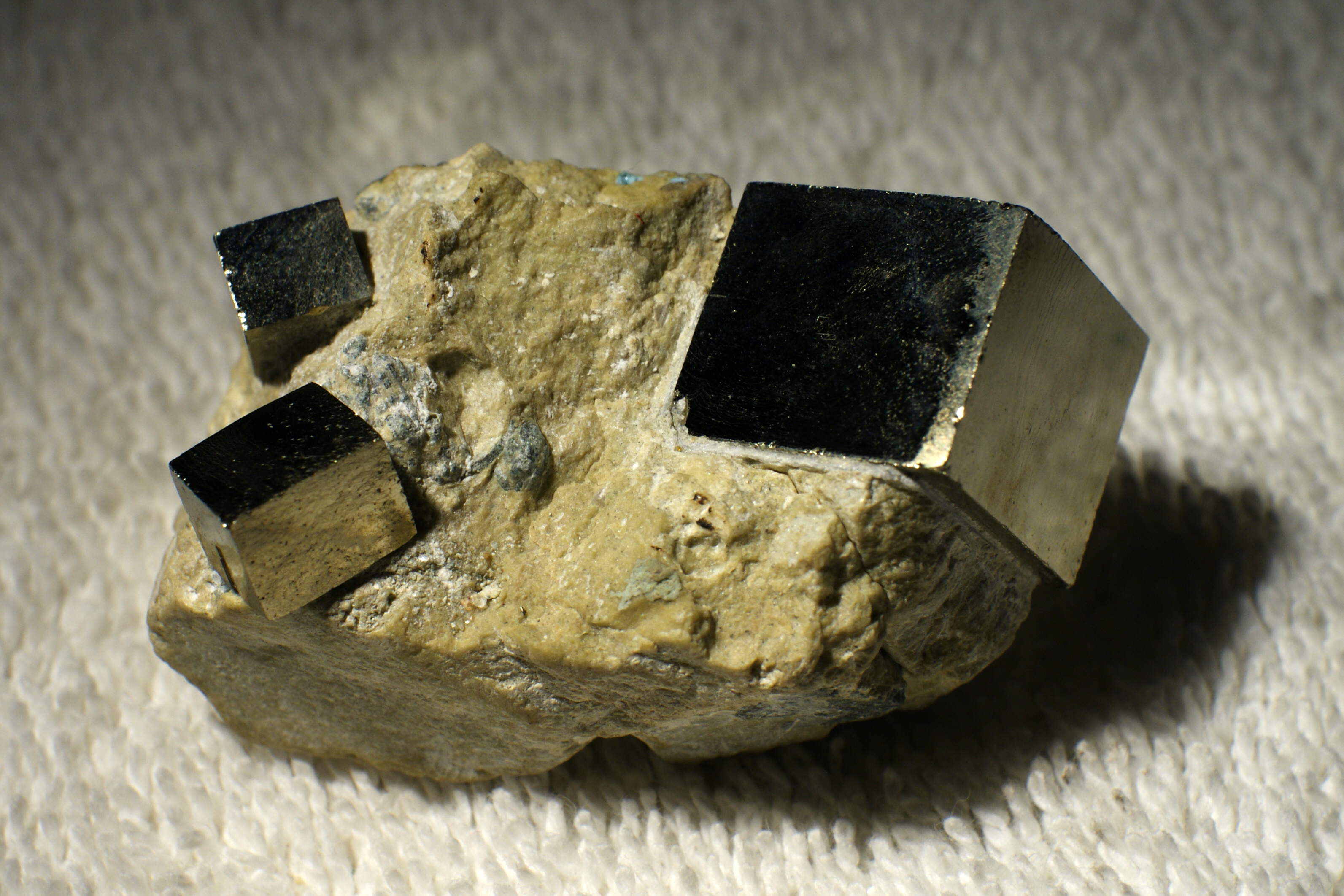
Halite structure on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In
In
 One structure is the "interpenetrating primitive cubic" structure, also called a "caesium chloride" or B2 structure. This structure is often confused for a body-centered cubic structure because the arrangement of atoms is the same. However, the caesium chloride structure has a basis composed of two different atomic species. In a body-centered cubic structure, there would be translational symmetry along the 11direction. In the caesium chloride structure, translation along the 11direction results in a change of species. The structure can also be thought of as two separate simple cubic structures, one of each species, that are superimposed within each other. The corner of the chloride cube is the center of the caesium cube, and vice versa.
One structure is the "interpenetrating primitive cubic" structure, also called a "caesium chloride" or B2 structure. This structure is often confused for a body-centered cubic structure because the arrangement of atoms is the same. However, the caesium chloride structure has a basis composed of two different atomic species. In a body-centered cubic structure, there would be translational symmetry along the 11direction. In the caesium chloride structure, translation along the 11direction results in a change of species. The structure can also be thought of as two separate simple cubic structures, one of each species, that are superimposed within each other. The corner of the chloride cube is the center of the caesium cube, and vice versa.
 It works the same way for the NaCl structure described in the next section. If you take out the Cl atoms, the leftover Na atoms still form an FCC structure, not a simple cubic structure.
In the unit cell of CsCl, each ion is at the center of a cube of ions of the opposite kind, so the
It works the same way for the NaCl structure described in the next section. If you take out the Cl atoms, the leftover Na atoms still form an FCC structure, not a simple cubic structure.
In the unit cell of CsCl, each ion is at the center of a cube of ions of the opposite kind, so the
 The
The
 The
The 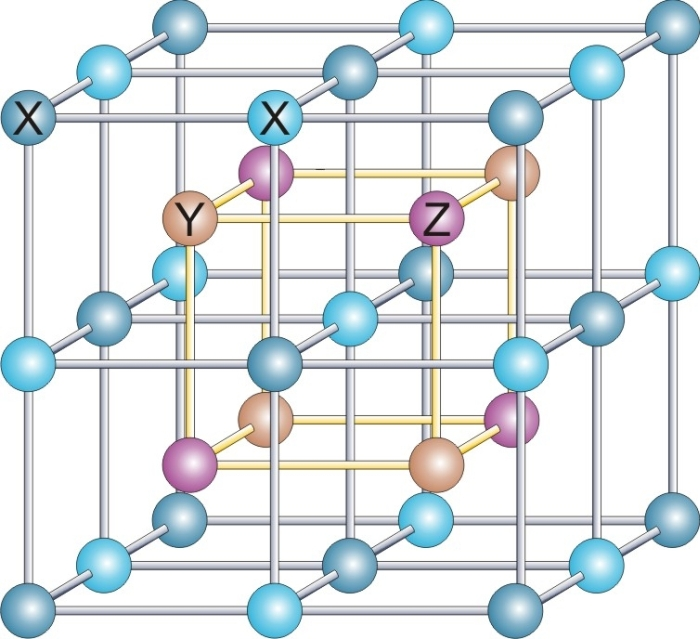
 The space group of the iron monosilicide structure is P213 (No. 198), and the
The space group of the iron monosilicide structure is P213 (No. 198), and the
 A
A
Simple cubic
BCC
FCC
HCPMaking crystal structure
with Molview {{DEFAULTSORT:Cubic Crystal System Crystal systems Cubes
crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In J ...
, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system
In crystallography, a crystal system is a set of point groups (a group of geometric symmetries with at least one fixed point). A lattice system is a set of Bravais lattices (an infinite array of discrete points). Space groups (symmetry groups ...
where the unit cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector
In mathematics, a unit vector i ...
is in the shape of a cube
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional space, three-dimensional solid object in geometry, which is bounded by six congruent square (geometry), square faces, a type of polyhedron. It has twelve congruent edges and eight vertices. It i ...
. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
s and mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s.
There are three main varieties of these crystals:
*Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic)
*Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc)
*Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc)
Note: the term fcc is often used in synonym for the ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp structure occurring in metals. However, fcc stands for a face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, which is not necessarily close-packed when a motif is set onto the lattice points. E.g. the diamond and the zincblende lattices are fcc but not close-packed.
Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive unit cells often are not.
Bravais lattices
The three Bravais latices in the cubic crystal system are: The primitive cubic lattice (cP) consists of onelattice
Lattice may refer to:
Arts and design
* Latticework, an ornamental criss-crossed framework, an arrangement of crossing laths or other thin strips of material
* Lattice (music), an organized grid model of pitch ratios
* Lattice (pastry), an or ...
point on each corner of the cube; this means each simple cubic unit cell has in total one lattice point. Each atom at a lattice point is then shared equally between eight adjacent cubes, and the unit cell therefore contains in total one atom ( × 8).
The body-centered cubic lattice (cI) has one lattice point in the center of the unit cell in addition to the eight corner points. It has a net total of two lattice points per unit cell ( × 8 + 1).
The face-centered cubic lattice (cF) has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of four lattice points per unit cell ( × 8 from the corners plus × 6 from the faces).
The face-centered cubic lattice is closely related to the hexagonal close packed
In geometry, close-packing of equal spheres is a dense arrangement of congruent spheres in an infinite, regular arrangement (or lattice). Carl Friedrich Gauss proved that the highest average density – that is, the greatest fraction of space occ ...
(hcp) system, where two systems differ only in the relative placements of their hexagonal layers. The 11plane of a face-centered cubic lattice is a hexagonal grid.
Attempting to create a base-centered cubic lattice (i.e., putting an extra lattice point in the center of each horizontal face) results in a simple tetragonal
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the Cube (geometry), cube becomes a rectangular Pri ...
Bravais lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by
: \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 ...
.
Coordination number
In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science, the coordination number, also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it. The ion/molecule/atom surrounding the central ion ...
(CN) is the number of nearest neighbors of a central atom in the structure. Each sphere in a cP lattice has coordination number 6, in a cI lattice 8, and in a cF lattice 12.
Atomic packing factor
In crystallography, atomic packing factor (APF), packing efficiency, or packing fraction is the Packing density, fraction of volume in a crystal structure that is occupied by constituent particles. It is a dimensionless quantity and always less tha ...
(APF) is the fraction of volume that is occupied by atoms. The cP lattice has an APF of about 0.524, the cI lattice an APF of about 0.680, and the cF lattice an APF of about 0.740.
Crystal classes
The ''isometric crystal system'' class names, point groups (inSchönflies notation
The Schoenflies (or Schönflies) notation, named after the German mathematician Arthur Moritz Schoenflies, is a notation primarily used to specify point groups in three dimensions. Because a point group alone is completely adequate to describe ...
, Hermann–Mauguin notation
In geometry, Hermann–Mauguin notation is used to represent the symmetry elements in point groups, plane groups and space groups. It is named after the German crystallographer Carl Hermann (who introduced it in 1928) and the French mineralogist ...
, orbifold
In the mathematical disciplines of topology and geometry, an orbifold (for "orbit-manifold") is a generalization of a manifold. Roughly speaking, an orbifold is a topological space that is locally a finite group quotient of a Euclidean space.
D ...
, and Coxeter notation
In geometry, Coxeter notation (also Coxeter symbol) is a system of classifying symmetry groups, describing the angles between fundamental reflections of a Coxeter group in a bracketed notation expressing the structure of a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, ...
), type, examples, international tables for crystallography space group number, and space group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that ...
s are listed in the table below. There are a total 36 cubic space groups.
Other terms for hexoctahedral are: normal class, holohedral, ditesseral central class, galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It crysta ...
type.
Single element structures
As a rule, since atoms in a solid attract each other, the more tightly packed arrangements of atoms tend to be more common. (Loosely packed arrangements do occur, though, for example if theorbital hybridization
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new ''hybrid orbitals'' (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to f ...
demands certain bond angles
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that deter ...
.) Accordingly, the primitive cubic structure, with especially low atomic packing factor, is rare in nature, but is found in polonium
Polonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Po and atomic number 84. A rare and highly radioactive metal (although sometimes classified as a metalloid) with no stable isotopes, polonium is a chalcogen and chemically similar to selenium and tel ...
. The ''bcc'' and ''fcc'', with their higher densities, are both quite common in nature. Examples of ''bcc'' include iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
, tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
, and niobium
Niobium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and Ductility, ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs h ...
. Examples of ''fcc'' include aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
.
Another important cubic crystal structure is the diamond cubic
In crystallography, the diamond cubic crystal structure is a repeating pattern of 8 atoms that certain materials may adopt as they solidify. While the first known example was diamond, other elements in group 14 also adopt this structure, in ...
structure, which can appear in carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
, silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
, germanium
Germanium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid or a nonmetal in the carbon group that is chemically ...
, and tin
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the ...
. Unlike fcc and bcc, this structure is not a lattice, since it contains multiple atoms in its primitive cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessaril ...
. Other cubic elemental structures include the A15 structure found in tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
, and the extremely complicated structure of manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
.
Multi-element structures
Compounds that consist of more than one element (e.g.binary compound
In materials chemistry, a binary phase or binary compound is a chemical compound containing two different elements. Some binary phase compounds are molecular, e.g. carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). More typically binary phase refers to extended soli ...
s) often have crystal structures based on the cubic crystal system. Some of the more common ones are listed here. These structures can be viewed as two or more interpenetrating sublattices where each sublattice occupies the interstitial site
In crystallography, interstitial sites, holes or voids are the empty space that exists between the packing of atoms (spheres) in the crystal structure.
The holes are easy to see if you try to Circle packing, pack circles together; no matter how ...
s of the others.
Caesium chloride structure
 It works the same way for the NaCl structure described in the next section. If you take out the Cl atoms, the leftover Na atoms still form an FCC structure, not a simple cubic structure.
In the unit cell of CsCl, each ion is at the center of a cube of ions of the opposite kind, so the
It works the same way for the NaCl structure described in the next section. If you take out the Cl atoms, the leftover Na atoms still form an FCC structure, not a simple cubic structure.
In the unit cell of CsCl, each ion is at the center of a cube of ions of the opposite kind, so the coordination number
In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science, the coordination number, also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it. The ion/molecule/atom surrounding the central ion ...
is eight. The central cation is coordinated to 8 anions on the corners of a cube as shown, and similarly, the central anion is coordinated to 8 cations on the corners of a cube. Alternately, one could view this lattice as a simple cubic structure with a secondary atom in its cubic void.
In addition to caesium chloride itself, the structure also appears in certain other alkali halides when prepared at low temperatures or high pressures.Seitz, ''Modern Theory of Solids'' (1940), p.49 Generally, this structure is more likely to be formed from two elements whose ions are of roughly the same size (for example, ionic radius of Cs+ = 167 pm, and Cl− = 181 pm).
The space group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that ...
of the caesium chloride
Caesium chloride or cesium chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula Caesium, CsChloride, Cl. This colorless salt is an important source of caesium ions in a variety of niche applications. Its crystal structure forms a major structural ...
(CsCl) structure is called Pmm (in Hermann–Mauguin notation
In geometry, Hermann–Mauguin notation is used to represent the symmetry elements in point groups, plane groups and space groups. It is named after the German crystallographer Carl Hermann (who introduced it in 1928) and the French mineralogist ...
), or "221" (in the International Tables for Crystallography). The Strukturbericht designation
In crystallography, a Strukturbericht designation or Strukturbericht type is a system of detailed crystal structure classification by analogy to another known structure. The designations were intended to be comprehensive but are mainly used as supp ...
is "B2".
There are nearly a hundred rare earth intermetallic compounds
An intermetallic (also called intermetallic compound, intermetallic alloy, ordered intermetallic alloy, long-range-ordered alloy) is a type of metallic alloy that forms an ordered solid-state compound between two or more metallic elements. Inte ...
that crystallize in the CsCl structure, including many binary compounds
In materials chemistry, a binary phase or binary compound is a chemical compound containing two different elements. Some binary phase compounds are molecular, e.g. carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). More typically binary phase refers to extended solid ...
of rare earths with magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, and with elements in groups 11, 12, and 13. Other compounds showing caesium chloride like structure are CsBr, CsI, high-temperature RbCl
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, commonly known by the abbreviations RuBisCo, rubisco, RuBPCase, or RuBPco, is an enzyme () involved in the Photosynthesis#Light-independent reactions, light-independent (or "dark") part of photosyn ...
, AlCo, AgZn, BeCu, MgCe, RuAl and SrTl.
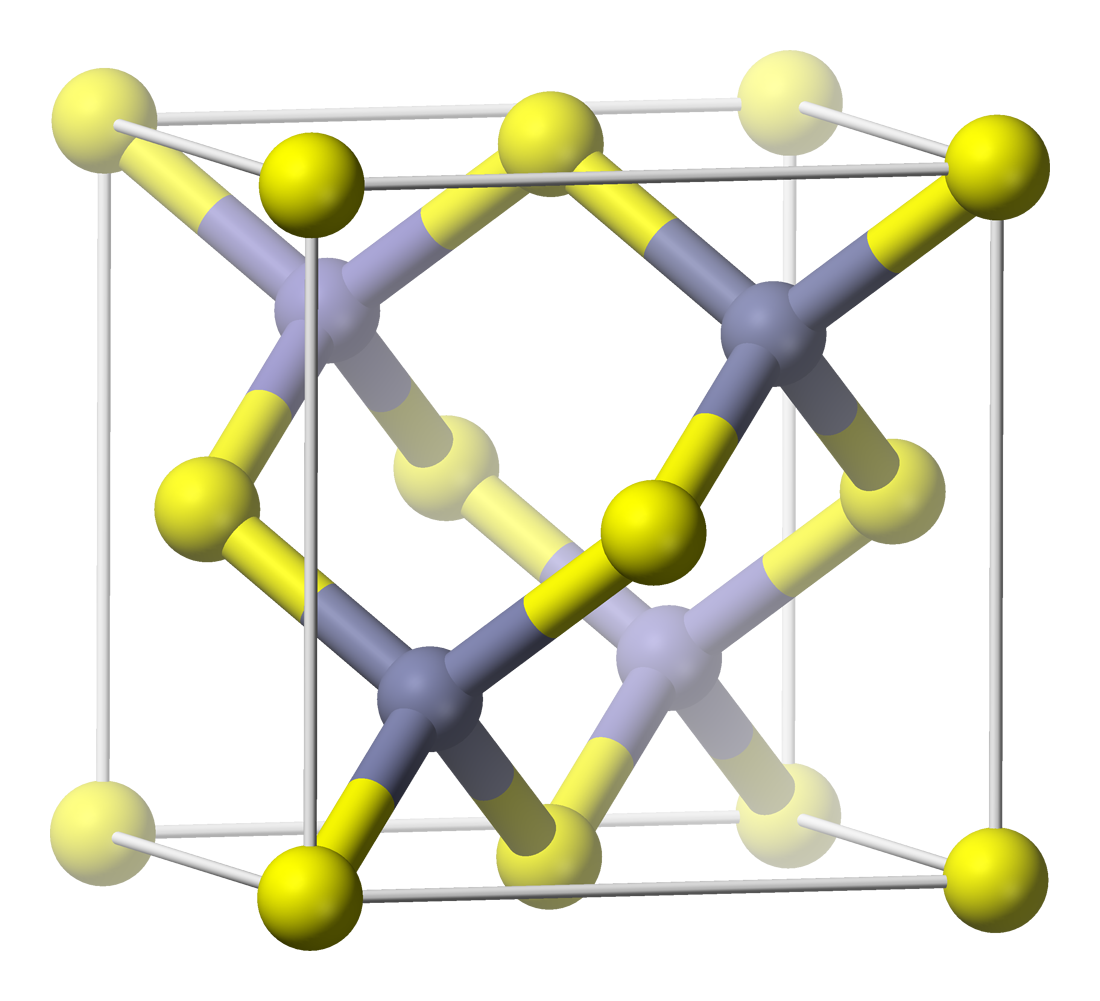
Rock-salt structure
space group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that ...
of the rock-salt or halite
Halite ( ), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pi ...
(sodium chloride) structure is denoted as Fmm (in Hermann–Mauguin notation
In geometry, Hermann–Mauguin notation is used to represent the symmetry elements in point groups, plane groups and space groups. It is named after the German crystallographer Carl Hermann (who introduced it in 1928) and the French mineralogist ...
), or "225" (in the International Tables for Crystallography). The Strukturbericht designation
In crystallography, a Strukturbericht designation or Strukturbericht type is a system of detailed crystal structure classification by analogy to another known structure. The designations were intended to be comprehensive but are mainly used as supp ...
is "B1".
In the rock-salt structure, each of the two atom types forms a separate face-centered cubic lattice, with the two lattices interpenetrating so as to form a 3D checkerboard pattern. The rock-salt structure has octahedral
In geometry, an octahedron (: octahedra or octahedrons) is any polyhedron with eight faces. One special case is the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. Many types of i ...
coordination
Coordination may refer to:
* Coordination (linguistics), a compound grammatical construction
* Coordination complex, consisting of a central atom or ion and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions
** A chemical reaction to form a coordinati ...
: Each atom's nearest neighbors consist of six atoms of the opposite type, positioned like the six vertices of a regular octahedron
In geometry, a regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. Regular octahedra occur in nature as crystal structures. An octahedron, more generally, can be any eight-sided polyh ...
. In sodium chloride there is a 1:1 ratio of sodium to chlorine atoms. The structure can also be described as an FCC lattice of sodium with chlorine occupying each octahedral void or vice versa.
Examples of compounds with this structure include sodium chloride itself, along with almost all other alkali halides, and "many divalent metal oxides, sulfides, selenides, and tellurides". According to the radius ratio rule, this structure is more likely to be formed if the cation is somewhat smaller than the anion (a cation/anion radius ratio of 0.414 to 0.732).
The interatomic distance (distance between cation and anion, or half the unit cell length ''a'') in some rock-salt-structure crystals are: 2.3 Å (2.3 × 10−10 m) for NaF, 2.8 Å for NaCl, and 3.2 Å for SnTe. Most of the alkali metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen (H−), a hydrogen ion with two electrons. In modern usage, this is typically only used for ionic bonds, but it is sometimes (and has been more frequently in the past) applied to all che ...
s and halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fl ...
s have the rock salt structure, though a few have the caesium chloride
Caesium chloride or cesium chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula Caesium, CsChloride, Cl. This colorless salt is an important source of caesium ions in a variety of niche applications. Its crystal structure forms a major structural ...
structure instead.
Many transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinid ...
monoxides also have the rock salt structure ( TiO, VO, CrO, MnO
Manganese(II) oxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula MnO.Arno H. Reidies "Manganese Compounds" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology 2007; Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. It forms green crystals. The compound is produced on a large s ...
, FeO, CoO, NiO
Nio or NIO may refer to:
* NI Opera, Opera company
* Nio (Buddhism), guardians of the Buddha
* Nio Inc., a Chinese electric automobile manufacturer
* Nicaraguan córdoba, currency by ISO 4217 currency code
* National Institute of Oceanography (d ...
, CdO). The early actinoid monocarbides also have this structure ( ThC, PaC
Pac or PAC may refer to:
Aviation
* IATA code PAC Albrook "Marcos A. Gelabert" International Airport in Panama City, Panama
* Pacific Aerospace Corporation, New Zealand, manufacturer of aircraft:
** PAC 750XL
** PAC Cresco
** PAC CT/4
** PA ...
, UC, NpC, PuC).
Fluorite structure
Much like the rock salt structure, thefluorite structure
The fluorite structure refers to a common motif for compounds with the formula MX2. The X ions occupy the eight tetrahedral interstitial sites whereas M ions occupy the regular sites of a face-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or is ...
(AB2) is also an Fmm structure but has 1:2 ratio of ions. The anti-fluorite structure is nearly identical, except the positions of the anions and cations are switched in the structure. They are designated Wyckoff positions
In crystallography, a Wyckoff position is any point in a set of points whose site symmetry groups (see below) are all conjugate subgroups one of another. Crystallography tables give the Wyckoff positions for different space groups.
History
The W ...
4a and 8c whereas the rock-salt structure positions are 4a and 4b.
Zincblende structure
 The
The space group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that ...
of the Zincblende structure is called F3m (in Hermann–Mauguin notation
In geometry, Hermann–Mauguin notation is used to represent the symmetry elements in point groups, plane groups and space groups. It is named after the German crystallographer Carl Hermann (who introduced it in 1928) and the French mineralogist ...
), or 216. The Strukturbericht designation is "B3".
The Zincblende structure (also written "zinc blende") is named after the mineral zincblende (sphalerite
Sphalerite is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hoste ...
), one form of zinc sulfide
Zinc sulfide (or zinc sulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of ZnS. This is the main form of zinc found in nature, where it mainly occurs as the mineral sphalerite. Although this mineral is usually black because of various i ...
(β-ZnS). As in the rock-salt structure, the two atom types form two interpenetrating face-centered cubic lattices. However, it differs from rock-salt structure in how the two lattices are positioned relative to one another. The zincblende structure has tetrahedral
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular Face (geometry), faces, six straight Edge (geometry), edges, and four vertex (geometry), vertices. The tet ...
coordination
Coordination may refer to:
* Coordination (linguistics), a compound grammatical construction
* Coordination complex, consisting of a central atom or ion and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions
** A chemical reaction to form a coordinati ...
: Each atom's nearest neighbors consist of four atoms of the opposite type, positioned like the four vertices of a regular tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular Face (geometry), faces, six straight Edge (geometry), edges, and four vertex (geometry), vertices. The tet ...
. In zinc sulfide the ratio of zinc to sulfur is 1:1. Altogether, the arrangement of atoms in zincblende structure is the same as diamond cubic
In crystallography, the diamond cubic crystal structure is a repeating pattern of 8 atoms that certain materials may adopt as they solidify. While the first known example was diamond, other elements in group 14 also adopt this structure, in ...
structure, but with alternating types of atoms at the different lattice sites. The structure can also be described as an FCC lattice of zinc with sulfur atoms occupying half of the tetrahedral voids or vice versa.
Examples of compounds with this structure include zincblende itself, lead(II) nitrate
Lead(II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb( NO3)2. It commonly occurs as a colourless crystal or white powder and, unlike most other lead(II) salts, is soluble in water.
Known since the Middle Ages by the name plumbum ...
, many compound semiconductors (such as gallium arsenide
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a Zincblende (crystal structure), zinc blende crystal structure.
Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monoli ...
and cadmium telluride
Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is a stable crystalline compound formed from cadmium and tellurium. It is mainly used as the semiconducting material in cadmium telluride photovoltaics and an infrared optical window. It is usually sandwiched with ...
), and a wide array of other binary compounds. The boron group
The boron group are the chemical elements in periodic table group, group 13 of the periodic table, consisting of boron (B), aluminium (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl) and nihonium (Nh). This group lies in the p-block of the perio ...
pnictogenides usually have a zincblende structure, though the nitride
In chemistry, a nitride is a chemical compound of nitrogen. Nitrides can be inorganic or organic, ionic or covalent. The nitride anion, N3−, is very elusive but compounds of nitride are numerous, although rarely naturally occurring. Some nitr ...
s are more common in the wurtzite structure
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal ...
, and their zincblende forms are less well known polymorphs.
This group is also known as the II-VI family of compounds, most of which can be made in both the zincblende (cubic) or wurtzite
Wurtzite is a zinc and iron sulfide mineral with the chemical formula , a less frequently encountered Polymorphism (materials science), structural polymorph form of sphalerite. The iron content is variable up to eight percent.Palache, Charles, H ...
(hexagonal) form.
This group is also known as the III-V family of compounds.

Heusler structure
The Heusler structure, based on the structure of Cu2MnAl, is a common structure forternary compound
In inorganic chemistry and materials chemistry, a ternary compound or ternary phase is a chemical compound containing three different elements.
While some ternary compounds are molecular, ''e.g.'' chloroform (), more typically ternary phases r ...
s involving transition metals
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinid ...
. It has the space group Fmm (No. 225), and the Strukturbericht designation
In crystallography, a Strukturbericht designation or Strukturbericht type is a system of detailed crystal structure classification by analogy to another known structure. The designations were intended to be comprehensive but are mainly used as supp ...
is L21. Together with the closely related half-Heusler and inverse-Huesler compounds, there are hundreds of examples.
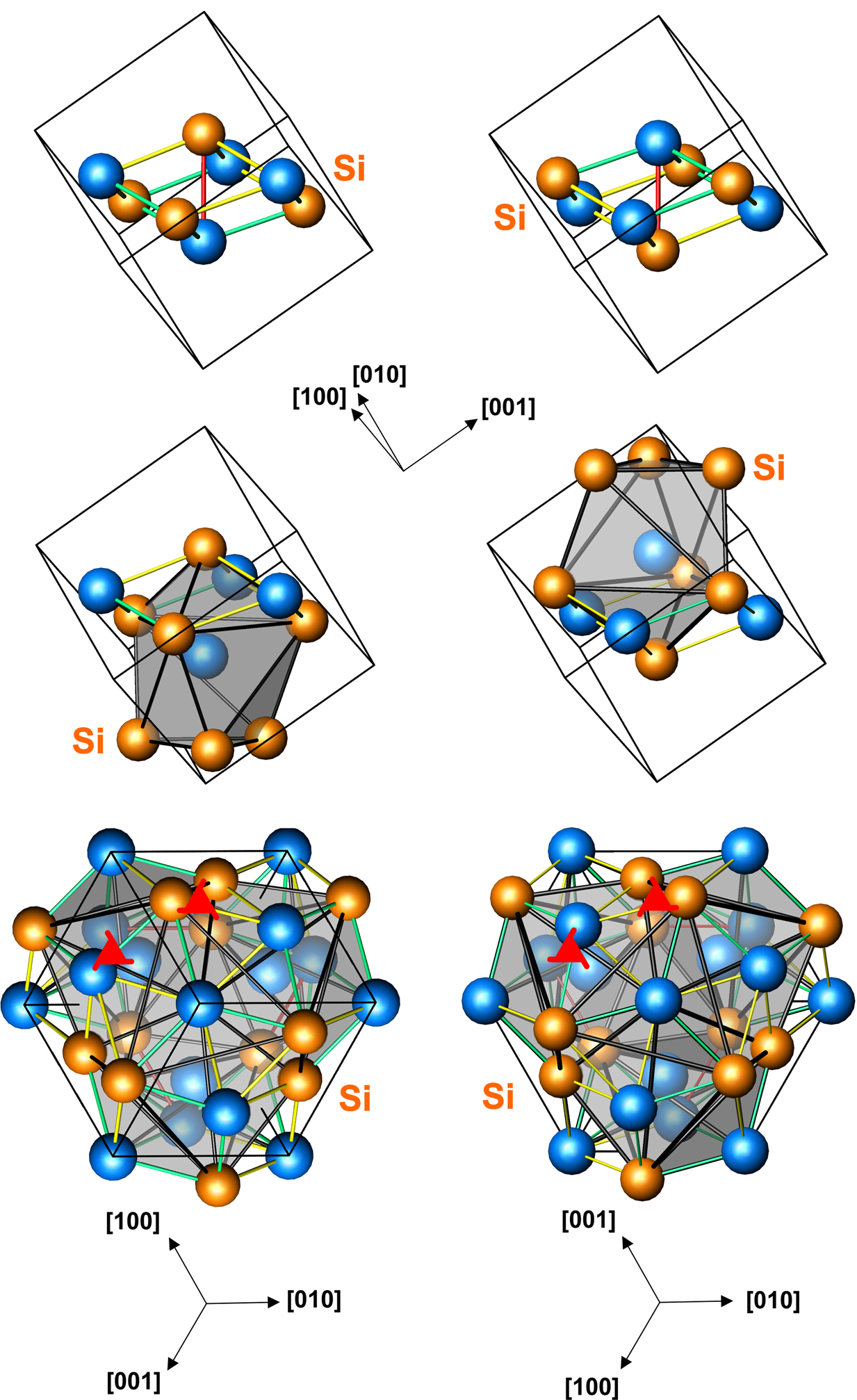
Iron monosilicide structure
 The space group of the iron monosilicide structure is P213 (No. 198), and the
The space group of the iron monosilicide structure is P213 (No. 198), and the Strukturbericht designation
In crystallography, a Strukturbericht designation or Strukturbericht type is a system of detailed crystal structure classification by analogy to another known structure. The designations were intended to be comprehensive but are mainly used as supp ...
is B20. This is a chiral
Chirality () is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is dist ...
structure, and is sometimes associated with helimagnetic properties. There are four atoms of each element for a total of eight atoms in the unit cell.
Examples occur among the transition metal silicides and germanides, as well as a few other compounds such as gallium palladide.
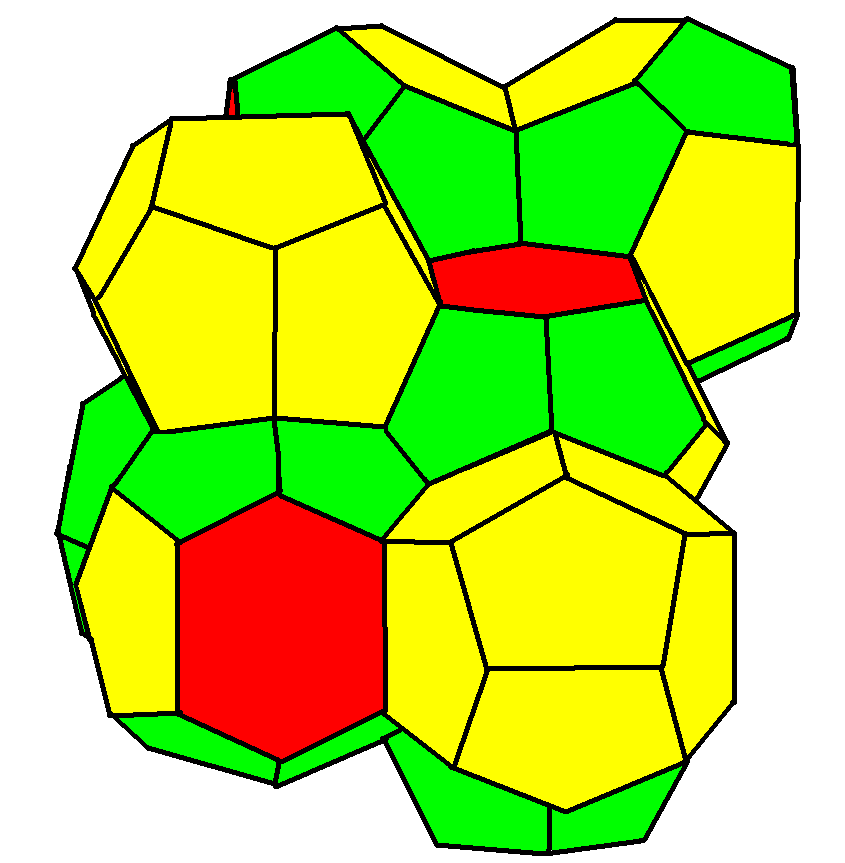
Weaire–Phelan structure
 A
A Weaire–Phelan structure
In geometry, the Weaire–Phelan structure is a three-dimensional structure representing an idealised foam of equal-sized bubbles, with two different shapes. In 1993, Denis Weaire and Robert Phelan found that this structure was a better solutio ...
has Pmn (223) symmetry.
It has three orientations of stacked tetradecahedrons with pyritohedral cells in the gaps. It is found as a crystal structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat ...
in chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
where it is usually known as a "type I clathrate
A clathrate is a chemical substance consisting of a lattice (group), lattice that traps or contains molecules. The word ''clathrate'' is derived from the Latin language, Latin (), meaning 'with bars, Crystal structure, latticed'. Most clathrate ...
structure". Gas hydrates formed by methane, propane, and carbon dioxide at low temperatures have a structure in which water molecules lie at the nodes of the Weaire–Phelan structure and are hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently b ...
ed together, and the larger gas molecules are trapped in the polyhedral cages.
See also
*Atomium
The Atomium ( , , ) is a landmark modernist building in Brussels, Belgium, originally constructed as the centrepiece of the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (Expo 58). Designed by the engineer André Waterkeyn and the architects André and Jean Pol ...
: building which is a model of a ''bcc'' unit cell, with vertical body diagonal.
*Close-packing
In geometry, close-packing of equal spheres is a dense arrangement of congruent spheres in an infinite, regular arrangement (or lattice). Carl Friedrich Gauss proved that the highest average density – that is, the greatest fraction of space occ ...
*Dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to sli ...
s
*Reciprocal lattice
Reciprocal lattice is a concept associated with solids with translational symmetry which plays a major role in many areas such as X-ray and electron diffraction as well as the energies of electrons in a solid. It emerges from the Fourier tran ...
References
Further reading
*Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., Wiley,External links
*JMol
Jmol is computer software for molecular modelling of chemical structures in 3 dimensions.
It is an open-source Java viewer for chemical structures in 3D.
The name originated from ''Jva (the programming language) + olcules, and also the m ...
simulations by Graz University
The University of Graz (, formerly: ''Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz'') is a public university, public research university located in Graz, Austria. It is the largest and oldest university in Styria, as well as the second-largest and second-old ...
:
Simple cubic
BCC
FCC
HCP
with Molview {{DEFAULTSORT:Cubic Crystal System Crystal systems Cubes