Harpooner on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A harpoon is a long,
A harpoon is a long,

 In the 1990s, harpoon points, known as the
In the 1990s, harpoon points, known as the
( NIV): "Can you fill its hide with harpoons or its head with fishing spears?" The Greek historian
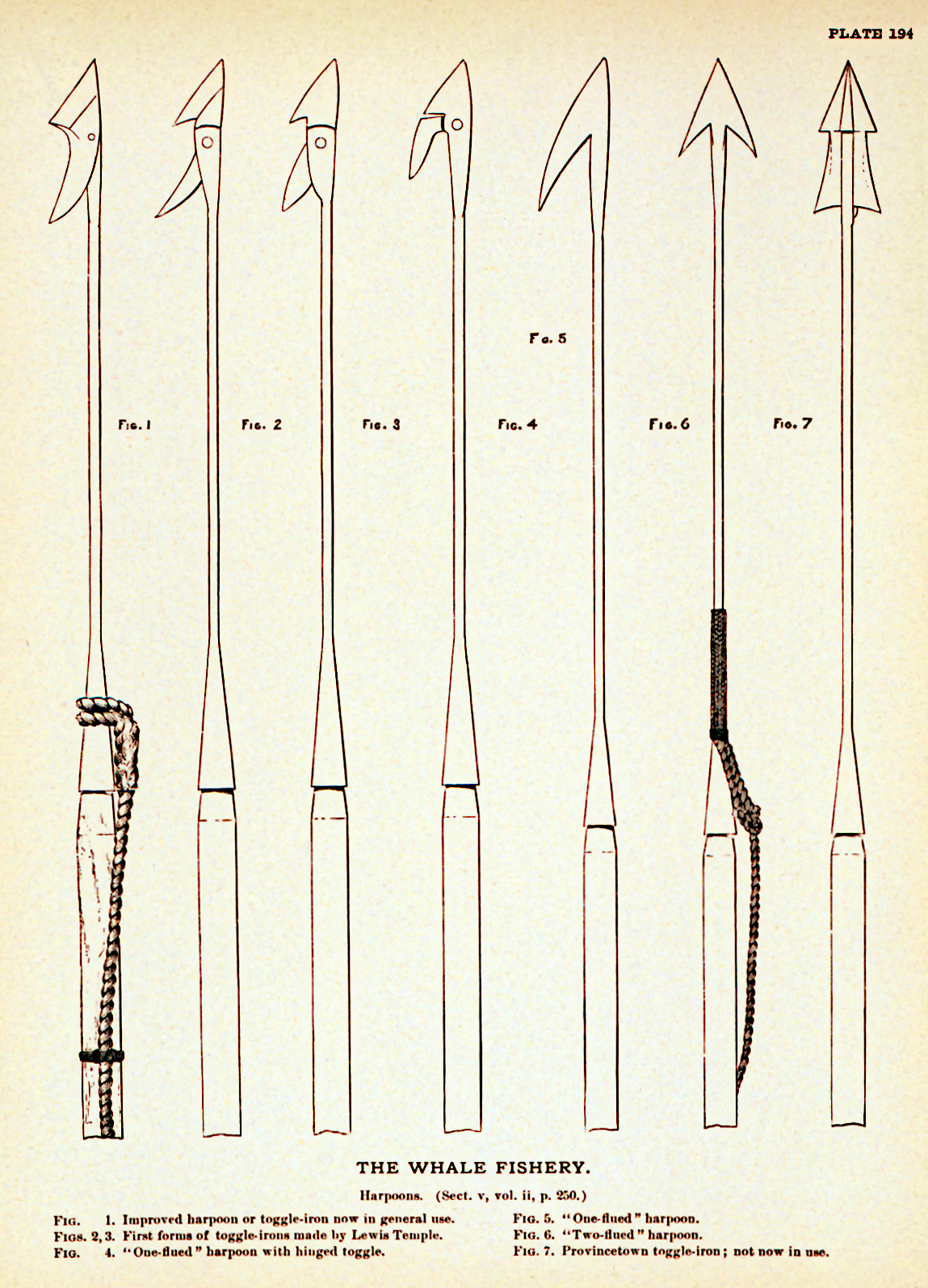 In the novel ''
In the novel ''
File:Bomb Lance Harpoon for whales.jpg, Bomb lance whaling harpoon, pictured in 1878, prominent in the famous whaling legal case ''
Problems hit Philae after historic first comet landing
''
Whalecraft: Harpoons
{{Authority control Ancient weapons Fishing equipment Inuit tools Projectile weapons

 A harpoon is a long,
A harpoon is a long, spear
A spear is a polearm consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with Fire hardening, fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable materia ...
-like projectile
A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found ...
used in fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
, whaling
Whaling is the hunting of whales for their products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that was important in the Industrial Revolution. Whaling was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16t ...
, sealing, and other hunting
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
to shoot, kill, and capture large fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
or marine mammal
Marine mammals are mammals that rely on marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine enviro ...
s such as seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
, sea cows
The Sirenia (), commonly referred to as sea cows or sirenians, are an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit swamps, rivers, estuaries, marine wetlands, and coastal marine waters. The extant Sirenia comprise two distinct famili ...
, and whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully Aquatic animal, aquatic placental mammal, placental marine mammals. As an informal and Colloquialism, colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea ...
s. It impales the target and secures it with barb or toggling claws, allowing the fishermen
A fisherman or fisher is someone who captures fish and other animals from a body of water, or gathers shellfish.
Worldwide, there are about 38 million commercial and subsistence fishers and fish farmers. Fishermen may be professional or recr ...
or hunters to use an attached rope or chain to pull and retrieve the animal. A harpoon can also be used as a ranged weapon against other watercraft
A watercraft or waterborne vessel is any vehicle designed for travel across or through water bodies, such as a boat, ship, hovercraft, submersible or submarine.
Types
Historically, watercraft have been divided into two main categories.
*Raf ...
in naval warfare
Naval warfare is combat in and on the sea, the ocean, or any other battlespace involving a major body of water such as a large lake or wide river.
The Military, armed forces branch designated for naval warfare is a navy. Naval operations can be ...
.
Certain harpoons are made with different builds to perform better with the type of target. For example, the Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
have short, fixed-foreshaft harpoons for hunting at breathing holes, while loose-shafted ones are made for throwing and remaining attached to the game
A game is a structured type of play usually undertaken for entertainment or fun, and sometimes used as an educational tool. Many games are also considered to be work (such as professional players of spectator sports or video games) or art ...
.
History
 In the 1990s, harpoon points, known as the
In the 1990s, harpoon points, known as the Semliki harpoon The Semliki harpoon, also known as the Katanda harpoon, refers to a group of complex barbed harpoon heads carved from bone, which were found at an archaeologic site on the Semliki River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly Zaire); the ...
s or the Katanda harpoons, were found in the Katanda region in Zaire
Zaire, officially the Republic of Zaire, was the name of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from 1971 to 18 May 1997. Located in Central Africa, it was, by area, the third-largest country in Africa after Sudan and Algeria, and the 11th-la ...
. As the earliest known harpoons, these weapons were made and used 90,000 years ago, most likely to spear catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order (biology), order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Catfish are common name, named for their prominent barbel (anatomy), barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, though not ...
es. Later, in Japan, spearfishing
Spearfishing is fishing using handheld elongated, sharp-pointed tools such as a spear, gig, or harpoon, to impale the fish in the body. It was one of the earliest fishing techniques used by mankind, and has been deployed in artisanal fishi ...
with poles was widespread in palaeolithic times, especially during the Solutrean
The Solutrean industry is a relatively advanced flint tool-making style of the Upper Paleolithic of the Final Gravettian, from around 22,000 to 17,000 BP. Solutrean sites have been found in modern-day France, Spain and Portugal.
Detai ...
and Magdalenian
Magdalenian cultures (also Madelenian; ) are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years before present. It is named after the type site of Abri de la Madeleine, a ro ...
periods. Cosquer Cave
Cosquer Cave () is located in the Calanque de Morgiou in Marseille, France, near Cap Morgiou. The entrance to the cave is located underwater, due to the Holocene sea level rise. The cave contains various prehistoric rock art engravings. Its s ...
in southern France has cave art over 16,000 years old, including drawings of seals that appear to have been harpooned.
There are references to harpoons in ancient literature, though in most cases the descriptions do not go into detail. An early example can be found in the Bible in Job
Work, labor (labour in Commonwealth English), occupation or job is the intentional activity people perform to support the needs and desires of themselves, other people, or organizations. In the context of economics, work can be seen as the huma ...
br>41:7( NIV): "Can you fill its hide with harpoons or its head with fishing spears?" The Greek historian
Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 ...
(c. 203 BC – 120 BC), in his ''Histories
Histories or, in Latin, Historiae may refer to:
* the plural of history
* ''Histories'' (Herodotus), by Herodotus
* ''The Histories'', by Timaeus
* ''The Histories'' (Polybius), by Polybius
* ''Histories'' by Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust) ...
'', describes hunting for swordfish by using a harpoon with a barbed and detachable head. Copper harpoons were known to the seafaring Harappa
Harappa () is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal, that takes its name from a modern village near the former course of the Ravi River, which now runs to the north. Harappa is the type site of the Bronze Age Indus ...
ns well into antiquity. Early hunters in India include the Mincopie people, aboriginal inhabitants of India's Andaman and Nicobar
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India comprising 572 islands, of which only 38 are inhabited. The islands are grouped into two main clusters: the northern Andaman Islands and the southern Nicobar Islands, separated by ...
islands, who have used harpoons with long cords for fishing since early times.
Whaling
 In the novel ''
In the novel ''Moby-Dick
''Moby-Dick; or, The Whale'' is an 1851 Epic (genre), epic novel by American writer Herman Melville. The book is centered on the sailor Ishmael (Moby-Dick), Ishmael's narrative of the maniacal quest of Captain Ahab, Ahab, captain of the whaler ...
'', Herman Melville
Herman Melville (Name change, born Melvill; August 1, 1819 – September 28, 1891) was an American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance (literature), American Renaissance period. Among his best-known works ar ...
explained the reason for the harpoon's effectiveness:
He also describes another device that was at times a necessary addition to harpoons:
Explosive harpoons
The first use of explosives in the hunting of whales was made by the BritishSouth Sea Company
The South Sea Company (officially: The Governor and Company of the merchants of Great Britain, trading to the South Seas and other parts of America and for the encouragement of the Fishery) was a British joint-stock company founded in Ja ...
in 1737, after some years of declining catches. A large fleet was sent, armed with cannon-fired harpoons. Although the weaponry was successful in killing the whales, most of the catch sank before being retrieved. However, the system was still occasionally used, and underwent successive improvements at the hands of various inventors over the next century, including Abraham Stagholt in the 1770s and George Manby
Captain George William Manby FRS (28 November 1765 – 18 November 1854) was an English author and inventor. He designed an apparatus for saving life from shipwrecks and also the "Pelican Gun", the first modern form of fire extinguisher.
Ear ...
in the early 19th century.
William Congreve
William Congreve (24 January 1670 – 19 January 1729) was an English playwright, satirist, poet, and Whig politician. He spent most of his career between London and Dublin, and was noted for his highly polished style of writing, being regard ...
, who invented some of the first rockets
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely fr ...
for British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
use, designed a rocket-propelled whaling harpoon in the 1820s. The shell was designed to explode on contact and impale the whale with the harpoon. The weapon was in turn attached by a line to the boat, and the hope was that the explosion would generate enough gas within the whale to keep it afloat for retrieval. Expeditions were sent out to try this new technology; many whales were killed, but most of them sank. These early devices, called bomb lances, became widely used for the hunting of humpbacks and right whale
Right whales are three species of large baleen whales of the genus ''Eubalaena'': the North Atlantic right whale (''E. glacialis''), the North Pacific right whale (''E. japonica'') and the southern right whale (''E. australis''). They are class ...
s. A notable user of these early explosive harpoons was the American Thomas Welcome Roys
Thomas Welcome Roys (c. 1816 - d. 1877) was an American whaleman. He was significant in the history of whaling in that he discovered the Western Arctic bowhead whale population and developed and patented whaling rockets in order to hunt the faster ...
in 1865, who set up a shore station in Seydisfjördur, Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
. A slump in oil prices after the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
forced their endeavor into bankruptcy in 1867.
An early version of the explosive harpoon was designed by Jacob Nicolai Walsøe, a Norwegian painter and inventor. His 1851 application was rejected by the interior ministry on the grounds that he had received public funding for his experiments. In 1867, a Danish fireworks manufacturer, Gaetano Amici, patented a cannon-fired harpoon, and in the same year, an Englishman, George Welch, patented a grenade harpoon very similar to the version which transformed whaling in the following decade.
In 1870, the Norwegian shipping magnate Svend Foyn
Svend Foyn (July 9, 1809 – November 30, 1894) was a Norwegian whaling, shipping magnate and philanthropist. He pioneered revolutionary methods for hunting and processing whales. Svend Foyn introduced the modern harpoon cannon and brought ...
patented and pioneered the modern exploding whaling harpoon and gun. Foyn had studied the American method in Iceland. His basic design is still in use today. He perceived the failings of other methods and solved these problems in his own system. He included, with the help of H.M.T. Esmark, a grenade tip that exploded inside the whale. This harpoon design also utilized a shaft that was connected to the head with a moveable joint. His original cannons were muzzle-loaded with special padding and also used a unique form of gunpowder. The cannons were later replaced with safer breech-loading types.
Together with the steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
, this development ushered in the modern age of commercial whaling. Euro-American whalers were now equipped to hunt faster and more powerful species, such as the rorquals
Rorquals () are the largest group of baleen whales, comprising the family Balaenopteridae, which contains nine extant species in two genera. They include the largest known animal that has ever lived, the blue whale, which can reach , and the fin ...
. Because rorquals sank when they died, later versions of the exploding harpoon injected air into the carcass to keep it afloat.
The modern whaling harpoon consists of a deck-mounted launcher (mostly a cannon) and a projectile which is a large harpoon with an explosive (penthrite) charge, attached to a thick rope. The spearhead is shaped in a manner which allows it to penetrate the thick layers of whale blubber and stick in the flesh. It has sharp spikes to prevent the harpoon from sliding out. Thus, by pulling the rope with a motor, the whalers can drag the whale back to their ship.
A recent development in harpoon technology is the hand-held speargun
A speargun is a ranged underwater fishing device designed to launch a tethered spear or harpoon to impale fish or other marine animals and targets. Spearguns are used in sport fishing and underwater target shooting. The two basic types are ' ...
. Divers use the speargun for spearing fish. They may also be used for defense against dangerous marine animals. Spearguns may be powered by pressurized gas
A compressed fluid (also called a compressed or unsaturated liquid, subcooled fluid or liquid) is a fluid under mechanical or thermodynamic conditions that force it to be a liquid.
At a given pressure, a fluid is a compressed fluid if it is at ...
or with mechanical means like springs or elastic bands.
Ghen v. Rich
''Ghen v. Rich'', 8 F. 159 (1881), is an American property law case from the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts involving ownership of a dead whale. The case is frequently used to illustrate the difficulties of est ...
''
File:Harpoon mounted on a whaling boat, Alaska, ca 1915 (COBB 76).jpeg, Harpoon mounted on a whaling boat in Alaska, c. 1915
File:Whaling harpoon.jpg, Modern whaling harpoon
Space
The Philae spacecraft carried harpoons for helping the probe anchor itself to the surface ofcomet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko
67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (abbreviated as 67P or 67P/C–G) is a Jupiter-family comet. It is originally from the Kuiper belt and has an orbital period of 6.45 years as of 2012, a rotation period of approximately 12.4 hours, and a maximum velo ...
. However, the harpoons failed to fire.Aron, Jacob.Problems hit Philae after historic first comet landing
''
New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a popular science magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organ ...
''.
See also
*Hawaiian sling
The Hawaiian sling is a device used in spearfishing. The sling operates much like a bow and arrow does on land, but energy is stored in rubber tubing rather than a wooden or fiberglass bow.
Description
Mechanically, the device is simple: the onl ...
* Kakivak
A kakivak is a leister used by Inuit for Spearfishing, spear fishing and fishing at short range. It is comparable to a harpoon or a trident in function and shape. The kakivak is notable for its tip's design, which has three prongs, the outer whi ...
* Leister
A leister is a type of spear used for spearfishing.
Leisters are three-pronged with backward-facing barbs, historically often built using materials such as bone and ivory, with tools such as the saw-knife. In many cases it could be disassembled ...
* Speargun
A speargun is a ranged underwater fishing device designed to launch a tethered spear or harpoon to impale fish or other marine animals and targets. Spearguns are used in sport fishing and underwater target shooting. The two basic types are ' ...
* Trident
A trident (), () is a three- pronged spear. It is used for spear fishing and historically as a polearm. As compared to an ordinary spear, the three tines increase the chance that a fish will be struck and decrease the chance that a fish will b ...
Notes
References
* Lødingen Local History Society (1986) Yearbook Lødingen. The modern history of whaling, . * Lødingen local historical society (1999/2000) Yearbook Lødingen. More about Jacob Nicolai Walsøe, granatharpunens inventor, . * Information aboutErik Eriksen
Erik Eriksen (20 November 1902 – 7 October 1972) was a Danish politician, who served as the prime minister of Denmark from 1950 to 1953 and as the president of the Nordic Council in 1956. Eriksen was leader of the Danish Liberal party '' Ve ...
based on ''The Discovery of King Karl Land, Spitsbergen'', by Adolf Hoel
Adolf Hoel (15 May 1879 – 19 February 1964) was a Norwegian geologist, environmentalist and Polar region researcher. He led several scientific expeditions to Svalbard and Greenland. Hoel has been described as one of the most iconic and influenti ...
, '' The Geographical Review'' Vol. XXV, No. 3, July, 1935, Pp. 476–478, American Geographical Society
The American Geographical Society (AGS) is an organization of professional geographers, founded in 1851 in New York City. Most fellows of the society are United States, Americans, but among them have always been a significant number of fellows f ...
, Broadway AT 156th Street, New York" and Store norske leksikon, Aschehoug & Gyldendal (Great Norwegian Encyclopedia, last edition)
* F.R. Allchin in ''South Asian Archaeology 1975: Papers from the Third International Conference of the Association of South Asian Archaeologists in Western Europe, Held in Paris'' (December 1979) edited by J.E.van Lohuizen-de Leeuw. Brill Academic Publishers, Incorporated. Pages 106–118. .
* Edgerton; et al. (2002). ''Indian and Oriental Arms and Armour''. Courier Dover Publications. .
* Ray, Himanshu Prabha (2003). ''The Archaeology of Seafaring in Ancient South Asia''. Cambridge University Press. .
External links
Whalecraft: Harpoons
{{Authority control Ancient weapons Fishing equipment Inuit tools Projectile weapons