Hindcasting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Backtesting is a term used in modeling to refer to testing a
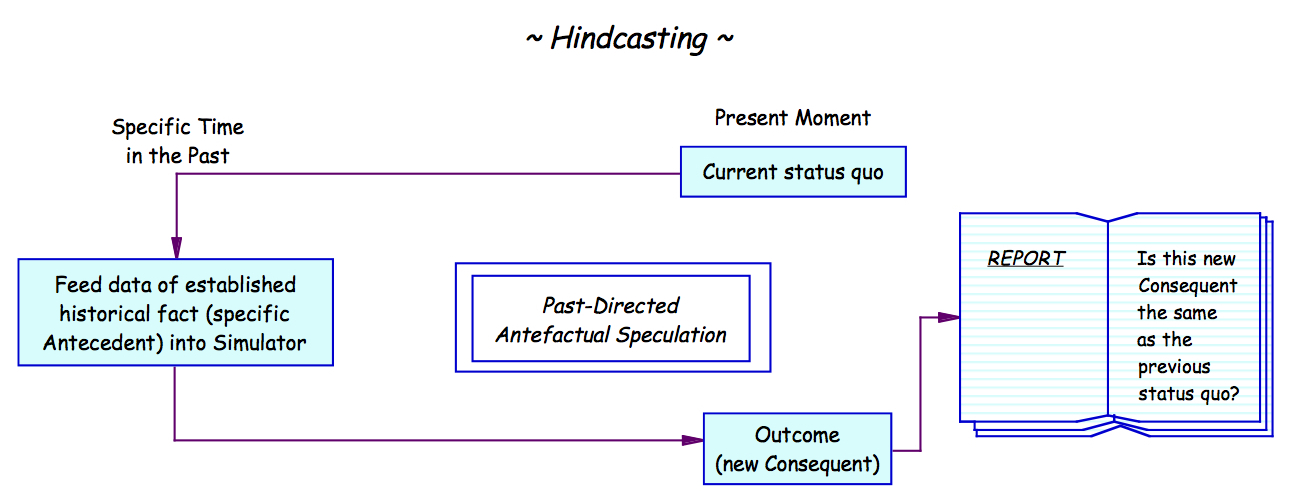 In
In
predictive model
Predictive modelling uses statistics to predict outcomes. Most often the event one wants to predict is in the future, but predictive modelling can be applied to any type of unknown event, regardless of when it occurred. For example, predictive mod ...
on historical data. Backtesting is a type of retrodiction
Retrodiction is the act of making a prediction about the past. It is also known as postdiction (but this should not be confused with the use of the term in criticisms of parapsychological research).
Activity
The activity of retrodiction (or po ...
, and a special type of cross-validation applied to previous time period(s).
Financial analysis
In the economic and financial field, backtesting seeks to estimate the performance of a strategy or model if it had been employed during a past period. This requires simulating past conditions with sufficient detail, making one limitation of backtesting the need for detailed historical data. A second limitation is the inability to model strategies that would affect historic prices. Finally, backtesting, like other modeling, is limited by potentialoverfitting
In mathematical modeling, overfitting is "the production of an analysis that corresponds too closely or exactly to a particular set of data, and may therefore fail to fit to additional data or predict future observations reliably". An overfi ...
. That is, it is often possible to find a strategy that would have worked well in the past, but will not work well in the future. Despite these limitations, backtesting provides information not available when models and strategies are tested on synthetic data.
Historically, backtesting was only performed by large institutions and professional money managers due to the expense of obtaining and using detailed datasets. However, backtesting is increasingly used on a wider basis, and independent web-based backtesting platforms have emerged. Although the technique is widely used, it is prone to weaknesses. Basel financial regulations require large financial institutions to backtest certain risk models.
For a Value at Risk
Value at risk (VaR) is a measure of the risk of loss of investment/capital. It estimates how much a set of investments might lose (with a given probability), given normal market conditions, in a set time period such as a day. VaR is typically us ...
1-day at 99% backtested 250 days in a row, the test is considered green (0-95%), orange (95-99.99%) or red (99.99-100%) depending on the following table:
For a Value at Risk
Value at risk (VaR) is a measure of the risk of loss of investment/capital. It estimates how much a set of investments might lose (with a given probability), given normal market conditions, in a set time period such as a day. VaR is typically us ...
10-day at 99% backtested 250 days in a row, the test is considered green (0-95%), orange (95-99.99%) or red (99.99-100%) depending on the following table:
Hindcast
 In
In oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the ocean, including its physics, chemistry, biology, and geology.
It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of to ...
and meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agricultur ...
, ''backtesting'' is also known as ''hindcasting'': a hindcast is a way of testing a mathematical model
A mathematical model is an abstract and concrete, abstract description of a concrete system using mathematics, mathematical concepts and language of mathematics, language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed ''mathematical m ...
; researchers enter known or closely estimated inputs for past events into the model to see how well the output matches the known results.
Hindcasting usually refers to a numerical-model integration of a historical period where no observations have been assimilated. This distinguishes a hindcast run from a reanalysis. Oceanographic observations of salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
and temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
as well as observations of surface-wave parameters such as the significant wave height
In physical oceanography, the significant wave height (SWH, HTSGW or ''H''s)
is defined traditionally as the mean ''wave height'' (trough (physics), trough to crest (physics), crest) of the highest third of the ocean surface wave, waves (''H''1/ ...
are much scarcer than meteorological observations, making hindcasting more common in oceanography than in meteorology. Also, since surface waves represent a forced system where the wind is the only generating force, wave hindcasting is often considered adequate for generating a reasonable representation of the wave climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
with little need for a full reanalysis. Hydrologists use hindcasting for model stream flows.
An example of hindcasting would be entering climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
forcings (events that force change) into a climate model
Numerical climate models (or climate system models) are mathematical models that can simulate the interactions of important drivers of climate. These drivers are the atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. Scientists use climate models to st ...
. If the hindcast showed reasonably-accurate climate response, the model would be considered successful.
The ECMWF re-analysis The ECMWF reanalysis project is a meteorological reanalysis project carried out by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), integrating historical meteorological observations onto a regularly spaced global grid for retrospect ...
is an example of a combined atmospheric reanalysis coupled with a wave-model integration where no wave parameters were assimilated, making the wave part a hindcast run.
See also
* Applied research (customer foresight) * Black box model *Climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
* ECMWF re-analysis The ECMWF reanalysis project is a meteorological reanalysis project carried out by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), integrating historical meteorological observations onto a regularly spaced global grid for retrospect ...
* Forecasting
Forecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data. Later these can be compared with what actually happens. For example, a company might Estimation, estimate their revenue in the next year, then compare it against the ...
* NCEP re-analysis
* Economic forecast
Economic forecasting is the process of making predictions about the economy. Forecasts can be carried out at a high level of aggregation—for example for GDP, inflation, unemployment or the fiscal deficit—or at a more disaggregated level, fo ...
* Retrodiction
Retrodiction is the act of making a prediction about the past. It is also known as postdiction (but this should not be confused with the use of the term in criticisms of parapsychological research).
Activity
The activity of retrodiction (or po ...
* Statistical arbitrage
In finance, statistical arbitrage (often abbreviated as Stat Arb or StatArb) is a class of short-term financial trading strategies that employ Mean reversion (finance), mean reversion models involving broadly diversified portfolios of securities (h ...
* Thought Experiment
A thought experiment is an imaginary scenario that is meant to elucidate or test an argument or theory. It is often an experiment that would be hard, impossible, or unethical to actually perform. It can also be an abstract hypothetical that is ...
* Value at risk
Value at risk (VaR) is a measure of the risk of loss of investment/capital. It estimates how much a set of investments might lose (with a given probability), given normal market conditions, in a set time period such as a day. VaR is typically us ...
References
{{reflist Tests Technical analysis Mathematical modeling Numerical climate and weather models Statistical forecasting