions are timed by the external circuitry, this should be taken into account.Font
The original HD44780 character generator ROM contains 208 characters in a 5×8 dot matrix, and 32 characters in a 5×10 dot matrix. More recent compatible chips are available with higher resolution, matched to displays with more pixels. Two versions of the ROM have been developed: * HD44780UA00, the standard (Japanese) version, which includeskatakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji and in some cases the Latin script (known as rōmaji).
The word ''katakana'' means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana characters are derived fr ...
characters and some Greek letters and mathematical symbol
A mathematical symbol is a figure or a combination of figures that is used to represent a mathematical object, an action on mathematical objects, a relation between mathematical objects, or for structuring the other symbols that occur in a formula ...
s
* HD44780UA02, a European version, which includes the complete set of Greek, Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
and Western European characters (with diacritic
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacrit ...
s)
The 7-bit ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
subset for the Japanese version is non-standard: it supplies a Yen symbol where the backslash
The backslash is a mark used mainly in computing and mathematics. It is the mirror image of the common slash (punctuation), slash . It is a relatively recent mark, first documented in the 1930s. It is sometimes called a hack, whack, Escape c ...
character is normally found, and left and right arrow symbols in place of tilde
The tilde (, also ) is a grapheme or with a number of uses. The name of the character came into English from Spanish , which in turn came from the Latin , meaning 'title' or 'superscription'. Its primary use is as a diacritic (accent) in ...
and the rubout character.
A limited number of custom characters can be programmed into the device in the form of a bitmap
In computing, a bitmap (also called raster) graphic is an image formed from rows of different colored pixels. A GIF is an example of a graphics image file that uses a bitmap.
As a noun, the term "bitmap" is very often used to refer to a partic ...
using special commands. These characters have to be written to the device each time it is switched on, as they are stored in volatile memory
Volatile memory, in contrast to non-volatile memory, is computer memory that requires power to maintain the stored information; it retains its contents while powered on but when the power is interrupted, the stored data is quickly lost.
Volatile ...
.
See also
* LCD Smartie – Open source display driver for Microsoft Windows * JIS X 0201 – Japanese standard 7-bit and 8-bit character encodingReferences
Further reading
* * {{Refend Hitachi products Liquid crystal displays Electronic display devices