GoboLinux on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
GoboLinux is a
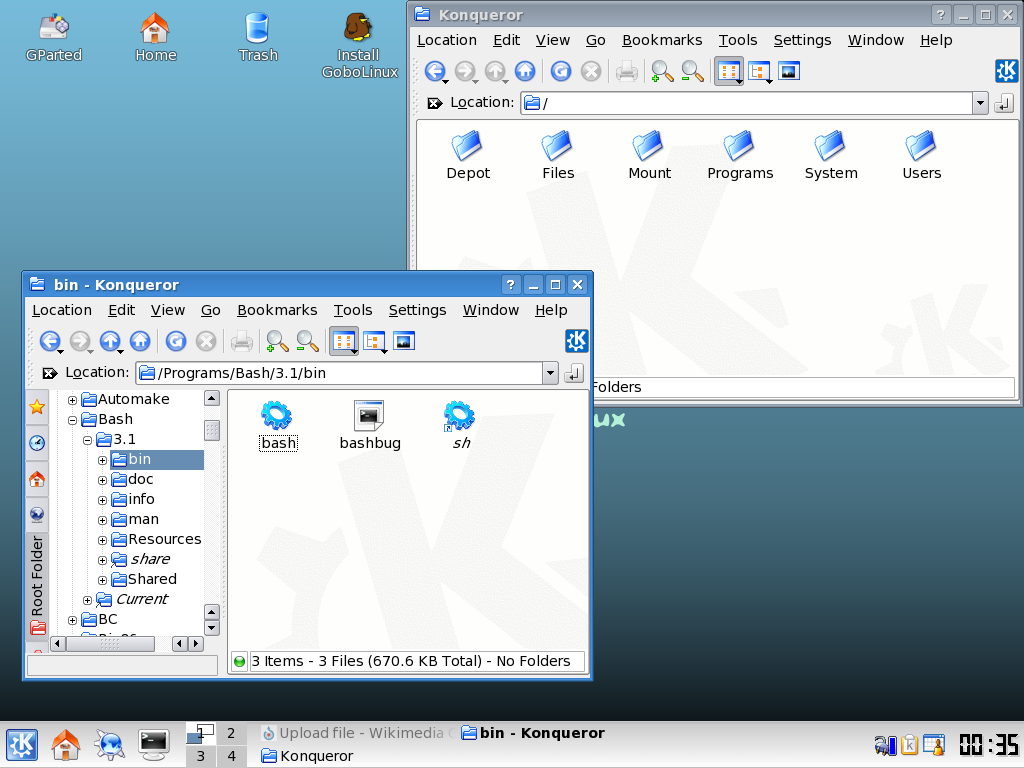 The design of GoboLinux was influenced by earlier systems such as
The design of GoboLinux was influenced by earlier systems such as
Linux distribution
A Linux distribution, often abbreviated as distro, is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro—if distributed on its own—is oft ...
whose most prominent feature is a reorganization of the traditional Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
file system. Rather than following the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard
The Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) is a reference describing the conventions used for the layout of Unix-like systems. It has been made popular by its use in Linux distributions, but it is used by other Unix-like systems as well. It is main ...
like most Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
systems, each program in a GoboLinux system has its own subdirectory
In computing, a directory is a file system cataloging structure that contains references to other computer files, and possibly other directories. On many computers, directories are known as folders or drawers, analogous to a workbench or the t ...
tree, where all of its files (including settings specific for that program) may be found. Thus, a program "Foo" has all of its specific files and libraries in /Programs/Foo, under the corresponding version of this program at hand. For example, the commonly known GCC compiler suite version 8.1.0, would reside under the directory /Programs/GCC/8.1.0.
According to the GoboLinux developers, this results in a cleaner system.
Overview
The GoboLinux hierarchy represents a radical departure from the filesystem traditionally employed by mostUNIX-like operating systems
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
where specific types of files are stored together in common standard subdirectories (such as /bin for executables and /etc for configuration files) and where package manager
A package manager or package management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner.
A package manager deals wi ...
s are used to keep track of what file belongs to which program. In GoboLinux, files from each program are placed under their respective program's own dedicated subdirectory. The makers of GoboLinux have said that "the filesystem is the package manager", and the GoboLinux package system uses the filesystem itself as a package database. This is said to produce a more straightforward, less cluttered directory tree. GoboLinux uses symlink
In computing, a symbolic link (also symlink or soft link) is a file whose purpose is to point to a file or directory (called the "target") by specifying a path thereto.
Symbolic links are supported by POSIX and by most Unix-like operating system ...
s and an optional kernel module
A loadable kernel module (LKM) is an executable library that extends the capabilities of a running kernel, or so-called ''base kernel'', of an operating system. LKMs are typically used to add support for new hardware (as device drivers) and/or ...
called ''GoboHide'' to achieve all this while maintaining full compatibility with the traditional Linux filesystem hierarchy.
The creators of GoboLinux have stated that their design has other "modernisms", such as the removal of some distinctions between similar traditional directories (such as the locations of executables /bin, /usr/bin, and /usr/local/bin). GoboLinux designers have claimed that this results in shell scripts
A shell script is a computer program designed to be run by a Unix shell, a command-line interpreter. The various dialects of shell scripts are considered to be command languages. Typical operations performed by shell scripts include file manipula ...
breaking less often than with other Linux distributions. This change, introduced by GoboLinux in 2003, has only been adopted by other distributions much later: Fedora
A fedora () is a hat with a soft brim and indented crown.Kilgour, Ruth Edwards (1958). ''A Pageant of Hats Ancient and Modern''. R. M. McBride Company. It is typically creased lengthwise down the crown and "pinched" near the front on both sides ...
merged /bin and /usr/bin in 2012; Debian
Debian () is a free and open-source software, free and open source Linux distribution, developed by the Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock in August 1993. Debian is one of the oldest operating systems based on the Linux kerne ...
enabled the /usr merge by default in 2018.
GoboLinux also allows the user to have different versions of the same program installed concurrently (and even run them concurrently). Furthermore, it has been claimed that the package management index could never become unsynchronized with the filesystem, because references to nonexistent files simply become broken links, and thus become inactive. GoboLinux's filesystem changes also allow other innovations, such as an entirely different scripts-based boot system that does not use System V
Unix System V (pronounced: "System Five") is one of the first commercial versions of the Unix operating system. It was originally developed by AT&T and first released in 1983. Four major versions of System V were released, numbered 1, 2, 3, an ...
or BSD
The Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), also known as Berkeley Unix or BSD Unix, is a discontinued Unix operating system developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group (CSRG) at the University of California, Berkeley, beginni ...
style init systems or one of their replacements.
File hierarchy
 The design of GoboLinux was influenced by earlier systems such as
The design of GoboLinux was influenced by earlier systems such as NeXTSTEP
NeXTSTEP is a discontinued object-oriented, multitasking operating system based on the Mach kernel and the UNIX-derived BSD. It was developed by NeXT, founded by Steve Jobs, in the late 1980s and early 1990s and was initially used for its ...
, AtheOS
Syllable Desktop is a discontinued free and open-source lightweight hobbyist operating system for Pentium and compatible processors. Its purpose was to create an easy-to-use desktop operating system for the home and small office user. Its develop ...
, and BeOS
BeOS is a discontinued operating system for personal computers that was developed by Be Inc. It was conceived for the company's BeBox personal computer which was released in 1995. BeOS was designed for multitasking, multithreading, and a graph ...
, all of which adopted original filesystem structures while still maintaining a considerable degree of compatibility with Unix. At the root of the GoboLinux tree, there are five directories: Programs, Users, System, Data, and Mount.
"Compile" program
''Compile'' is a program that downloads, unpacks, compiles source code tarballs, and installs the resulting executable code, all with a single command (such asCompile foo) using simple compilation scripts known as "recipes".
The Compile system is somewhat similar to Gentoo's Portage
Portage or portaging ( CA: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a '' ...
system, which is based on the FreeBSD Ports
The FreeBSD Ports collection is a package management system for the FreeBSD operating system. Ports in the collection vary with contributed software. There were 38,487 ports available in February 2020 and 36,504 in September 2024. It has also be ...
collection. However, Portage is made for a traditional filesystem hierarchy, compatible with the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard
The Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) is a reference describing the conventions used for the layout of Unix-like systems. It has been made popular by its use in Linux distributions, but it is used by other Unix-like systems as well. It is main ...
, while Compile extends the capability of GoboLinux's distinctive filesystem hierarchy into the area of package management. Thus, in GoboLinux, the filesystem itself serves naturally as a kind of package manager database.
The Compile program was introduced in GoboLinux version 011. Before that, there were discussions about porting Gentoo's Portage system to GoboLinux and developing the port as a SourceForge.net project under the name ''GoboPortage''.
Compile's other features included:
; The use of each program's own download site
: The distribution's repository (or one of its mirrors) is only used for downloading recipes. Recipes may be downloaded on-the-fly or in batch.
; Minimalistic and declarative-oriented compilation scripts
: Typical "configure; make; make install" software may be scripted in two lines, greatly easing maintenance.
; Support of GoboLinux-style dependencies
: Software compiled "by hand" by the user is taken into account by a detection mechanism.
; Path-agnosticism
: It also works in a rootless GoboLinux installation (that is, inside a home directory
A home directory is a directory (file systems), file system directory on a multi-user operating system containing computer file, files for a given user (computing), user of the system. The specifics of the home directory (such as its name and loc ...
of any other distribution).
Releases
Releases have been numbered using theoctal
Octal (base 8) is a numeral system with eight as the base.
In the decimal system, each place is a power of ten. For example:
: \mathbf_ = \mathbf \times 10^1 + \mathbf \times 10^0
In the octal system, each place is a power of eight. For ex ...
base system. According to the authors, this scheme was chosen because it keeps the typical leading zero that is present in many free software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribut ...
version numbers (since a leading zero often indicates that a number is octal), and it is a play on the " version numbers race" that happened among Linux distributions around 1999. When read as decimal numbers, using octal numbers causes a deterministic "version bump" each eight releases. Up to version 013, GoboLinux made no "point releases", in order to avoid the implication that some releases were more stable than others. This tradition was broken with version 014.01, an update of 014 focused on bug fix
A patch is data that is intended to be used to modify an existing software resource such as a program or a file, often to fix bugs and security vulnerabilities. A patch may be created to improve functionality, usability, or performance. A pa ...
es.
Ports
GoboLinux is currently developed forx86-64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set architecture, instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new ope ...
. It was officially made for the i686
The P6 microarchitecture is the sixth-generation Intel x86 microarchitecture, implemented by the Pentium Pro microprocessor that was introduced in November 1995. It is frequently referred to as i686. It was planned to be succeeded by the NetBur ...
only until release 015, but at one point an incomplete port to the i386
The Intel 386, originally released as the 80386 and later renamed i386, is the third-generation x86 architecture microprocessor from Intel. It was the first 32-bit processor in the line, making it a significant evolution in the x86 archite ...
was made. Ports have also been made to embedded architectures, such as ARM
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between ...
and SuperH
SuperH (or SH) is a 32-bit reduced instruction set computing (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Hitachi and currently produced by Renesas. It is implemented by microcontrollers and microprocessors for embedded systems.
At the ...
; these tasks were achieved with Bootstrap, a tool developed especially to automate making ports.
Reception
LWN.net
LWN.net is a computing webzine with an emphasis on free software and software for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. It consists of a weekly issue, separate stories which are published most days, and threaded discussion attached to ever ...
reviewed GoboLinux 010 in 2004:
Linux.com wrote review about GoboLinux 013:
Jesse Smith from DistroWatch Weekly reviewed GoboLinux 015:
Smith also reviewed GoboLinux 016.
Name and logo
''Gobo'' is a fictional character.Not much is known about him, because those who saw him never survived to tell information about him.He also has a fictional loyal servant named ''Fibo''. GoboLinux's mascot ''Que'' is a
penguin
Penguins are a group of aquatic flightless birds from the family Spheniscidae () of the order Sphenisciformes (). They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere. Only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is equatorial, with a sm ...
wearing Fibo's clothes
Clothing (also known as clothes, garments, dress, apparel, or attire) is any item worn on a human human body, body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin s ...
.
References
External links
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Gobolinux Linux distributions without systemd Source-based Linux distributions Linux distributions Independent Linux distributions