Hawaii (island) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hawaii is the largest island in the United States, located in the state of Hawaii, the southernmost state in the union. It is the southeasternmost of the Hawaiian Islands, a chain of
 Oral tradition holds one of the most famous ''aliinui'' of Hawaii to be Umi-a-Līloa, who united the island by force. He was the illegitimate son of Līloa, aliinui of Hawaii who ruled from Waipio Valley in the Hāmākua district. When Līloa died, the island passed to Umi's half-brother Hakau. However, Umi attacked and killed Hakau along with the ''alii (nobles)'' who served him, winning control of Hāmākua. He then proceeded to conquer the rebelling districts of Hilo, Puna, Kaū, and Kona. He placed the seat of his new government in Kailua in the Kona district.
In 1779, Captain James Cook made his second voyage to the Hawaiian islands, anchoring in Kealakekua Bay on the island of Hawaii. He spent several weeks there, meeting and trading with locals and readying his ships for a planned trip to the Arctic. The Hawaiians received him hospitably, considering him to be an incarnation of the god Lono. Early in 1780, Cook departed. However, his ships were damaged in a storm immediately after setting sail, and he was forced to return to Kealakekua after only a week at sea. During this second anchoring, an altercation between the Europeans and the Hawaiians turned violent, resulting in the death of multiple people on both sides, including Cook himself. Peaceful relations were eventually restored with the crew of his ships, who departed for good later that month.
In 1780 CE, the island of Hawaiii was controlled by the ''aliinui'' Kalaniōpuu, a descendant of Umi-a-Līloa. On his death in 1782, he designated his son Kīwalaō as his heir. However, a feud between Kīwalaō and Kalaniōpuu's nephew Paiea Kamehameha soon escalated into a civil war. Kīwalaō was killed in the Battle of Mokuōhai later that same year, leaving control of the island divided between Kamehameha in the west, Kīwalaō's uncle and advisor Keawemauhili in the northeast, and Kīwalaō's half-brother Keōua Kūahuula in the south. The three chiefs, aided by Western ships and weapons, fought to a standstill for eight years until 1790, when Keōua defeated and killed Keawemauhili. In 1791 Kamehameha's men killed Keōua at a diplomatic meeting, leaving control of Hawaii to Kamehameha.
Kamehameha went on to conquer the rest of the Hawaiian islands, consolidating his control in 1810 with the peaceful surrender of Kaumualii, king of Kauai. He gave his new kingdom, and by extension the island chain itself, the name of his native island – the
Oral tradition holds one of the most famous ''aliinui'' of Hawaii to be Umi-a-Līloa, who united the island by force. He was the illegitimate son of Līloa, aliinui of Hawaii who ruled from Waipio Valley in the Hāmākua district. When Līloa died, the island passed to Umi's half-brother Hakau. However, Umi attacked and killed Hakau along with the ''alii (nobles)'' who served him, winning control of Hāmākua. He then proceeded to conquer the rebelling districts of Hilo, Puna, Kaū, and Kona. He placed the seat of his new government in Kailua in the Kona district.
In 1779, Captain James Cook made his second voyage to the Hawaiian islands, anchoring in Kealakekua Bay on the island of Hawaii. He spent several weeks there, meeting and trading with locals and readying his ships for a planned trip to the Arctic. The Hawaiians received him hospitably, considering him to be an incarnation of the god Lono. Early in 1780, Cook departed. However, his ships were damaged in a storm immediately after setting sail, and he was forced to return to Kealakekua after only a week at sea. During this second anchoring, an altercation between the Europeans and the Hawaiians turned violent, resulting in the death of multiple people on both sides, including Cook himself. Peaceful relations were eventually restored with the crew of his ships, who departed for good later that month.
In 1780 CE, the island of Hawaiii was controlled by the ''aliinui'' Kalaniōpuu, a descendant of Umi-a-Līloa. On his death in 1782, he designated his son Kīwalaō as his heir. However, a feud between Kīwalaō and Kalaniōpuu's nephew Paiea Kamehameha soon escalated into a civil war. Kīwalaō was killed in the Battle of Mokuōhai later that same year, leaving control of the island divided between Kamehameha in the west, Kīwalaō's uncle and advisor Keawemauhili in the northeast, and Kīwalaō's half-brother Keōua Kūahuula in the south. The three chiefs, aided by Western ships and weapons, fought to a standstill for eight years until 1790, when Keōua defeated and killed Keawemauhili. In 1791 Kamehameha's men killed Keōua at a diplomatic meeting, leaving control of Hawaii to Kamehameha.
Kamehameha went on to conquer the rest of the Hawaiian islands, consolidating his control in 1810 with the peaceful surrender of Kaumualii, king of Kauai. He gave his new kingdom, and by extension the island chain itself, the name of his native island – the
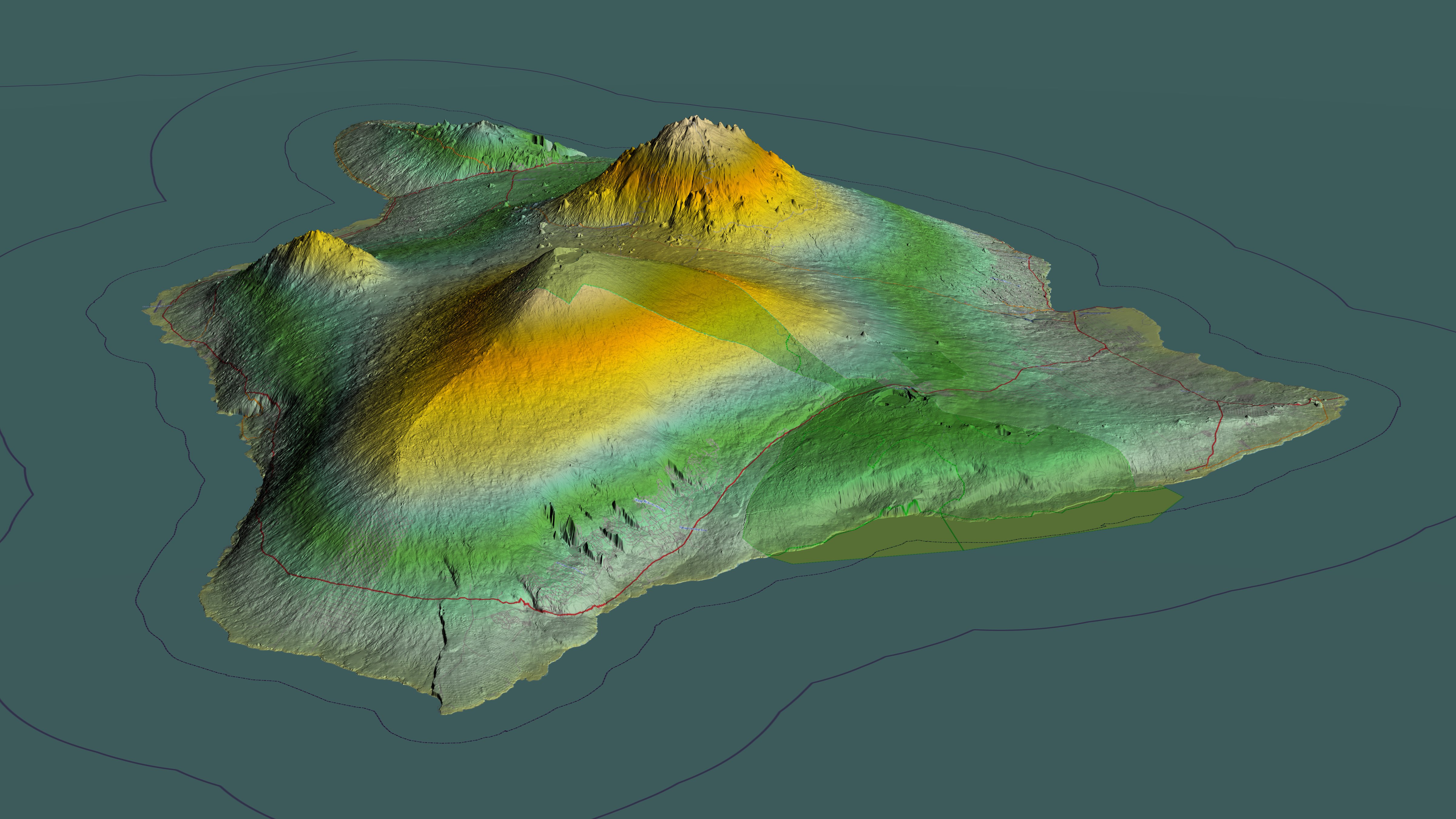 According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (20.8%) is water. The county's land area comprises 62.7 percent of the state's land area. It is the highest percentage by any county in the United States.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (20.8%) is water. The county's land area comprises 62.7 percent of the state's land area. It is the highest percentage by any county in the United States.

 The island of Hawaii is built from five separate
The island of Hawaii is built from five separate
 The Great Crack is an , and fissure in the island, in the district of Kaū. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the Great Crack is the result of crustal dilation from
The Great Crack is an , and fissure in the island, in the district of Kaū. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the Great Crack is the result of crustal dilation from
 The Hilina Slump is a section of the south slope of Kīlauea that is moving away from the island. Between 1990 and 1993,
The Hilina Slump is a section of the south slope of Kīlauea that is moving away from the island. Between 1990 and 1993,
 The island hosts many specialized ecosystems/microclimates, including many protected by federal designation:
* Ala Kahakai National Historic Trail
* Hakalau Forest National Wildlife Refuge
* Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
* Kaloko-Honokōhau National Historical Park
* Kohala Historical Sites State Monument ( Mookini Heiau)
* Kona Forest National Wildlife Refuge
* Puuhonua o Hōnaunau National Historical Park
* Puukoholā Heiau National Historic Site
The island hosts many specialized ecosystems/microclimates, including many protected by federal designation:
* Ala Kahakai National Historic Trail
* Hakalau Forest National Wildlife Refuge
* Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
* Kaloko-Honokōhau National Historical Park
* Kohala Historical Sites State Monument ( Mookini Heiau)
* Kona Forest National Wildlife Refuge
* Puuhonua o Hōnaunau National Historical Park
* Puukoholā Heiau National Historic Site
File:Downtown Kona, Hawaii.jpg, Downtown Kailua-Kona
File:Downtown Hilo, Hawaii.jpg, Downtown Hilo

 * Akaka Falls, one of the tallest waterfalls on the island.
* Amy B. H. Greenwell Ethnobotanical Garden houses many endangered endemic plants.
* East Hawaii Cultural Center
* Hawaii Tropical Botanical Garden
* Hawaii Volcanoes National Park, comprising the active volcanoes Kīlauea and Mauna Loa
* Hulihee Palace, a royal palace in Kailua-Kona
* Imiloa Astronomy Center in Hilo
* Ka Lae, the southernmost point in the United States
* Laupāhoehoe Train Museum
* Lyman House Memorial Museum in Hilo
* Manuka State Wayside Park
*
* Akaka Falls, one of the tallest waterfalls on the island.
* Amy B. H. Greenwell Ethnobotanical Garden houses many endangered endemic plants.
* East Hawaii Cultural Center
* Hawaii Tropical Botanical Garden
* Hawaii Volcanoes National Park, comprising the active volcanoes Kīlauea and Mauna Loa
* Hulihee Palace, a royal palace in Kailua-Kona
* Imiloa Astronomy Center in Hilo
* Ka Lae, the southernmost point in the United States
* Laupāhoehoe Train Museum
* Lyman House Memorial Museum in Hilo
* Manuka State Wayside Park
*
File:Hawaii national parks map.gif, National parks, mountains and cities on the island
File:Hawaii Island topographic map-en.svg, Topographic map of the island of Hawaii
File:HawaiiBigIsland2021OSM.png, Detailed map of the island of Hawaii
Interactive 3D model for Chrome or Firefox
Official Hawaii County website
Hawaii (island)
at ''
''Hawaii Tribune-Herald''
– official website of the '' Hawaii Tribune-Herald'', a daily newspaper in Hilo
''West Hawaii Today''
– official website of '' West Hawaii Today''
Island of Hawaii from the International Space Station
– NASA satellite image, taken from the
volcanic island
Geologically, a volcanic island is an island of volcanic origin. The term high island can be used to distinguish such islands from low islands, which are formed from sedimentation or the uplifting of coral reefs (which have often formed ...
s in the North Pacific Ocean. With an area of , it has 63% of the Hawaiian archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
's combined landmass. However, it has only 13% of the archipelago's population. The island of Hawaii is the third largest island in Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
, behind the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and South Island
The South Island ( , 'the waters of Pounamu, Greenstone') is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand by surface area, the others being the smaller but more populous North Island and Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by ...
s of New Zealand.
The island is often referred to as the Island of Hawaii or Hawaii Island to distinguish it from the state. It is also referred to as The Big Island, due to its size relative to the other islands. In Hawaiian, the island is sometimes called ''Moku o Keawe''. The word ''keawe'' has several meanings. One definition, "southern cross", is said to be the name of an ancient chief. Another definition is "the bearer".
Hawaii County is the local administrative unit. As of the 2020 census, the population was 200,629. The county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or parish (administrative division), civil parish. The term is in use in five countries: Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, and the United States. An equiva ...
and largest city is Hilo. Hawaii County has no incorporated cities.
History
Hawaii is allegedly named after Hawaiiloa, a legendary Polynesian navigator who is said to have discovered the island. Other accounts attribute the name to the legendary realm of Hawaiki, a place from which some Polynesians are said to have originated, the place where they transition to in the afterlife, or the realm of the gods and goddesses. The indigenous Hawaiian name of the island was originally rendered and published as "Owyhee" or "Owhyhee". It is uncertain when Hawaii was first discovered by humans. Early archaeological studies suggested that Polynesian explorers from the Marquesas Islands orSociety Islands
The Society Islands ( , officially ; ) are an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean that includes the major islands of Tahiti, Mo'orea, Moorea, Raiatea, Bora Bora and Huahine. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country ...
may have arrived in the Hawaiian islands as early as the 3rd century CE, possibly with a second wave arriving from Tahiti around 1100 CE. However, more recent analyses suggest that the first settlers arrived around 900–1200 CE.
 Oral tradition holds one of the most famous ''aliinui'' of Hawaii to be Umi-a-Līloa, who united the island by force. He was the illegitimate son of Līloa, aliinui of Hawaii who ruled from Waipio Valley in the Hāmākua district. When Līloa died, the island passed to Umi's half-brother Hakau. However, Umi attacked and killed Hakau along with the ''alii (nobles)'' who served him, winning control of Hāmākua. He then proceeded to conquer the rebelling districts of Hilo, Puna, Kaū, and Kona. He placed the seat of his new government in Kailua in the Kona district.
In 1779, Captain James Cook made his second voyage to the Hawaiian islands, anchoring in Kealakekua Bay on the island of Hawaii. He spent several weeks there, meeting and trading with locals and readying his ships for a planned trip to the Arctic. The Hawaiians received him hospitably, considering him to be an incarnation of the god Lono. Early in 1780, Cook departed. However, his ships were damaged in a storm immediately after setting sail, and he was forced to return to Kealakekua after only a week at sea. During this second anchoring, an altercation between the Europeans and the Hawaiians turned violent, resulting in the death of multiple people on both sides, including Cook himself. Peaceful relations were eventually restored with the crew of his ships, who departed for good later that month.
In 1780 CE, the island of Hawaiii was controlled by the ''aliinui'' Kalaniōpuu, a descendant of Umi-a-Līloa. On his death in 1782, he designated his son Kīwalaō as his heir. However, a feud between Kīwalaō and Kalaniōpuu's nephew Paiea Kamehameha soon escalated into a civil war. Kīwalaō was killed in the Battle of Mokuōhai later that same year, leaving control of the island divided between Kamehameha in the west, Kīwalaō's uncle and advisor Keawemauhili in the northeast, and Kīwalaō's half-brother Keōua Kūahuula in the south. The three chiefs, aided by Western ships and weapons, fought to a standstill for eight years until 1790, when Keōua defeated and killed Keawemauhili. In 1791 Kamehameha's men killed Keōua at a diplomatic meeting, leaving control of Hawaii to Kamehameha.
Kamehameha went on to conquer the rest of the Hawaiian islands, consolidating his control in 1810 with the peaceful surrender of Kaumualii, king of Kauai. He gave his new kingdom, and by extension the island chain itself, the name of his native island – the
Oral tradition holds one of the most famous ''aliinui'' of Hawaii to be Umi-a-Līloa, who united the island by force. He was the illegitimate son of Līloa, aliinui of Hawaii who ruled from Waipio Valley in the Hāmākua district. When Līloa died, the island passed to Umi's half-brother Hakau. However, Umi attacked and killed Hakau along with the ''alii (nobles)'' who served him, winning control of Hāmākua. He then proceeded to conquer the rebelling districts of Hilo, Puna, Kaū, and Kona. He placed the seat of his new government in Kailua in the Kona district.
In 1779, Captain James Cook made his second voyage to the Hawaiian islands, anchoring in Kealakekua Bay on the island of Hawaii. He spent several weeks there, meeting and trading with locals and readying his ships for a planned trip to the Arctic. The Hawaiians received him hospitably, considering him to be an incarnation of the god Lono. Early in 1780, Cook departed. However, his ships were damaged in a storm immediately after setting sail, and he was forced to return to Kealakekua after only a week at sea. During this second anchoring, an altercation between the Europeans and the Hawaiians turned violent, resulting in the death of multiple people on both sides, including Cook himself. Peaceful relations were eventually restored with the crew of his ships, who departed for good later that month.
In 1780 CE, the island of Hawaiii was controlled by the ''aliinui'' Kalaniōpuu, a descendant of Umi-a-Līloa. On his death in 1782, he designated his son Kīwalaō as his heir. However, a feud between Kīwalaō and Kalaniōpuu's nephew Paiea Kamehameha soon escalated into a civil war. Kīwalaō was killed in the Battle of Mokuōhai later that same year, leaving control of the island divided between Kamehameha in the west, Kīwalaō's uncle and advisor Keawemauhili in the northeast, and Kīwalaō's half-brother Keōua Kūahuula in the south. The three chiefs, aided by Western ships and weapons, fought to a standstill for eight years until 1790, when Keōua defeated and killed Keawemauhili. In 1791 Kamehameha's men killed Keōua at a diplomatic meeting, leaving control of Hawaii to Kamehameha.
Kamehameha went on to conquer the rest of the Hawaiian islands, consolidating his control in 1810 with the peaceful surrender of Kaumualii, king of Kauai. He gave his new kingdom, and by extension the island chain itself, the name of his native island – the Kingdom of Hawaii
The Hawaiian Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ɛ ɐwˈpuni həˈvɐjʔi, was an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country from 1795 to 1893, which eventually encompassed all of the inhabited Hawaii ...
.
In 1822, missionary William Ellis arrived and was one of a party that completed a tour of the island, descriptions of which were later published in his journal.
In July, 1898, Hawaii and all the Hawaiian islands were annexed by the United States, becoming the Territory of Hawaii
The Territory of Hawaii or Hawaii Territory (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Panalāʻau o Hawaiʻi'') was an organized incorporated territories of the United States, organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from Apri ...
. In 1905, the passage of the County Act established the County of Hawaii, providing the island with local government for the first time since 1810.
Geology and geography
 According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (20.8%) is water. The county's land area comprises 62.7 percent of the state's land area. It is the highest percentage by any county in the United States.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (20.8%) is water. The county's land area comprises 62.7 percent of the state's land area. It is the highest percentage by any county in the United States. Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
's Sussex County comes in second at 48.0 percent, while Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
's Providence County is third at 39.6 percent.
At its greatest dimension, the island is across. Measured from its sea floor base to its highest peak, Mauna Kea at is the world's tallest mountain, taller than even Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
, since the base of Mount Everest is above sea level.
The most southern point of Hawaii, Ka Lae, is the southernmost point of the United States. The nearest landfall to the south is the Line Islands
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands () are a chain of 11 atolls (with partly or fully enclosed lagoons, except Vostok and Jarvis) and coral islands (with a surrounding reef) in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawa ...
. To the northwest of the island of Hawaii is the island of Maui
Maui (; Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ) is the second largest island in the Hawaiian archipelago, at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2). It is the List of islands of the United States by area, 17th-largest in the United States. Maui is one of ...
, whose Haleakalā volcano is visible from Hawai Volcanism
 The island of Hawaii is built from five separate
The island of Hawaii is built from five separate shield volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more viscous lava ...
es that erupted somewhat sequentially, one overlapping the other. These are (from oldest to youngest):
* Kohala – extinct
* Mauna Kea – dormant
* Hualālai – active
* Mauna Loa – active, partly within Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
* Kīlauea – active, part of Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
Geological evidence from exposures of old surfaces on the south and west flanks of Mauna Loa led to the proposal that two ancient volcanic shields (named Nīnole and Kulani) were all but buried by the younger Mauna Loa. Geologists now consider these "outcrops" to be part of Mauna Loa.
Based on geochemical
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the ...
(including trace elements) and isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
differences in their eruptive products, Hawaiian volcanoes fall into two families. The differences are believed due to their separate magma systems. Hualālai and Mauna Loa are members of one family, while Kohala, Mauna Kea, and Kilauea are members of the other.
Because Mauna Loa and Kīlauea are active volcanoes, the island is growing. Between January 1983 and September 2002, lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fractu ...
flows added to the island. Lava flowing from Kīlauea destroyed several towns, including Kapoho in 1960 and again in 2018, and Kalapana and Kaimū in 1990. In 1987 lava filled in "Queen's Bath", a large, L-shaped, freshwater pool in the Kalapana area. Another 875 acres were added between May and July 2018 by the 2018 lower Puna eruption, with "Fissure 8" located within Leilani Estates subdivision being a primary source of the lava. A lake known as "Green Lake" was covered by lava in that eruption as well as Ahalanui Beach Park and part of Isaac Hale Beach Park, the latter of which was inundated with black sand, rendering its boatramp unusable. Mauna Loa erupted briefly in 2022, 38 years after the prior activity.
Some geologists also count two undersea volcanoes in the base of the island. Māhukona off the northwest corner of the island has eroded below the ocean surface. Kamaehuakanaloa (formerly Lōihi) is under water southeast of Hawaii. It is an erupting seamount that has grown to reach below the ocean surface, and it is forecast to break the surface in 10,000 to 100,000 years.
Great Crack
 The Great Crack is an , and fissure in the island, in the district of Kaū. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the Great Crack is the result of crustal dilation from
The Great Crack is an , and fissure in the island, in the district of Kaū. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the Great Crack is the result of crustal dilation from magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also ...
tic intrusions into the southwest rift zone of Kīlauea. While neither the earthquake of 1868 nor that of 1975 caused a measurable change in the Great Crack, lava welled out of its lower in 1823.
Trails, rock walls, and archaeological sites from as old as the 12th century exist near the Great Crack. In August 2018, the National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government, within the US Department of the Interior. The service manages all List ...
purchased nearly of private land adjacent to Hawaii Volcanoes National Park, claiming that the area had important geological features to be studied and preserved.
Hilina Slump
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide ge ...
(GPS) measurements showed a southward displacement of about per year. Undersea measurements show a "bench" that has formed a buttress and that this buttress may tend to reduce the likelihood of catastrophic detachment.
Earthquakes and tsunamis
On 2 April 1868, an earthquake with a magnitude estimated between 7.25 and 7.9 rocked the southeast coast of Hawaii. This was the most destructive earthquake in the Hawaii's recorded history. It triggered alandslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, rockslips or rockslides, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, mudflows, shallow or deep-seated slope failures and debris flows. Landslides ...
on Mauna Loa, north of Pāhala, killing 31 people. A tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
claimed 46 more lives. The villages of Punaluu, Nīnole, Kawaa, Honuapo, and Keauhou were severely damaged. The tsunami reportedly rolled over the tops of the coconut trees up to high, and it reached inland a distance of a quarter of a mile (400 meters) in some places.
On 29 November 1975, a section of the Hilina Slump dropped and slid toward the ocean. This movement caused a 7.2 magnitude earthquake and a tsunami. Oceanfront property was washed off its foundations in Punaluu. Two deaths were reported at Halape, and 19 other people were injured.
The island suffered damage from a tsunami caused by earthquakes in Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
on 1 April 1946, and in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
on 23 May 1960. Downtown Hilo was damaged by both tsunamis, with many lives lost. Just north of Hilo, Laupāhoehoe lost 16 schoolchildren and five teachers in the tsunami of 1946.
In March 2011, a 9.0 magnitude earthquake off the east coast of Japan again created a tsunami that caused minor damage in Hawaii. The estimated damage to public buildings was about US$3 million. In the Kona area this tsunami washed a house into Kealakekua Bay, destroyed a yacht club and tour boat offices in Keauhou Bay, caused extensive damage in Kailua-Kona, flooded the ground floor of the King Kamehameha Hotel, and temporarily closed the Kona Village Resort.
In early May 2018, hundreds of small earthquakes were detected on Kīlauea's East Rift Zone
A rift zone is a feature of some volcanoes, especially shield volcanoes, in which a set of linear cracks (or rifts) develops in a volcanic edifice, typically forming into two or three well-defined regions along the flanks of the vent. Believed ...
, leading officials to issue evacuation warnings. On 3 May 2018, the volcano erupted in Puna after a 5.0 earthquake earlier in the day, causing evacuations of Leilani Estates and Lanipuna Gardens subdivisions. A seemingly related 5.3 magnitude quake and a subsequent 6.9 magnitude earthquake occurred on 4 May.
Volcanic fog
Vog (volcanic fog) can envelop the island of Hawaii when Kīlauea is active. Since the termination of volcanic activity in September 2018, vog has largely disappeared on the west side of the island. The gas plumes created a blanket of vog that the trade winds mostly deflect toward the Kona coast. Vog can damage the health of plants, humans, and other animals. Most of theaerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be generated from natural or Human impact on the environment, human causes. The term ''aerosol'' co ...
s are acidic and of a size where they can remain in the lungs to damage them. Flu-like symptoms and general lethargy are reported, and are especially pronounced in people with respiratory conditions. on USGS web site. U.S. Geological Service. Retrieved 29 December 2009. on USGS web site. on "Airnow" US Government web site. on State of Hawaii Office of the Governor web site.
National protected areas
 The island hosts many specialized ecosystems/microclimates, including many protected by federal designation:
* Ala Kahakai National Historic Trail
* Hakalau Forest National Wildlife Refuge
* Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
* Kaloko-Honokōhau National Historical Park
* Kohala Historical Sites State Monument ( Mookini Heiau)
* Kona Forest National Wildlife Refuge
* Puuhonua o Hōnaunau National Historical Park
* Puukoholā Heiau National Historic Site
The island hosts many specialized ecosystems/microclimates, including many protected by federal designation:
* Ala Kahakai National Historic Trail
* Hakalau Forest National Wildlife Refuge
* Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
* Kaloko-Honokōhau National Historical Park
* Kohala Historical Sites State Monument ( Mookini Heiau)
* Kona Forest National Wildlife Refuge
* Puuhonua o Hōnaunau National Historical Park
* Puukoholā Heiau National Historic Site
Economy
Sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
was the backbone of the island economy for more than a century. In the mid-20th century, sugarcane plantations began to downsize, and in 1995 the island's last plantation closed.
Most of the island's economy depends on tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as ...
, centered primarily in resort areas on the western coast of the island in the North Kona and South Kohala districts. Sustainable tourism
Sustainable tourism is a concept that covers the complete tourism experience, including concern for Impacts of tourism, economic, social, and environmental issues as well as attention to improving tourists' experiences and addressing the needs o ...
is increasing.
Diversified agriculture is a growth sector. Major crops include macadamia nuts, papaya, flowers, tropical and temperate vegetables, aquaculture, and coffee beans. The island's orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Eart ...
production is the state's largest. The island is home to one of the United States' largest cattle ranches: Parker Ranch, on in Waimea.
The island is known for astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
, with numerous telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
s positioned on the summit of Mauna Kea at the Mauna Kea Observatories
The Mauna Kea Observatories (MKO) are a group of independent astronomical research facilities and large telescope observatories that are located at the summit of Mauna Kea on Hawaii (island), Hawaiʻi, United States. The facilities are located i ...
, where atmospheric clarity is excellent and little light pollution
Light pollution is the presence of any unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive artificial Visible spectrum, lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting sources, during the ...
intrudes. Astronomy has become somewhat controversial, given accusations of mismanagement by the observatory manager, the University of Hawaii
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
. The proposed addition of the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) generated protests that stalled the project and led to the transfer of management responsibility to a Governor-appointed body.
NELHA (Natural Energy Laboratory of Hawaii Authority), a state developed site, is a green economic development ocean science and technology park on the west side of the island. It provides resources and facilities for energy and ocean-related research, education, and commercial activities in an environmentally sound and culturally sensitive manner. Business tenants on this coastal site include microalgae farms, aquaculture, solar technology and marine biotech. Tenants have access to three sets of pipelines delivering deep-sea water from a depth of up to , as well as pristine sea surface water and almost constant sunshine. A 2012 study by the University of Hawaii Economic Research Organization reported that the total economic impact of activities at NELHA was $87.7 million and created 583 jobs.
Top employers
According to the county's 2021 Annual Comprehensive Financial Report, the top employers in the county are the following:Transportation
Air
Two commercial airports serve Hawaii Island: * Hilo International Airport (ITO) * Kona International Airport (KOA) The 2 private airports are: * Waimea-Kohala Airport (MUE) * Upolu Airport (UPP)Rail
No railroad or tram service exists today on Hawaii Island. The Hawaii Consolidated Railway (originally the Hilo Railroad) operated in varying magnitudes from 1899 until 1947. The railway ran out of Hilo, northbound to Paauilo and southbound to Pāhoa, Glenwood (nearVolcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most oft ...
), and Kamaili.
Other smaller freight only railroads also operated on the island, primarily for the transport of sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
and other crops. Some of these include Waiākea Plantation Railroad (in Hilo), Honokaa Plantation Railroad, Hawaii Railway (on the north shore), Hawaiian Agricultural Company Railroad (in Pāhala) and West Hawaii Railway (between Kailua-Kona and Captain Cook).
Bus
Island-wide bus service is provided by Hele-On Bus.Major highways
* (part of Hawaii Belt Road) * (part of Hawaii Belt Road) * (from Keaau to Kalapana) * (from Pāhoa to Kapoho) * (from Kalapana to Kapoho; also known as " Red Road") * (part of Hawaii Belt Road) * (also known as " Saddle Road", a cross island route from Hilo to Route 190) * (from Honokaa to Waipio Valley) * ( Kohala Mountain Road, from Waimea to Hāwī) * ( Akoni Pule Highway, from Kawaihae to Pololū Valley) * (a modernized portion of " Saddle Road" extending 6.2 miles west from Hilo) The 3 Hawaii Scenic Byways are: * Māmalahoa Kona Heritage Center * Royal Footsteps Along the Kona Coast * Kaū Scenic Byway – The Slopes of Mauna LoaMaritime
The major ports are Hilo Harbor on the east side and Kawaihae Harbor and Kailua Pier on the west side. Cruise ships often stop at Kailua-Kona (90 times in 2017) and Hilo (108 times in 2017). There are several small boatramps throughout the island for public and private use.
Tourism
Places of interest

 * Akaka Falls, one of the tallest waterfalls on the island.
* Amy B. H. Greenwell Ethnobotanical Garden houses many endangered endemic plants.
* East Hawaii Cultural Center
* Hawaii Tropical Botanical Garden
* Hawaii Volcanoes National Park, comprising the active volcanoes Kīlauea and Mauna Loa
* Hulihee Palace, a royal palace in Kailua-Kona
* Imiloa Astronomy Center in Hilo
* Ka Lae, the southernmost point in the United States
* Laupāhoehoe Train Museum
* Lyman House Memorial Museum in Hilo
* Manuka State Wayside Park
*
* Akaka Falls, one of the tallest waterfalls on the island.
* Amy B. H. Greenwell Ethnobotanical Garden houses many endangered endemic plants.
* East Hawaii Cultural Center
* Hawaii Tropical Botanical Garden
* Hawaii Volcanoes National Park, comprising the active volcanoes Kīlauea and Mauna Loa
* Hulihee Palace, a royal palace in Kailua-Kona
* Imiloa Astronomy Center in Hilo
* Ka Lae, the southernmost point in the United States
* Laupāhoehoe Train Museum
* Lyman House Memorial Museum in Hilo
* Manuka State Wayside Park
*Mauna Kea Observatories
The Mauna Kea Observatories (MKO) are a group of independent astronomical research facilities and large telescope observatories that are located at the summit of Mauna Kea on Hawaii (island), Hawaiʻi, United States. The facilities are located i ...
* Nani Mau Gardens
* Onizuka Center for International Astronomy
* Pacific Tsunami Museum overlooking Hilo Bay
* Panaewa Rainforest Zoo in Hilo
* Pua Mau Place Arboretum and Botanical Garden
* Puuhonua o Hōnaunau National Historical Park
* Puukohoā Heiau National Historic Site, the site of one of the most significant heiau in Hawaii
* Rainbow Falls State Park
* Sadie Seymour Botanical Gardens
* Umauma Falls
* University of Hawaii at Hilo Botanical Gardens
* Waipio Valley
* Wao Kele o Puna
* World Botanical Gardens
Hotels on the east coast
The larger hotels on the east coast are: * Grand Naniloa Hotel, Hilo * Hilo Hawaiian Hotel * Volcano House, KīlaueaHotels on the west coast
The larger hotels on the west coast, from north ( Puakō) to south ( Captain Cook): * Mauna Kea Beach Hotel * The Fairmont Orchid * Hilton Waikoloa Village * Waikoloa Beach Marriott * King Kamehameha Hotel * Four Seasons Resort Hualalai *Royal Kona Resort
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family or royalty
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Roy ...
* Sheraton Kona Resort & Spa at Keauhou Bay
* Manago Hotel
*Mauna Lani Resort by Auberge
Maps
Interactive 3D model for Chrome or Firefox
See also
* National Register of Historic Places listings on the island of HawaiiNotes
References
External links
Official Hawaii County website
at ''
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
''''Hawaii Tribune-Herald''
– official website of the '' Hawaii Tribune-Herald'', a daily newspaper in Hilo
''West Hawaii Today''
– official website of '' West Hawaii Today''
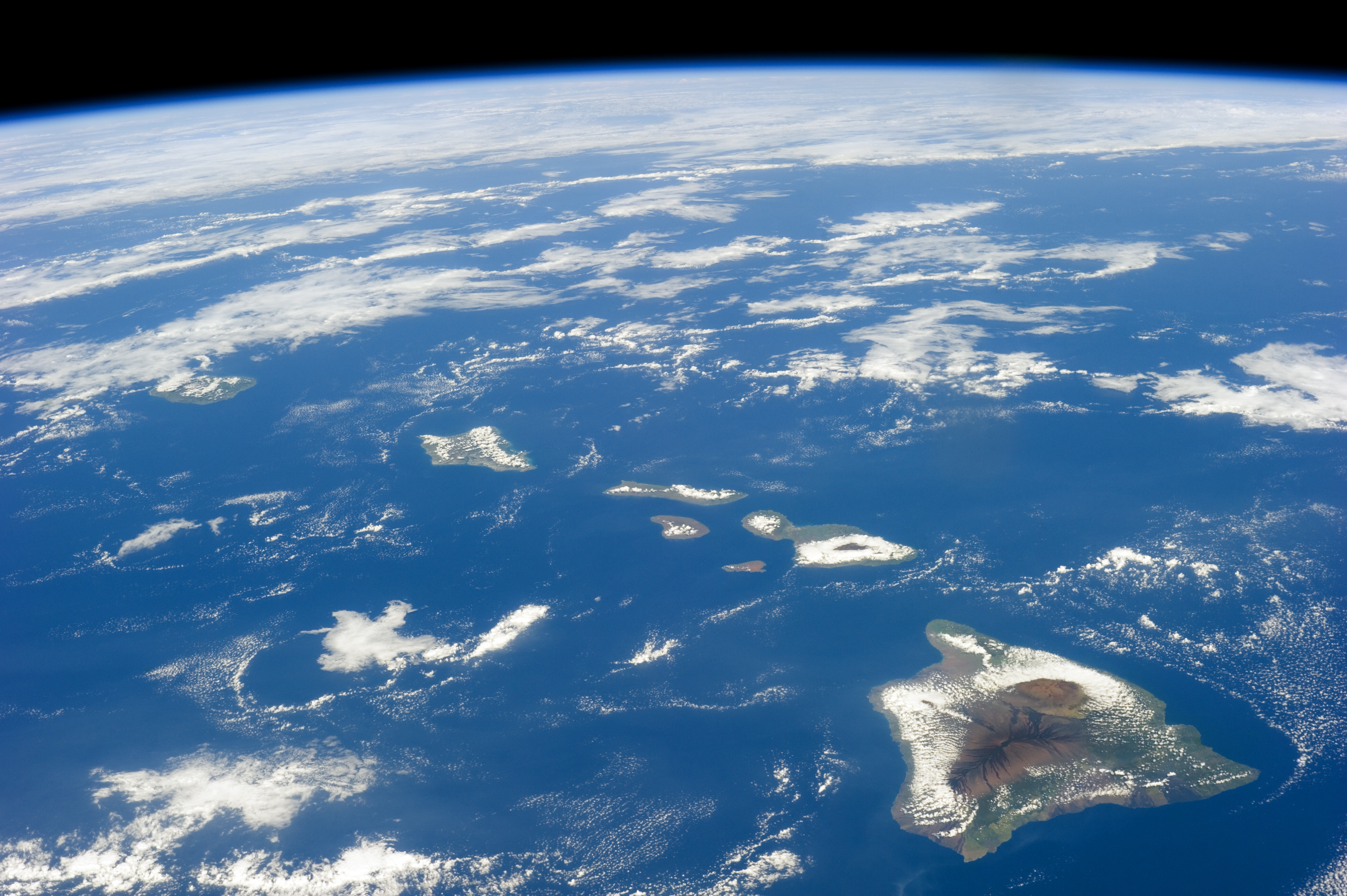
Island of Hawaii from the International Space Station
– NASA satellite image, taken from the
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
on 28 February 2015
*
{{Authority control
*
*
Islands of Hawaii
Endemic Bird Areas