Health Intervention And Technology Assessment Program on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Health Intervention and Technology Assessment Program (HITAP) is a semi-autonomous
www.ucbp.net
). The project incorporates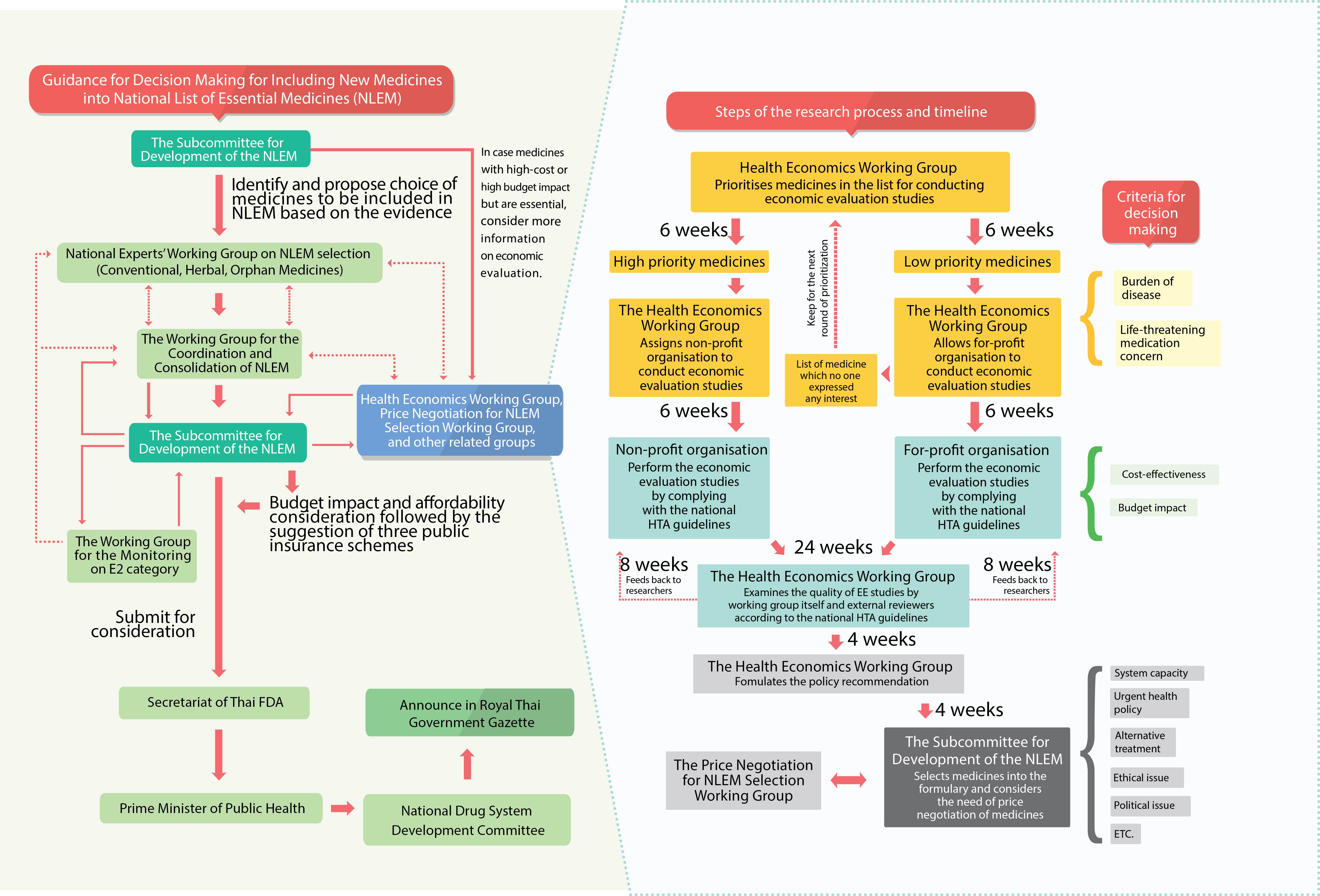 In 1981, Thailand’s National List of Essential Medicines was created. Subsequently, in 1983, the Subcommittee for the Development of the National List of Essential Medicines who works in collaboration with the
In 1981, Thailand’s National List of Essential Medicines was created. Subsequently, in 1983, the Subcommittee for the Development of the National List of Essential Medicines who works in collaboration with the
research
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to ...
unit under Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
’s Ministry of Public Health. It was established in 2007 as a non-profit organization
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a nonbusiness entity, nonprofit institution, not-for-profit organization, or simply a nonprofit, is a non-governmental (private) legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public, or so ...
in order to take responsibility for appraising a wide range of health technologies and programs, including pharmaceuticals, medical devices, interventions, individual and community health promotion, and disease prevention as well as social health policy to inform policy decisions in Thailand.
HITAP assumes an advisory role to health governmental authorities by providing rigorous scientific evidence
Scientific evidence is evidence that serves to either support or counter a scientific theory or hypothesis, although scientists also use evidence in other ways, such as when applying theories to practical problems. "Discussions about empirical ev ...
through professional assessment of health data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
in support of public decision-making. These assessments cover a range of topics including system design, selection of technologies for assessment, and the actual assessment of those selected and agreed upon by relevant government agencies.
In this effort, HITAP publishes research
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to ...
and studies in the following areas: methodological development, (HTA and cost
Cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it i ...
) databases and guidelines; knowledge transfer and exchange (KTE) and capacity development; technology assessments on drugs
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestio ...
, medical devices
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assura ...
, medical procedures, disease prevention and health promotion measures; benefit packages of care – mixing screening and treatments; and other public health policies, e.g. evaluation of Thailand’s government compulsory license policy.
Strategies
In operationalizing HITAP’s goals and in fulfilling its advisory role in the decision making process HITAP follows the five key strategies of having an 1) HTA Fundamental System; 2) strengthening Human Capacity; 3) HTA Research; 4) Knowledge Management; and 5) creating an HTA Network. Having an HTA fundamental system entails basicresearch and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in some countries as OKB, experiment and design, is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage ...
for HTA or the creation of infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and pri ...
to support health intervention and technology assessment by developing standards Standard may refer to:
Symbols
* Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs
* Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification
Norms, conventions or requirements
* Standard (metrology), an object t ...
that are on par with the international level whilst taking into account resource constraints in the Thai context. Under this strategy, methodological guidelines, a database of HTA studies in Thailand, tools and quality of life measures for cost-utility analysis, and a social value based threshold ceiling were developed.
HTA in the public health system
The National Health Security Office, which institutes and manages the largest health plan in Thailand (Universal Coverage Scheme C, initiated a collaborative research and development project with two independent research institutes – the Health Intervention and Technology Assessment Program and the International Health Policy Program – in 2009. The aim of the project was to develop an optimal strategy for the development of the UC benefit package, that is, to determine which interventions should be candidate for public reimbursement. The project is named ''research for development of health benefit package under theuniversal health care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized a ...
coverage scheme'', or known as UCBP (sewww.ucbp.net
). The project incorporates
multiple-criteria decision analysis
Multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) or multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) is a sub-discipline of operations research that explicitly evaluates multiple conflicting wikt:criterion, criteria in decision making (both in daily life a ...
(MCDA) and a deliberative process and multi stakeholders’ involvement to guide national-level priority setting in health care coverage decision. The review documented the experience of seven health technology assessment organizations in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
and Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, which all use an explicit process of priority setting. Its findings concluded that all these organizations consider multiple criteria, involved multiple stakeholders, and distinguish, in one way or another, four basic steps in their priority setting Process. These steps were then also applied in the Thai setting and included. The results of the review were adapted to the Thai setting, resulting in 4 steps of explicit priority setting including: 1) nomination of interventions for assessments, 2) selection of interventions for assessment, 3) technology assessment of interventions, and 4) appraisal of interventions. Since the beginning of the research project up to 119 topics have been proposed for inclusion into the benefit package, with 53 topics selected for further research or HTA analysis.
One of the benefit packages revised through UCBP is the development of a health screening package under the universal health coverage in 2010. Currently, the three public insurance schemes in Thailand offer different health screening packages. The study was designed as a response to requests from stakeholders including decision-makers and representatives from the general public, to develop an evidenced-based health screening package for the population that could ensure equitable access to essential health screening under the three schemes. The results led to advice against elements of current clinical practice
''Clinical Practice'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed open access medical journal. It covers good clinical practice and health care. The journal was established in 2004 as ''Therapy'' by Future Drugs Ltd, obtaining its current name in 2012 when it wa ...
, such as annual chest X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s and particular blood test
A blood test is a medical laboratory, laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose ...
(e.g. kidney function
Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and medical sign, signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.
Renal physiology, Functions of a healthy kidney include ...
test), and indicated that the introduction of certain new population-based health screening programs, such as for chronic hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pa ...
B, would provide substantial health and economic benefits to the Thais. The final results were presented to a wide group of stakeholders, including decision-makers at the Ministry of Public Health and the public health insurance
Publicly funded healthcare is a form of health care financing designed to meet the cost of all or most healthcare needs from a publicly managed fund. Usually this is under some form of democratic accountability, the right of access to which are se ...
schemes, to verify and validate the findings and policy recommendations. The package has been endorsed by the Thai UHC Benefit Package Committee for implementation in fiscal year 2016.
 In 1981, Thailand’s National List of Essential Medicines was created. Subsequently, in 1983, the Subcommittee for the Development of the National List of Essential Medicines who works in collaboration with the
In 1981, Thailand’s National List of Essential Medicines was created. Subsequently, in 1983, the Subcommittee for the Development of the National List of Essential Medicines who works in collaboration with the Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
as its secretariat. In the latter years, the function of the subcommittee became the maintenance of an optimal list of medicines, wherein the criteria for selection were cost
Cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it i ...
, safety
Safety is the state of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
The word 'safety' entered the English language in the 1 ...
, efficacy
Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as '' effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a distinction is now often made betwee ...
and effectiveness
Effectiveness or effectivity is the capability of producing a desired result or the ability to produce desired output. When something is deemed effective, it means it has an intended or expected outcome, or produces a deep, vivid impression.
Et ...
of drugs
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestio ...
. In each of these criteria, the subcommittee’s was to consider scientific evidence to determine which medicines are to be included in the list. Twenty-eight specialist working groups undertake the task of determining what should be on the list as well as informing price negotiations between manufacturers and the NLEM.
Increasingly, awareness and realization that the evidence required for optimal coverage decisions involved analyses in cost-effectiveness
Cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) is a form of economic analysis that compares the relative costs and outcomes (effects) of different courses of action. Cost-effectiveness analysis is distinct from cost–benefit analysis, which assigns a moneta ...
as a fifth criterion. In 2009, the Health Economics
Health economics is a branch of economics concerned with issues related to Health care efficiency, efficiency, effectiveness, value and behavior in the production and consumption of health and healthcare. Health economics is important in dete ...
Working Group was established under the subcommittee. The working group was composed of health economists, representatives from the subcommittee, academics and representatives from the three health insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
schemes and the working group secretariat. In this process, HITAP in collaboration with the Food and Drug Administration was involved as the secretariat of the working group whose function was to generate procedures and assure quality of the evidence provided. The HEWG then prioritized the requests based on burden of disease, the risk to life and financial burden on households posed by the condition and social consideration and commissions the cost-effectiveness research from non-profit agencies (like HITAP).
International work
In late 2013 in response to the increasing requests for involvement in international projects, HITAP created the HITAP International Unit in order to collaborate with international partners and networks working to improve health intervention and technology assessment (HITA) forUniversal Health Care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized a ...
(UHC) and priority-setting capacity in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). The HIU has previously worked with the National Center for Pharmaceutical Access and Management (NCPAM), Philippines, Health Technology Assessment Committee (HTAC), Indonesia, Health Systems and Policy Institute (HSPI), Vietnam, the International Decision Support Initiative (IDSI), UK and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care (United Kingdom), Department of Health and Social Care.
As the national health technolog ...
International (NI), UK.
In the past HITAP has been instrumental in pushing HTA forward in international policy by becoming part of the delegation representing Thailand as sponsors and writers of several resolutions in the World Health Assembly
The World Health Assembly (WHA) is the forum through which the World Health Organization (WHO) is governed by its 194 World Health Organization#Membership, member states. It is the world's highest health policy setting body and is composed of h ...
(WHA) and the South-East Asia Regional Office (SEARO) of the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO), including:
* Health Intervention and Technology Assessment in Support of Universal Health Coverage Agenda. 15.7 A67/VR/9, WHA 67.23 24 May 2014.
* Health Intervention and Technology Assessment in Support of Universal Health Coverage. SEA/RC66/R4 May, 2014.
HITAP has also worked to establish regional collaboration amongst HTA units in Asia. Along with the National Evidence-based Health Care Collaborating Agency, South Korea (NECA) and the Center for Drug Evaluation, Taiwan (CDE), HITAP founded the HTAsiaLink Network in 2010. The network is a collaborative platform for knowledge sharing and best practices of HTA in the Asia-Pacific region. One of its many activities is the production of a biannual HTAsialink Newsletter and an Annual HTAsiaLink Conference held in different member countries in Asia. Currently the Network has 30 member organizations from 16 Countries.
References
{{authority control Research institutes in Thailand Medical and health organizations based in Thailand Sub-departmental government bodies of Thailand Ministry of Public Health (Thailand)