Hagi Castle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
is a
 Hagi Castle is located at the seashore of Hagi city, in northeastern Yamaguchi Prefecture. The Hagi area borders the
Hagi Castle is located at the seashore of Hagi city, in northeastern Yamaguchi Prefecture. The Hagi area borders the
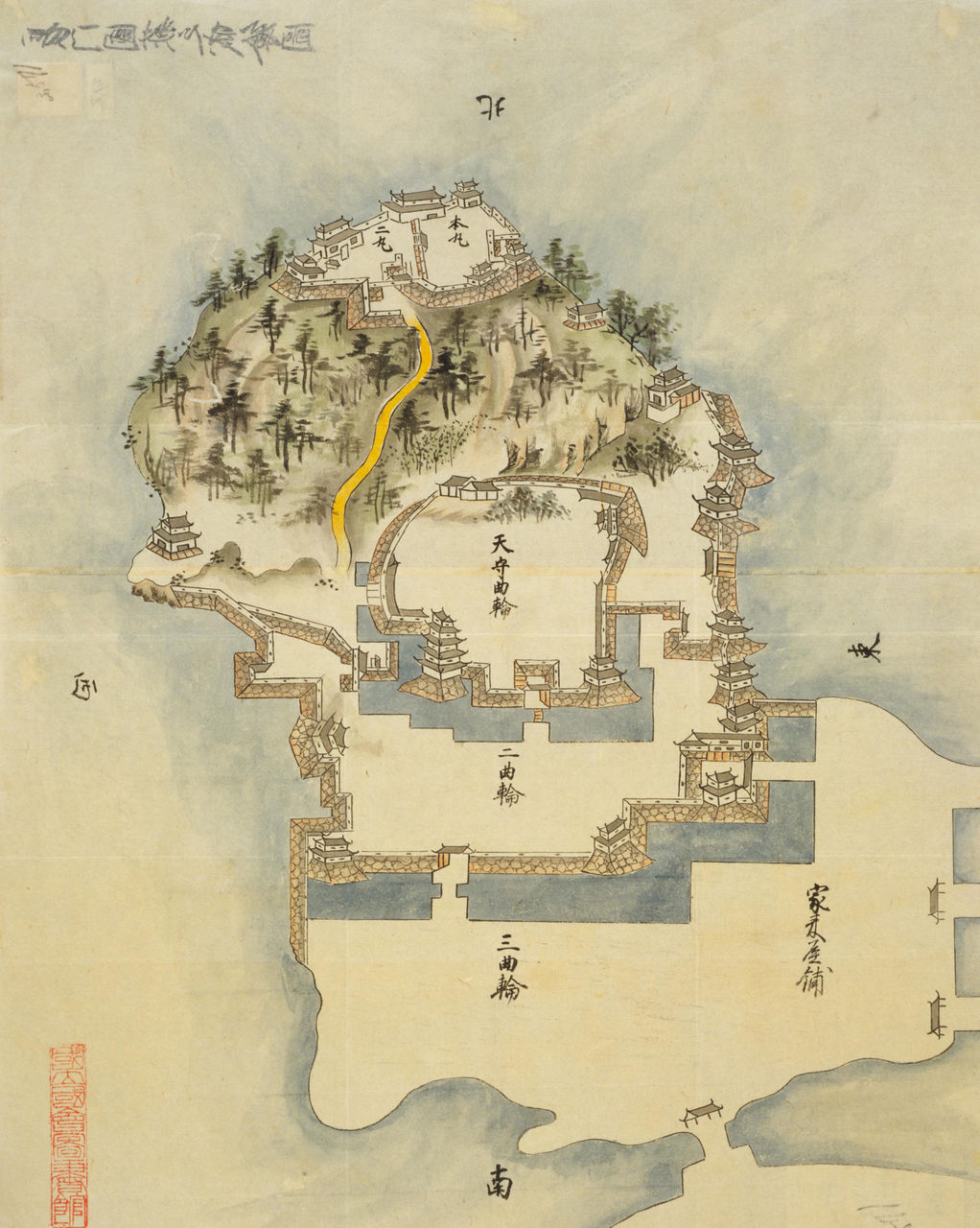 Hagi Castle consisted of two square enclosures on Mount Shigetsu and the sandbank connecting it to the mainland. The ocean forms a natural moat on the back side of the castle and a water moat connected to the ocean protects the front. From the landward approach, these enclosures are at an angle, such that a corner of the enclosure faces the mainland to the southeast. Both areas are protected by stone walls and compound gates.
The ''
Hagi Castle consisted of two square enclosures on Mount Shigetsu and the sandbank connecting it to the mainland. The ocean forms a natural moat on the back side of the castle and a water moat connected to the ocean protects the front. From the landward approach, these enclosures are at an angle, such that a corner of the enclosure faces the mainland to the southeast. Both areas are protected by stone walls and compound gates.
The ''
 The site was originally occupied by a minor fortification erected by the Yoshimi clan, who were based at
The site was originally occupied by a minor fortification erected by the Yoshimi clan, who were based at
File:Hagi Castle 02.jpg, Remaining walls
File:Moat of Hagi Castle 1.jpg, The inner moat
File:Hagi, Yamaguchi Prefecture, Japan - panoramio.jpg, The outer moat
Japan's Meiji Industrial Revolution official home pageHagi Sightseeing Guide
{{Sites of Japan's Meiji Industrial Revolution: Iron and Steel, Shipbuilding and Coal Mining Castles in Yamaguchi Prefecture Hagi, Yamaguchi Historic Sites of Japan 100 Fine Castles of Japan World Heritage Sites in Japan 1604 establishments in Japan Mōri clan Nagato Province
Japanese castle
are fortresses constructed primarily of wood and stone. They evolved from the wooden stockades of earlier centuries and came into their best-known form in the 16th century. Castles in Japan were built to guard important or strategic sites, such a ...
located in the city of Hagi, Yamaguchi Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Chūgoku region of Honshu. Yamaguchi Prefecture has a population of 1,377,631 (1 February 2018) and has a geographic area of 6,112 Square kilometre, km2 (2,359 Square mile, sq mi). ...
, in the San'yō region
The San'yō Region (山陽地方 ''San'yō-chihō'') is an area in the south of Honshū, the main island of Japan. It consists of the southern part of the Chūgoku region, facing the Seto Inland Sea. The name ''San'yō'' means "southern, sunny ( ...
of Japan. Built in 1604 at the beginning of the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
as the main castle of the Mōri clan
The was a Japanese clan, Japanese samurai clan descended from Ōe no Hiromoto. Ōe no Hiromoto was descended from the Fujiwara clan. The family's most illustrious member, Mōri Motonari, greatly expanded the clan's power in Aki Province. Durin ...
, it served as the seat of the Chōshū Domain
The , also known as the , was a domain (''han'') of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1600 to 1871.Deal, William E. (2005) ''Handbook to Life in Medieval and Early Modern Japan,'' p. 81
The Chōshū Domain was based ...
for over 250 years until 1863. It was demolished in 1874 shortly after the Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored Imperial House of Japan, imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Althoug ...
. Its ruins were designated a National Historic Site in 1924. Hagi Castle has been designed as a component of the Sites of Japan's Meiji Industrial Revolution: Iron and Steel, Shipbuilding and Coal Mining, which received UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
status in 2015.
Location
 Hagi Castle is located at the seashore of Hagi city, in northeastern Yamaguchi Prefecture. The Hagi area borders the
Hagi Castle is located at the seashore of Hagi city, in northeastern Yamaguchi Prefecture. The Hagi area borders the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it ...
and occupies the delta of the Abu River. The edge of the delta is Mount Shigetsu, with an elevation of 150 meters, which was formerly an island but is connected to the land by sandbank. The castle is built on Mount Shigetsu.
Like elsewhere in Japan, a town grew around the castle, and the area is now known as Hagi Castle Town.
Layout
 Hagi Castle consisted of two square enclosures on Mount Shigetsu and the sandbank connecting it to the mainland. The ocean forms a natural moat on the back side of the castle and a water moat connected to the ocean protects the front. From the landward approach, these enclosures are at an angle, such that a corner of the enclosure faces the mainland to the southeast. Both areas are protected by stone walls and compound gates.
The ''
Hagi Castle consisted of two square enclosures on Mount Shigetsu and the sandbank connecting it to the mainland. The ocean forms a natural moat on the back side of the castle and a water moat connected to the ocean protects the front. From the landward approach, these enclosures are at an angle, such that a corner of the enclosure faces the mainland to the southeast. Both areas are protected by stone walls and compound gates.
The ''tenshu
is an architectural typology found in Japanese castle, Japanese castle complexes. They are easily identifiable as the highest tower within the castle. Common translations of ''tenshu'' include keep, main keep, or ''donjon''.
''Tenshu'' are cha ...
'' (keep) was a five-story structure, and many ''yagura'' (turrets) were constructed at intervals on the stone walls. On the mainland was a tertiary area, also protected by moats, for the higher-ranked retainer's residences, and the castle town
A castle town is a settlement built adjacent to or surrounding a castle. Castle towns were common in Medieval Europe. Some examples include small towns like Alnwick and Arundel, which are still dominated by their castles. In Western Europe, ...
.
History
Founding
 The site was originally occupied by a minor fortification erected by the Yoshimi clan, who were based at
The site was originally occupied by a minor fortification erected by the Yoshimi clan, who were based at Tsuwano Castle
was a Japanese castle located in what is now the city of Tsuwano, Shimane Prefecture, in the San'in region of far western Japan. Its ruins have been protected by the central government as a National Historic Site since 1942. In its early histor ...
in Iwami Province
was an old province of Japan in the area that is today the western part of Shimane Prefecture. It was sometimes called . Iwami bordered Aki, Bingo, Izumo, Nagato, and Suō provinces.
In the Heian period (794–1192) the capital was at moder ...
. The Yoshimi were retainers of the Ōuchi clan
was one of the most powerful and important families in Western Japan during the reign of the Ashikaga shogunate in the 14th to 16th centuries. Their domains, ruled from the castle town of Yamaguchi in the western tip of Honshu island, compris ...
, who were ''shugo
, commonly translated as ' ilitarygovernor', 'protector', or 'constable', was a title given to certain officials in feudal Japan. They were each appointed by the shogun to oversee one or more of the provinces of Japan. The position gave way to th ...
'' of the provinces on Nagato and Suō from the late Kamakura period
The is a period of History of Japan, Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura by the first ''shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the G ...
. In the mid-Muromachi period
The , also known as the , is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate ( or ), which was officially established in 1338 by the first Muromachi ...
, the Ōuchi were overthrown by their own general, Sue Harukata
was a samurai who served as a senior retainer of the Ōuchi clan in the Sengoku period in Japan. He was the second son of Sue Okifusa, a senior retainer of the Ōuchi clan. His childhood name was Goro, and he previously had the name Takafusa ...
, who was in turn defeated by the Mōri clan
The was a Japanese clan, Japanese samurai clan descended from Ōe no Hiromoto. Ōe no Hiromoto was descended from the Fujiwara clan. The family's most illustrious member, Mōri Motonari, greatly expanded the clan's power in Aki Province. Durin ...
.
Mōri Motonari
was a prominent ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) in the western Chūgoku region of Japan during the Sengoku period of the 16th century. The Mōri clan claimed descent from Ōe no Hiromoto (大江広元), an adviser to Minamoto no Yoritomo. Motonari w ...
was originally a minor warlord from Aki Province
or Geishū () was a province in the Chūgoku region of western Honshu, comprising the western part of what is today Hiroshima Prefecture.
History
When Emperor Shōmu ordered two official temples for each province (one for male Buddhist prie ...
, but after defeating Sue Harutaka and later the Amago clan
The , descended from the Emperor Uda (868–897) by the Kyogoku clan, descending from the Sasaki clan (Uda Genji).
Kyogoku Takahisa in the 14th century, lived in Amako-go (Izumo Province), and took the name 'Amago'. The family crest is also t ...
of Izumo Province
was an Old provinces of Japan, old province of Japan which today consists of the eastern part of Shimane Prefecture. It was sometimes called . The province is in the Chūgoku region.
History
During the early Kofun period (3rd century) this reg ...
, rose to become the ruler of most of the Chugoku region of western Japan. Under his grandson, Mōri Terumoto
Mōri Terumoto (毛利 輝元, January 22, 1553 – June 2, 1625) was a Japanese ''daimyō''. The son of Mōri Takamoto, and grandson and successor of the great warlord Mōri Motonari, he fought against Oda Nobunaga but was eventually overc ...
and with the support of Kikkawa Motoharu
was the second son of Mōri Motonari, and featured prominently in all the wars of the Mōri clan.
He became an active commander of the Mōri army and he with his brother Kobayakawa Takakage became known as the “Mōri Ryōsen", or “Mōri's T ...
and Kobayakawa Takakage
was a samurai and daimyō (feudal military lord) during the Sengoku period and Azuchi–Momoyama period. He was the third son of Mōri Motonari who was adopted by the Kobayakawa clan and became its 14th clan head. He merged the two branches of ...
, the Mōri continued to expand, but eventually came into conflict with Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods. He was the and regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. He is sometimes referred as the "Demon Daimyō" and "Demo ...
, who general Hashiba Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innov ...
and gradually were forced back into the western half of the Chugoku region. Nobunaga was assassinated before the Mōri could be completely defeated, and agreed to become vassals of his successor, Toyotomi Hideyoshi. Under Toyotomi rule, the Mōri constructed Hiroshima Castle
, sometimes called , is a Japanese castle, castle in Hiroshima, Japan that was the residence of the ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the Hiroshima Domain. The castle was originally constructed in the 1590s, but was largely destroyed by the Atomic bom ...
as their main stronghold.
After the death of Hideyoshi, the Mōri supported his son, Toyotomi Hideyori
was the son and designated successor of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, the general who united all of Japan toward the end of the Sengoku period. His mother, Yodo-dono, was the niece of Oda Nobunaga.
Early life
Born in 1593, he was Hideyoshi's sec ...
, at the 1600 Battle of Sekigahara
The Battle of Sekigahara (Shinjitai: ; Kyūjitai: , Hepburn romanization: ''Sekigahara no Tatakai'') was an important battle in Japan which occurred on October 21, 1600 (Keichō 5, 15th day of the 9th month) in what is now Gifu Prefecture, ...
against Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu (born Matsudaira Takechiyo; 31 January 1543 – 1 June 1616) was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, which ruled from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was the third of the three "Gr ...
. However, the Mōri did not actually participate in any combat during that battle, as Kikkawa Hiroie
(December 7, 1561 – October 22, 1625) was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Azuchi–Momoyama period through early Edo period.
Hiroie's father was Kikkawa Motoharu and his mother was a daughter of Kumagai Nobunao.
Biography
He initially ...
was in secret communication with the Tokugawa forces and prevented the Mōri army from receiving orders to move forward. After the battle and the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
, Tokugawa Ieyasu betrayed his agreement with the Mōri and seized two-thirds of their holdings, including their home province of Aki. Forced back to only Nagato and Suō, the Mōri needed a new stronghold. Initially they petitioned to be allowed to construct their stronghold in either Yamaguchi or Hōfu
file:Hofu City Hall 2021-08 ac (2).jpg, 270px, Hōfu City Hall
file:Hofu city center area Aerial photograph.2010.jpg, 270px, Aerial photograph of central Hōfu
file:Hofu-tenmangu, roumon-1.jpg, 270px, Hōfu Tenman-gu
is a Cities of Japan, city ...
, which were on the strategic Sanyōdō highway which connected Kyoto
Kyoto ( or ; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan's largest and most populous island of Honshu. , the city had a population of 1.46 million, making it t ...
with Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's Japanese archipelago, four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa Island, Okinawa and the other Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Ryukyu Islands, Islands ...
. However, the shogunate rejected these proposals and ordered that they build their stronghold at Hagi, which was at the time only a small fishing village, distant from important roads and was a swampy area hemmed in by hills and rivers. Construction of Hagi Castle began in 1604 and was completed in 1608.
Although Chōshū Domain
The , also known as the , was a domain (''han'') of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1600 to 1871.Deal, William E. (2005) ''Handbook to Life in Medieval and Early Modern Japan,'' p. 81
The Chōshū Domain was based ...
played a major role in the history of Bakumatsu
were the final years of the Edo period when the Tokugawa shogunate Meiji Restoration, ended. Between 1853 and 1867, under foreign diplomatic and military pressure, Japan ended its isolationist foreign policy known as and changed from a Feudali ...
Japan and the Meiji restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored Imperial House of Japan, imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Althoug ...
, Hagi Castle was not the site of any major conflict. In 1863, the Mōri clan moved their seat from Hagi Castle to Yamaguchi Castle for fear of attack by foreign naval forces following the Shimonoseki campaign.
Destruction and ruins
In 1874, most of the castle structures were demolished by order of the newMeiji government
The was the government that was formed by politicians of the Satsuma Domain and Chōshū Domain in the 1860s. The Meiji government was the early government of the Empire of Japan.
Politicians of the Meiji government were known as the Meiji ...
and some moats were reclaimed. However, the stone walls of central area and hilltop area remain largely intact, and the outer gate and a corner turret was later restored. The ruins were declared a National Historic Site in 1951, as was Hagi Castle Town in 1967. Mount Shigetsu was designated a National Natural Monument in 1971. In 2006, Hagi Castle was selected as one of Japan's Top 100 Castles
The Japanese castle, castles in were chosen based on their significance in culture, history, and in their regions by the in 2006.
In 2017, the Japanese Castle Association created an additional finest 100 castles list as Continued Top 100 Japane ...
by the Japan Castle Foundation in 2006.
It was registered as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
on July 5, 2015, as part of the Sites of Japan’s Meiji Industrial Revolution: Iron and Steel, Shipbuilding and Coal Mining. It is registered as part of Hagi's Castle Town.
See also
*List of Historic Sites of Japan (Yamaguchi)
This list is of the Monuments of Japan, Historic Sites of Japan located within the Prefectures of Japan, Prefecture of Yamaguchi Prefecture, Yamaguchi.
National Historic Sites
As of 1 July 2019, forty-three Sites have been Cultural Properties of ...
* Sites of Japan’s Meiji Industrial Revolution: Iron and Steel, Shipbuilding and Coal Mining
References
Literature
* * * * *External links
Japan's Meiji Industrial Revolution official home page
{{Sites of Japan's Meiji Industrial Revolution: Iron and Steel, Shipbuilding and Coal Mining Castles in Yamaguchi Prefecture Hagi, Yamaguchi Historic Sites of Japan 100 Fine Castles of Japan World Heritage Sites in Japan 1604 establishments in Japan Mōri clan Nagato Province