Gurjaratra on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
find spot
Provenance () is the chronology of the ownership, custody or location of a historical object. The term was originally mostly used in relation to works of art, but is now used in similar senses in a wide range of fields, including archaeology, p ...
s of inscriptions (blue). The neighbouring places are shown as triangles (gray)." width="200" height="194" zoom="5" longitude="74.080811" latitude="26.303264">
Gurjaradesa, (, or Gurjaratra)*
* is a historical region in India comprising the southern

 ''Gurjaradēśa'', or Gurjara country, is first attested in Bana's ''
''Gurjaradēśa'', or Gurjara country, is first attested in Bana's ''
Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of ...
and northern Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
during the period of 6th–12th century CE. The predominant power of the region, the Gurjara-Pratihara
The Pratihara dynasty, also called the Gurjara-Pratiharas, the Pratiharas of Kannauj or the Imperial Pratiharas, was a prominent medieval Indian dynasty which ruled over the Kingdom of Kannauj. It initially ruled the Gurjaradesa until its vi ...
s eventually controlled a major part of North India centered at Kannauj
Kannauj (Hindustani language, Hindustani pronunciation: ) is an ancient city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar palika, Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Ut ...
. The modern state of "Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
" derives its name from the ancient Gurjaratra.
Early references to Gurjara country

 ''Gurjaradēśa'', or Gurjara country, is first attested in Bana's ''
''Gurjaradēśa'', or Gurjara country, is first attested in Bana's ''Harshacharita
The ''Harshacharita'' (, ; English: ''The deeds of Harsha'') is the biography of Indian emperor Harsha by Banabhatta, also known as Bana, who was a Sanskrit writer of seventh-century CE India. He was the ''Asthana Kavi'', meaning ''Court Poet ...
'' (7th century CE). Its king is said to have been subdued by Harsha
Harshavardhana (Sanskrit: हर्षवर्धन; 4 June 590 – 647) was an emperor of Kannauj from April 606 until his death in 647. He was the king of Thanesar who had defeated the Alchon Huns, and the younger brother of Rajyava ...
's father Prabhakaravardhana
Prabhakaravardhana (also known as Prabhakara Vardhana) was a king of Thanesar in northern India around the time of the decline of the Gupta Empire. According to the historian R. C. Majumdar, he was the first notable king of the Vardhana dynasty ...
(died c. 605 CE). The bracketing of the country with Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
a (Sindh), Lāta (southern Gujarat) and Malava
Malwa () is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also sy ...
(western Malwa) indicates that the region including the northern Gujarat and Rajasthan is meant.
Hieun Tsang, the Chinese Buddhist pilgrim who visited India between 631–645 CE during Harsha's reign, mentioned the Gurjara country (''Kiu-che-lo'') with its capital at Bhinmal
Bhinmal (previously Shrimal Nagar) is an ancient town in the Jalore District of Rajasthan, India. It is south of Jalore. Bhinmal was the early capital of Gurjaradesa, comprising modern-day southern Rajasthan and northern Gujarat. The town was ...
(''Pi-lo-mo-lo'') as the second largest kingdom of Western India. He distinguished it from the neighbouring kingdoms of Bharukaccha
Bharuch () is a city at the mouth of the river Narmada in Gujarat in western India. Bharuch is the administrative headquarters of Bharuch District.
The city of Bharuch and surroundings have been settled since times of antiquity. It was a ship ...
(Bharuch), Ujjayini (Ujjain), Malava
Malwa () is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also sy ...
(Malwa), Valabhi and Surashtra. The Gurjara kingdom was said to have measured 833 miles in circuit and its ruler was a 20-year old kshatriya
Kshatriya () (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority"; also called Rajanya) is one of the four varnas (social orders) of Hindu society and is associated with the warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the con ...
, who was distinguished for his wisdom and courage. It is known that, in 628 CE, the kingdom at Bhinmal was ruled by a Chapa dynasty ruler ''Vyāgrahamukha'', under whose reign the mathematician-astronomer Brahmagupta
Brahmagupta ( – ) was an Indian Indian mathematics, mathematician and Indian astronomy, astronomer. He is the author of two early works on mathematics and astronomy: the ''Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta'' (BSS, "correctly established Siddhanta, do ...
wrote his famous treatise. It is believed that the young ruler mentioned by Hieun Tsang must have been his immediate successor.
It appears that the Gurjara country at that time comprised modern Rajasthan. Following the death of Harsha
Harshavardhana (Sanskrit: हर्षवर्धन; 4 June 590 – 647) was an emperor of Kannauj from April 606 until his death in 647. He was the king of Thanesar who had defeated the Alchon Huns, and the younger brother of Rajyava ...
, his empire split up into small kingdoms. Gurjaradesa is believed to have become independent.
The Arab chroniclers of Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
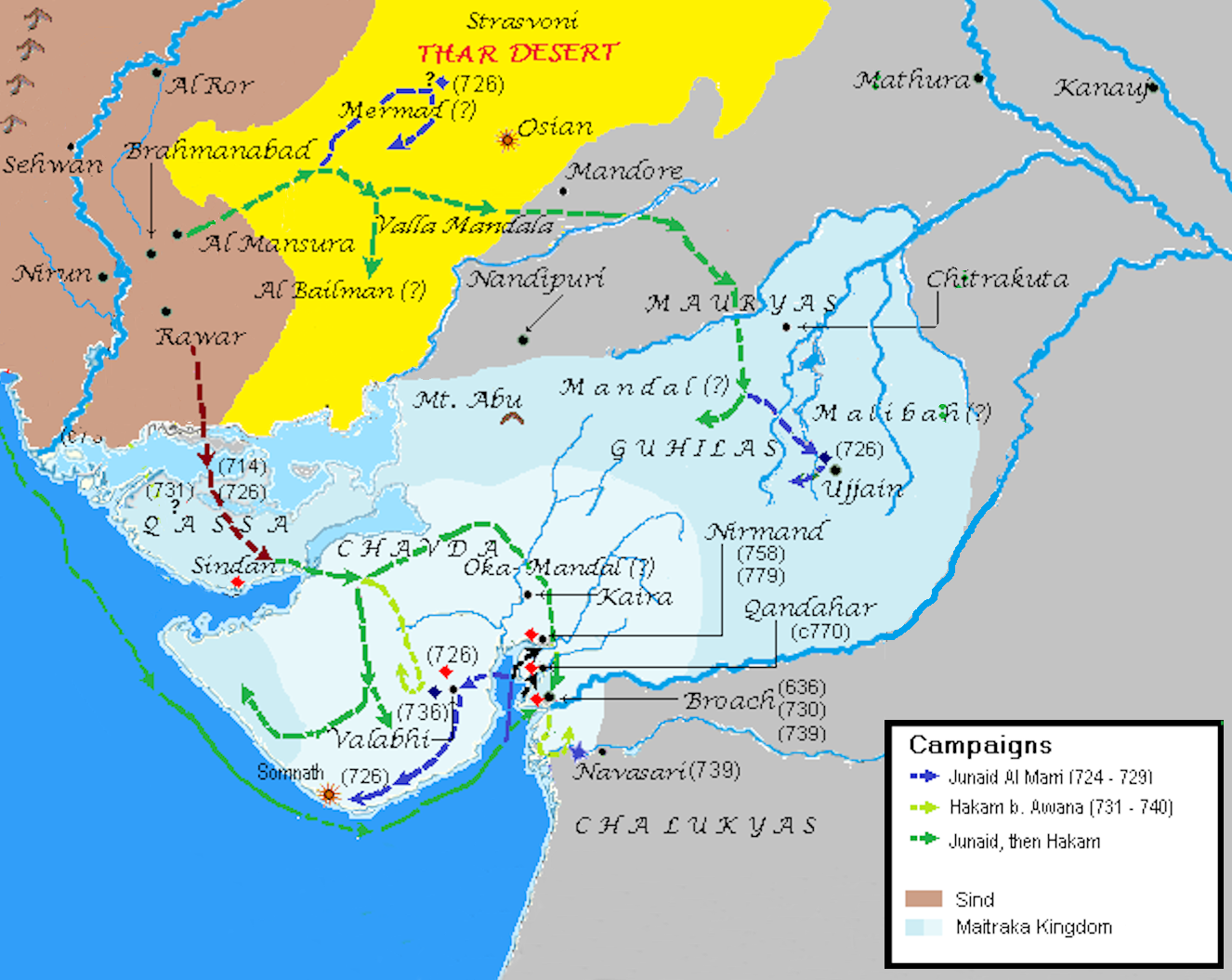
(an Arab province from 712 CE onward), narrated the campaigns of Arab governors on ''Jurz'', the Arabic term for Gurjara. They mentioned it jointly with ''Mermad'' (Marumāda, in Western Rajasthan) and ''Al Baylaman'' (Bhinmal). The country was first conquered by Mohammad bin Qasim (712-715) and, for a second time, by Junayd (723-726). Upon bin Qasim's victory, Al-Baladhuri
ʾAḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Jābir al-Balādhurī () was a 9th-century West Asian historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and enjoyed great influence at the court of the caliph al ...
mentioned that the Indian rulers, including that of Bhinmal, accepted Islam and paid tribute. They presumably recanted after bin Qasim's departure, which made Junayd's attack necessary. After Junayd's reconquest, the kingdom at Bhinmal appears to have been annexed by the Arabs.
Successor Gurjara kingdoms
A Gurjara kingdom was founded by Harichandra Rohilladhi atMandore
Mandore is a suburb and historical town located 9 km north of Jodhpur city in the Jodhpur district of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan.
History
Mandore is an ancient town, and was the seat of the Gurjar Pratiharas of Mandavy ...
(''Mandavyapura'') in about 600 CE. This is expected to have been a small kingdom. His descendant, Nagabhata, shifted the capital to Merta (Medāntakapura) in about 680 CE. Eventually, this dynasty adopted the designation of "Gurjara Pratihara" in line with the Gurjara Pratiharas, to whom it became feudatory. They are often referred to as Mandore Pratiharas by historians.
The Bharuch line of Gurjaras (Gurjaras of Lata
The Gurjaras of Lata, also known as Gurjaras of Nandipuri or Bharuch Gurjaras, was a Gurjara dynasty which ruled Lata region (now South Gujarat, India) as a feudatory of different dynasties from c. 580 CE to c. 738 CE.
Sources of Informati ...
) was founded by Dadda I, who is identified with Harichandra's youngest son of the same name by many historians. These Gurjaras were always recognized as vassals (''sāmanthas'') though their allegiance might have varied over time. They are believed to have wrested a fair portion of the Lata province of the Chaulukyas and their kingdom also came to be regarded as part of Gurjaradesa.
A final line of Gurjaras was founded by Nagabhata I
Nagabhata I (r. c. 730 – 760 CE) was the founder of the imperial Pratihara dynasty in northern India. He ruled the Avanti (or Malava) region in present-day Madhya Pradesh, from his capital at Ujjain. He may have extended his control over ...
at Jalore
Jalore () (ISO 15919 : ''Jālora'' ), also known as Granite City, is a city in the western Indian state of Rajasthan. It is the administrative headquarters of Jalore District.
It has a river known as Jawai Nadi. Jalore lies to south of Sukri ...
, in the vicinity of Bhinmal, in about 730 CE, soon after Junayd's end of term in Sindh. Nagabhata is said to have defeated the "invincible Gurjaras," presumably those of Bhinmal. Another account credits him for having defeated a "Muslim ruler." Nagabhata is also known to have repelled the Arabs during a later raid. His dynasty later expanded to Ujjain
Ujjain (, , old name Avantika, ) or Ujjayinī is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative as well as religious centre of Ujjain ...
and called itself Pratihara. The rival kingdoms of Pratiharas, the Rashtrakuta
The Rashtrakuta Empire was a royal Indian polity ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the 6th and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their rule from Manapu ...
s and Palas
A ''palas'' () is a German term for the imposing or prestigious building of a medieval '' Pfalz'' or castle that contained the great hall. Such buildings appeared during the Romanesque period (11th to 13th century) and, according to Thompson ...
, however continued to call them Gurjaras or kings of Gurjaras (''Gurjaresa''). The Pratiharas
The Pratihara dynasty, also called the Gurjara-Pratiharas, the Pratiharas of Kannauj or the Imperial Pratiharas, was a prominent medieval Indian dynasty which ruled over the Kingdom of Kannauj. It initially ruled the Gurjaradesa until its vict ...
became the dominant force of the entire Rajasthan and Gujarat regions, establishing a powerful empire centered at Kannauj
Kannauj (Hindustani language, Hindustani pronunciation: ) is an ancient city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar palika, Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Ut ...
, the former capital of Harshavardhana
Harshavardhana (Sanskrit: हर्षवर्धन; 4 June 590 – 647) was an emperor of Kannauj from April 606 until his death in 647. He was the king of Thanesar who had defeated the Alchon Huns, and the younger brother of Rajya ...
.
Later references
Udyotana Suri's '' Kuvalayamala'' composed inJalore
Jalore () (ISO 15919 : ''Jālora'' ), also known as Granite City, is a city in the western Indian state of Rajasthan. It is the administrative headquarters of Jalore District.
It has a river known as Jawai Nadi. Jalore lies to south of Sukri ...
in 778 CE describes in detail the Gurjara country as a beautiful country, whose residents are also referred to as Gurjaras. They were differentiated from the ''Saindhavas'' (people of Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
), ''Latas'' (in southern Gujarat), ''Malavas'' (people of Malwa
Malwa () is a historical region, historical list of regions in India, region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic plateau, volcanic upland north of the ...
) and ''Meravas''. They were mentioned to be devotees of dharma
Dharma (; , ) is a key concept in various Indian religions. The term ''dharma'' does not have a single, clear Untranslatability, translation and conveys a multifaceted idea. Etymologically, it comes from the Sanskrit ''dhr-'', meaning ''to hold ...
and clever in matters of peace as well as war.
The term ''Gurjaratra'' is first mentioned in the Ghatiyala inscription of Kakkuka (Mandore Pratihara) in 861 CE. Kakkuka is said to have won the love of the people of Gurjaratra along with those Marumada, Valla and Travani. Later records suggest that this Gurjaratra mandala was in the region of Didwana in the old Jodhpur State
Kingdom of Marwar, also known as Jodhpur State during the modern era, was a kingdom in the Marwar region from 1243 to 1818 and a princely state under British rule from 1818 to 1947. It was established in Pali by ''Rao Siha'', possibly a migran ...
.
In later times, the term Gurjaratra is used to connote the present day Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
. Jinadatta Suri (1075-1154 CE) mentions a country of ''Gujaratta'' with its capital at Anahilapataka ( Patan) in northern Gujarat. The Chaulukya
The Chaulukya dynasty (), also Solanki dynasty, was a dynasty that ruled parts of what are now Gujarat and Rajasthan in north-western India, between and . Their capital was located at Anahilavada (modern Patan). At times, their rule extended ...
s ( Solankis) are also referred to as Gurjaras in inscriptions and their country as ''Gurjaradesa''.
Culture and science
Bhinmal
Bhinmal (previously Shrimal Nagar) is an ancient town in the Jalore District of Rajasthan, India. It is south of Jalore. Bhinmal was the early capital of Gurjaradesa, comprising modern-day southern Rajasthan and northern Gujarat. The town was ...
was a great centre of learning. According to ''Kanhadade Prabandha
''Kānhaḍade Prabandha'' is a book by Indian poet Padmanābha written in 1455, in a western Apabhramsha dialect. The book tells the story of Raval Kanhadade ( Kanhadadeva), the Chahamana ruler of Jalore.
Textual history
Padmanabha wro ...
'', it had 45,000 Brahmins
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...
who never tired of studying the ancient sacred books.
Brahmagupta
Brahmagupta ( – ) was an Indian Indian mathematics, mathematician and Indian astronomy, astronomer. He is the author of two early works on mathematics and astronomy: the ''Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta'' (BSS, "correctly established Siddhanta, do ...
, the well-known mathematicians astronomer, was born in 598 CE in Bhinmal. He is likely to have lived most of his life in the town, during the empire of Harsha
Harshavardhana (Sanskrit: हर्षवर्धन; 4 June 590 – 647) was an emperor of Kannauj from April 606 until his death in 647. He was the king of Thanesar who had defeated the Alchon Huns, and the younger brother of Rajyava ...
. He wrote two texts on mathematics and astronomy: The Brahma Sphuta Siddhanta in 628, and the Khandakhadyaka in 665. He made seminal contributions to mathematics, including the first mathematical treatment of zero
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. Adding (or subtracting) 0 to any number leaves that number unchanged; in mathematical terminology, 0 is the additive identity of the integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and compl ...
, rules for manipulating positive and negative numbers, as well as algorithms for algebraic operations on decimal numbers. His work on astronomy and mathematics was transmitted to the court of the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 C ...
Caliph Al-Mansur
Abū Jaʿfar ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad al-Manṣūr (; ; 714 – 6 October 775) usually known simply as by his laqab al-Manṣūr () was the second Abbasid caliph, reigning from 754 to 775 succeeding his brother al-Saffah (). He is known ...
(r. 754-775 CE), who had the Indian astronomical texts translated into Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
. Through these texts, the decimal number system spread through the Arab world and later Europe.
The Sanskrit poet Magha, the author of '' Sisupalavadha,'' lived here in 680 CE.
The Jain scholar Siddharshi Gani, a resident of Bhinmal wrote
''Upmitibahava prapancha katha'' in 905 CE. The '' Jain Ramayana'' was written by Jain monk Vijayagani in 1595 CE. Jain acharya Udyotana Suri wrote '' Kuvalayamala'' here.
See also
*Rajasthani people
Rajasthani people or Rajasthanis are a group of Indo-Aryan peoples native to Rajasthan ("the land of kings"), a states of India, state in Northern India. Their language, Rajasthani language, Rajasthani, is a part of the western group of Indo-Ar ...
* Architecture of Rajasthan
The architecture of the Indian state of Rajasthan has usually been a regional variant of the style of Indian architecture prevailing in north India at the time. Rajasthan is especially notable for the forts and palaces of the many Rajput ruler ...
* Brahmagupta
Brahmagupta ( – ) was an Indian Indian mathematics, mathematician and Indian astronomy, astronomer. He is the author of two early works on mathematics and astronomy: the ''Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta'' (BSS, "correctly established Siddhanta, do ...
* Hindu-Arabic numerals
* Mandore
Mandore is a suburb and historical town located 9 km north of Jodhpur city in the Jodhpur district of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan.
History
Mandore is an ancient town, and was the seat of the Gurjar Pratiharas of Mandavy ...
References
; Sources * * * * ** * * * * * {{cite book , title=The Glory That was Gurjardesha, Part 3 , last=Munshi , first=K.M., publisher=Bhartiya Vidya Bhavan , year=1944 , location=Bombay Historical Indian regions Geography of Rajasthan Geography of Gujarat History of Gujarat