Heat Exhaustion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heat exhaustion is a heat-related illness characterized by the body's inability to effectively cool itself, typically occurring in high ambient temperatures or during intense physical exertion. In heat exhaustion, core body temperature ranges from 37 °C to 40 °C (98.6 °F to 104 °F). Symptoms include profuse sweating, weakness, dizziness, headache, nausea, and lowered blood pressure, resulting from dehydration and serum electrolyte depletion. Heat-related illnesses lie on a spectrum of severity, where heat exhaustion is considered less severe than
Heat Safety Tool app
that notifies their users with real time data on weather forecasts in a certain location, common side effects of heat related illnesses, and how the temperature feels like outside allowing individuals to safely plan out their day based on the weather. Additional resources include monitoring weather in your area of the United States based on zip code using weather.gov, being aware of cooling centers in your area, knowing how to save and use less energy within your household, and being well informed of certain populations who are more vulnerable to heat related illnesses than others. Apart from these resources, there are radio stations and news weather forecasts that continue to provide information on changes in the weather and temperature both globally and within your area.
heat stroke
Heat stroke or heatstroke, also known as sun-stroke, is a severe heat illness that results in a body temperature greater than , along with red skin, headache, dizziness, and confusion. Sweating is generally present in exertional heatstro ...
but more severe than heat cramps and heat syncope.
Climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
and increasing global temperatures have led to more frequent and intense heat wave
A heat wave or heatwave, sometimes described as extreme heat, is a period of abnormally hot weather generally considered to be at least ''five consecutive days''. A heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and ...
s, raising the incidence of heat exhaustion. Risk factors include hot and humid weather, prolonged heat exposure, intense physical exertion, limited access to water or cooling, and certain medications that can exacerbate fluid and serum electrolyte losses including diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics ...
s, antihypertensives, anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
s, and antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
s. Children, older adults, and individuals with certain pre-existing health conditions are more susceptible to heat exhaustion due to their reduced ability to regulate core body temperature.
Prevention strategies include wearing loose and lightweight clothing, avoiding strenuous activity in extreme heat, maintaining adequate hydration, and gradually acclimatizing to hot conditions. Public health measures, such as heat warnings and community cooling centers, also help prevent heat exhaustion during extreme weather events. Treatment involves moving to a cooler environment, rehydrating, and cooling the body. Untreated heat exhaustion can progress to heat stroke, a life-threatening condition characterized by a core body temperature above 40 °C (104 °F) and central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
dysfunction.
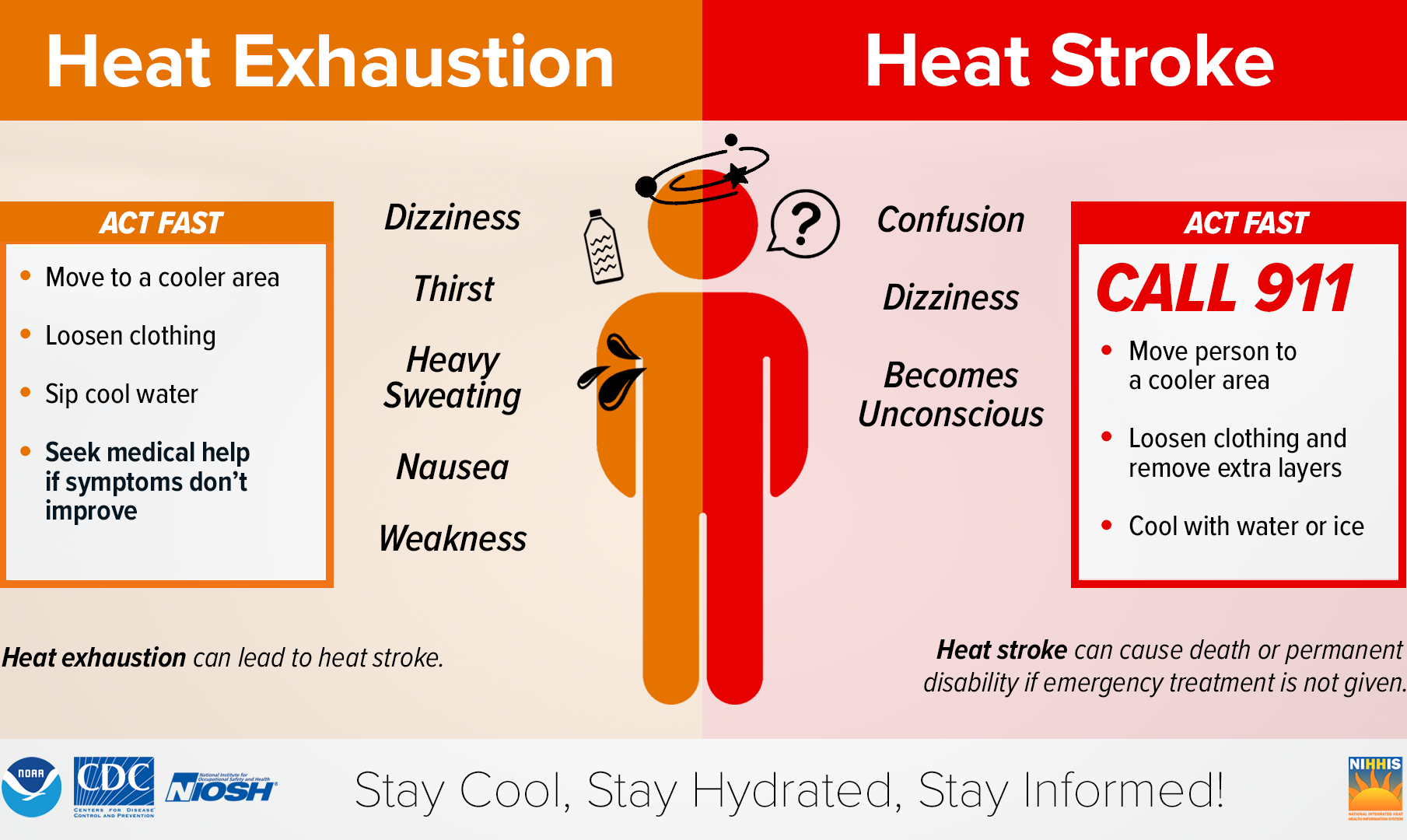
Signs and symptoms

Common
Sources: * Elevated heart rate * Lowered blood pressure * Elevated core body temperature (not exceeding 40 °C or 104 °F) * Elevatedrespiratory rate
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
Measurement
The respiratory rate in humans is mea ...
* Profuse sweating
* Dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
* Serum electrolyte depletion
* Weakness
Weakness is a symptom of many different medical conditions. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, ...
and fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
* Persistent muscle cramps
A cramp is a sudden, involuntary, painful skeletal muscle contraction or overshortening associated with electrical activity. While generally temporary and non-damaging, they can cause significant pain and a paralysis-like immobility of the affe ...
* Skin tingling
* Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
and vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
* Dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to Balance disorder, disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.
Dizziness is a ...
and light-headedness
* Irritability
Irritability is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessive sensitivity to stimul ...
* Headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
Less common
Sources: *Pallor
Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eye ...
* Hot and dry skin
* Core body temperature exceeding 40 °C or 104 °F
* Syncope
* Central nervous system dysfunction (e.g., altered mental status, loss of spatial awareness, loss of bodily movement control, seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
s, etc.)
Comparison with other heat-related illnesses
Common signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion can also be observed in other heat-related illnesses such as heat cramps, heat syncope, andheat stroke
Heat stroke or heatstroke, also known as sun-stroke, is a severe heat illness that results in a body temperature greater than , along with red skin, headache, dizziness, and confusion. Sweating is generally present in exertional heatstro ...
. Heat cramps, a mild form of heat-related illness, is characterized by persistent abdominal
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
, quadricipital, and calf muscle contractions. Heat syncope, also referred to as exercise-associated collapse, is a moderate form of heat-related illness characterized by a temporary loss of consciousness. Unlike heat exhaustion, heat cramps and heat syncope do not have systemic effects.
Heat exhaustion is a precursor to heat stroke, a severe form of heat-related illness. Heat stroke is more likely than heat exhaustion to cause pallor, hot and dry skin, syncope, and dysfunction of the central nervous system (e.g., altered mental status, loss of spatial awareness, loss of bodily movement control, seizures, etc.). Central nervous system dysfunction and a core body temperature exceeding 40 °C or 104 °F are the primary differentiators between heat exhaustion and heat stroke. One of the earliest indicators of heat stroke is altered mental status, which can manifest as delirium, confusion, reduced alertness, loss of consciousness, etc. Prompt recognition and treatment are crucial to prevent multi-organ failure and death.
Physiology
The human body maintains acore body temperature
Normal human body temperature (normothermia, euthermia) is the typical temperature range found in humans. The normal human body temperature range is typically stated as .
Human body temperature varies. It depends on sex, age, time of day, exert ...
at around 37 °C or 98.6 °F through mechanisms controlled by the thermoregulatory center within the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
. When the body is exposed to high ambient temperatures, intense physical exertion, or both, the thermoregulatory center will initiate several processes to dissipate more heat:
* Blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s near the skin surface dilate, increasing blood flow to the skin to facilitate heat loss through radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
and convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
* Heart rate increases to support elevated blood flow to the skin
* Eccrine sweat gland
Eccrine sweat glands (; from Greek '' ek(s)+krinein'' 'out(wards)/external+ secrete') are the major sweat glands of the human body. Eccrine sweat glands are found in virtually all skin, with the highest density in the palms of the hands, and sol ...
s in the skin produce sweat, which evaporates from the skin surface
Heat cramps and heat syncope
Heat-related illnesses lie on a spectrum of severity. Conditions on the lower end of this spectrum include heat cramps and heat syncope. The electrolyte depletion theory proposes that increased sweating during intense physical exertion in high ambient temperatures results in a depletion of serum electrolytes (e.g., sodium, potassium, etc.) that causes sustained involuntary muscle contractions, or heat cramps. However, the contribution of intense physical exertion and high ambient temperatures to serum electrolyte depletion in the absence of significantdehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
has been contested by more recent research, which proposes an alternative theory. The neuromuscular theory proposes that muscle fatigue increases the excitability of α1 muscle spindle
Muscle spindles are stretch receptors within the body of a skeletal muscle that primarily detect changes in the length of the muscle. They convey length information to the central nervous system via afferent nerve fibers. This information can be ...
s and decreases the inhibitory input from Golgi tendon organ
The Golgi tendon organ (GTO) (also called Golgi organ, tendon organ, neurotendinous organ or neurotendinous spindle) is a proprioceptor – a type of sensory receptor that senses changes in muscle tension. It lies at the interface between a mus ...
s, leading to sustained involuntary muscle contractions.
In heat syncope, or exercise-associated collapse, there is an increased dilation of blood vessels near the skin's surface and a pooling of blood in the lower extremities due to a decrease in vasomotor tone, which is the extent of control over the constriction and dilation of blood vessels. This results in a drop in blood pressure when not lying down and a temporary reduction in blood flow to the brain, leading to fainting.
Heat exhaustion
Heat exhaustion is a moderate form of heat-related illness characterized by increasingly overwhelmed thermoregulatory mechanisms. In heat exhaustion, the core body temperature rises to between 37 °C and 40 °C (98.6 °F and 104 °F). To dissipate heat, blood flow to the skin can increase up to 8 liters per minute, accounting for a significant proportion of thecardiac output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: tha ...
. This increase in peripheral circulation leads to a reduction in central blood volume—the volume of blood contained within the heart, lungs, and large blood vessels. The heart rate further increases, but the cardiac output and blood pressure continue to drop. At the same time, profuse sweating occurs, with losses up 1-2 liters of sweat per hour. This sweating exacerbates the reduction in central blood volume and leads to dehydration and serum electrolyte depletion, particularly hyponatremia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the Serum (blood), blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symp ...
(low serum sodium) and hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an a ...
(low serum potassium). The combination of decreased blood flow to vital organs and serum electrolyte losses results in various symptoms, mentioned in "Signs and symptoms." Additionally, the body's respiratory rate
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
Measurement
The respiratory rate in humans is mea ...
increases to aid in heat dissipation through the lungs.
Heat stroke
Heat exhaustion can progress toheat stroke
Heat stroke or heatstroke, also known as sun-stroke, is a severe heat illness that results in a body temperature greater than , along with red skin, headache, dizziness, and confusion. Sweating is generally present in exertional heatstro ...
, a severe form of heat-related illness characterized by complete failure of thermoregulatory mechanisms. Heat stroke is defined by two key features: a core body temperature above 40 °C (104 °F) and central nervous system dysfunction. In classic heat stroke, sweating ceases due to sweat gland dysfunction or depletion. This loss of evaporative cooling further accelerates heat accumulation. The resulting hyperthermia
Hyperthermia, also known as overheating, is a condition in which an individual's body temperature is elevated beyond normal due to failed thermoregulation. The person's body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. When extreme te ...
leads to widespread cellular dysfunction, including:
* Alterations in enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
function
* Protein denaturation
* Disruption of cellular membranes.
Hyperthermia causes direct cellular damage, triggering a systemic inflammatory response. This inflammatory cascade can result in multi-organ dysfunction, potentially leading to:
* Acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in renal function, kidney function that develops within seven days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
...
* Liver failure
Liver failure is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic functions as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognised, acute and chronic (cirrhosis). Recently, a third form of liver failure known as acute- ...
* Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking Microvessel, small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems ...
Causes
There is increasing evidence linking higher temperatures to a variety of diseases and disorders as well as elevated mortality and morbidity rates. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) projects that temperatures will rise by up to 1.5 °C in the future due to ongoing greenhouse gas emissions.Climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
exacerbates extreme temperatures, resulting in more intense and frequent heat wave
A heat wave or heatwave, sometimes described as extreme heat, is a period of abnormally hot weather generally considered to be at least ''five consecutive days''. A heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and ...
s. As this trend continues, populations with greater susceptibility to heat exhaustion, such as children, older adults, and individuals with chronic diseases, are at an increased risk.
Common causes of heat exhaustion and other heat-related illnesses include:
* Prolonged exposure to hot, sunny, or humid weather conditions
* Extended time spent in high-temperature environments without adequate cooling
* Engaging in strenuous activities through work, exercise, or sports, particularly in hot conditions
* Insufficient fluid intake leading to dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
* Overconsumption of fluids without adequate electrolyte replacement, leading to serum electrolyte depletion
* Wearing tight or non-breathable clothing that does not allow heat to escape, trapping heat close to the body
* Use of certain medications that impair thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
, such as diuretics, antihypertensives, anticholinergics, and antidepressants
* Sudden exposure to high temperatures without gradual acclimatization
Acclimatization or acclimatisation ( also called acclimation or acclimatation) is the process in which an individual organism adjusts to a change in its environment (such as a change in altitude, temperature, humidity, photoperiod, or pH), ...
Risk factors
Risk factors for heat exhaustion include: * Wearing dark, padded, or insulated clothing, hats, and helmets (e.g., football pads,turnout gear
Firefighters in Chicago wearing rubber three-quarter boots and jacket
Firefighters in Montreal in full turnout gear during a fire
Bunker gear (also known as turnout gear, fire kit and incident gear) is the personal protective equipment (PPE) ...
, etc.) that trap heat and impede cooling
* Higher body fat percentage, which can hinder heat dissipation
* Presence of fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, which elevates body temperature and lowers heat tolerance
* Children younger than four years old and adults older than 65 are at a higher risk of serious heat illness due to impaired thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
, even at rest, especially in hot and humid conditions without adequate cooling
* Insufficient access to water, air conditioning, or other cooling methods
* Use of medications that increase the risk of heat exhaustion, including diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics ...
s, first-generation antihistamine
H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic reactions. Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of his ...
s, beta-blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention) ...
s, antipsychotics
Antipsychotics, previously known as neuroleptics and major tranquilizers, are a class of psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), principally in schizo ...
, MDMA ('Ecstasy', 'Molly'), and other amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
s
Medication impact
Medications such asdiuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics ...
s, antihypertensives, anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
s, and antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
s can cause electrolyte imbalances, drug-induced hypohidrosis
Hypohidrosis is a medical condition in which a person exhibits diminished sweating in response to appropriate stimuli. In contrast with hyperhidrosis, which is a socially troubling yet often benign condition, the consequences of untreated hypohidr ...
(reduced sweating), or drug-induced hyperhydrosis (excessive sweating). This disrupts the body's ability to regulate core temperature and increases the risk of heat exhaustion.
Anticholinergic medications inhibit the parasympathetic arm of the autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervo ...
involving the muscarinic M3 acetylcholine receptors, which often results in symptoms of dry mouth, increased thirst, as well as an increased risk of dehydration. Other medications containing anticholinergic properties, such as certain antidepressants and first-generation antihistamines, have comparable side effects. For patients at risk of or experiencing heat exacerbation, taking these medications can further increase their risk.
Certain antidepressants, such as tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and were marketed later in the decade. They are named after their chemical structure, which contains ...
s and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), as well as opioids that stimulate histamine release, can cause hyperhidrosis, leading to significant fluid and serum electrolyte depletion Though the mechanisms are not fully understood, antihypertensives such as ACE inhibitor
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. This class of medicine works by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decr ...
s, beta-blockers, and diuretics have shown to decrease heat tolerance. In addition, ACE inhibitors and diuretics can cause electrolyte imbalances, increase thirst, and increase risk of dehydration Beta-blockers limit the body's ability to redirect hyperthermic blood away from the body's core and towards the skin for cooling. If dehydration and electrolyte imbalances are left untreated, they can lead to severe complications, progress to a more severe heat-related illness such as a heatstroke, and can potentially be fatal.
The management of drug-induced hypohidrosis and hyperhidrosis should be thoroughly evaluated and discussed with a healthcare professional. Treatment options may include discontinuation of the medication, a dose adjustment, a drug substitution to a different drug-class, adaptation to new behavioral and environmental changes, or the addition of another agent that can counteract the side effects.
Special populations
Pediatrics
Children (under the age of 18 years old) have a lower heat tolerance compared to adults due to decreased homeostatic regulatory systems, increased metabolic rates, and decreased cardiac output. Strenuous exercise in high-temperature conditions is the leading cause of heat-related illness in children. The dehydration stemming from heat-related illness is what puts children at risk for thermoregulatory dysfunction. Thermoregulatory dysfunction only worsens the ability for children to fight heat exhaustion because it leads to decreased sweat capabilities and increased core temperature response. Similar to that of adults, the best way to combat and prevent heat exhaustion in children is to properly condition prior to exercise exertion, hydrate, allow for temperature adjustment, and clothe accordingly.Pregnancy
Although there are not many studies on how the rates of heat exhaustion differ amongst the pregnant population, the adverse effects due to heat exhaustion in the pregnant population can be fatal. Heat exhaustion becomes much more common within pregnant women who perform the same tasks they had while not pregnant. While their symptoms are no different than the most common, such as dizziness, fatigue, and dehydration, the extreme adverse effects include increased preterm births, miscarriages, and birth defects. The reason for these more serious adverse effects is that pregnancy causes higher metabolic and cardiovascular demands, and the presence of heat exhaustion only amplifies these demands further. The dehydration symptom of heat exhaustion is vital to overcome because proper hydration is deeply necessary for proper development of the fetus and metabolic activity. To combat the dehydration aspect, the amount of water intake must be increased from the intake amount prior to pregnancy and hot environments should be avoided to prevent sweating.Prevention
Ways to prevent and lower risk of heat exhaustion include: * Public widespread announcements of heat waves or rapid increases in temperature * Staying up to date on daily weather reports * Heat shelters throughout communities * Wearing loose fitting and lighter fabric clothing * Try to stay well hydrated unless fluid intake is limited * For those who are doing lots of outdoor activities or work, find shady cool areas to rest * Avoid prolonged exposure to hot environments, such as tropical sunshine in the middle of the day, Mediterranean forests, or a boiler room * Drink adequate fluids * Avoid exertion and exercise in hot weather * Avoid medications that can be detrimental to the regulation of body heatDiagnosis
A diagnosis of heat exhaustion most commonly is diagnosed by medical professionals with various physical examinations. Through examination a person would have their temperature checked and questioned about their recent activity. If the medical professionals suspect a person's heat exhaustion has progressed into heat stroke they may then lead with these varying tests to verify; *Blood test
A blood test is a medical laboratory, laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose ...
, medical professionals when conducting a blood test look for low blood sugar or potassium. They may also look for the presence of unwanted gases in a person's blood.
* Urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a Test panel, panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and #Microscopic examination, m ...
, an urinalysis or urine test is a test to measure color, clarity, pH levels, glucose concentration, and protein levels. The test additionally can check a person's kidney function, which is common to be affected by classic heat stroke.
* Muscle function tests, medical professionals use muscle function tests to check for rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis (shortened as rhabdo) is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle breaks down rapidly. Symptoms may include muscle pains, weakness, vomiting, and confusion. There may be tea-colored urine or an irregular heartbeat. Some o ...
, which is severe damage to a person's skeletal muscle tissue.
Treatment
First aid
First aid
First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person with a medical emergency, with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, or to promote recovery until medical services arrive. First aid is gener ...
for heat exhaustion or heat stroke includes:
* Moving the person to a shaded, fanned, or air-conditioned place
* Removing any excess or tight clothing to facilitate cooling
* Applying wet towels or ice packs wrapped in cloth to the forehead, neck, armpits, and groin, and using a fan to cool the person down
* Lying the person down on their back and elevating their feet above head level to improve blood circulation
* Having the person drink cool water or sports drinks, also referred to as electrolyte drinks, provided they are conscious, alert, and not vomiting (Only applies to heat exhaustion)
* Turning the person on their side if they are vomiting to prevent choking
* Monitoring the person's vital signs, which includes their heart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ...
, blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
, breathing rate, and body temperature
* Monitoring the person's mental status (i.e., confusion, delirium, reduced alertness etc.)
* Contacting emergency medical services
Emergency medical services (EMS), also known as ambulance services, pre-hospital care or paramedic services, are emergency services that provide urgent pre-hospital treatment and stabilisation for serious illness and injuries and transport to d ...
if their situation does not improve rapidly or worsens
Emergency medical treatment
If an individual with heat exhaustion receives medical treatment,Emergency Medical Technicians
An emergency medical technician (often, more simply, EMT) is a medical professional that provides emergency medical services. EMTs are most commonly found serving on ambulances and in fire departments in the US and Canada, as full-time and some ...
(EMTs), doctors, and/or nurses may also:
* Provide supplemental oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
* Administer intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
fluids and electrolytes if they are too confused to drink and/or are vomiting
Do Not
If an individual is experiencing heat exhaustion or any other heat related illness DO NOT: * Administer fever medications such as aspirin or Tylenol as they can be harmful for the individual * Administer salt tablets as they can worsen dehydration * Use alcohol or caffeine containing products as they can make it harder for the individual to control their body temperature * Give anything by mouth if the person is vomiting or unconsciousHeat warning resources
With high temperatures becoming more frequent, there are resources available to stay up to date on sudden changes in the weather. In the United States,OSHA
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA; ) is a regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established ...
in collaboration with the NIOSH
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury, illness, disability, and death. It ...
have Heat Safety Tool app
that notifies their users with real time data on weather forecasts in a certain location, common side effects of heat related illnesses, and how the temperature feels like outside allowing individuals to safely plan out their day based on the weather. Additional resources include monitoring weather in your area of the United States based on zip code using weather.gov, being aware of cooling centers in your area, knowing how to save and use less energy within your household, and being well informed of certain populations who are more vulnerable to heat related illnesses than others. Apart from these resources, there are radio stations and news weather forecasts that continue to provide information on changes in the weather and temperature both globally and within your area.
Prognosis
After adequate rest and rehydration, most individuals typically recover from their heat exhaustion. However, when heat exhaustion is left untreated, the most common disease progression is heat stroke. According to the CDC, a typical trait indicating a person is having a heat stroke is when their body temperature reaches 104 °F or higher in a span of 10 to 15 minutes. In addition to a high body temperature, they will also experience central nervous system dysfunction such as alteration in their mental status and slurred speech. Another possible illness that heat stroke can lead to isrhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis (shortened as rhabdo) is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle breaks down rapidly. Symptoms may include muscle pains, weakness, vomiting, and confusion. There may be tea-colored urine or an irregular heartbeat. Some o ...
or rapid injury to skeletal muscle especially when heat stroke is caused by physical exertion. When an individual experiences rhabdomyolysis, that damaged skeletal tissue releases toxic muscle components such as myoglobin
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle, skeletal Muscle, muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compar ...
into the bloodstream and can cause issues such as coca cola colored urine, myalgia
Myalgia or muscle pain is a painful sensation evolving from muscle tissue. It is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another likely cause is viral infection, espec ...
, and kidney damage due to the blocked tubules to name a few. If a person is experiencing a heat stroke and is not properly treated, that can further progress to metabolic abnormalities, irreversible damage to multiple organs in the body, and death as a result.
See also
* Occupational heat stressReferences
{{reflist Effects of external causes Thermal medicine Wilderness medical emergencies