Heinz Sachsenberg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heinz ''Wimmersal'' Sachsenberg (12 July 1922 – 17 June 1951) was a German
 In 1945, he transferred briefly to jet fighters in ''Jagdgeschwader'' 7 (JG 7—7th Fighter Wing) as ''
In 1945, he transferred briefly to jet fighters in ''Jagdgeschwader'' 7 (JG 7—7th Fighter Wing) as ''
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
fighter ace
A flying ace, fighter ace or air ace is a military aviation, military aviator credited with shooting down a certain minimum number of enemy aircraft during aerial combat; the exact number of aerial victories required to officially qualify as an ...
who served in the Luftwaffe
The Luftwaffe () was the aerial warfare, aerial-warfare branch of the before and during World War II. German Empire, Germany's military air arms during World War I, the of the Imperial German Army, Imperial Army and the of the Imperial Ge ...
. He was also a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. While it was order of precedence, lower in preceden ...
, the highest award in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. Sachsenberg claimed 104 aerial victories.
Early life
Sachsenberg was born on 12 July 1922 inDessau
Dessau is a district of the independent city of Dessau-Roßlau in Saxony-Anhalt at the confluence of the rivers Mulde and Elbe, in the ''States of Germany, Bundesland'' (Federal State) of Saxony-Anhalt. Until 1 July 2007, it was an independent ...
. "Heino", also called "Wimmersaal" by his comrades, was the nephew of Gotthard Sachsenberg
Gotthard Sachsenberg (6 December 1891 – 23 August 1961) was a German World War I fighter ace with 31 victories who went on to command the world's first naval air wing. In later life, he founded the airline ''Deutscher Aero Lloyd'', became an ant ...
, a World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
fighter pilot and recipient of the Pour le Mérite
The (; , ), also informally known as the ''Blue Max'' () after German WWI flying ace Max Immelmann, is an order of merit established in 1740 by King Frederick II of Prussia. Separated into two classes, each with their own designs, the was ...
. He had a brother also named Gotthard, who also served in the Luftwaffe, and was killed in action
Killed in action (KIA) is a casualty classification generally used by militaries to describe the deaths of their personnel at the hands of enemy or hostile forces at the moment of action. The United States Department of Defense, for example, ...
on 8 March 1944 during a night fighter mission.
Flying on the Eastern Front
After flight training he was assigned, as a ''Feldwebel'', to ''Jagdgeschwader'' 52 (JG 52—52nd Fighter Wing) in the fall of 1942. He was sent to the Eastern Front in late 1942 and was assigned to 6. '' Staffel'' (6th squadron) of JG 52.For an explanation of the meaning of Luftwaffe unit designations see Organisation of the Luftwaffe during World War II At the time, 6. ''Staffel'' was commanded by ''Oberleutnant'' Rudolf Resch and was subordinated to II. '' Gruppe'' (2nd group) of JG 52 under the leadership of ''Hauptmann''Johannes Steinhoff
Johannes "Macky" Steinhoff (15 September 1913 – 21 February 1994) was a Luftwaffe fighter ace during World War II, German general, and NATO official. He was one of very few Luftwaffe pilots who survived to fly operationally through the whole ...
. On 21 April 1943, Sachsenberg claimed his first aerial victory, shooting down an Ilyushin Il-2
The Ilyushin Il-2 ( Russian: Илью́шин Ил-2) is a ground-attack plane that was produced by the Soviet Union in large numbers during the Second World War. The word ''shturmovík'' (Cyrillic: штурмовик), the generic Russian term ...
ground attack aircraft southwest of Novorossiysk
Novorossiysk (, ; ) is a city in Krasnodar Krai, Russia. It is one of the largest ports on the Black Sea. It is one of the few cities designated by the Soviet Union as a Hero City. The population was
History
In antiquity, the shores of the ...
. On 5 May, Sachsenberg was shot down in his Messerschmitt Bf 109
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a monoplane fighter aircraft that was designed and initially produced by the Nazi Germany, German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt#History, Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW). Together with the Focke-Wulf Fw 190, the ...
G-4, (''Werknummer'' 14956—factory number) by a Supermarine Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft that was used by the Royal Air Force and other Allies of World War II, Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. It was the only British fighter produced conti ...
in combat northeast of Anapa
Anapa (, , ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, located on the northern coast of the Black Sea near the Sea of Azov. As of the 2021 Russian census, it had a population of 81,863. It is one of the largest ...
.
By the end of July 1943, he had shot down 22 enemy airplanes in heavy air combat over the Kuban bridgehead. His unit was then transferred to cover the retreat from the southern Kursk salient where he scored a further 16 victories. After a spell of leave from September to November due to overstress (when he was also awarded the German Cross
The War Order of the German Cross (), normally abbreviated to the German Cross or ''Deutsches Kreuz'', was instituted by Adolf Hitler on 28 September 1941. It was awarded in two divisions: in gold for repeated acts of bravery or military leade ...
in Gold () and Honor Goblet of the Luftwaffe (), he returned to the Crimea and the intense air-battles over the Kerch Straits.
After 76 victories, and on leave, Sachsenberg was recommended for the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. While it was order of precedence, lower in preceden ...
() in March 1944. Upon returning to the Crimea at the beginning of May, he shot down 25 aircraft in just a month including six aircraft on 7 May, making him an " ace-in-a-day" for the first time. On 31 May, over Iași
Iași ( , , ; also known by other #Etymology and names, alternative names), also referred to mostly historically as Jassy ( , ), is the Cities in Romania, third largest city in Romania and the seat of Iași County. Located in the historical ...
, in the battles for Romania, he claimed four victories (89-92v.) and five more were claimed on 8 June 1944, bringing his total to 101 air victories. He was the 76th Luftwaffe pilot to achieve the century mark. ''Fahnenjunker
''Fahnenjunker'' (short Fhj or FJ, ; ) is a military rank of the Bundeswehr and of some former German armed forces. In earlier German armed forces it was also the collective name for many officer aspirant ranks. It was established by the ''Pre ...
''-''Feldwebel
'' '' (Fw or F, ) is a non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank in several countries. The rank originated in Germany, and is also used in Switzerland, Finland, Sweden, and Estonia. The rank has also been used in Russia, Austria-Hungary, occupied Serbia ...
'' Sachsenberg was awarded the Knight's Cross on 9 June 1944. Returning from leave, his unit was then transferred to cover the Ploiești
Ploiești ( , , ), formerly spelled Ploești, is a Municipiu, city and county seat in Prahova County, Romania. Part of the historical region of Muntenia, it is located north of Bucharest.
The area of Ploiești is around , and it borders the Ble ...
oilfields in Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
. On 23 August 1944, he was seriously wounded during an air battle with United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
(USAAF) North American P-51 Mustang
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang is an American long-range, single-seat fighter and fighter-bomber used during World War II and the Korean War, among other conflicts. The Mustang was designed in 1940 by a team headed by James H. Kin ...
fighters, resulting in a forced landing
A forced landing is a landing by an aircraft made under factors outside the pilot's control, such as the failure of engines, systems, components, or weather which makes continued flight impossible. However, the term also means a landing that has ...
of his Bf 109 G-6, (''Werknummer'' 166233) "Yellow 1". Promoted to ''Leutnant'', he claimed his final victories over Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, including a USAAF P-51 and a Soviet Bell P-39 Airacobra
The Bell P-39 Airacobra is a fighter produced by Bell Aircraft for the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. It was one of the principal American fighters in service when the United States entered combat. The P-39 was used by th ...
.
The Sachsenberg ''Schwarm''
 In 1945, he transferred briefly to jet fighters in ''Jagdgeschwader'' 7 (JG 7—7th Fighter Wing) as ''
In 1945, he transferred briefly to jet fighters in ''Jagdgeschwader'' 7 (JG 7—7th Fighter Wing) as ''Staffelkapitän
''Staffelkapitän'' is a command appointment, rather than a military rank, in the air force units of German-speaking countries.
The rank normally held by a ''Staffelkapitän'' has changed over time. In the present-day German ''Luftwaffe'' – p ...
'' (squadron leader) of 9. ''Staffel'' of JG 7, but in April 1945 he joined ''Jagdverband'' 44 (JV 44—44th Fighter Detachment) based at Munich-Riem. His task was to provide top cover for the Messerschmitt Me 262
The Messerschmitt Me 262, nicknamed (German for "Swallow") in fighter versions, or ("Storm Bird") in fighter-bomber versions, is a fighter aircraft and fighter-bomber that was designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Messers ...
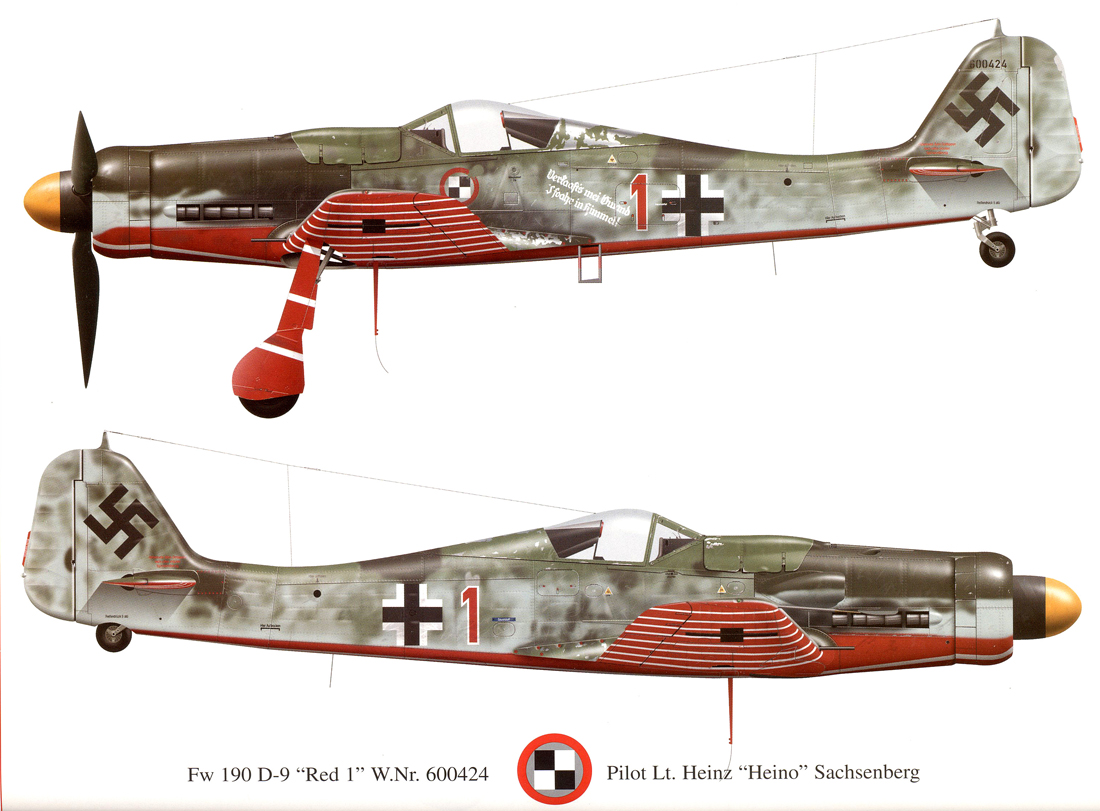
jet fighters during takeoff and landing. Sachsenberg was assigned as ''Staffelkapitän'' of the ''Platzschutzstaffel'' or airfield-protection squadron, flying the Focke-Wulf Fw 190
The Focke-Wulf Fw 190, nicknamed ''Würger'' (Shrike) is a German single-seat, single-engine fighter aircraft designed by Kurt Tank at Focke-Wulf in the late 1930s and widely used during World War II. Along with its well-known counterpart, the ...
D-9 fighter. As squadron commander, his particular aircraft was known as "Red 1". The inscription on his Fw 190 D-9 was "''Verkaaft's mei Gwand I foahr in Himmel!''" meaning "Sell my clothes I'm going to heaven" in a Bavarian dialect. The Me 262 jet was vulnerable to strafing
Strafing is the military practice of attacking ground targets from low-flying aircraft using aircraft-mounted automatic weapons.
Less commonly, the term is used by extension to describe high-speed firing runs by any land or naval craft such a ...
attacks during takeoff and landing. ''Generalleutnant'' Adolf Galland
Adolf Josef Ferdinand Galland (19 March 1912 – 9 February 1996) was a German Luftwaffe general and flying ace who served throughout the Second World War in Europe. He flew 705 combat missions and fought on the Western Front and in the Defenc ...
, the commanding officer of JV 44, ordered the formation of the ''Platzschutzstaffel''. Already in 1944, III. ''Gruppe'' of ''Jagdgeschwader'' 54 (JG 54—54th Fighter Wing), flying the Fw 190 D, had provided fighter protection to ''Kommando'' Nowotny, the first experimental Me 262 jet fighter unit.
The aircraft in the protection squadron were painted red on their underbelly with prominent white stripes to help in their identification by ground crews. The legend of the ''Papagei Staffel'' (parrot squadron) was born (the name was given after the war and is truly misleading as it was not used by the squadron itself). The decision to paint the aircraft in this manner was made by the pilots themselves, perhaps as result of the failed Operation Bodenplatte
Operation Bodenplatte (; "Baseplate"), launched on 1 January 1945, was an attempt by the German Luftwaffe to cripple Allies of World War II, Allied air forces in the Low Countries during the World War II, Second World War. The goal of ''Bodenpl ...
, where a number of German aircraft were lost to friendly fire.Quote from Franz Stigler
The protection squadron was tasked with flying ''Start- und Landeschutz'' (Takeoff and landing cover). During takeoff and landing, the jets were very vulnerable to attacks by strafing Allied ground-attack airplanes, because their engines were not very responsive at those times and the jets could not accelerate and decelerate quickly. Thus to give additional protection besides the light and medium AA-guns around the airfields, parts of JG 52 and JG 54
''Jagdgeschwader'' 54 (JG 54) ''Grünherz'' was a Luftwaffe fighter wing that was founded in late 1936 and operated from 1939, the entire length of the Second World War. It later existed under the reformed Luftwaffe from 1947 to 1991 as BG54/B54 ...
were delegated to fly protective missions to cover the takeoff-and-landing phase of the 'Stormbirds'. JV 44 was a special case in that they had their own protection squadron.
After the war
He died on 17 June 1951 inLich
In fantasy fiction, a lich () is a type of undead creature with magical powers.
Various works of fantasy fiction, such as Clark Ashton Smith's " The Empire of the Necromancers" (1932), had used ''lich'' as a general term for any corpse, animat ...
, following complications from wounds he received on 23 October 1944.
Quotations
"I don't trust anything without a Propeller at least." - Sachsenberg in reply to being asked why he didn't fly jet aircraft.Summary of career
Aerial victory claims
According to US historian David T. Zabecki, Sachsenberg was credited with 104 aerial victories. Obermaier also lists Sachsenberg with 104 aerial victories, claimed in 520 combat missions, one on the Western Front and 103 on the Eastern Front. He was also credited with the destruction of one fast attack craft. Mathews and Foreman, authors of ''Luftwaffe Aces — Biographies and Victory Claims'', researched theGerman Federal Archives
The German Federal Archives or Bundesarchiv (BArch) (, lit. "Federal Archive") are the national archives of Germany. They were established at the current location in Koblenz in 1952.
They are subordinated to the Federal Commissioner for Culture ...
and found records for 104 aerial victory claims, 103 aerial victories on the Eastern Front and one on the Western Front.
Victory claims were logged to a map-reference (PQ = ''Planquadrat''), for example "PQ 34 Ost 7545". The ''Luftwaffe'' grid map () covered all of Europe, western Russia and North Africa and was composed of rectangles measuring 15 minutes
Minutes, also known as minutes of meeting, protocols or, informally, notes, are the instant written record of a meeting or hearing. They typically describe the events of the meeting and may include a list of attendees, a statement of the activit ...
of latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
by 30 minutes of longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
, an area of about . These sectors were then subdivided into 36 smaller units to give a location area in size.
Awards
*Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the in ...
(1939) 2nd and 1st Class
* Honor Goblet of the Luftwaffe on 11 October 1943 as ''Feldwebel
'' '' (Fw or F, ) is a non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank in several countries. The rank originated in Germany, and is also used in Switzerland, Finland, Sweden, and Estonia. The rank has also been used in Russia, Austria-Hungary, occupied Serbia ...
'' and pilot
*German Cross
The War Order of the German Cross (), normally abbreviated to the German Cross or ''Deutsches Kreuz'', was instituted by Adolf Hitler on 28 September 1941. It was awarded in two divisions: in gold for repeated acts of bravery or military leade ...
in Gold on 17 October 1943 as ''Feldwebel
'' '' (Fw or F, ) is a non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank in several countries. The rank originated in Germany, and is also used in Switzerland, Finland, Sweden, and Estonia. The rank has also been used in Russia, Austria-Hungary, occupied Serbia ...
'' in the 6./''Jagdgeschwader'' 52
*Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. While it was order of precedence, lower in preceden ...
on 9 June 1944 as ''Fahnenjunker
''Fahnenjunker'' (short Fhj or FJ, ; ) is a military rank of the Bundeswehr and of some former German armed forces. In earlier German armed forces it was also the collective name for many officer aspirant ranks. It was established by the ''Pre ...
-Feldwebel
'' '' (Fw or F, ) is a non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank in several countries. The rank originated in Germany, and is also used in Switzerland, Finland, Sweden, and Estonia. The rank has also been used in Russia, Austria-Hungary, occupied Serbia ...
'' and pilot in the 6./''Jagdgeschwader'' 52
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Sachsenberg, Heinz 1922 births 1951 deaths Luftwaffe pilots German World War II flying aces People from Dessau-Roßlau Recipients of the Gold German Cross Recipients of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross Military personnel from Saxony-Anhalt