Gouraud shading on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Gouraud shading ( ), named after Henri Gouraud, is an
Gouraud shading ( ), named after Henri Gouraud, is an
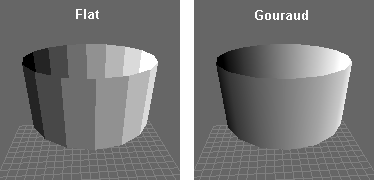 Gouraud shading is considered superior to
Gouraud shading is considered superior to
Image:Gouraud_low_anim.gif, A Gouraud-shaded sphere-like mesh - note the poor behaviour of the specular highlight.
Image:Gouraud_high.gif, Another sphere-like mesh rendered with a higher polygon count
 Gouraud shading ( ), named after Henri Gouraud, is an
Gouraud shading ( ), named after Henri Gouraud, is an interpolation
In the mathematics, mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one ...
method used in computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. ...
to produce continuous shading
Shading refers to the depiction of depth perception in 3D models (within the field of 3D computer graphics) or illustrations (in visual art) by varying the level of darkness. Shading tries to approximate local behavior of light on the object's ...
of surfaces represented by polygon meshes. In practice, Gouraud shading is most often used to achieve continuous lighting on triangle mesh
In computer graphics, a triangle mesh is a Types of mesh, type of polygon mesh. It comprises a set of triangles (typically in three dimensions) that are connected by their common Edge (geometry), edges or Vertex (geometry), vertices.
Many gra ...
es by computing the lighting at the corners of each triangle and linearly interpolating the resulting colours for each pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
covered by the triangle. Gouraud first published the technique in 1971. However, enhanced hardware support for superior shading models has yielded Gouraud shading largely obsolete in modern rendering.
Description
Gouraud shading works as follows: An estimate to thesurface normal
In geometry, a normal is an object (e.g. a line, ray, or vector) that is perpendicular to a given object. For example, the normal line to a plane curve at a given point is the infinite straight line perpendicular to the tangent line to the ...
of each vertex in a polygonal 3D model is either specified for each vertex or found by averaging the surface normals of the polygons that meet at each vertex. Using these estimates, lighting computations based on a reflection model, e.g. the Phong reflection model, are then performed to produce colour intensities at the vertices. For each screen pixel that is covered by the polygonal mesh, colour intensities can then be interpolated from the colour values calculated at the vertices.
Comparison with other shading techniques
 Gouraud shading is considered superior to
Gouraud shading is considered superior to flat shading
Shading refers to the depiction of depth perception in 3D models (within the field of 3D computer graphics) or illustrations (in visual art) by varying the level of darkness. Shading tries to approximate local behavior of light on the object's ...
and requires significantly less processing than Phong shading
In 3D computer graphics, Phong shading, Phong interpolation, or normal-vector interpolation shading is an interpolation technique for surface shading invented by computer graphics pioneer Bui Tuong Phong. Phong shading interpolates surface no ...
, but usually results in a faceted look.
In comparison to Phong shading, Gouraud shading's strength and weakness lies in its interpolation. If a mesh covers more pixels in screen space than it has vertices, interpolating colour values from samples of expensive lighting calculations at vertices is less processor intensive than performing the lighting calculation for each pixel as in Phong shading. However, highly localized lighting effects (such as specular highlight
A specular highlight is the bright spot of light that appears on shiny objects when illuminated (for example, see image on right). Specular highlights are important in 3D computer graphics, as they provide a strong visual cue for the shape of ...
s, e.g. the glint of reflected light on the surface of an apple) will not be rendered correctly, and if a highlight lies in the middle of a polygon, but does not spread to the polygon's vertex, it will not be apparent in a Gouraud rendering; conversely, if a highlight occurs at the vertex of a polygon, it will be rendered correctly at this vertex (as this is where the lighting model is applied), but will be spread unnaturally across all neighboring polygons via the interpolation method.
The problem is easily spotted in a rendering which ought to have a specular highlight moving smoothly across the surface of a model as it rotates. Gouraud shading will instead produce a highlight continuously fading in and out across neighboring portions of the model, peaking in intensity when the intended specular highlight aligns with a vertex of the model. While this problem can be fixed by increasing the density of vertices in the object, at some point the diminishing returns
In economics, diminishing returns means the decrease in marginal (incremental) output of a production process as the amount of a single factor of production is incrementally increased, holding all other factors of production equal ('' ceter ...
of this approach will favour switching to a more detailed shading model.
Linear vs. hyperbolic interpolation
Gouraud's original paper described linear color interpolation. In 1992, Blinn published an efficient algorithm for hyperbolic interpolation{{cite journal , last1=Blinn , first1=James F. , title=Hyperbolic Interpolation , journal=IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications , date=July 1992 , volume=12 , issue=4 , page=89-94 , doi=10.1109/MCG.1992.10028 , s2cid=207973430 , url=https://resolver.caltech.edu/CaltechAUTHORS:20191107-073429669 , ref=blinn that is used inGPUs
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
as a perspective correct alternative to linear interpolation. Both the linear and hyperbolic variants of interpolation of colors from vertices to pixels are commonly called "Gouraud shading".
Mach bands
Any linear interpolation of intensity causes derivative discontinuities which triggers Mach bands, a common visual artifact of Gouraud shading.See also
*List of common shading algorithms {{Short description, none
This article lists common shading algorithms used in computer graphics.
Interpolation techniques
These techniques can be combined with any illumination model:
* Flat shading
* Gouraud shading
* Phong shading
Illuminat ...
* Blinn–Phong reflection model
* Phong shading
In 3D computer graphics, Phong shading, Phong interpolation, or normal-vector interpolation shading is an interpolation technique for surface shading invented by computer graphics pioneer Bui Tuong Phong. Phong shading interpolates surface no ...
References