high-pass on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A high-pass filter (HPF) is an
A high-pass filter (HPF) is an
 A resistor and either a capacitor or an inductor can be configured as a first-order high-pass filter. The simple first-order capacitive high-pass filter shown in Figure 1 is implemented by placing an input voltage across the series combination of a
A resistor and either a capacitor or an inductor can be configured as a first-order high-pass filter. The simple first-order capacitive high-pass filter shown in Figure 1 is implemented by placing an input voltage across the series combination of a
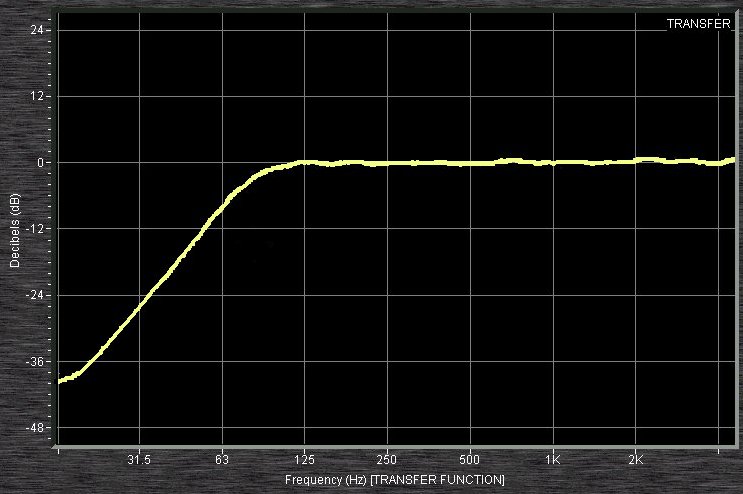 Mixing consoles often include high-pass filtering at each channel strip. Some models have fixed-slope, fixed-frequency high-pass filters at 80 or 100 Hz that can be engaged; other models have sweepable high-pass filters, filters of fixed slope that can be set within a specified frequency range, such as from 20 to 400 Hz on the
Mixing consoles often include high-pass filtering at each channel strip. Some models have fixed-slope, fixed-frequency high-pass filters at 80 or 100 Hz that can be engaged; other models have sweepable high-pass filters, filters of fixed slope that can be set within a specified frequency range, such as from 20 to 400 Hz on the
Common Impulse Responses
ECE 209: Review of Circuits as LTI Systems
a short primer on the mathematical analysis of (electrical) LTI systems.
ECE 209: Sources of Phase Shift
an intuitive explanation of the source of phase shift in a high-pass filter. Also verifies simple passive LPF
 A high-pass filter (HPF) is an
A high-pass filter (HPF) is an electronic filter
Electronic filters are a type of signal processing filter in the form of electrical circuits. This article covers those filters consisting of lumped-element model, lumped electronic components, as opposed to distributed-element filters. That ...
that passes signals
A signal is both the process and the result of Signal transmission, transmission of data over some transmission media, media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processin ...
with a frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
higher than a certain cutoff frequency
In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced ( attenuated or reflected) rather than ...
and attenuate
In physics, attenuation (in some contexts, extinction) is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and sound at variable at ...
s signals with frequencies lower than the cutoff frequency. The amount of attenuation
In physics, attenuation (in some contexts, extinction) is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a Transmission medium, medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and ...
for each frequency depends on the filter design. A high-pass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-invariant system
In system analysis, among other fields of study, a linear time-invariant (LTI) system is a system that produces an output signal from any input signal subject to the constraints of Linear system#Definition, linearity and Time-invariant system, ...
. It is sometimes called a low-cut filter or bass-cut filter in the context of audio engineering. High-pass filters have many uses, such as blocking DC from circuitry sensitive to non-zero average voltages or radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the u ...
devices. They can also be used in conjunction with a low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
to produce a band-pass filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects ( attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
It is the inverse of a '' band-stop filter''.
Description
In electronics and s ...
.
In the optical domain filters are often characterised by wavelength rather than frequency. High-pass and low-pass have the opposite meanings, with a "high-pass" filter (more commonly "short-pass") passing only ''shorter'' wavelengths (higher frequencies), and vice versa for "low-pass" (more commonly "long-pass").
Description
In electronics, a filter is a two-portelectronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or Conductive trace, traces through which electric current can flow. It is a t ...
which removes frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
components from a signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
(time-varying voltage or current) applied to its input port. A high-pass filter attenuates frequency components below a certain frequency, called its cutoff frequency, allowing higher frequency components to pass through. This contrasts with a low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
, which attenuates frequencies higher than a certain frequency, and a bandpass filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects ( attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
It is the inverse of a '' band-stop filter''.
Description
In electronics and s ...
, which allows a certain band of frequencies through and attenuates frequencies both higher and lower than the band.
In optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
a high pass filter is a transparent or translucent window of colored material that allows light longer than a certain wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
to pass through and attenuates light of shorter wavelengths. Since light is often measured not by frequency but by wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
, which is inversely related to frequency, a high pass optical filter, which attenuates light frequencies below a cutoff frequency, is often called a short-pass filter; it attenuates longer wavelengths.
Continuous-time circuits
First-order passive
capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
and a resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
and using the voltage across the resistor as an output. The transfer function
In engineering, a transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of a system, sub-system, or component is a function (mathematics), mathematical function that mathematical model, models the system's output for each possible ...
of this linear time-invariant system
In system analysis, among other fields of study, a linear time-invariant (LTI) system is a system that produces an output signal from any input signal subject to the constraints of Linear system#Definition, linearity and Time-invariant system, ...
is:
:
The product of the resistance and capacitance (''R''×''C'') is the time constant
In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek language, Greek letter (tau), is the parameter characterizing the response to a step input of a first-order, LTI system theory, linear time-invariant (LTI) system.Concre ...
(τ); it is inversely proportional to the cutoff frequency ''f''''c'', that is,
:
where ''f''''c'' is in hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in ter ...
, ''τ'' is in second
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of U ...
s, ''R'' is in ohm
Ohm (symbol Ω) is a unit of electrical resistance named after Georg Ohm.
Ohm or OHM may also refer to:
People
* Georg Ohm (1789–1854), German physicist and namesake of the term ''ohm''
* Germán Ohm (born 1936), Mexican boxer
* Jörg Ohm (1 ...
s, and ''C'' is in farad
The farad (symbol: F) is the unit of electrical capacitance, the ability of a body to store an electrical charge, in the International System of Units, International System of Units (SI), equivalent to 1 coulomb per volt (C/V). It is named afte ...
s. At the cutoff frequency, the filter's frequency response
In signal processing and electronics, the frequency response of a system is the quantitative measure of the magnitude and Phase (waves), phase of the output as a function of input frequency. The frequency response is widely used in the design and ...
reaches -3dB referenced to the gain at an infinite frequency.
First-order active
Figure 2 shows an active electronic implementation of a first-order high-pass filter using anoperational amplifier
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a direct coupling, DC-coupled Electronic component, electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input, a (usually) Single-ended signaling, single-ended output, and an extremely high gain ( ...
. The transfer function of this linear time-invariant system is:
:
In this case, the filter has a passband
A passband is the range of frequency, frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a Filter (signal processing), filter. For example, a radio receiver contains a bandpass filter to select the frequency of the desired radio signal out of all t ...
gain of −''R''2/''R''1 and has a cutoff frequency of
:
Because this filter is active, it may have non-unity passband gain. That is, high-frequency signals are inverted and amplified by ''R''2/''R''1.
All of these first-order high-pass filters are called differentiators, because they perform differentiation for signals whose frequency band
Spectral bands are regions of a given spectrum, having a specific range of wavelengths or frequencies. Most often, it refers to electromagnetic bands, regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
More generally, spectral bands may also be means in ...
is well below the filter's cutoff frequency.Higher orders
Filters of higher order have steeper slope in the stopband, such that the slope of n-order filters equals 20n dB per decade. Higher order filters can be achieved simply by cascading these first order filters. Whileimpedance matching
In electrical engineering, impedance matching is the practice of designing or adjusting the input impedance or output impedance of an electrical device for a desired value. Often, the desired value is selected to maximize power transfer or ...
and loading must be taken into account when chaining passive filters, active filters can be easily chained because the signal is restored by the output of the op amp at each stage. Various filter topologies and network synthesis filters
In signal processing, network synthesis filters are filters designed by the network synthesis method. The method has produced several important classes of filter including the Butterworth filter, the Chebyshev filter and the Elliptic filter. ...
for higher orders exist, which ease design.
Discrete-time realization
Discrete-time high-pass filters can also be designed. Discrete-time filter design is beyond the scope of this article; however, a simple example comes from the conversion of the continuous-time high-pass filter above to a discrete-time realization. That is, the continuous-time behavior can be discretized. From the circuit in Figure 1 above, according to Kirchhoff's Laws and the definition ofcapacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related ...
:
:
where is the charge stored in the capacitor at time . Substituting Equation (Q) into Equation (I) and then Equation (I) into Equation (V) gives:
:
This equation can be discretized. For simplicity, assume that samples of the input and output are taken at evenly spaced points in time separated by time. Let the samples of be represented by the sequence , and let be represented by the sequence which correspond to the same points in time. Making these substitutions:
:
And rearranging terms gives the recurrence relation
In mathematics, a recurrence relation is an equation according to which the nth term of a sequence of numbers is equal to some combination of the previous terms. Often, only k previous terms of the sequence appear in the equation, for a parameter ...
:
That is, this discrete-time implementation of a simple continuous-time RC high-pass filter is
:
By definition, . The expression for parameter yields the equivalent time constant
In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek language, Greek letter (tau), is the parameter characterizing the response to a step input of a first-order, LTI system theory, linear time-invariant (LTI) system.Concre ...
in terms of the sampling period and :
:.
Recalling that
: so
then and are related by:
:
and
:.
If , then the time constant equal to the sampling period. If , then is significantly smaller than the sampling interval, and .
Algorithmic implementation
The filter recurrence relation provides a way to determine the output samples in terms of the input samples and the preceding output. The followingpseudocode
In computer science, pseudocode is a description of the steps in an algorithm using a mix of conventions of programming languages (like assignment operator, conditional operator, loop) with informal, usually self-explanatory, notation of actio ...
algorithm will simulate the effect of a high-pass filter on a series of digital samples, assuming equally spaced samples:
// Return RC high-pass filter output samples, given input samples,
// time interval ''dt'', and time constant ''RC''
function highpass(''real ..n' x, ''real'' dt, ''real'' RC)
var ''real ..n' y
var ''real'' α := RC / (RC + dt)
y := x for i from 2 to n
y := α × y−1
In mathematics, −1 (negative one or minus one) is the additive inverse of 1, that is, the number that when added to 1 gives the additive identity element, 0. It is the negative integer greater than negative two (−2) and less than 0.
...
+ α × (x − x−1
In mathematics, −1 (negative one or minus one) is the additive inverse of 1, that is, the number that when added to 1 gives the additive identity element, 0. It is the negative integer greater than negative two (−2) and less than 0.
...
return y
The loop which calculates each of the outputs can be refactored into the equivalent:
for i from 2 to n
y := α × (y−1
In mathematics, −1 (negative one or minus one) is the additive inverse of 1, that is, the number that when added to 1 gives the additive identity element, 0. It is the negative integer greater than negative two (−2) and less than 0.
...
+ x − x−1
In mathematics, −1 (negative one or minus one) is the additive inverse of 1, that is, the number that when added to 1 gives the additive identity element, 0. It is the negative integer greater than negative two (−2) and less than 0.
...
However, the earlier form shows how the parameter α changes the impact of the prior output and current ''change'' in input . In particular,
* A large α implies that the output will decay very slowly but will also be strongly influenced by even small changes in input. By the relationship between parameter α and time constant
In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek language, Greek letter (tau), is the parameter characterizing the response to a step input of a first-order, LTI system theory, linear time-invariant (LTI) system.Concre ...
above, a large α corresponds to a large and therefore a low corner frequency of the filter. Hence, this case corresponds to a high-pass filter with a very narrow stopband. Because it is excited by small changes and tends to hold its prior output values for a long time, it can pass relatively low frequencies. However, a constant input (i.e., an input with ) will always decay to zero, as would be expected with a high-pass filter with a large .
* A small α implies that the output will decay quickly and will require large changes in the input (i.e., is large) to cause the output to change much. By the relationship between parameter α and time constant above, a small α corresponds to a small and therefore a high corner frequency of the filter. Hence, this case corresponds to a high-pass filter with a very wide stopband. Because it requires large (i.e., fast) changes and tends to quickly forget its prior output values, it can only pass relatively high frequencies, as would be expected with a high-pass filter with a small .
Applications
Audio
High-pass filters have many applications. They are used as part of anaudio crossover
Audio crossovers are a type of electronic filter circuitry that splits an audio signal into two or more frequency ranges, so that the signals can be sent to loudspeaker drivers that are designed to operate within different frequency ranges. Th ...
to direct high frequencies to a tweeter
A tweeter or treble speaker is a special type of loudspeaker (usually dome, inverse dome or horn-type) that is designed to produce high audio frequencies, typically from 2,000 to 20,000 Hertz, Hz. The name is derived from the high pitched sound ...
while attenuating bass signals which could interfere with, or damage, the speaker. When such a filter is built into a loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
cabinet it is normally a passive filter
Passivity is a property of engineering systems, most commonly encountered in analog electronics and control systems. Typically, analog designers use ''passivity'' to refer to incrementally passive components and systems, which are incapable of ...
that also includes a low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
for the woofer
A woofer or bass speaker is a technical term for a loudspeaker driver designed to produce low frequency sounds, typically from 50 up to 200 Hz. The name is from the onomatopoeic English word for a dog's deep bark, " woof" (in contrast to a ' ...
and so often employs both a capacitor and inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typic ...
(although very simple high-pass filters for tweeters can consist of a series capacitor and nothing else).
As an example, the formula above, applied to a tweeter with a resistance of 10 Ω, will determine the capacitor value for a cut-off frequency of 5 kHz.
, or approx 3.2 μF.
An alternative, which provides good quality sound without inductors (which are prone to parasitic coupling, are expensive, and may have significant internal resistance) is to employ bi-amplification with active RC filters or active digital filters with separate power amplifiers for each loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
. Such low-current and low-voltage line level
Line level is the specified Audio power, strength of an audio signal used to transmit analog (signal), analog sound between audio components such as compact disc, CD and Digital Versatile Disc, DVD players, television sets, audio amplifiers, and ...
crossovers are called active crossovers.
Rumble filters are high-pass filters applied to the removal of unwanted sounds near to the lower end of the audible range
Hearing range describes the frequency range that can be heard by humans or other animals, though it can also refer to the range of levels. The human range is commonly given as 20 to 20,000 Hz, although there is considerable variation bet ...
or below. For example, noises (e.g., footsteps, or motor noises from record player
A phonograph, later called a gramophone, and since the 1940s a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogue reproduction of sound. The sound vibration Waveform, waveforms are recorded as correspond ...
s and tape decks) may be removed because they are undesired or may overload the RIAA equalization
RIAA equalization is a specification for the recording and playback of phonograph records, established by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA). The purposes of the equalization are to permit greater recording times (by decreasi ...
circuit of the preamp.
High-pass filters are also used for AC coupling at the inputs of many audio power amplifier
An audio power amplifier (or power amp) amplifies low-power electronic audio signals, such as the signal from a radio receiver or an electric guitar pickup, to a level that is high enough for driving loudspeakers or headphones. Audio power a ...
s, for preventing the amplification of DC currents which may harm the amplifier, rob the amplifier of headroom, and generate waste heat at the loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
s voice coil
A voice coil (consisting of a former, collar, and winding) is the coil of wire attached to the apex of a loudspeaker cone. It provides the motive force to the cone by the reaction of a magnetic field to the current passing through it.
Th ...
. One amplifier, the professional audio
Professional audio, abbreviated as pro audio, refers to both an activity and a category of high-quality, studio-grade audio equipment. Typically it encompasses sound recording, sound reinforcement system setup and audio mixing, and studio mus ...
model DC300 made by Crown International beginning in the 1960s, did not have high-pass filtering at all, and could be used to amplify the DC signal of a common 9-volt battery at the input to supply 18 volts DC in an emergency for mixing console
A mixing console or mixing desk is an electronic device for Audio mixing (recorded music), mixing audio signals, used in sound recording and reproduction and sound reinforcement systems. Inputs to the console include microphones, signals fro ...
power. However, that model's basic design has been superseded by newer designs such as the Crown Macro-Tech series developed in the late 1980s which included 10 Hz high-pass filtering on the inputs and switchable 35 Hz high-pass filtering on the outputs. Another example is the QSC Audio PLX amplifier series which includes an internal 5 Hz high-pass filter which is applied to the inputs whenever the optional 50 and 30 Hz high-pass filters are turned off.
 Mixing consoles often include high-pass filtering at each channel strip. Some models have fixed-slope, fixed-frequency high-pass filters at 80 or 100 Hz that can be engaged; other models have sweepable high-pass filters, filters of fixed slope that can be set within a specified frequency range, such as from 20 to 400 Hz on the
Mixing consoles often include high-pass filtering at each channel strip. Some models have fixed-slope, fixed-frequency high-pass filters at 80 or 100 Hz that can be engaged; other models have sweepable high-pass filters, filters of fixed slope that can be set within a specified frequency range, such as from 20 to 400 Hz on the Midas
Midas (; ) was a king of Phrygia with whom many myths became associated, as well as two later members of the Phrygian royal house.
His father was Gordias, and his mother was Cybele. The most famous King Midas is popularly remembered in Greek m ...
Heritage 3000, or 20 to 20,000 Hz on the Yamaha M7CL
The Yamaha M7CL is a digital mixer that was introduced by Yamaha Pro Audio in 2005. Two models with onboard analog input exist: the M7CL-32 and M7CL-48. These models have 40 (32 microphone and 4 stereo line)- and 56 (48 microphone and 4 stereo li ...
digital mixing console. Veteran systems engineer and live sound mixer Bruce Main recommends that high-pass filters be engaged for most mixer input sources, except for those such as kick drum, bass guitar
The bass guitar (), also known as the electric bass guitar, electric bass, or simply the bass, is the lowest-pitched member of the guitar family. It is similar in appearance and construction to an Electric guitar, electric but with a longer nec ...
and piano, sources which will have useful low-frequency sounds. Main writes that DI unit
A DI unit (direct input or direct inject) is an electronic device typically used in recording studios and in sound reinforcement systems to connect a high output impedance unbalanced output signal to a low-impedance, microphone level, balanced ...
inputs (as opposed to microphone
A microphone, colloquially called a mic (), or mike, is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and publi ...
inputs) do not need high-pass filtering as they are not subject to modulation by low-frequency stage wash—low frequency sounds coming from the subwoofer
A subwoofer (or sub) is a loudspeaker designed to reproduce low-pitched audio frequencies, known as bass and sub-bass, that are lower in frequency than those which can be (optimally) generated by a woofer. The typical frequency range that is ...
s or the public address
A public address system (or PA system) is an electronic system comprising microphones, amplifiers, loudspeakers, and related equipment. It increases the apparent volume (loudness) of a human voice, musical instrument, or other acoustic sound sou ...
system and wrapping around to the stage. Main indicates that high-pass filters are commonly used for directional microphones which have a proximity effect—a low-frequency boost for very close sources. This low-frequency boost commonly causes problems up to 200 or 300 Hz, but Main notes that he has seen microphones that benefit from a 500 Hz high-pass filter setting on the console.
Image
Example of high-pass filter applied to the right half of a photograph. The left side is unmodified, Right side is with a high-pass filter applied (in this case, with a radius of 4.9). High-pass and low-pass filters are also used in digitalimage processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ...
to perform image modifications, enhancements, noise reduction, etc., using designs done in either the spatial domain or the frequency domain
In mathematics, physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency (and possibly phase), rather than time, as in time ser ...
.
The unsharp masking
Unsharp masking (USM) is an image sharpening technique, first implemented in darkroom photography, but now commonly used in digital image processing software. Its name derives from the fact that the technique uses a blurred, or "unsharp", negat ...
, or sharpening, operation used in image editing software is a high-boost filter, a generalization of high-pass.
See also
*DSL filter
A DSL filter (also DSL splitter or microfilter) is an analog low-pass filter installed between analog devices (such as telephones or analog modems) and a plain old telephone service (POTS) line. The DSL filter prevents interference between su ...
* Band-stop filter
In signal processing, a band-stop filter or band-rejection filter is a filter that passes most frequencies unaltered, but attenuates those in a specific range to very low levels. It is the inverse of a ''band-pass filter''. A notch filter is ...
* Bias tee
A bias tee is a three-port network used for setting the DC biasing, bias point of some electronic components without disturbing other components. The bias tee is a diplexer. The low-frequency port is used to set the bias; the high-frequency port pa ...
* Differentiator
In electronics, a differentiator is a Electrical network, circuit that outputs a signal approximately proportional to the rate of change (mathematics), rate of change (i.e. the derivative with respect to time) of its input signal. Because the Sine ...
* Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions f and g that produces a third function f*g, as the integral of the product of the two ...
* Circular convolution
References
External links
Common Impulse Responses
ECE 209: Review of Circuits as LTI Systems
a short primer on the mathematical analysis of (electrical) LTI systems.
ECE 209: Sources of Phase Shift
an intuitive explanation of the source of phase shift in a high-pass filter. Also verifies simple passive LPF
transfer function
In engineering, a transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of a system, sub-system, or component is a function (mathematics), mathematical function that mathematical model, models the system's output for each possible ...
by means of trigonometric identity.
{{DEFAULTSORT:High-Pass Filter
Linear filters
Synthesiser modules
Filter frequency response