Groombridge Transit Circle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
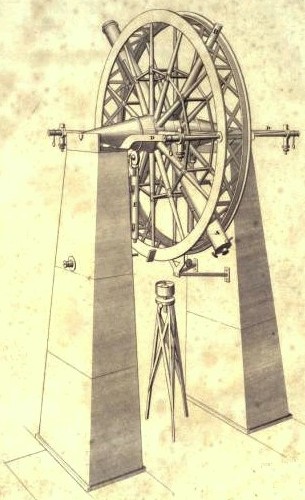 Groombridge Transit Circle was a meridian transit circle made by
Groombridge Transit Circle was a meridian transit circle made by Groombridge Transit Circle, 1820. -- Science and Society Picture Library
/ref> The advantage of a transit circle over a mural circle (which can measure polar distances) is that it allows measuring right ascension and declination at the same time. It had an aperture of 3.5 inches and a 5-foot focal length, mounted inside two 4 foot circles on stone piers. Groombridge used the instrument to determine the positions of over 4000 circumpolar stars. It was eventually bought by
 Groombridge Transit Circle was a meridian transit circle made by
Groombridge Transit Circle was a meridian transit circle made by Edward Troughton
Edward Troughton (October 1753 – 12 June 1835) was a British instrument maker who was notable for making telescopes and other astronomical instruments.
Life
Troughton was born at Corney, Cumberland, the youngest of six children to Francis ...
for the English astronomer Stephen Groombridge
Stephen Groombridge FRS (7 January 1755 – 30 March 1832) was a British merchant and astronomer.
Life
He was born at Goudhurst in Kent on 7 January 1755. He succeeded when about 21 to the business in West Smithfield of a linen draper named ...
in 1806, which Groombridge used to compile data for the star catalogue
A star catalogue is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the year ...
, ''Catalogue of Circumpolar Stars''./ref> The advantage of a transit circle over a mural circle (which can measure polar distances) is that it allows measuring right ascension and declination at the same time. It had an aperture of 3.5 inches and a 5-foot focal length, mounted inside two 4 foot circles on stone piers. Groombridge used the instrument to determine the positions of over 4000 circumpolar stars. It was eventually bought by
James South
Sir James South (October 1785 – 19 October 1867) was a British astronomer.
He was a joint founder of the Astronomical Society of London, and it was under his name, as President of the Society in 1831, that a petition was successfully subm ...
, and it remained at his observatory at Kensington until 1870.
See also
* Groombridge 1830References
Further reading
*{{cite book, author=Royal Institution of Great Britain, title=The Quarterly Journal, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kgIXAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA189, volume=16, year=1823, publisher=John Murray, page=189 Astronomical instruments