Greater Yugoslavia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
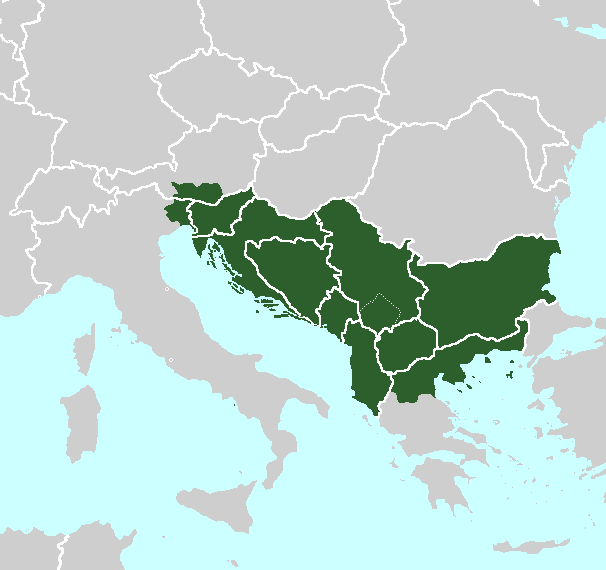 Yugoslav irredentism was a political idea advocating merging of
Yugoslav irredentism was a political idea advocating merging of
 Yugoslav irredentism was a political idea advocating merging of
Yugoslav irredentism was a political idea advocating merging of South Slav
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hu ...
-populated territories within Yugoslavia
, common_name = Yugoslavia
, life_span = 1918–19921941–1945: World War II in Yugoslavia#Axis invasion and dismemberment of Yugoslavia, Axis occupation
, p1 = Kingdom of SerbiaSerbia
, flag_p ...
with several adjacent territories, including Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, Western Thrace
Western Thrace or West Thrace (, '' ytikíThráki'' ), also known as Greek Thrace or Aegean Thrace, is a geographical and historical region of Greece, between the Nestos and Evros rivers in the northeast of the country; East Thrace, which lie ...
and Greek Macedonia. The government of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast Europe, Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () h ...
sought the union with Bulgaria or its incorporation into Yugoslavia. The government of the communist-ruled Yugoslavia under Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito ( ; , ), was a Yugoslavia, Yugoslav communist revolutionary and politician who served in various positions of national leadership from 1943 unti ...
also sought to create an integral Yugoslavia that would incorporate within its borders: Greek Macedonia, Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
, Pirin Macedonia, at least some of Austrian Carinthia, and for a time the entire Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia () is one of the 20 regions of Italy and one of five autonomous regions with special statute. The regional capital is Trieste on the Gulf of Trieste, a bay of the Adriatic Sea.
Friuli-Venezia Giulia has an area of and a ...
.
History
Proponents of Yugoslav irredentism included bothmonarchists
Monarchism is the advocacy of the system of monarchy or monarchical rule. A monarchist is an individual who supports this form of government independently of any specific monarch, whereas one who supports a particular monarch is a royalist. C ...
and republicans. Days prior to Yugoslavia's creation in 1918, Yugoslavist politician Svetozar Pribićević
Svetozar Pribićević ( sr-Cyrl, Светозар Прибићевић}, ; 26 October 1875 – 15 September 1936) was a Croatian Serb politician in Austria-Hungary and later the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. He was one of the main proponents of Yugoslavi ...
declared that Yugoslavia's borders should extend "from the Soča
Soča (, in Slovene) or Isonzo (, in Italian; other names: ; ; or ') is a long river that flows through western Slovenia () and northeastern Italy ().
An Alpine river in character, its source lies in the Trenta Valley in the Julian Alps ...
up to Salonika
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
". Proposals in the interwar period to include Bulgaria within Yugoslavia, included claims by republicans that a republic was necessary for an Integral Yugoslavia with Bulgaria, while others claimed that a republic would not because Bulgaria at that time was a tsardom, and instead claimed that a limited constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
would be an appropriate form of state that could include Bulgaria within it. The militant movement Zveno in Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
supported an Integral Yugoslavia that included Bulgaria as well as Albania within it. The Zveno movement participated in the Bulgarian coup d'état of 1934
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
, the coup supporters declared their intention to immediately form an alliance with France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and to seek the unification of Bulgaria into an Integral Yugoslavia.
Once World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
began, in 1940 General Milan Nedić
Milan Nedić ( sr-Cyrl, Милан Недић; 2 September 1878 – 4 February 1946) was a Yugoslav and Serbian army general and politician who served as the Chief of the General Staff of the Royal Yugoslav Army and minister of war in the ...
proposed that Yugoslavia join the Axis Powers
The Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis and also Rome–Berlin–Tokyo Axis, was the military coalition which initiated World War II and fought against the Allies of World War II, Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Ge ...
and attack Greece to seize Salonika. During World War II, the British government supported the creation of a Greater Yugoslavia after the war due to opposition to the Bulgarian government's accession to the Axis Powers, in May 1941 endorsing Dr. Malcom Burr's paper in favour of the incorporation of Bulgaria into Yugoslavia after the war.Dimitris Livanios. ''The Macedonian question: Britain and the southern Balkans: 1939-1949''. Oxford, England, UK: Oxford University Press, 2008 Pp. 103.
In June 1945, Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito ( ; , ), was a Yugoslavia, Yugoslav communist revolutionary and politician who served in various positions of national leadership from 1943 unti ...
declared that Yugoslavia had the right to have Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
and all of Carinthia
Carinthia ( ; ; ) is the southernmost and least densely populated States of Austria, Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The Lake Wolayer is a mountain lake on the Carinthian side of the Carnic Main ...
, including Austrian Carinthia, saying "We have liberated Carinthia but international conditions were such that we had to leave it temporarily. Carinthia is ours and we shall fight for it". Neither the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
nor the Western Allies supported Yugoslav claims against Austria and Italy. Yugoslavia abandoned such claims after the 1948 Tito–Stalin split
The Tito–Stalin split or the Soviet–Yugoslav split was the culmination of a conflict between the political leaderships of Yugoslavia and the Soviet Union, under Josip Broz Tito and Joseph Stalin, respectively, in the years following World W ...
.
See also
* 1920 Carinthia Plebiscite *Banat Republic
The Banat Republic (, or ''Bánsági Köztársaság'', or ''Republica Banatului'', sr-Cyrl-Latn, Банатска република, Banatska republika, separator=" / ") was a short-lived state proclaimed in Timișoara 31 October 1918, dur ...
* Banat, Bačka and Baranja
Banat, Bačka and Baranya ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Banat, Bačka i Baranja, Банат, Бачка и Барања) was a province of the Kingdom of Serbia and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes between November 1918 and 1922. It ...
* Republic of Prekmurje
References
Sources
* {{Pan-nationalist concepts Irredentism Pan-Slavism South Slavic history Yugoslavism Yugoslav unification