Haemoglobinopathies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hemoglobinopathy is the medical term for a group of inherited
 Normal human hemoglobins are
Normal human hemoglobins are
 Thalassemias are quantitative defects that lead to reduced levels of one type of globin chain, creating an imbalance in the ratio of alpha-like chains to beta-like chains. This ratio is normally tightly regulated to prevent excess globin chains of one type from accumulating. The excess chains that fail to incorporate into normal hemoglobin can form non-functional aggregates that precipitate. This can lead to premature RBC destruction in the bone marrow and/or in the peripheral blood. Thalassemia subtypes of clinical significance are
Thalassemias are quantitative defects that lead to reduced levels of one type of globin chain, creating an imbalance in the ratio of alpha-like chains to beta-like chains. This ratio is normally tightly regulated to prevent excess globin chains of one type from accumulating. The excess chains that fail to incorporate into normal hemoglobin can form non-functional aggregates that precipitate. This can lead to premature RBC destruction in the bone marrow and/or in the peripheral blood. Thalassemia subtypes of clinical significance are
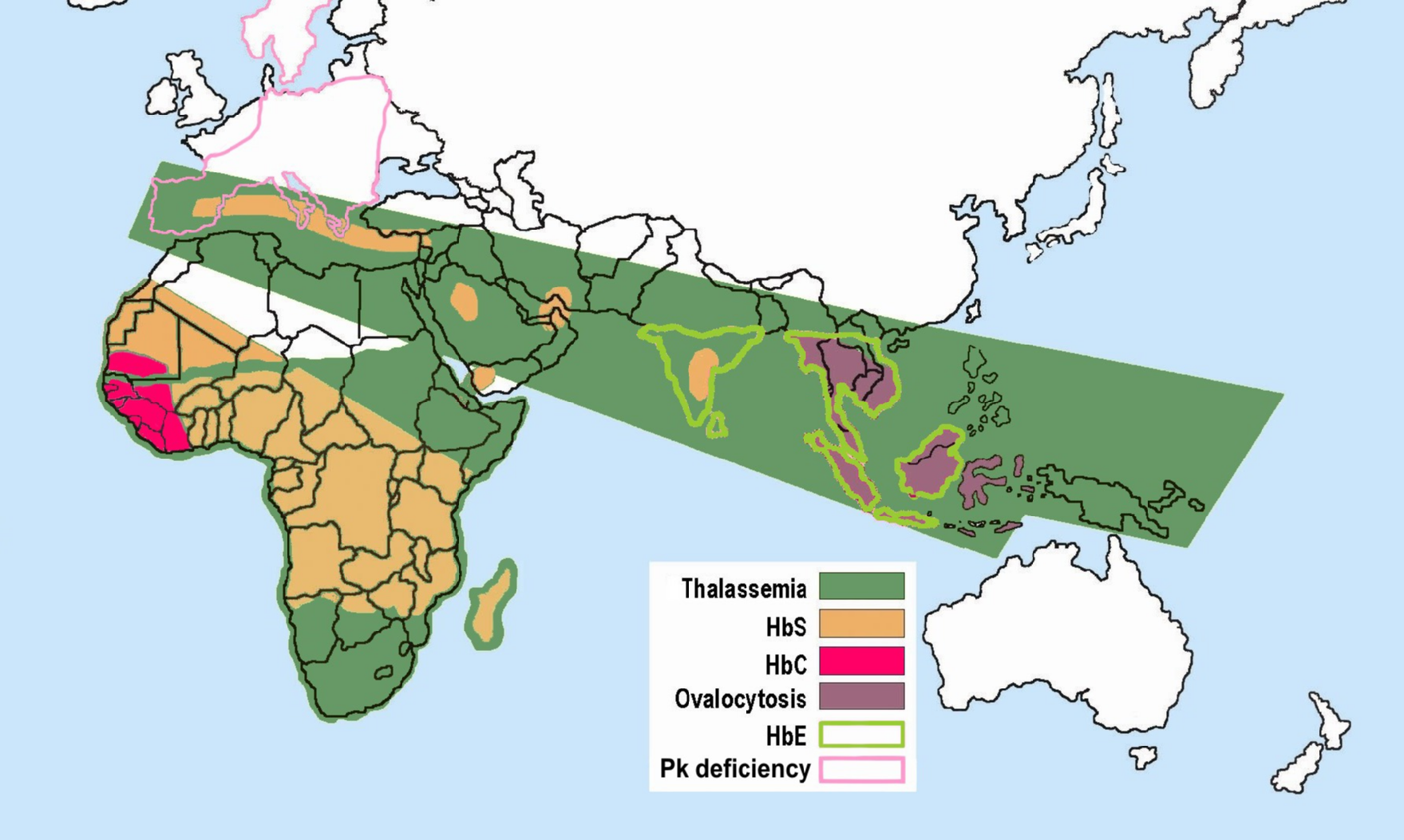 Some hemoglobinopathies seem to have given an evolutionary benefit, especially to
Some hemoglobinopathies seem to have given an evolutionary benefit, especially to
blood disorders
Hematologic diseases are disorders which primarily affect the blood and Blood formation, blood-forming organs. Hematologic diseases include rare genetic disorders, anemia, HIV, sickle cell disease and complications from chemotherapy or transfusio ...
involving the hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
, the major protein of red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
s. They are generally single-gene disorders and, in most cases, they are inherited as autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosome ...
recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and ...
traits.
There are two main groups: abnormal structural hemoglobin variants caused by mutations in the hemoglobin genes, and the thalassemia
Thalassemias are a group of Genetic disorder, inherited blood disorders that manifest as the production of reduced hemoglobin. Symptoms depend on the type of thalassemia and can vary from none to severe, including death. Often there is mild to ...
s, which are caused by an underproduction of otherwise normal hemoglobin molecules. The main structural hemoglobin variants are HbS, HbE and HbC. The main types of thalassemia are alpha-thalassemia
Alpha-thalassemia (α-thalassemia, α-thalassaemia) is an inherited blood disorder and a form of thalassemia. Thalassemias are a group of inherited blood conditions which result in the impaired production of hemoglobin, the molecule that carrie ...
and beta thalassemia
Beta-thalassemia (β-thalassemia) is an genetic disorder, inherited hemoglobinopathy, blood disorder, a form of thalassemia resulting in variable outcomes ranging from clinically asymptomatic to severe anemia individuals. It is caused by reduce ...
.
Hemoglobin functions
Hemoglobin is aprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
containing iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
that facilitates the transportation of oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
in red blood cells
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
. Hemoglobin in the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
carries oxygen from the lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
to the other tissues of the body, where it releases the oxygen to enable aerobic respiration
Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing biological fuels using an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores chemical energy in a biologically accessible form. Cellu ...
which powers the metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
. Normal levels of hemoglobin vary according to sex and age in the range 9.5 to 17.2 grams of hemoglobin in every deciliter of blood.
Hemoglobin also transports other gases. It carries off some of the body's respiratory carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
(about 20–25% of the total) as carbaminohemoglobin
Carbaminohemoglobin (carbaminohaemoglobin BrE) (CO2Hb, also known as carbhemoglobin and carbohemoglobin) is a Chemical compound, compound of hemoglobin and carbon dioxide, and is one of the forms in which carbon dioxide exists in the blood. In bl ...
, in which CO2 binds to the heme protein
A hemeprotein (or haemprotein; also hemoprotein or haemoprotein), or heme protein, is a protein that contains a heme prosthetic group. They are a very large class of metalloproteins. The heme group confers functionality, which can include oxyg ...
. The molecule also carries the important regulatory molecule nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
bound to a thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl grou ...
group in the globin protein, releasing it at the same time as oxygen.
Hemoglobin structural biology
 Normal human hemoglobins are
Normal human hemoglobins are tetrameric protein
A tetrameric protein is a protein with a quaternary structure of four subunits (tetrameric). Homotetramers have four identical subunits (such as glutathione S-transferase), and heterotetramers are complexes of different subunits. A tetramer ...
s composed of two pairs of globin chains, each of which contains one alpha-like (α) globin and one beta-like (β) globin. Each globin chain is associated with an iron-containing heme
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced /Help:IPA/English, hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand of various proteins, more notably as a Prostheti ...
moiety. Throughout life, the synthesis of the α and the β chains is balanced so that their ratio is relatively constant and there is no excess of either type.
The specific α and β chains that are incorporated into Hb are highly regulated during development:
* Embryonic Hb are expressed as early as four to six weeks of embryogenesis
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male ...
and disappear around the eighth week of gestation as they are replaced by fetal Hb. Embryonic Hbs include:
** Hb Gower-1, composed of two ζ (zeta) globins and two ε (epsilon) globins, i.e., ζ2ε2
** Hb Gower-2, composed of two α globins and two ε globins (α2ε2)
** Hb Portland, composed of two ζ globins and two γ (gamma) globins (ζ2γ2)
* Fetal Hb (HbF) is produced from approximately eight weeks of gestation through birth and constitutes approximately 80 percent of Hb in the full-term neonate. It declines during the first few months of life and, in the normal state, constitutes <1 percent of total Hb by early childhood. HbF is composed of two α globins and two γ globins (α2γ2).
* Adult Hb (HbA) is the predominant Hb in children by six months of age and onward; it constitutes 96-97% of total Hb in individuals without a hemoglobinopathy. It is composed of two α globins and two β globins (α2β2).
* HbA2
Hemoglobin, alpha 2 also known as ''HBA2'' is a gene that in humans codes for the alpha globin chain of hemoglobin.
Function
The human alpha globin gene cluster is located on chromosome 16 and spans about 30 kb, including seven alpha like glo ...
is a minor adult Hb that normally accounts for approximately 2.5–3.5% of total Hb from six months of age onward. It is composed of two α globins and two δ (delta) globins (α2δ2).
Classification of hemoglobinopathies
A) Qualitative
Structural abnormalities
Hemoglobin structural variants manifest a change in the structure of the Hb molecule. The majority of hemoglobin variants do not cause disease and are most commonly discovered either incidentally or through newborn screening. Hb variants can usually be detected by protein-basedassay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity ...
methods such as electrophoresis
Electrophoresis is the motion of charged dispersed particles or dissolved charged molecules relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. As a rule, these are zwitterions with a positive or negative net ch ...
, isoelectric focusing
Isoelectric focusing (IEF), also known as electrofocusing, is a technique for separating different charged molecules by differences in their isoelectric point (pI). It is a type of zone electrophoresis usually performed on proteins in a gel tha ...
, or high-performance liquid chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify specific components in mixtures. The mixtures can origin ...
. Diagnosis is commonly confirmed by DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The ...
.
The hemoglobin structural variants can be broadly classified as follows:
* Sickle cell disorders, which are the most prevalent form of hemoglobinopathy. Sickle hemoglobin (HbS) is prone to polymerize
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many form ...
when deoxygenated, precipitating within the red blood cell. This damages the RBC membrane resulting in its premature destruction and consequent anemia.
* Unstable hemoglobin variants are mutations that cause the hemoglobin molecule to precipitate
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the "sedimentation of a solid material (a precipitate) from a liquid solution". The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemic ...
, spontaneously or upon oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal ...
, resulting in hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels (intravascular hemolysis) or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonl ...
. Precipitated, denatured hemoglobin can attach to the inner layer of the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
of the red blood cell (RBC) forming Heinz bodies, leading to premature destruction of the RBC and anemia.
* Change in oxygen affinity. High or low oxygen affinity hemoglobin molecules are more likely than normal to adopt the relaxed (R, oxy) state or the tense (T, deoxy) state, respectively. High oxygen affinity variants (R state) cause polycythemia
Polycythemia (also known as polycythaemia) is a laboratory finding in which the hematocrit (the volume percentage of red blood cells in the blood) and/or hemoglobin concentration are increased in the blood. Polycythemia is sometimes called erythr ...
(e.g., Hb Chesapeake, Hb Montefiore). Low oxygen affinity variants can cause cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of Tissue (biology), tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the Tissue (bi ...
(e.g., Hb Kansas, Hb Beth Israel).
Chemical abnormalities
Methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia, or methaemoglobinaemia, is a condition of elevated methemoglobin in the blood. Symptoms may include headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, nausea, poor muscle coordination, and blue-colored skin (cyanosis). Complications ma ...
is a condition caused by elevated levels of methemoglobin
Methemoglobin (British: methaemoglobin, shortened MetHb) (pronounced "met-hemoglobin") is a hemoglobin ''in the form of metalloprotein'', in which the iron in the heme group is in the Fe3+ (ferric) state, not the Fe2+ (ferrous) of normal hemoglobin ...
in the blood. Methaemoglobin is a form of hemoglobin that contains the ferric
In chemistry, iron(III) or ''ferric'' refers to the chemical element, element iron in its +3 oxidation number, oxidation state. ''Ferric chloride'' is an alternative name for iron(III) chloride (). The adjective ''ferrous'' is used instead for i ...
e3+form of iron, instead of the ferrous
In chemistry, iron(II) refers to the chemical element, element iron in its +2 oxidation number, oxidation state. The adjective ''ferrous'' or the prefix ''ferro-'' is often used to specify such compounds, as in ''ferrous chloride'' for iron(II ...
e2+form . Methemoglobin cannot bind oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
, which means it cannot carry oxygen to tissues. In human blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
a trace amount of methemoglobin is normally produced spontaneously; the enzyme methemoglobin reductase
Cytochrome-''b''5 reductase is a NADH-dependent enzyme that converts ferricytochrome from a Fe3+ form to a Fe2+ form. It contains FAD and catalyzes the reaction:
In its b5-reducing capacity, this enzyme is involved in desaturation and elongati ...
is responsible for converting methemoglobin back to hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
. Methemoglobinemia can be hereditary but more commonly occurs as a side effect of certain medications or by abuse of recreational drugs
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for enjoyment, amusement, or plea ...
.
B) Quantitative
Production abnormalities
 Thalassemias are quantitative defects that lead to reduced levels of one type of globin chain, creating an imbalance in the ratio of alpha-like chains to beta-like chains. This ratio is normally tightly regulated to prevent excess globin chains of one type from accumulating. The excess chains that fail to incorporate into normal hemoglobin can form non-functional aggregates that precipitate. This can lead to premature RBC destruction in the bone marrow and/or in the peripheral blood. Thalassemia subtypes of clinical significance are
Thalassemias are quantitative defects that lead to reduced levels of one type of globin chain, creating an imbalance in the ratio of alpha-like chains to beta-like chains. This ratio is normally tightly regulated to prevent excess globin chains of one type from accumulating. The excess chains that fail to incorporate into normal hemoglobin can form non-functional aggregates that precipitate. This can lead to premature RBC destruction in the bone marrow and/or in the peripheral blood. Thalassemia subtypes of clinical significance are alpha thalassemia
Alpha-thalassemia (α-thalassemia, α-thalassaemia) is an inherited blood disorder and a form of thalassemia. Thalassemias are a group of inherited blood conditions which result in the impaired production of hemoglobin, the molecule that carrie ...
and beta thalassemia
Beta-thalassemia (β-thalassemia) is an genetic disorder, inherited hemoglobinopathy, blood disorder, a form of thalassemia resulting in variable outcomes ranging from clinically asymptomatic to severe anemia individuals. It is caused by reduce ...
. A third subtype, delta thalassemia, affects production of HBA2 and is generally asymptomatic.
The severity of alpha thalassemia depends on how many of the four genes that code for alpha globin are faulty. In the fetus, a deficiency of alpha globin results in the production of Hemoglobin Barts
Hemoglobin Barts, abbreviated Hb Barts, is an abnormal type of hemoglobin that consists of four gamma globins. It is moderately insoluble, and therefore accumulates in the red blood cells. Hb Barts has an extremely high affinity for oxygen, so it ...
- a dysfunctional hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
that consists of four gamma globins. In this situation, a fetus will develop hydrops fetalis
Hydrops fetalis or hydrops foetalis is a condition in the fetus characterized by an accumulation of fluid, or edema, in at least two fetal compartments. By comparison, hydrops allantois or hydrops amnion is an accumulation of excessive fluid in ...
and normally die before or shortly after birth. In adults alpha thalassemia manifests as HbH disease. In this, excess beta-globin
Hemoglobin subunit beta (beta globin, β-globin, haemoglobin beta, hemoglobin beta) is a globin protein, coded for by the ''HBB'' gene, which along with alpha globin (HBA1, HBA), makes up the most common form of haemoglobin in adult humans, hem ...
forms β4-tetramers, which accumulate and precipitate in red blood cells, damaging their membranes. Damaged RBCs are removed by the spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
resulting in moderate to severe anemia.
In beta thalassemia, reduced production of beta globin, combined with a normal synthesis of alpha globin, results in an accumulation of excess unmatched alpha globin. This precipitates in the red cell precursors in the bone marrow, triggering their premature destruction. Anemia in beta thalassemia results from a combination of ineffective production of RBCs, peripheral hemolysis
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by #Nomenclature, several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may ...
, and an overall reduction in hemoglobin synthesis.
Combination hemoglobinopathies
A combination hemoglobinopathy occurs when someone inherits two different abnormal hemoglobin genes. If these are different versions of the same gene, one having been inherited from each parent it is an example ofcompound heterozygosity
In medical genetics, compound heterozygosity is the condition of having two or more heterogeneous recessive alleles at a particular locus that can cause genetic disease in a heterozygous state; that is, an organism is a compound heterozygote when i ...
.
Both alpha- and beta- thalassemia can coexist with other hemoglobinopathies. Combinations involving alpha thalassemia are generally benign.
Some examples of clinically significant combinations involving beta thalassemia include:
* Hemoglobin C/ beta thalassemia: common in Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and African populations generally results in a moderate form of anemia with splenomegaly.
* Hemoglobin D
Hemoglobin D (HbD) is a variant of hemoglobin, a protein complex that makes up red blood cells. Based on the locations of the original identification, it has been known by several names such as hemoglobin D-Los Angeles, hemoglobin D-Punjab, D-No ...
/ beta thalassemia: common in the northwestern parts of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
(Punjab region
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
).
* Hemoglobin E/ beta thalassemia: common in Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
, Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, and parts of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, it is clinically similar to β thalassemia major or β thalassemia intermedia.
* Hemoglobin S/ beta thalassemia: common in African and Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
populations, it is clinically similar to sickle-cell anemia
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying ...
.
* Delta-beta thalassemia
Delta-beta thalassemia is a rare form of thalassemia in which there is a reduced production of hemoglobin subunit delta and hemoglobin subunit beta and raised levels of hemoglobin subunit gamma. It is an autosomal recessive disorder.
Signs and ...
is a rare form of thalassemia in which there is a reduced production of both the delta and beta globins. It is generally asymptomatic.
There are two clinically significant combinations involving the sickle cell gene:
* Hemoglobin S/ beta thalassemia: (see above).
* Hemoglobin S/ hemoglobin C ( Hemoglobin SC disease) occurs when an individual inherits one gene for hemoglobin S (sickle cell) and one gene for hemoglobin C, The symptoms are very similar to sickle cell disease.
Hemoglobin variants
Hemoglobin variants are not necessarily pathological. For example, Hb Lepore-Boston and G-Waimanalo are two variants which are non-pathological. There are in excess of 1,000 known hemoglobin variants. A research database of hemoglobin variants is maintained byPenn State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsyl ...
. A few of these variants are listed below.
Normal hemoglobins
Source: ; Embryonic * HbE Gower 1 (ζ2ε2) * HbE Gower 2 (α2ε2) * HbE Portland I (ζ2γ2) * HbE Portland II (ζ2β2) ; Fetal * HbF/Fetal (α2γ2) dominating during pregnancy and reducing close to zero a few weeks after birth * HbA (α2β2) Adult hemoglobin, present in small quantities during pregnancy ; Adult * HbA (α2β2) comprising approximately 97% of adult hemoglobin * HbA2 (α2δ2) comprising approximately 3% of adult hemoglobin * HbF/Fetal (α2γ2) dominating during pregnancy and reducing close to zero after birthRelatively common abnormal hemoglobins
Source: * HbS (α2βS2) causing sickle cell disease * HbC (α2βC2) causing mild anemia if homozygous * HbE (α2βE2) causing mild anemia if homozygous * HbD causing mild anemia if homozygous * HbH formed from 4 beta globins in severe alpha thalassemia causing severe anemiaEvolutionary advantage
 Some hemoglobinopathies seem to have given an evolutionary benefit, especially to
Some hemoglobinopathies seem to have given an evolutionary benefit, especially to heterozygotes
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
, in areas where malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
is endemic. Malaria parasites infect red blood cells, but subtly disturb normal cellular function and subvert the immune response. A number of mechanisms have been proposed to explain the increased chance of survival for the carrier of an abnormal hemoglobin trait.
References
{{Diseases of RBCs Hereditary hemolytic anemias Disorders of globin and globulin proteins Blood disorders