Gordon–Loeb Model on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
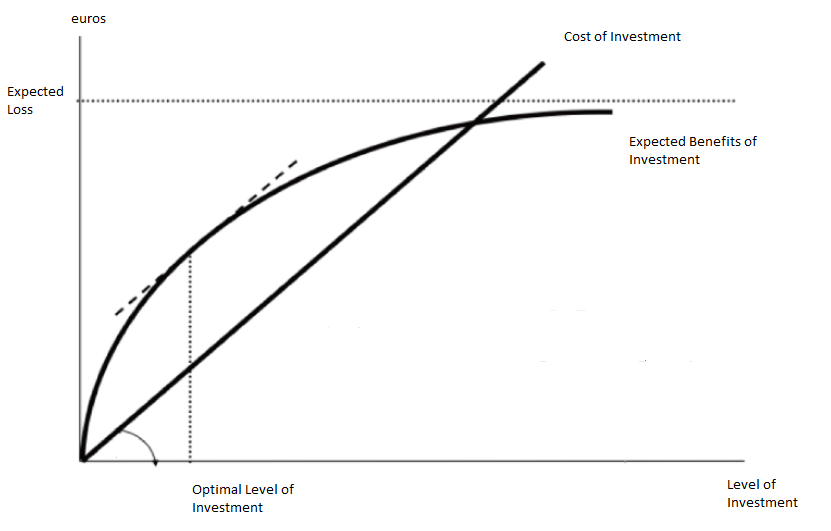 The Gordon–Loeb model is an economic model that analyzes the optimal level of investment in
The Gordon–Loeb model is an economic model that analyzes the optimal level of investment in
 The Gordon–Loeb model is an economic model that analyzes the optimal level of investment in
The Gordon–Loeb model is an economic model that analyzes the optimal level of investment in information security
Information security is the practice of protecting information by mitigating information risks. It is part of information risk management. It typically involves preventing or reducing the probability of unauthorized or inappropriate access to data ...
.
The benefits of investing in cybersecurity stem from reducing the costs associated with cyber breaches. The Gordon-Loeb model provides a framework for determining how much to invest in cybersecurity, using a cost-benefit approach.
The model includes the following key components:
* Organizational data vulnerable to cyber-attacks, with vulnerability denoted by (), representing the probability of a breach occurring under current conditions.
* The potential loss from a breach, represented by , which can be expressed in monetary terms. The expected loss is calculated as before additional cybersecurity investments.
* Investment in cybersecurity, denoted as , reduces based on the effectiveness of the security measures, known as the security breach probability function.
Gordon and Loeb demonstrated that the optimal level of security investment, , does not exceed 37% of the expected loss from a breach. Specifically, .
Overview
The model was first introduced by Lawrence A. Gordon and Martin P. Loeb in a 2002 paper published in ''ACM Transactions on Information and System Security'', titled "The Economics of Information Security Investment". It was reprinted in the 2004 book ''Economics of Information Security''. Both authors are professors at theUniversity of Maryland
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD is the flagship institution of the Univ ...
's Robert H. Smith School of Business.
The model is widely regarded as one of the leading analytical tools in cybersecurity economics. It has been extensively referenced in academic and industry literature. It has also been tested in various contexts by researchers such as Marc Lelarge and Yuliy Baryshnikov.
The model has also been covered by mainstream media, including ''The Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' (''WSJ''), also referred to simply as the ''Journal,'' is an American newspaper based in New York City. The newspaper provides extensive coverage of news, especially business and finance. It operates on a subscriptio ...
'' and ''The Financial Times
The ''Financial Times'' (''FT'') is a British daily newspaper printed in broadsheet and also published digitally that focuses on business and economic Current affairs (news format), current affairs. Based in London, the paper is owned by a Jap ...
''.
Subsequent research has critiqued the model's assumptions, suggesting that some security breach functions may require fixing no less than the expected loss, challenging the universality of the factor. Alternative formulations even propose that some loss functions may justify investment at the full estimated loss.
See also
* Genuine progress indicatorReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gordon-Loeb model Data security Mathematical economics