Greco-Bactrian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a
 Diodotus, the
Diodotus, the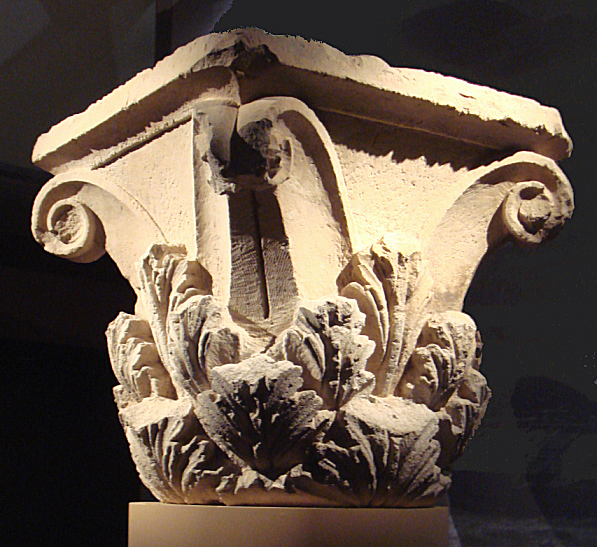  In 247 BC, the Ptolemaic empire (the Greek rulers of Egypt following the death of
In 247 BC, the Ptolemaic empire (the Greek rulers of Egypt following the death of
 Euthydemus, an Ionian Greek from Magnesia according to
Euthydemus, an Ionian Greek from Magnesia according to
Greek Culture in Afghanistan and India: Old Evidence and New Discoveries
p.206 a Greek by the name of Heliodotus, dedicating a fire altar to

 A nomadic steppe people called the
A nomadic steppe people called the  Around 140 BC, eastern
Around 140 BC, eastern  This invasion of Bactria is also described in western Classical sources from the 1st century BC:
This invasion of Bactria is also described in western Classical sources from the 1st century BC:
 Overall, the
Overall, the
 One of the inscriptions in Greek found at Ai-Khanoum, the Herôon of Kineas, has been dated to 300–250 BC, and describes Delphic maxims:
One of the inscriptions in Greek found at Ai-Khanoum, the Herôon of Kineas, has been dated to 300–250 BC, and describes Delphic maxims:
File:HeraklesStatuette.jpg, Bronze
File:Ionic pillar, cella of the Temple of the Oxus, Takht-i Sangin, late 4th - early 3rd century BCE.jpg, Ionic pillar, cella of the Temple of the Oxus, Takht-i Sangin, late 4th – early 3rd century BCE.
File:Head of a Greco-Bactrian ruler, Temple of the Oxus, Takht-i-Sangin, 3rd-2nd century BCE.jpg, Head of a Greco-Bactrian ruler with diadem, Temple of the Oxus, Takht-i Sangin, 3rd–2nd century BCE. This could also be a portrait of Seleucus I.
File:Altar to God Oxus, with Marsias playing the aolos, Temple of the Oxus, Takht-i Sangin, dated 2nd century BCE.jpg, Hellenistic silenus
 Such portraits show high levels of detail with some kings seen smiling, while others are shown aging throughout their reign, even depicting old age on their coins. Such realistic imagery on coins seems to have been very important to the Greco-Bactrian kings, who wanted to display their individuality or to distinguish themselves from the style of other contemporary Hellenistic kingdoms.
Greco-Bactrian coins also depict the kings wearing distinct headgear, such as helmets modelled on the Boeotian cavalry helmet of
Such portraits show high levels of detail with some kings seen smiling, while others are shown aging throughout their reign, even depicting old age on their coins. Such realistic imagery on coins seems to have been very important to the Greco-Bactrian kings, who wanted to display their individuality or to distinguish themselves from the style of other contemporary Hellenistic kingdoms.
Greco-Bactrian coins also depict the kings wearing distinct headgear, such as helmets modelled on the Boeotian cavalry helmet of
 Several statuettes and representations of Greek soldiers have been found north of the
Several statuettes and representations of Greek soldiers have been found north of the  The purpose of Zhang Qian's journey was to look for civilizations on the steppe that the Han could ally with against the Xiongnu. Upon his return, Zhang Qian informed the Chinese emperor Han Wudi of the level of sophistication of the urban civilizations of Ferghana, Bactria and Parthia, who became interested in developing commercial relationships with them:
The purpose of Zhang Qian's journey was to look for civilizations on the steppe that the Han could ally with against the Xiongnu. Upon his return, Zhang Qian informed the Chinese emperor Han Wudi of the level of sophistication of the urban civilizations of Ferghana, Bactria and Parthia, who became interested in developing commercial relationships with them:
 Chandragupta's grandson
Chandragupta's grandson
 The Greco-Bactrian city of
The Greco-Bactrian city of
 One of the last Greco-Bactrian kings, Agathocles of Bactria (ruled 190–180 BC), issued remarkable Indian-standard square coins bearing the first known representations of Indian deities, which have been variously interpreted as
One of the last Greco-Bactrian kings, Agathocles of Bactria (ruled 190–180 BC), issued remarkable Indian-standard square coins bearing the first known representations of Indian deities, which have been variously interpreted as
/ref>Peter Thonemann, (2016), ''The Hellenistic World: Using coins as sources'', Cambridge University Press, p. 10
/ref> These coins seem to be the first known representations of Rigvedic deities, Vedic deities on coins, and they display early
 Overall, the Greco-Bactrians and their successors the Indo-Greeks, created a significant and influential civilisation in the region. During their 250-year-long rule, and with their highly developed Hellenistic tradition, they firmly established the Greek language and religious ideas in both Central Asia and northwestern India. The Greek language and writing was so prominent in Bactria in particular, that the invading tribes who settled in the region adopted the
Overall, the Greco-Bactrians and their successors the Indo-Greeks, created a significant and influential civilisation in the region. During their 250-year-long rule, and with their highly developed Hellenistic tradition, they firmly established the Greek language and religious ideas in both Central Asia and northwestern India. The Greek language and writing was so prominent in Bactria in particular, that the invading tribes who settled in the region adopted the
/ref> The Greco-Bactrians and especially the Indo-Greeks were highly influential in the creation of syncretic artistic movements in India. The most important example being the
Greco-Bactrian and Indo-Greek Kingdoms in Ancient Texts
Some new hypotheses on the Greco-Bactrian and Indo-Greek kingdoms
by Antoine Simonin
{{Hellenistic rulers 125 BC 250s BC establishments 256 BC Former countries in Central Asia Former countries in South Asia Former kingdoms Former monarchies of Central Asia Former monarchies of South Asia Hellenistic states Lists of monarchs States and territories disestablished in the 2nd century BC States and territories established in the 3rd century BC
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
state of the Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
located in Central-South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid satrap Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, and continued to dominate Central Asia until its fall around 120 BC. At its peak the kingdom consisted of present-day Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
, Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
, and for a short time, small parts of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. An extension further east, with military campaigns and settlements, may have reached the borders of the Qin State in China by about 230 BC.
Although a Greek population was already present in Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
by the 5th century BC, Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
conquered the region by 327 BC and founded many cities, most of them named Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
, and further settled with Macedonians and other Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
. After the death of Alexander, control of Bactria passed on to his general Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ, ''Séleukos Nikátōr'', "Seleucus the Victorious"; ) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to fo ...
. The fertility and the prosperity of the land by the early 3rd century BC led to the creation of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom by Diodotus as a successor state of the Seleucid empire. The Bactrian Greeks grew increasingly more powerful and invaded north-western India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
between 190 and 180 BC under king Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinization of names, Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male name, male Greek given names, given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, ...
, the son of Euthydemus. This invasion led to the creation of the Indo-Greek kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
, as a successor state of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom, and was subsequently ruled by kings Pantaleon and Apollodotus I. Historical records indicate that many rich and prosperous cities were present in the kingdom, but only a few such cities have been excavated, such as Ai-Khanoum
Ai-Khanoum (, meaning 'Lady Moon'; ) is the archaeological site of a Hellenistic city in Takhar Province, Afghanistan. The city, whose original name is unknown, was likely founded by an early ruler of the Seleucid Empire and served as a mili ...
and Bactra. The city of Ai-Khanoum, in north-eastern Afghanistan, had all the hallmarks of a true Hellenistic city with a Greek theater, gymnasium and some houses with colonnaded courtyards.
The kingdom reached its peak under Eucratides the Great, who seems to have seized power through a coup around 171 BC and created his own dynasty. Eucratides also invaded India and successfully fought against the Indo-Greek kings. However, soon the kingdom began to decline. The Parthians and nomadic tribes such as Saka
The Saka, Old Chinese, old , Pinyin, mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit (Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples, Eastern Iranian peoples who lived in the Eurasian ...
s and Yuezhi
The Yuezhi were an ancient people first described in China, Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defea ...
became a major threat. Eucratides was killed by his own son in about 145 BC, which may have further destabilised the kingdom. Heliocles was the last Greek king to rule in Bactria.
Even after the fall of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom, their rich Hellenistic influence remained strong for many more centuries. The Yuezhi invaders settled in Bactria and became Hellenized. They subsequently founded the Kushan empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
around 30 AD, and adopted the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as wel ...
to write their language and added Greek deities to their pantheon. The Greco-Bactrian city of Ai-Khanoum was at the doorstep of India and known for its high level of Hellenistic sophistication. Greek art travelled from Bactria with the Indo-Greeks and influenced Indian art, religion and culture, leading to new syncretic
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thus ...
art called Greco-Buddhist art
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara, located in the northwestern fringe of t ...
.
History
Origins
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
was inhabited by Greek settlers since the time of Darius I
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West A ...
, when the majority of the population of Barca, in Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika (, , after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between the 16th and 25th meridians east, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, als ...
, was deported to the region for refusing to surrender assassins. Greek influence increased under Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was a List of monarchs of Persia, Persian ruler who served as the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC. He was ...
, after the descendants of Greek priests who had once lived near Didyma
Didyma (; ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek sanctuary on the coast of Ionia in the domain of the famous city of Miletus. Apollo was the main deity of the sanctuary of Didyma, also called ''Didymaion''. But it was home to both of the Ancient ...
(western Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
) were forcibly relocated in Bactria, and later on with other exiled Greeks, most of them prisoners of war. Greek communities and language were already common in the area by the time that Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
conquered Bactria in 328 BC.
Independence and Diodotid dynasty
 Diodotus, the
Diodotus, the satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median kingdom, Median and Achaemenid Empire, Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empi ...
of Bactria (and probably the surrounding provinces) founded the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom when he seceded from the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
around 250 BC and became Basileus
''Basileus'' () is a Greek term and title that has signified various types of monarchs throughout history. In the English language, English-speaking world, it is perhaps most widely understood to mean , referring to either a or an . The title ...
, or king Diodotus I
Diodotus I Soter (Greek language, Greek: , ''Diódotos Sōtḗr''; c. 300 BC – c. 235 BC) was the first Hellenistic period, Hellenistic king of Bactria. Diodotus was initially satrap of Bactria, but became independent of the Seleucid Empire, Se ...
of Bactria. The preserved ancient sources (see below) are somewhat contradictory, and the exact date of Bactrian independence has not been settled. Somewhat simplified, there is a high chronology ( BC) and a low chronology (c. 246 BC) for Diodotus' secession. The high chronology has the advantage of explaining why the Seleucid king Antiochus II issued very few coins in Bactria, as Diodotus would have become independent there early in Antiochus' reign. On the other hand, the low chronology, from the mid-240s BC, has the advantage of connecting the secession of Diodotus I with the Third Syrian War, a catastrophic conflict for the Seleucid Empire.
The new kingdom, highly urbanized and considered one of the richest of the Orient (''opulentissimum illud mille urbium Bactrianum imperium'' "The extremely prosperous Bactrian empire of the thousand cities", according to the historian Justin
Justin may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Justin (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Justin (historian), Latin historian who lived under the Roman Empire
* Justin I (c. 450–527) ...
), was to further grow in power and engage in territorial expansion to the east and the west:
 In 247 BC, the Ptolemaic empire (the Greek rulers of Egypt following the death of
In 247 BC, the Ptolemaic empire (the Greek rulers of Egypt following the death of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
) captured the Seleucid capital, Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
. In the resulting power vacuum, Andragoras, the Seleucid satrap of Parthia, proclaimed independence from the Seleucids, declaring himself king. A decade later, he was defeated and killed by Arsaces Arsaces or Arsakes (, , Graecized form of Old Persian ) is the eponymous Greek form of the dynastic name of the Parthian Empire of Iran adopted by all epigraphically attested rulers of the Parthian Empire, Arsacid dynasties. The indigenous Parthian ...
of Parthia, leading to the rise of a Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power centered in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe ...
. This cut Bactria off from contact with the Greek world. Overland trade continued at a reduced rate, while sea trade between Greek Egypt and Bactria developed.
Diodotus was succeeded by his son Diodotus II, who allied himself with the Parthian Arsaces Arsaces or Arsakes (, , Graecized form of Old Persian ) is the eponymous Greek form of the dynastic name of the Parthian Empire of Iran adopted by all epigraphically attested rulers of the Parthian Empire, Arsacid dynasties. The indigenous Parthian ...
in his fight against Seleucus II:
Euthydemid dynasty and Seleucid invasion
 Euthydemus, an Ionian Greek from Magnesia according to
Euthydemus, an Ionian Greek from Magnesia according to Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 ...
, and possibly satrap of Sogdiana, overthrew the dynasty of Diodotus II around 230–220 BC and started his own dynasty. Euthydemus's control extended to Sogdiana, going beyond the city of Alexandria Eschate founded by Alexander the Great in Ferghana:
And they also held Sogdiana, situated above Bactriana towards the east between the Oxus River, which forms the boundary between the Bactrians and the Sogdians, and the Iaxartes River. And the Iaxartes forms also the boundary between the Sogdians and the nomads.Euthydemus was attacked by the Seleucid ruler
Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; , ; 3 July 187 BC) was the sixth ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 223 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of West Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to th ...
around 210 BC. Although he commanded 10,000 horsemen, Euthydemus initially lost a battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force co ...
on the Arius
Arius (; ; 250 or 256 – 336) was a Cyrenaica, Cyrenaic presbyter and asceticism, ascetic. He has been regarded as the founder of Arianism, which holds that Jesus Christ was not Eternity, coeternal with God the Father, but was rather created b ...
and had to retreat. He then successfully resisted a three-year siege in the fortified city of Bactra, before Antiochus finally decided to recognize the new ruler, and to offer one of his daughters to Euthydemus's son Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinization of names, Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male name, male Greek given names, given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, ...
around 206 BC. Classical accounts also relate that Euthydemus negotiated peace with Antiochus III by suggesting that he deserved credit for overthrowing the original rebel Diodotus and that he was protecting Central Asia from nomadic invasions thanks to his defensive efforts:
In an inscription found in the Kuliab area of Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
, in eastern Greco-Bactria, and dated to 200–195 BC,Shane WallacGreek Culture in Afghanistan and India: Old Evidence and New Discoveries
p.206 a Greek by the name of Heliodotus, dedicating a fire altar to
Hestia
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Hestia (; ) is the virgin goddess of the hearth and the home. In myth, she is the firstborn child of the Titans Cronus and Rhea, and one of the Twelve Olympians.
In Greek mythology, newborn Hestia, alo ...
, mentions Euthydemus as the greatest of all kings, and his son Demetrius I as "Demetrios Kallinikos", meaning "Demetrius the Glorious Conqueror":
Following the departure of the Seleucid army, the Bactrian kingdom seems to have expanded. In the west, areas in north-eastern''tónde soi bōmòn thuṓdē, présba kydístē theôn Hestía, Diòs kat' álsos kallídendron éktisen kaì klytaîs ḗskēse loibaîs empýrois Hēliódotos óphra tòm pántōn mégiston Euthýdēmon basiléōn toû te paîda kallínikon ekprepê Dēmḗtrion preumenḕs sṓizēis ekēdeî(s) sỳn Týchai theόphron(i).'' "Heliodotus dedicated this fragrant altar for Hestia In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Hestia (; ) is the virgin goddess of the hearth and the home. In myth, she is the firstborn child of the Titans Cronus and Rhea, and one of the Twelve Olympians. In Greek mythology, newborn Hestia, alo ..., venerable goddess, illustrious amongst all, in the grove ofZeus Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus. Zeus is the child ..., with beautiful trees; he made libations and sacrifices so that the greatest of all kings Euthydemus, as well as his son, the glorious, victorious and remarkableDemetrius Demetrius is the Latinization of names, Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male name, male Greek given names, given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning "devoted to goddess Demeter". Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, ..., be preserved of all pains, with the help of Tyche with divine thoughts."
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
may have been absorbed, possibly as far as into Parthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemeni ...
, whose ruler had been defeated by Antiochus the Great. These territories possibly are identical with the Bactrian satrapies of Tapuria and Traxiane.
Expansion into the Indian subcontinent (around 180 BC)
Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinization of names, Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male name, male Greek given names, given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, ...
, the son of Euthydemus, started an invasion of the subcontinent before 180 BC, and a few years after the Mauryan empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
had been overthrown by the Shunga dynasty
The Shunga Empire (IAST: ') was a ruling entity centred around Magadha and controlled most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 187 to 75 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of Magadha from the ...
. Historians differ on the motivations behind the invasion. Some historians suggest that the invasion of the subcontinent was intended to show their support for the Mauryan empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
, and to protect the Buddhist faith from the religious persecutions of the Shungas as alleged by Buddhist scriptures (Tarn). Other historians have argued however that the accounts of these persecutions have been exaggerated ( Thapar, Lamotte).
Demetrius may have been as far as the imperial capital Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
in today's eastern India (today Patna
Patna (; , ISO 15919, ISO: ''Paṭanā''), historically known as Pataliputra, Pāṭaliputra, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, ...
). However, these campaigns are typically attributed to Menander
Menander (; ; c. 342/341 – c. 290 BC) was a Greek scriptwriter and the best-known representative of Athenian Ancient Greek comedy, New Comedy. He wrote 108 comedies and took the prize at the Lenaia festival eight times. His record at the Cit ...
. His conquests were mentioned along with that of Menander by the historian Strabo, as having "subdued more tribes than Alexander." The invasion was completed by 175 BC. This established in the northwestern Indian Subcontinent what is called the Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
, which lasted for almost two centuries until around 10 AD. The Buddhist faith flourished under the Indo-Greek kings, especially Menander who was arguably the most powerful of them all. It was also a period of great cultural syncretism, exemplified by the development of Greco-Buddhism
Greco-Buddhism or Graeco-Buddhism was a cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism developed between the 4th century BC and the 5th century AD in Gandhara, which was in present-day Pakistan and parts of north-east Afghanis ...
in the region of Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
.
Eucratides the Great
Back in Bactria, Eucratides I, either a general of Demetrius or an ally of the Seleucids, managed to overthrow the Euthydemid dynasty and establish his own rule, the short-lived Eucratid dynasty, around 170 BC, probably dethroning Antimachus I and Antimachus II. The Indian branch of the Euthydemids tried to strike back. An Indian king called Demetrius (very likely Demetrius II) is said to have returned to Bactria with 60,000 men to oust the usurper, but he apparently was defeated and killed in the encounter:
Eucratides led many wars with great courage, and, while weakened by them, was put under siege by Demetrius, king of the Indians. He made numerous sorties, and managed to vanquish 60,000 enemies with 300 soldiers, and thus liberated after four months, he put India under his rule.Eucratides campaigned extensively in present-day northwestern India, and ruled a vast territory, as indicated by his minting of coins in many Indian mints, possibly as far as the Jhelum River in
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
. In the end, however, he was repulsed by the Indo-Greek king Menander I, who managed to create a huge unified territory.
In a rather confused account, Justin
Justin may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Justin (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Justin (historian), Latin historian who lived under the Roman Empire
* Justin I (c. 450–527) ...
explains that Eucratides was killed on the field by "his son and joint king", who would be his own son, either Eucratides II or Heliocles I (although there are speculations that it could have been his enemy's son Demetrius II). The son drove over Eucratides' bloodied body with his chariot and left him dismembered without a sepulcher:
As Eucratides returned from India, he was killed on the way back by his son, whom he had associated to his rule, and who, without hiding his parricide, as if he didn't kill a father but an enemy, ran with his chariot over the blood of his father, and ordered the corpse to be left without a sepulture.
Defeats by Parthia
During or after his Indian campaigns, Eucratides was attacked and defeated by theParthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemeni ...
n king Mithridates I, possibly in alliance with partisans of the Euthydemids:
The Bactrians, involved in various wars, lost not only their rule but also their freedom, as, exhausted by their wars against the Sogdians, the Arachotes, the Dranges, the Arians and the Indians, they were finally crushed, as if drawn of all their blood, by an enemy weaker than them, the Parthians.Following his victory, Mithridates I gained Bactria's territory west of the
Arius
Arius (; ; 250 or 256 – 336) was a Cyrenaica, Cyrenaic presbyter and asceticism, ascetic. He has been regarded as the founder of Arianism, which holds that Jesus Christ was not Eternity, coeternal with God the Father, but was rather created b ...
, the regions of Tapuria and Traxiane: "The satrapy Turiva and that of Aspionus were taken away from Eucratides by the Parthians."
In the year 141 BC, the Greco-Bactrians seem to have entered in an alliance with the Seleucid king Demetrius II to fight again against Parthia:
The people of the Orient welcomed his (Demetrius II's) arrival, partly because of the cruelty of the Arsacid king of the Parthians, partly because, used to the rule of the Macedonians, they disliked the arrogance of this new people. Thus, Demetrius, supported by the Persians, Elymes and Bactrians, routed the Parthians in numerous battles. At the end, deceived by a false peace treaty, he was taken prisoner.The 5th century historian
Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in '' Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), ...
reports that Mithridates I managed to occupy territory between the Indus and the Hydaspes
The Jhelum River is a major river in South Asia, flowing through India and Pakistan, and is the westernmost of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It originates at Verinag and flows through the Indian-administered territory of Jammu an ...
towards the end of his reign ( BC, before his kingdom was weakened by his death in 136 BC).
Heliocles I ended up ruling what territory remained. The defeat, both in the west and the east, may have left Bactria very weakened and open to nomadic invasions.
Nomadic invasions and fall
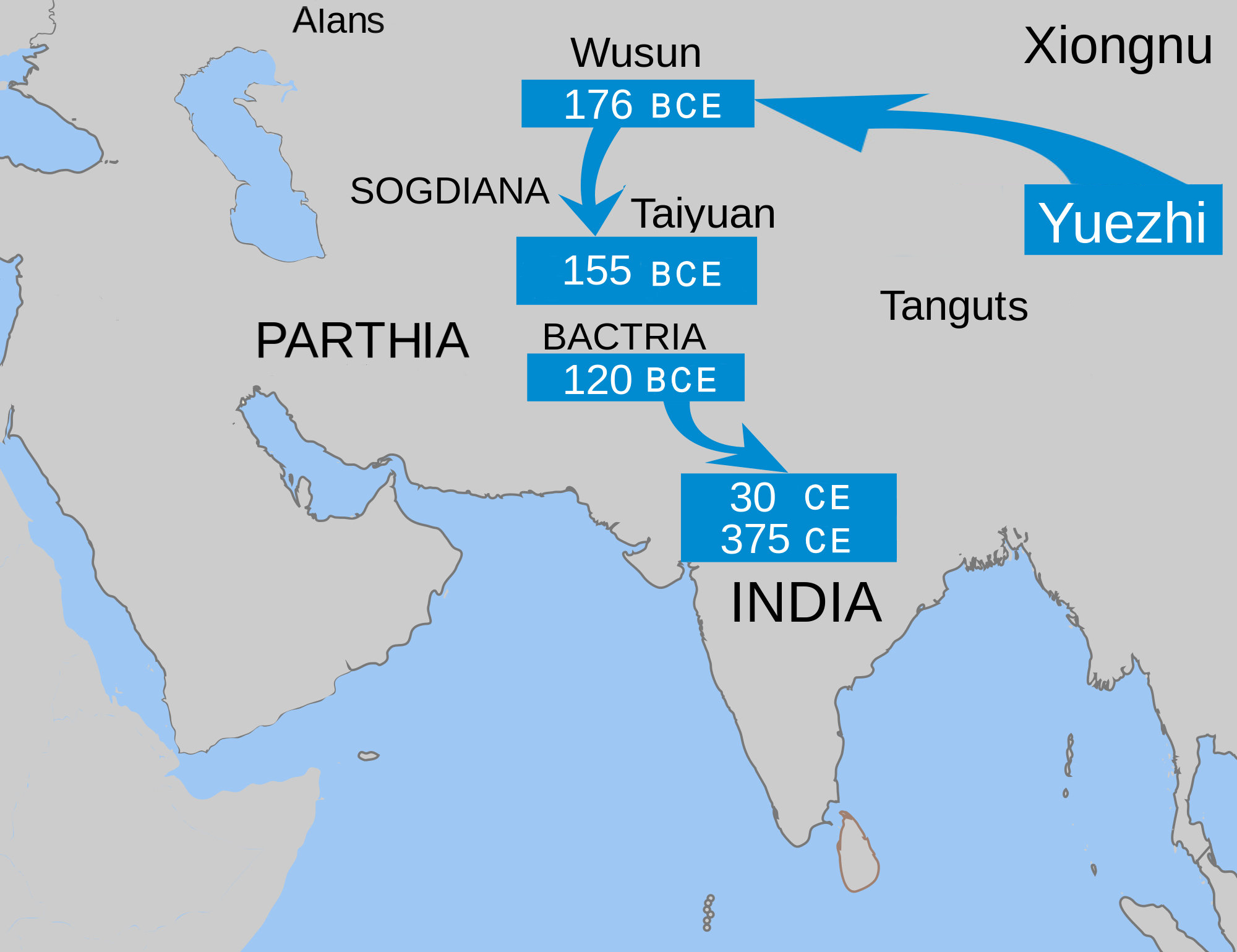
 A nomadic steppe people called the
A nomadic steppe people called the Yuezhi
The Yuezhi were an ancient people first described in China, Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defea ...
inhabited a region thousands of miles to the east of Bactria on the edges of the Han Empire
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
called the Hexi Corridor
The Hexi Corridor ( ), also known as the Gansu Corridor, is an important historical region located in the modern western Gansu province of China. It refers to a narrow stretch of traversable and relatively arable plain west of the Yellow River's O ...
. Shortly before 176 BC, the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, t ...
invaded the Hexi Corridor, forcing the Yuezhi to flee the region. In 162 BC the Yuezhi were driven west to the Ili River valley by the Xiongnu. In 132 they were driven out of the Ili valley by the Wusun
The Wusun ( ) were an ancient semi-Eurasian nomads, nomadic Eurasian Steppe, steppe people of unknown origin mentioned in Chinese people, Chinese records from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD.
The Wusun originally l ...
. The surviving Yuezhi migrated again south towards the territory just north of the Oxus River where they encountered and expelled a nomadic steppe nation called Sakastan.
 Around 140 BC, eastern
Around 140 BC, eastern Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
(the Saka
The Saka, Old Chinese, old , Pinyin, mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit (Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples, Eastern Iranian peoples who lived in the Eurasian ...
, or Sacaraucae of Greek sources), apparently being pushed forward by the southward migration of the Yuezhi
The Yuezhi were an ancient people first described in China, Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defea ...
started to invade various parts of Parthia and Bactria. Their invasion of Parthia is well documented: they attacked in the direction of the cities of Merv
Merv (, ', ; ), also known as the Merve Oasis, was a major Iranian peoples, Iranian city in Central Asia, on the historical Silk Road, near today's Mary, Turkmenistan. Human settlements on the site of Merv existed from the 3rd millennium& ...
, Hecatompolis and Ecbatana
Ecbatana () was an ancient city, the capital of the Median kingdom, and the first capital in History of Iran, Iranian history. It later became the summer capital of the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid and Parthian Empire, Parthian empires.Nardo, Do ...
. They managed to defeat and kill the Parthian king Phraates II
Phraates II (also spelled Frahad II; ''Frahāt'') was king of the Parthian Empire from 132 BC to 127 BC. He was the son and successor of Mithridates I ().
Because he was still very young when he came to the throne, his mother Rinnu initially ru ...
, son of Mithridates I, routing the Greek mercenary troops under his command (troops he had acquired during his victory over Antiochus VII). Again in 123 BC, Phraates's successor, his uncle Artabanus I, was killed by the Scythians.
When the Han Chinese
The Han Chinese, alternatively the Han people, are an East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Greater China. With a global population of over 1.4 billion, the Han Chinese are the list of contemporary ethnic groups, world's la ...
diplomat Zhang Qian visited the Yuezhi around 126 BC, trying to obtain their alliance to fight the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, t ...
, he explained that the Yuezhi were settled north of the Oxus but also held under their sway the territory south of Oxus, which makes up the remainder of Bactria.
According to Zhang Qian, the Yuezhi represented a considerable force of between 100,000 and 200,000 mounted archer warriors, with customs identical to those of the Xiongnu, which would probably have easily defeated Greco-Bactrian forces (in 208 BC when the Greco-Bactrian king Euthydemus I confronted the invasion of the Seleucid king Antiochus III the Great
Antiochus III the Great (; , ; 3 July 187 BC) was the sixth ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 223 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of West Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to th ...
, he commanded 10,000 horsemen). Zhang Qian actually visited Bactria (named Daxia in Chinese) in 126 BC, and portrays a country which was totally demoralized and whose political system had vanished, although its urban infrastructure remained:
Daxia (Bactria) is located over 2,000 li southwest of Dayuan, south of the Gui (Oxus) river. Its people cultivate the land and have cities and houses. Their customs are like those of Dayuan. It has no great ruler but only a number of petty chiefs ruling the various cities. The people are poor in the use of arms and afraid of battle, but they are clever at commerce. After the Great Yuezhi moved west and attacked Daxia, the entire country came under their sway. The population of the country is large, numbering some 1,000,000 or more persons. The capital is called the city of Lanshi ( Bactra) and has a market where all sorts of goods are bought and sold. ('' Records of the Great Historian'' byThe Yuezhi further expanded southward into Bactria around 120 BC, apparently further pushed out by invasions from the northernSima Qian Sima Qian () was a Chinese historian during the early Han dynasty. He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for the ''Shiji'' (sometimes translated into English as ''Records of the Grand Historian''), a general history of China cov ..., quoting Zhang Qian, translation by Burton Watson)
Wusun
The Wusun ( ) were an ancient semi-Eurasian nomads, nomadic Eurasian Steppe, steppe people of unknown origin mentioned in Chinese people, Chinese records from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD.
The Wusun originally l ...
. It seems they also pushed Scythian tribes before them, which continued to India, where they came to be identified as Indo-Scythians.
 This invasion of Bactria is also described in western Classical sources from the 1st century BC:
This invasion of Bactria is also described in western Classical sources from the 1st century BC:
The best known tribes are those who deprived the Greeks of Bactriana, the Asii, Pasiani, Tochari, and Sacarauli, who came from the country on the other side of theAround that time the king Heliocles abandoned Bactria and moved his capital to theJaxartes The Syr Darya ( ),; ; ; ; ; /. historically known as the Jaxartes ( , ), is a river in Central Asia. The name, which is Persian, literally means ''Syr Sea'' or ''Syr River''. It originates in the Tian Shan Mountains in Kyrgyzstan and eastern ..., opposite the Sacae and Sogdiani.
Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
valley, from where he ruled his Indian holdings. Apparently there were two other Greco-Bactrian kings preceding Heliocles in the same region and from the same dynasty, named Eucratides II and Plato Epiphanes, the latter probably being a brother of Eucratides I. Since Heliocles left the Bactrian territory, he is technically the last Greco-Bactrian king, although several of his descendants, moving beyond the Hindu Kush, would form the western part of the Indo-Greek kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
. The last of these "western" Indo-Greek kings, Hermaeus
Hermaeus Soter (, ''Hermaîos ho Sōtḗr,'' meaning "Hermaeus the Saviour") was a Western Indo-Greek king of the Eucratid dynasty, who ruled the territory of Paropamisadae in the Hindu-Kush region, with his capital in Alexandria of the Caucasus ( ...
, would rule until around 70 BC, when the Yuezhi again invaded his territory in the Paropamisadae (while the "eastern" Indo-Greek kings would continue to rule until around AD 10 in the area of the Punjab region
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
).
 Overall, the
Overall, the Yuezhi
The Yuezhi were an ancient people first described in China, Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defea ...
remained in Bactria for more than a century. They became Hellenized to some degree, as suggested by their adoption of the Greek alphabet to write their later Iranian court language, and by numerous remaining coins, minted in the style of the Greco-Bactrian kings, with the text in Greek.
There is evidence for the persistence of Greek populations in Bactria after the collapse of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom. For example, an obol of a previously unknown ruler called Antigonus has been found and it seems he ruled after the kingdom's collapse, as evidenced by the use of a lunate sigma and the lower art quality of the coin, perhaps dating from the end of the 1st century BC. Antigonus might have briefly won a battle against the Yuezhi or the Saka before he was overrun himself.
Around 12 BC the Yuezhi then moved further to northern India where they established the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
.
Military forces
Before the Greek conquest, the armies of Bactria were overwhelmingly composed of cavalry and were well known as effective soldiers, making up large portions of theAchaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the large ...
cavalry contingents. 2,000 Bactrian horsemen fought at the Granicus against Alexander and 9,000 at the Battle of Gaugamela
The Battle of Gaugamela ( ; ), also called the Battle of Arbela (), took place in 331 BC between the forces of the Ancient Macedonian army, Army of Macedon under Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Army, Persian Army under Darius III, ...
on the left flank of Darius' army. Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
also mentions the widespread use of chariots among the Bactrians. After Alexander's conquest of Bactria, Bactrian cavalry units served in his army during the invasion of India and after the Indian campaign, Alexander enlarged his elite companion cavalry by adding Bactrians, Sogdians and other east Iranian cavalrymen.Nikonorov, Valerii; The Armies of Bactria 700 B.C. – 450 A.D Both Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; ; /524 – /455 BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek Greek tragedy, tragedian often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek tragedy is large ...
(The Persians, v. 318) and Curtius mention that Bactria was able to field a force of 30,000 horse. Most of these horsemen were lightly armed, using bows and javelins before closing with sword and spear. Herodotus describes the Persian cavalry of Mardonius at the Battle of Plataea (which included Bactrians) as horse archers (''hippotoxotai''). Bactrian infantry is described by Herodotus as wearing caps in the Median style, short spears and reed Scythian
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people who had migrated during the 9th to 8th centuries BC fr ...
style bows.
Alexander and Seleucus I both settled Macedonians and other Greeks in Bactria, and archeological finds in the region have also attested to a major Macedonian presence, as evidenced by the presence of symbols, style of coinage, and epigraphic names.Willy, Clarysse & Thompson, Dorothy. (2007). Two greek texts on skin from hellenistic bactria. 159. 273–279. Greek garrisons in the satrapy of Bactria were housed in fortresses called ''phrouria'' and at major cities. Military colonists were settled in the countryside and were each given an allotment of land called a ''kleros''. These colonists numbered in the tens of thousands, and were trained in the fashion of the Macedonian army. A Greek army in Bactria during the anti-Macedonian revolt of 323 BC numbered 23,000.
The army of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom was then a multi-ethnic force with Greek colonists making up large portions of the infantry as pike phalanxes, supported by light infantry units of local Bactrians and mercenary javelin-wielding Thureophoroi. The cavalry arm was very large for a Hellenistic army and composed mostly of native Bactrian, Sogdia
Sogdia () or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemen ...
n and other Indo-Iranian light horsemen. Polybius mentions 10,000 horse at the Battle of the Arius river in 208 BC. Greco-Bactrian armies also included units of heavily armored cataphracts
A cataphract was a form of armoured heavy cavalry that originated in Persia and was fielded in ancient warfare throughout Eurasia and Northern Africa.
Historically, the cataphract was a very heavily armoured horseman, with both the rider and ...
and small elite units of companion cavalry. The third arm of the Greco-Bactrian army was the Indian war elephants
A war elephant is an elephant that is trained and guided by humans for combat purposes. Historically, the war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks, and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific mil ...
, which are depicted in some coins with a tower (''thorakion'') or howdah housing men armed with bows and javelins. This force grew as the Greco-Bactrian kingdom expanded into India and was widely depicted in Greco-Bactrian coinage. Other units in the Bactrian military included mercenaries or levies from various surrounding peoples such as the Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
, Dahae, Indians, and Parthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemeni ...
ns.
Culture and legacy
Greek culture in Bactria
Greeks first began settling the region long before Alexander conquered it. ThePersia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
n Empire had a policy of exiling rebelling Greek communities to that region long before it fell to Greek conquest. Therefore, it had a considerable Greek community that was expanded upon after Macedonian conquest.
The Greco-Bactrians were known for their high level of Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
sophistication, and kept regular contact with both the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and neighbouring India. They were on friendly terms with India and exchanged ambassadors.
Their cities, such as Ai-Khanoum
Ai-Khanoum (, meaning 'Lady Moon'; ) is the archaeological site of a Hellenistic city in Takhar Province, Afghanistan. The city, whose original name is unknown, was likely founded by an early ruler of the Seleucid Empire and served as a mili ...
in northeastern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
(probably Alexandria on the Oxus), and Bactra (modern Balkh) where Hellenistic remains have been found, demonstrate a sophisticated Hellenistic urban culture. This site gives a snapshot of Greco-Bactrian culture around 145 BC, as the city was burnt to the ground around that date during nomadic invasions and never re-settled. Ai-Khanoum "has all the hallmarks of a Hellenistic city, with a Greek theater
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors to present experiences of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The performers may communi ...
, gymnasium and some Greek houses with colonnaded courtyards" (Boardman). Remains of Classical Corinthian columns were found in excavations of the site, as well as various sculptural fragments. In particular a huge foot fragment in excellent Hellenistic style was recovered, which is estimated to have belonged to a 5–6 meter tall statue.
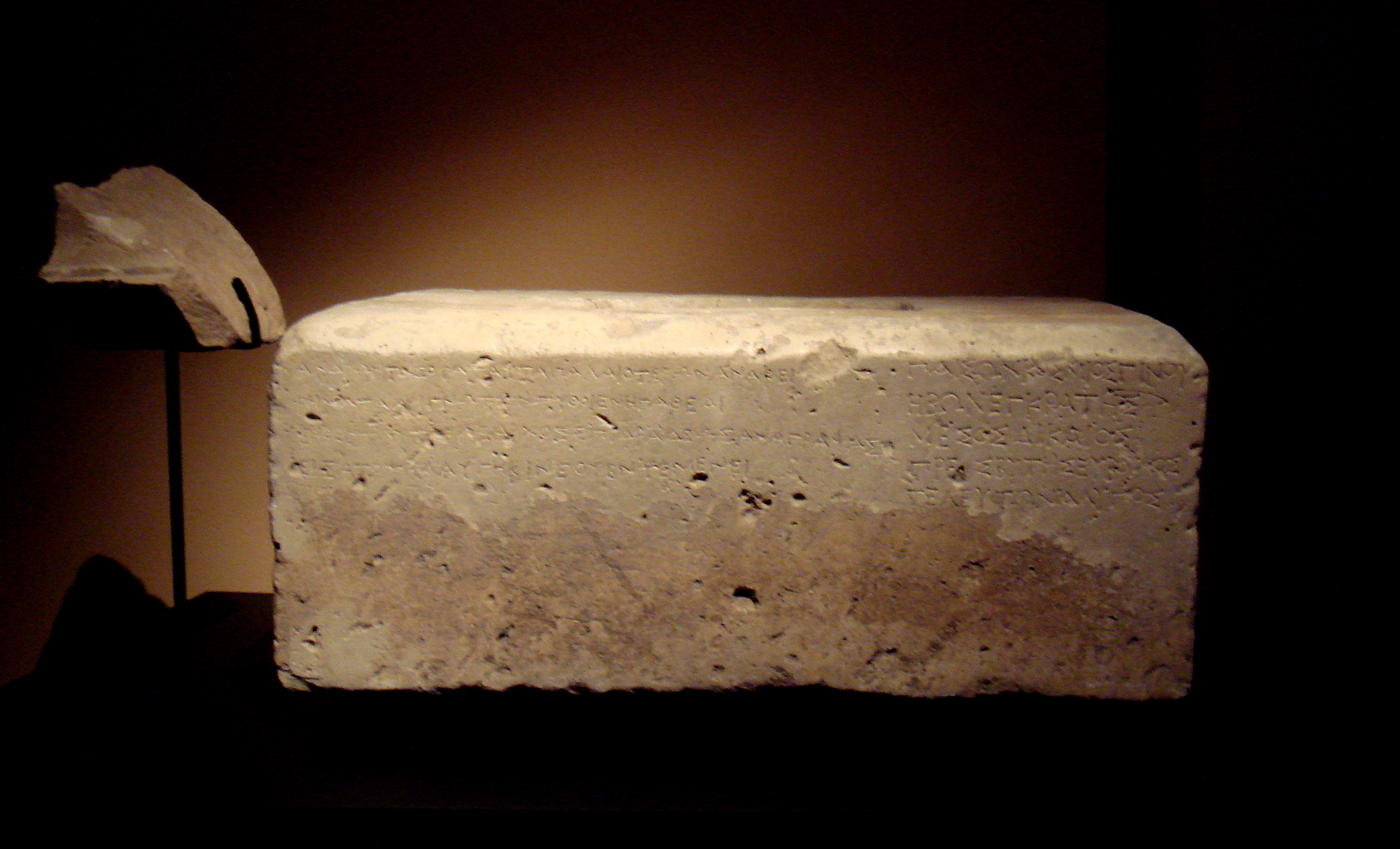
 One of the inscriptions in Greek found at Ai-Khanoum, the Herôon of Kineas, has been dated to 300–250 BC, and describes Delphic maxims:
One of the inscriptions in Greek found at Ai-Khanoum, the Herôon of Kineas, has been dated to 300–250 BC, and describes Delphic maxims:
Many other Greco-Bactrian cities have been identified, for example Alexandria Eschate (in modernπαῖς ὢν κόσμιος γίνου ἡβῶν ἐγκρατής μέσος δίκαιος πρεσβύτης εὔβουλος τελευτῶν ἄλυπος As children, learn good manners. As young men, learn to control the passions. In middle age, be just. In old age, give good advice. Then die, without regret.
Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
), Eucratideia, and another city named Amphipolis. The latter being a previously unknown city which was mentioned on a Bactrian document and was clearly named after Amphipolis in ancient Macedonia. Excavated cities include Kampir Tepe in Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
, as well as Saksanokhur and Takht-i Sangin in Tajikistan (archaeological searches by a Soviet team under B.A. Litvinski), or in Dal'verzin Tepe.
Heracles
Heracles ( ; ), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a Divinity, divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of ZeusApollodorus1.9.16/ref> and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive descent through ...
statuette. Ai Khanoum. 2nd century BC.
File:Philosopher2.JPG, Sculpture of an old man, possibly a philosopher. Ai Khanoum, 2nd century BC.
File:ManWithChlamys5.jpg, Frieze of a naked man wearing a chlamys. Ai Khanoum, 2nd century BC.
File:GorgoyleSharp.jpg, Gargoyle in the form of a Greek comic mask. Ai Khanoum, 2nd century BC.
File:AiKhanoumPlateSharp.jpg, Plate depicting Cybele
Cybele ( ; Phrygian: ''Matar Kubileya, Kubeleya'' "Kubeleya Mother", perhaps "Mountain Mother"; Lydian: ''Kuvava''; ''Kybélē'', ''Kybēbē'', ''Kybelis'') is an Anatolian mother goddess; she may have a possible forerunner in the earliest ...
pulled by lions. Ai Khanoum.
File:Ai-Khanoum mosaic.jpg, Mosaic depicting the Macedonian sun, Ai Khanoum, 2nd century BC.
File:Ai Khanoum Portrait of a man, found in the administrative palace.jpg, Portrait of a man, found in the administrative palace, 2nd century BC.
File:Bactrian tax receipt.jpg, A Bactrian tax receipt written in Greek mentioning the kings Antimachus I, Eumenes and perhaps Antimachus II, 2nd century BC.
Takht-i Sangin
Takht-i Sangin ( Tajik: "Throne of Stone") is an archaeological site located near the confluence of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers, the source of theAmu Darya
The Amu Darya ( ),() also shortened to Amu and historically known as the Oxus ( ), is a major river in Central Asia, which flows through Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Ku ...
, in southern Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
. During the Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
it was a city of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom with a large temple dedicated to the Oxus (Vakhsh river), which remained in use in the following Kushan period, until the third century AD. The site may have been the source of the Oxus Treasure.
Marsyas
In Greek mythology, the satyr Marsyas (; ) is a central figure in two stories involving music: in one, he picked up the double oboe (''aulos'') that had been abandoned by Athena and played it; in the other, he challenged Apollo to a contest of ...
from Takhti Sangin, with dedication in Greek to the god of the Oxus, by "Atrosokes" (a Bactrian name). Temple of the Oxus, Takht-i Sangin, 200–150 BCE. Tajikistan National Museum.
File:Alexander-Herakles head, Takht-i Sangin, Temple of the Oxus, 3rd century BCE.jpg, Alexander-Heracles head, Takht-i Sangin, Temple of the Oxus, 3rd century BCE.
Coinage
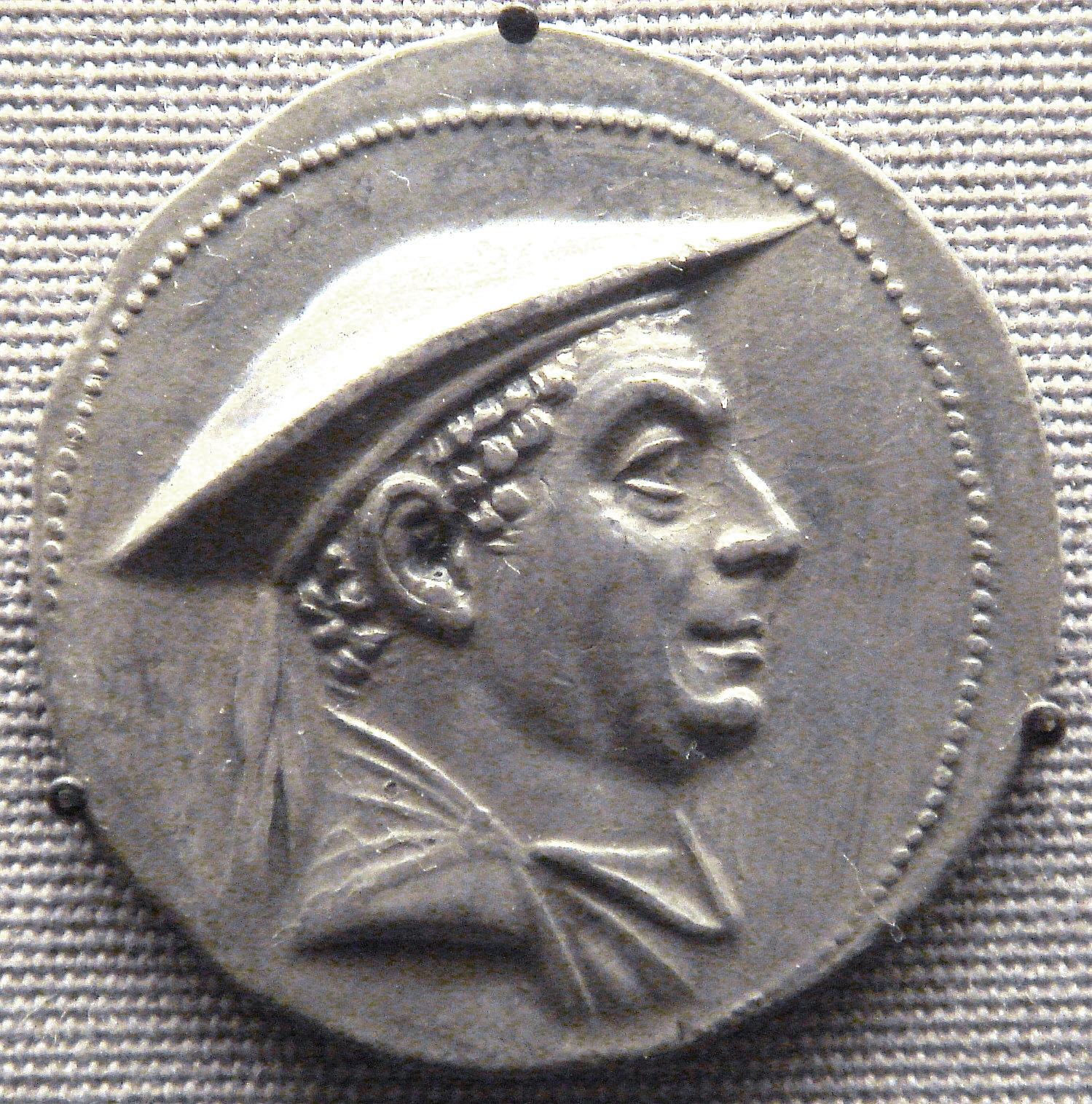
Some of the Greco-Bactrian coins, and those of their successors the Indo-Greeks, are considered the finest examples of Greek numismatic art with "a nice blend of realism and idealization", including the largest coins to be minted in the Hellenistic world: the largest gold coin was minted by Eucratides (reigned 171–145 BC), the largest silver coin by the Indo-Greek king Amyntas Nicator (reigned c. 95–90 BC). The portraits "show a degree of individuality never matched by the often bland depictions of their royal contemporaries further West" (Roger Ling, "Greece and the Hellenistic World"). Such portraits show high levels of detail with some kings seen smiling, while others are shown aging throughout their reign, even depicting old age on their coins. Such realistic imagery on coins seems to have been very important to the Greco-Bactrian kings, who wanted to display their individuality or to distinguish themselves from the style of other contemporary Hellenistic kingdoms.
Greco-Bactrian coins also depict the kings wearing distinct headgear, such as helmets modelled on the Boeotian cavalry helmet of
Such portraits show high levels of detail with some kings seen smiling, while others are shown aging throughout their reign, even depicting old age on their coins. Such realistic imagery on coins seems to have been very important to the Greco-Bactrian kings, who wanted to display their individuality or to distinguish themselves from the style of other contemporary Hellenistic kingdoms.
Greco-Bactrian coins also depict the kings wearing distinct headgear, such as helmets modelled on the Boeotian cavalry helmet of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
, or the Macedonian kausia. This is unique to the Greco-Bactrian kings, who first featured such designs on their coins as other Hellenistic rulers are shown to only wear the diadem. As such the Greco-Bactrians are especially known for their innovative coinage designs. Further examples include the use of different metal alloys for their coins and the issue of bilingual coinage, using Greek on the obverse and an Indian language (such as Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
) in the Kharoshti
Kharosthi script (), also known as the Gandhari script (), was an ancient script originally developed in the Gandhara Region of modern-day Pakistan, between the 5th and 3rd century BCE. used primarily by the people of Gandhara alongside var ...
or Brahmi
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or ...
scripts on the reverse. Local Indian symbols and deities are also depicted, i.e. Buddhist symbols and some Hindu deities (see Influence on Indian art subsection below). This syncretic design was first introduced after king Demetrius I of Bactria conquered areas of the Indian subcontinent between 190 and 180 BC, with king Pantaleon being the first to issue coins of the Indian standard, when the Greeks truly started ruling over Indian populations.
Contacts with Han China
To the north, Euthydemus also ruled Sogdiana and Ferghana, and there are indications that from Alexandria Eschate the Greco-Bactrians may have led expeditions as far as Kashgar andÜrümqi
Ürümqi, , is the capital of the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwestern China. With a census population of 4 million in 2020, Ürümqi is the second-largest city in China's northwestern interior after Xi'an, also the ...
in Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
, leading to the first known contacts between China and the West around 220 BC. The Greek historian Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
too writes that: "they extended their empire even as far as the Seres (Chinese) and the Phryni". (Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
, XI.XI.I). Several statuettes and representations of Greek soldiers have been found north of the
Several statuettes and representations of Greek soldiers have been found north of the Tian Shan
The Tian Shan, also known as the Tengri Tagh or Tengir-Too, meaning the "Mountains of God/Heaven", is a large system of mountain ranges in Central Asia. The highest peak is Jengish Chokusu at high and located in Kyrgyzstan. Its lowest point is ...
, on the doorstep to China, and are today on display in the Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
museum at Ürümqi
Ürümqi, , is the capital of the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwestern China. With a census population of 4 million in 2020, Ürümqi is the second-largest city in China's northwestern interior after Xi'an, also the ...
(Boardman). Middle Eastern or Greek influences on Chinese art have also been suggested ( Hirth, Rostovtzeff). Designs with rosette flowers, geometric lines, meanders
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank ( cut bank or river cliff) and deposits sediments on an inn ...
and glass inlays, suggestive of Egyptian, Persian, and/or Hellenistic influences, can be found on some early Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
bronze mirrors.
Some speculate that Greek influence is found in the artworks of the burial site of China's first Emperor Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; February 25912 July 210 BC), born Ying Zheng () or Zhao Zheng (), was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of China. He is widely regarded as the first ever supreme leader of a unitary state, unitary d ...
, dating back to the 3rd century BC, including in the manufacture of the famous Terracotta Army
The Terracotta Army is a collection of terracotta sculptures depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China. It is a form of funerary art buried with the emperor in 210–209 BCE with the purpose of protecting him in his aft ...
. This idea suggested that Greek artists may have come to China at that time to train local artisans in making sculptures However, this idea is disputed.
Numismatics
Numismatics is the study or collection of currency, including coins, tokens, paper money, medals, and related objects.
Specialists, known as numismatists, are often characterized as students or collectors of coins, but the discipline also inclu ...
also suggest that some technology exchanges may have occurred on these occasions: the Greco-Bactrians were the first in the world to issue cupro-nickel
Cupronickel or copper–nickel (CuNi) is an alloy of copper with nickel, usually along with small quantities of other metals added for strength, such as iron and manganese. The copper content typically varies from 60 to 90 percent. ( Monel is a ...
(75:25 ratio) coins, an alloy technology only known by the Chinese at the time under the name "White copper" (some weapons from the Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
were in copper-nickel alloy). The practice of exporting Chinese metals, in particular iron, for trade is attested around that period. Kings Euthydemus I, Euthydemus II, Agathocles
Agathocles ( Greek: ) is a Greek name. The most famous person called Agathocles was Agathocles of Syracuse, the tyrant of Syracuse. The name is derived from and .
Other people named Agathocles include:
*Agathocles, a sophist, teacher of Damon
...
and Pantaleon made these coin issues around 170 BC. An alternative suggestion is that the metal in the coinage derived from a mine where a cupro-nickel alloy occurred naturally, perhaps Anarak in eastern Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. Copper-nickel would not be used again in coinage until the 19th century.
The presence of Chinese people in India from ancient times is also suggested by the accounts of the " Ciñas" in the ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
'' and the '' Manu Smriti''. When the famous Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
explorer and ambassador Zhang Qian visited Bactria in approximately 126 BC, he reported the presence of Chinese products in the Bactrian markets:
"When I was in Bactria ( Daxia)", Zhang Qian reported, "I saw bamboo canes from Qiong and cloth made in the province of Shu (territories of southwestern China). When I asked the people how they had gotten such articles, they replied, "Our merchants go buy them in the markets of Shendu (India)." :— ''Shiji The ''Shiji'', also known as ''Records of the Grand Historian'' or ''The Grand Scribe's Records'', is a Chinese historical text that is the first of the Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written during the late 2nd and early 1st cen ...'' 123,Sima Qian Sima Qian () was a Chinese historian during the early Han dynasty. He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for the ''Shiji'' (sometimes translated into English as ''Records of the Grand Historian''), a general history of China cov ..., translation by Burton Watson).
 The purpose of Zhang Qian's journey was to look for civilizations on the steppe that the Han could ally with against the Xiongnu. Upon his return, Zhang Qian informed the Chinese emperor Han Wudi of the level of sophistication of the urban civilizations of Ferghana, Bactria and Parthia, who became interested in developing commercial relationships with them:
The purpose of Zhang Qian's journey was to look for civilizations on the steppe that the Han could ally with against the Xiongnu. Upon his return, Zhang Qian informed the Chinese emperor Han Wudi of the level of sophistication of the urban civilizations of Ferghana, Bactria and Parthia, who became interested in developing commercial relationships with them:
The Son of Heaven on hearing all this reasoned thus: Ferghana ( Dayuan) and the possessions ofA number of Chinese envoys were then sent to Central Asia, triggering the development of theBactria Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...( Daxia) andParthia Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemeni ...(Anxi) are large countries, full of rare things, with a population living in fixed abodes and given to occupations somewhat identical with those of the Chinese people, and placing great value on the rich produce of China. ('' Hanshu'', Former Han History).
Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
from the end of the 2nd century BC.
Contacts with the Indian subcontinent (250–180 BC)
The Indian emperor Chandragupta, founder of theMaurya Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary source ...
, conquered the northwestern subcontinent upon the death of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
around 323 BC. However, contacts were kept with his Greek neighbours in the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
, a dynastic alliance or the recognition of intermarriage between Greeks and Indians were established (described as an agreement on Epigamia in Ancient sources), and several Greeks, such as the historian Megasthenes, resided at the Mauryan court. Subsequently, each Mauryan emperor had a Greek ambassador at his court.
 Chandragupta's grandson
Chandragupta's grandson Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
converted to the Buddhist faith and became a great proselytizer in the line of the traditional Pali canon of Theravada
''Theravāda'' (; 'School of the Elders'; ) is Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed ''Theravādins'' (anglicized from Pali ''theravādī''), have preserved their version of the Buddha's teaching or ''Dharma (Buddhi ...
Buddhism, directing his efforts towards the Indo-Iranic and the Hellenistic worlds from around 250 BC. According to the Edicts of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who ruled most of the Indian subcontinent from 268 BCE to 2 ...
, set in stone, some of them written in Greek, he sent Buddhist emissaries to the Greek lands in Asia and as far as the Mediterranean. The edicts name each of the rulers of the Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
world at the time.
The conquest bySome of the Greek populations that had remained in northwestern India apparently converted to Buddhism:Dharma Dharma (; , ) is a key concept in various Indian religions. The term ''dharma'' does not have a single, clear Untranslatability, translation and conveys a multifaceted idea. Etymologically, it comes from the Sanskrit ''dhr-'', meaning ''to hold ...has been won here, on the borders, and even six hundred yojanas (4,000 miles) away, where the Greek king Antiochos rules, beyond there where the four kings namedPtolemy Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ..., Antigonos, Magas andAlexander Alexander () is a male name of Greek origin. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here ar ...rule, likewise in the south among the Cholas, the Pandyas, and as far as Tamraparni. (Edicts of Ashoka The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who ruled most of the Indian subcontinent from 268 BCE to 2 ..., 13th Rock Edict, S. Dhammika).
Here in the king's domain among the Greeks, theFurthermore, according toKambojas The Kambojas were a southeastern Iranian peoples, Iranian people who inhabited the northeastern most part of the territory populated by Iranian tribes, which bordered the Indian subcontinent, Indian lands. They only appear in Indo-Aryan langua ..., the Nabhakas, the Nabhapamkits, the Bhojas, the Pitinikas, the Andhras and the Palidas, everywhere people are following Beloved-of-the-Gods' instructions inDharma Dharma (; , ) is a key concept in various Indian religions. The term ''dharma'' does not have a single, clear Untranslatability, translation and conveys a multifaceted idea. Etymologically, it comes from the Sanskrit ''dhr-'', meaning ''to hold .... (Edicts of Ashoka The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who ruled most of the Indian subcontinent from 268 BCE to 2 ..., 13th Rock Edict, S. Dhammika).
Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
sources, some of Ashoka's emissaries were Greek Buddhist monks, indicating close religious exchanges between the two cultures:
When the (elder) Moggaliputta, the illuminator of the religion of the Conqueror (Ashoka), had brought the (third) council to an end ... he sent forth theras, one here and one there: ... and to Aparantaka (the "Western countries" corresponding toGreco-Bactrians probably received these Buddhist emissaries (at least Maharakkhita, lit. "The Great Saved One", who was "sent to the country of the Yona") and somehow tolerated the Buddhist faith, although little proof remains. In the 2nd century AD, the Christian dogmatistGujarat Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...andSindh Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...) he sent the Greek (Yona The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit, were used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for "Ionians" (), who were probably the first Gr ...) named Dhammarakkhita ... and the Maharakkhita he sent into the country of the Yona. ( Mahavamsa, XII).
Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens, also known as Clement of Alexandria (; – ), was a Christian theology, Christian theologian and philosopher who taught at the Catechetical School of Alexandria. Among his pupils were Origen and Alexander of Jerusalem. A ...
recognized the existence of Buddhist Sramanas among the Bactrians ("Bactrians" meaning "Oriental Greeks" in that period), and even their influence on Greek thought:
Thus philosophy, a thing of the highest utility, flourished in antiquity among the barbarians, shedding its light over the nations. And afterwards it came to Greece. First in its ranks were the prophets of theEgyptians Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretchi ...; and the Chaldeans among theAssyrians Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from ot ...; and theDruids A druid was a member of the high-ranking priestly class in ancient Celtic cultures. The druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no wr ...among theGauls The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). Th ...; and the Sramanas among the Bactrians (""); and the philosophers of theCelts The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...; and theMagi Magi (), or magus (), is the term for priests in Zoroastrianism and earlier Iranian religions. The earliest known use of the word ''magi'' is in the trilingual inscription written by Darius the Great, known as the Behistun Inscription. Old Per ...of thePersians Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ..., who foretold the Saviour's birth, and came into the land ofJudea Judea or Judaea (; ; , ; ) is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the pres ...guided by a star. The Indian gymnosophists are also in the number, and the other barbarian philosophers. And of these there are two classes, some of them called Sramanas (""), and othersBrahmins Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...("").
Influence on Indian art during the 3rd century BC
 The Greco-Bactrian city of
The Greco-Bactrian city of Ai-Khanoum
Ai-Khanoum (, meaning 'Lady Moon'; ) is the archaeological site of a Hellenistic city in Takhar Province, Afghanistan. The city, whose original name is unknown, was likely founded by an early ruler of the Seleucid Empire and served as a mili ...
, being located at the doorstep of India, interacting with the Indian subcontinent, and having a rich Hellenistic culture, was in a unique position to influence Indian culture as well. It is considered that Ai-Khanoum may have been one of the primary actors in transmitting Western artistic influence to India, for example in the creation of the Pillars of Ashoka
The pillars of Ashoka are a series of Monolith, monolithic columns dispersed throughout the Indian subcontinent, erected—or at least inscribed with Edicts of Ashoka, edicts—by the 3rd Mauryan Emperor Ashoka the Great, who reigned from to ...
or the manufacture of the quasi-Ionic Pataliputra capital, all of which were posterior to the establishment of Ai-Khanoum.
The scope of adoption goes from designs such as the bead and reel pattern, the central flame palmette design and a variety of other moldings, to the lifelike rendering of animal sculpture and the design and function of the Ionic anta capital in the palace of Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
.
First visual representations of Indian deities
 One of the last Greco-Bactrian kings, Agathocles of Bactria (ruled 190–180 BC), issued remarkable Indian-standard square coins bearing the first known representations of Indian deities, which have been variously interpreted as
One of the last Greco-Bactrian kings, Agathocles of Bactria (ruled 190–180 BC), issued remarkable Indian-standard square coins bearing the first known representations of Indian deities, which have been variously interpreted as Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
, Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
, Vasudeva
Vasudeva (; Sanskrit: वसुदेव ), also called Anakadundubhi (''anakas'' and ''dundubhis'' both refer to ''drums'', after the musicians who played these instruments at the time of his birth), is the father of the Hindu deities Krishna ( ...
, Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist legends, he was ...
or Balarama. Altogether, six such Indian-standard silver drachmas
Drachma may refer to:
* Ancient drachma, an ancient Greek currency
* Modern drachma, a modern Greek currency (1833...2002)
* Cretan drachma, currency of the former Cretan State
* Drachma proctocomys, moth species, the only species in the Genus '' ...
in the name of Agathocles were discovered at Ai-Khanoum in 1970.Iconography of Balarāma, Nilakanth Purushottam Joshi, Abhinav Publications, 1979, p.2/ref>Peter Thonemann, (2016), ''The Hellenistic World: Using coins as sources'', Cambridge University Press, p. 10
/ref> These coins seem to be the first known representations of Rigvedic deities, Vedic deities on coins, and they display early
Avatar
Avatar (, ; ) is a concept within Hinduism that in Sanskrit literally means . It signifies the material appearance or incarnation of a powerful deity, or spirit on Earth. The relative verb to "alight, to make one's appearance" is sometimes u ...
s of Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
: Balarama- Sankarshana with attributes consisting of the Gada mace and the plow
A plough or (Differences between American and British spellings, US) plow (both pronounced ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses but modern ploughs ...
, and Vasudeva
Vasudeva (; Sanskrit: वसुदेव ), also called Anakadundubhi (''anakas'' and ''dundubhis'' both refer to ''drums'', after the musicians who played these instruments at the time of his birth), is the father of the Hindu deities Krishna ( ...
-Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c ...
with the Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
attributes of the Shankha
A Turbinella pyrum, shankha () has religious ritual importance in Hinduism.
In Hinduism, the shankha called panchajanya is a sacred emblem of the Hindu preserver deity Vishnu. It is still used as a trumpet in Hindu ritual, and in the past was us ...
(a pear-shaped case or conch) and the Sudarshana Chakra wheel. Some other coins by Agathocles are also thought to represent the Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
lion and the Indian goddess Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, , ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the goddess of wealth, fortune, prosperity, beauty, fertility, sovereignty, and abundance. She along with Parvat ...
, consort of Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
. The Indian coinage of Agathocles is few but spectacular. These coins at least demonstrate the readiness of Greek kings to represent deities of foreign origin. The dedication of a Greek envoy to the cult of Garuda
Garuda (; ; Vedic Sanskrit: , ) is a Hindu deity who is primarily depicted as the mount (''vahana'') of the Hindu god Vishnu. This divine creature is mentioned in the Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain faiths. Garuda is also the half-brother of the D ...
at the Heliodorus pillar
The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BCE in central India in Besnagar (Vidisha), Madhya Pradesh. The pillar is commonly named after Heliodorus (identified by him as a Garuda-standard), who was an ambassador of the In ...
in Besnagar could also be indicative of some level of religious syncretism
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various school of thought, schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or religious assimilation, assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the ...
.
Legacy in Central Asia and South Asia
 Overall, the Greco-Bactrians and their successors the Indo-Greeks, created a significant and influential civilisation in the region. During their 250-year-long rule, and with their highly developed Hellenistic tradition, they firmly established the Greek language and religious ideas in both Central Asia and northwestern India. The Greek language and writing was so prominent in Bactria in particular, that the invading tribes who settled in the region adopted the
Overall, the Greco-Bactrians and their successors the Indo-Greeks, created a significant and influential civilisation in the region. During their 250-year-long rule, and with their highly developed Hellenistic tradition, they firmly established the Greek language and religious ideas in both Central Asia and northwestern India. The Greek language and writing was so prominent in Bactria in particular, that the invading tribes who settled in the region adopted the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as wel ...
to write their own language. The Bactrian language
Bactrian (, , meaning "Iranian") was an Eastern Iranian language formerly spoken in the Central Asian region of Bactria (present-day Afghanistan) and used as the official language of the Kushan and the Hephthalite empires.
Name
It was long tho ...
used in the region of modern-day Afghanistan continued to be written in the Greek script until the 9th century AD (nearly 1,000 years after the fall of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom). These tribes also heavily incorporated the Greek gods into their own religion and art. The Indo-Scythians, Indo-Parthians and the Yuezhi
The Yuezhi were an ancient people first described in China, Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defea ...
(who later became the Kushans), extensively copied the coin designs of the Greco-Bactrians (and the Indo-Greeks), but eventually this gave way to more diverse coin designs by the 1st century AD.
To the south, in the region of Arachosia, which was later controlled by the Indo-Greek kings, there is also evidence of persistence of Greek cities and language. For example, in his 1st-century AD ''Parthian stations'' itinerary, Isidore of Charax
Isidore of Charax (; , ''Isídōros o Charakēnós''; ) was a Greek geographer of the 1st century BC and 1st century AD, a citizen of the Parthian Empire, about whom nothing is known but his name and that he wrote at least one work.
Name
Isidore ...
describes an " Alexandropolis, the metropolis of Arachosia", which he said was still Greek even at such a late time. The Kandahar Sophytos inscription from the same city, shows a real refinement of Greek language and culture so far east, and was likely written by a native man who had mastered the Greek language.The Muse at Play: Riddles and Wordplay in Greek and Latin Poetry, Jan Kwapisz, David Petrain, Mikolaj Szymanski, Walter de Gruyter, 2013, p.284-28/ref> The Greco-Bactrians and especially the Indo-Greeks were highly influential in the creation of syncretic artistic movements in India. The most important example being the
Greco-Buddhist art
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara, located in the northwestern fringe of t ...
of Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
found in the region of modern-day Pakistan and Afghanistan, which includes designs such as the ornate Indo-Corinthian capitals, and the drapery of Buddhist clothing, with some elements later spreading as far as Pataliputra in India.
List of Greco-Bactrian kings
The below table lists the known Greek rulers of Bactria, along with their dates and titles or epithets. Dates that overlap show that multiple kings ruled at the same time, but in different regions whose exact details are not known very well. For example, Apollodotus I likely ruled areas south of Bactria and the Indian subcontinent while Antimachus I ruled in Bactria. Eucratides II and Heliocles I would have each ruled smaller parts of southern Bactria.See also
*Greco-Buddhism
Greco-Buddhism or Graeco-Buddhism was a cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism developed between the 4th century BC and the 5th century AD in Gandhara, which was in present-day Pakistan and parts of north-east Afghanis ...
* Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
* Indo-Scythians
* Ptolemaic Kingdom
The Ptolemaic Kingdom (; , ) or Ptolemaic Empire was an ancient Greek polity based in Ancient Egypt, Egypt during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 305 BC by the Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general Ptolemy I Soter, a Diadochi, ...
* Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
* Yuezhi
The Yuezhi were an ancient people first described in China, Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defea ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * Boardman, John (1994). ''The Diffusion of Classical Art in Antiquity''. Princeton University Press. . * Boardman, John, Jasper Griffin, and Oswyn Murray (2001). ''The Oxford Illustrated History of Greece and the Hellenistic World''. Oxford University Press. . * Bopearachchi, Osmund (1991). ''Monnaies Gréco-Bactriennes et Indo-Grecques, Catalogue Raisonné''.Bibliothèque Nationale
A library is a collection of books, and possibly other materials and media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or digital (soft copies) materials, and may be a p ...
de France, .
* Bopearachchi, Osmund and Christine Sachs (2003). ''De l'Indus à l'Oxus, Archéologie de l'Asie Centrale: catalogue de l'exposition''. .
*
*
* McEvilley, Thomas (2002). ''The Shape of Ancient Thought. Comparative studies in Greek and Indian Philosophies''. Allworth Press and the School of Visual Arts.
*
* Puri, B. N. (2000). ''Buddhism in Central Asia''. Motilal Banarsidass, Delhi. .
* Tarn, W. W. (1966). ''The Greeks in Bactria and India''. 2nd Edition. Cambridge University Press.
* Watson, Burton, trans. (1993). ''Records of the Great Historian: Han Dynasty II'', by Sima Qian
Sima Qian () was a Chinese historian during the early Han dynasty. He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for the ''Shiji'' (sometimes translated into English as ''Records of the Grand Historian''), a general history of China cov ...
. Columbia University Press. .
External links
Greco-Bactrian and Indo-Greek Kingdoms in Ancient Texts
Some new hypotheses on the Greco-Bactrian and Indo-Greek kingdoms
by Antoine Simonin
{{Hellenistic rulers 125 BC 250s BC establishments 256 BC Former countries in Central Asia Former countries in South Asia Former kingdoms Former monarchies of Central Asia Former monarchies of South Asia Hellenistic states Lists of monarchs States and territories disestablished in the 2nd century BC States and territories established in the 3rd century BC