The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".
[United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development]
A/RES/71/313
) The goals are:
No poverty,
zero hunger,
good health and well-being,
quality education,
gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing d ...
,
clean water and sanitation,
affordable and clean energy,
decent work and economic growth,
industry, innovation and infrastructure,
Reduced Inequality,
Sustainable Cities and Communities,
Responsible Consumption and Production,
Climate Action,
Life Below Water,
Life On Land,
Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions,
Partnerships for the Goals. The SDGs emphasize the interconnected environmental, social and economic aspects of
sustainable development by putting
sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livin ...
at their center.
The SDGs were formulated in 2015 by the
United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Cur ...
(UNGA) as part of the
Post-2015 Development Agenda, which sought to create a future global development framework to succeed the
Millennium Development Goals, which ended that year. They were formally articulated and adopted in a
UNGA Resolution called the 2030 Agenda, known colloquially as Agenda 2030. On 6 July 2017, the SDGs were made more "actionable" by a UNGA resolution that identifies
specific targets for each goal and provides indicators to measure progress.
[United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development]
A/RES/71/313
) Most targets are to be achieved by 2030, although some have no end date.
There are cross-cutting issues and synergies between the different goals; for example, for SDG 13 on climate action, the
IPCC sees robust synergies with SDGs 3 (health), 7 (clean energy), 11 (cities and communities), 12 (responsible consumption and production) and 14 (oceans).
Conversely, critics and observers have also identified
trade-off
A trade-off (or tradeoff) is a situational decision that involves diminishing or losing one quality, quantity, or property of a set or design in return for gains in other aspects. In simple terms, a tradeoff is where one thing increases, and anot ...
s between the goals,
such as between ending hunger and promoting environmental sustainability.
Other concerns include there being too many goals (resulting in compounding trade-offs), weak emphasis on
environmental sustainability, and difficulties with tracking qualitative indicators.
The SDGs are monitored by the UN
High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development, an annual forum under the auspices of the
United Nations Economic and Social Council
The United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC; french: links=no, Conseil économique et social des Nations unies, ) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, responsible for coordinating the economic and social fields ...
. However, it has so far failed to act as an orchestrator to promote system-wide coherence due to a lack of political leadership owing to divergent
national interest
The national interest is a sovereign state's goals and ambitions (economic, military, cultural, or otherwise), taken to be the aim of government.
Etymology
The Italian phrase ''ragione degli stati'' was first used by Giovanni della Casa around ...
s.
To facilitate monitoring of progress on SDG implementation, the online "SDG Tracker" was launched in June 2018 to present all available data across all indicators.
The
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified ...
had serious negative impacts on all 17 SDGs in 2020;
[United Nations Economic and Social Council (2020]
Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals Report of the Secretary-General
, High-level political forum on sustainable development, convened under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council (E/2020/57), 28 April 2020 a scientific assessment released in 2022 determined that the world is not on track to achieve the SDGs by 2030 and concluded the SDGs have so far had only limited political effects in global, national and local governance.
Adoption by the UN General Assembly
On 25 September 2015, the 193 countries of the UN General Assembly adopted the 2030 Development Agenda titled "Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development".
This agenda has 92 paragraphs. Paragraph 59 outlines the 17 Sustainable Development Goals and the associated 169 targets and 232 indicators.
The SDGs were an outcome from a UN conference that was not criticized by any major
non-governmental organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from g ...
(NGO). Instead, the SDGs received broad support from many NGOs.
Content
Structure of goals, targets and indicators
The lists of targets and indicators for each of the 17 SDGs was published in a UN resolution in July 2017.
Each goal typically has 812 targets, and each target has between one and four indicators used to measure progress toward reaching the targets. The targets are either "outcome" targets (circumstances to be attained) or "means of implementation" targets.
The latter targets were introduced late in the process of negotiating the SDGs to address the concern of some Member States about how the SDGs were to be achieved.
Goal 17
Sustainable Development Goal 17 (SDG 17 or Global Goal 17) is about "partnerships for the goals." One of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015, the official wording is: "Strengthen the means of implement ...
is wholly about how the SDGs will be achieved.
The numbering system of targets is as follows: "Outcome targets" use numbers, whereas "means of implementation targets" use lower case letters.
For example,
SDG 6 has a total of 8 targets. The first six are outcome targets and are labeled Targets 6.1 to 6.6. The final two targets are "means of
implementation targets" and are labeled as Targets 6.a and 6.b.
The
United Nations Statistics Division
The United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD), formerly the United Nations Statistical Office, serves under the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA) as the central mechanism within the Secretariat of the United Nations t ...
(UNSD) website provides a current official indicator list which includes all updates until the 51st session Statistical Commission in March 2020.
The indicators were classified into three tiers based on their level of methodological development and the availability of data at the global level.
Tier 1 and Tier 2 are indicators that are conceptually clear, have an internationally established
methodology
In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bri ...
, and data are regularly produced by at least some countries. Tier 3 indicators had no internationally established methodology or standards. The global indicator framework was adjusted so that Tier 3 indicators were either abandoned, replaced or refined.
As of 17 July 2020, there were 231 unique indicators.
Reviews of indicators
The indicator framework was comprehensively reviewed at the 51st session of the
United Nations Statistical Commission in 2020. It will be reviewed again in 2025.
At the 51st session of the Statistical Commission (held in
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
from 3–6 March 2020) a total of 36 changes to the global indicator framework were proposed for the Commission's consideration. Some indicators were replaced, revised or deleted.
Between 15 October 2018 and 17 April 2020, other changes were made to the indicators. Yet their measurement continues to be fraught with difficulties.
Listing of 17 goals with their targets and indicators
Many goals build on existing agreements and are integral parts of other political processes, such as international agreements on biodiversity, climate, oceans or standards and programs set by the
International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
, the World Health Organization and so forth.
Goal 1: No poverty
SDG 1 is to: "End poverty in all its forms everywhere". Achieving SDG 1 would end
extreme poverty
Extreme poverty, deep poverty, abject poverty, absolute poverty, destitution, or penury, is the most severe type of poverty, defined by the United Nations (UN) as "a condition characterized by severe deprivation of basic human needs, includi ...
globally by 2030. A study published in September 2020 found that poverty increased by 7 per cent in just a few months due to the
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified ...
, even though it had been steadily decreasing for the last 20 years.
[BMGF (2020]
Covid-19 A Global Perspective - 2020 Goalkeepers Report
, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Seattle, USA
Goal 2: Zero hunger (No hunger)

SDG 2 is to: "End
hunger
In politics, humanitarian aid, and the social sciences, hunger is defined as a condition in which a person does not have the physical or financial capability to eat sufficient food to meet basic nutritional needs for a sustained period. In t ...
, achieve
food security and improved nutrition, and promote
sustainable agriculture". Globally, 1 in 9 people are undernourished, the vast majority of whom live in developing countries. Under nutrition causes wasting or severe wasting of 52 million children worldwide.
It contributes to nearly half (45%) of deaths in children under five – 3.1 million children per year.
Goal 3: Good health and well-being

SDG 3
Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3 or Global Goal 3), regarding "Good Health and Well-being", is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The official wording is: "To ensure healthy lives and promo ...
is to: "Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages". Significant strides have been made in increasing life expectancy and reducing some of the common causes of child and maternal mortality. Between 2000 and 2016, the worldwide under-five
mortality rate decreased by 47 percent (from 78 deaths per 1,000 live births to 41 deaths per 1,000 live births).
Still, the number of children dying under age five is very high: 5.6 million in 2016.
A 2018 study in the journal ''
Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans ar ...
'' found that while "nearly all African countries demonstrated improvements for children under 5 years old for stunting, wasting, and underweight... much, if not all of the continent will fail to meet the Sustainable Development Goal target—to end
malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
by 2030".
Goal 4: Quality education
SDG 4
Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4 or Global Goal 4) is about quality education and is among the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in September 2015.United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Asse ...
is to: "Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all". Major progress has been made in access to education, specifically at the
primary school
A primary school (in Ireland, the United Kingdom, Australia, Trinidad and Tobago, Jamaica, and South Africa), junior school (in Australia), elementary school or grade school (in North America and the Philippines) is a school for primary ed ...
level, for both boys and girls. The number of out-of-school children has almost halved from 112 million in 1997 to 60 million in 2014. In terms of the progress made, global participation in tertiary education reached 224 million in 2018, equivalent to a gross enrollment ratio of 38%.
Goal 5: Gender equality
SDG 5 is to: "Achieve
gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing d ...
and empower all women and girls". In 2020, representation by women in single or lower houses of
national parliament reached 25 per cent, up slightly from 22 per cent in 2015.
Women now have better access to decision-making positions at the local level, holding 36 per cent of elected seats in local deliberative bodies, based on data from 133 countries and areas. Whilst
female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) is becoming less common, at least 200 million girls and women have been subjected to this harmful practice.
Goal 6: Clean water and sanitation
SDG 6 is to: "Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all".
The eight targets are measured by 11 indicators. The Joint Monitoring Programme (
JMP) of World Health Organisation
WHO And United Nations International Children's Emergency fund
UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid t ...
reported in 2017 that 4.5 billion people currently do not have
safely managed sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems a ...
.
[WHO and UNICEF (2017]
Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: 2017 Update and SDG Baselines
. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), 2017 Also in 2017, only 71 per cent of the global population used safely managed drinking water, and 2.2 billion persons were still without safely managed drinking water. With regards to
water stress
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity: physical or economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is whe ...
: "In 2017, Central and Southern Asia and
Northern Africa registered very high water stress – defined as the ratio of fresh water withdrawn to total renewable freshwater resources – of more than 70 per cent".
Official development assistance
Official development assistance (ODA) is a category used by the Development Assistance Committee (DAC) of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) to measure foreign aid. The DAC first adopted the concept in 1969. It i ...
(ODA)
disbursements to the water sector increased to $9 billion in 2018.
Evidence shows that both supply- and demand-side interventions financed by aid can contribute to promoting access to water, but consistent long-term investments are needed.
Goal 7: Affordable and clean energy
 SDG 7
SDG 7 is to: "Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all".
Progress in expanding access to electricity has been made in several countries, notably
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
,
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million pe ...
, and
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
.
[IEA, IRENA, UNSD, WB, WHO (2019)]
Tracking SDG 7: The Energy Progress Report 2019
, Washington DC (o
Tracking SDG 7 website
) The global population without access to electricity decreased to about 840 million in 2017 from 1.2 billion in 2010 (
sub-Saharan Africa remains the region with the largest access deficit).
accounted for 17.5% of global total energy consumption in 2016.
Of the three end uses of
renewables
Goal 8: Decent work and economic growth
SDG 8
Sustainable Development Goal 8 (SDG 8 or Global Goal 8) is about "decent work and economic growth" and is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals which were established by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015. The full title is to "F ...
is to: "Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all".
Over the past five years, economic growth in least developed countries has been increasing at an average rate of 4.3 per cent.
In 2018, the global growth rate of real Lists of countries by GDP per capita">GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is the measurement of prices i ...
was 2 per cent. In addition, the rate for least developed countries was 4.5 per cent in 2018 and 4.8 per cent in 2019, less than the 7 per cent growth rate targeted in SDG 8.
In 2019, 22 per cent of the world's young people were not in employment, education or training, a figure that has hardly changed since 2005.
Addressing youth
employment means finding solutions with and for young people who are seeking a decent and productive job. Such solutions should address both supply, i.e. education, skills development and training, and demand. In 2018, the number of women engaged in the labor force was put at 48 per cent while that of men was 75 per cent.
Goal 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
SDG 9 is to: "Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation". In 2019, 14% of the world's workers were employed in
manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a ...
activities. This percentage has not changed much since 2000. The share of manufacturing employment was the largest in Eastern and South-Eastern Asia (18 percent) and the smallest in sub-Saharan Africa (6 percent).
The intensity of global
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
emissions has declined by nearly one quarter since 2000, showing a general decoupling of carbon dioxide emissions from GDP growth.
As at 2020, nearly the entire world population lives in an area covered by a mobile network.
Millions of people are still unable to access the internet due to cost, coverage, and other reasons.
It is estimated that just 53% of the world's population are currently internet users.
Goal 10: Reduced inequality
SDG 10
Sustainable Development Goal 10 (Goal 10 or SDG 10) is about reduced inequality and is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The full title is: "Reduce inequality within and among countries".Unite ...
is to: "Reduce
income inequality within and among countries". In 73 countries during the period 2012–2017, the bottom 40 per cent of the population saw its incomes grow. Still, in all countries with data, the bottom 40 per cent of the population received less than 25 per cent of the overall income or consumption.
Women are more likely to be victims of discrimination than men. Among those with disabilities, 3 in 10 personally experienced discrimination, with higher levels still among women with disabilities. The main grounds of discrimination mentioned by these women was not the disability itself, but religion, ethnicity and sex, pointing to the urgent need for measures to tackle multiple and intersecting forms of discrimination.
[United Nations (2020]
Sustainable development goals report
, New York In 2019, 54 per cent of countries have a comprehensive set of policy measures to facilitate orderly, safe, regular and responsible migration and mobility of people.
Goal 11: Sustainable cities and communities
SDG 11 is to: "Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable". The number of slum dwellers reached more than 1 billion in 2018, or 24 per cent of the urban population.
The number of people living in urban slums is highest in Eastern and South-Eastern Asia,
sub-Saharan Africa and Central and Southern Asia. In 2019, only half of the world's urban population had convenient access to public transport, defined as living within 500 metres' walking distance from a low-capacity transport system (such as a bus stop) and within 1 km of a high-capacity transport system (such as a railway).
In the period 1990–2015, most
urban area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, ...
s recorded a general increase in the extent of built-up area per person.
Goal 12: Responsible consumption and production
SDG 12
Sustainable Development Goal 12 (SDG 12 or Global Goal 1), titled "responsible consumption and production", is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The official wording of SDG 12 is "Ensure su ...
is to: "Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns". By 2019, 79 countries and the European Union have reported on at least one national policy instrument to promote
sustainable consumption and production patterns.
This was done to work towards the implementation of the "10-Year Framework of Programmes on Sustainable Consumption and Production Patterns".
Global fossil fuel subsidies in 2018 were $400 billion.
This was double the estimated subsidies for renewables and is detrimental to the task of reducing global carbon dioxide emissions.
To ensure that plastic products are more sustainable, thus reducing plastic waste, changes such as decreasing usage and increasing the circularity of the plastic economy are expected to be required. An increase in domestic recycling and a reduced reliance on the global plastic waste trade are other actions that might help meet the goal.
Goal 13: Climate action
SDG 13 is to: "Take urgent action to combat
climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
and its impacts by regulating emissions and promoting developments in renewable energy". Accelerating climate actions and progress towards a
just transition is essential to reducing climate risks and addressing sustainable development priorities, including water, food and human security (robust evidence, high agreement). Accelerating action in the context of sustainable development involves not only expediting the pace of change (speed) but also addressing the underlying drivers of vulnerability and high emissions (quality and depth of change) and enabling diverse communities, sectors, stakeholders, regions and cultures (scale and breadth of change) to participate in just, equitable and inclusive processes that improve the health and well-being of people and the planet.
Goal 14: Life below water
SDG 14 is to: "Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for
sustainable development".
The current efforts to protect oceans, marine environments and small-scale fishers are not meeting the need to protect the resources.
One of the key drivers of global overfishing is
illegal fishing
Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing (IUU) is an issue around the world. Fishing industry observers believe IUU occurs in most fisheries, and accounts for up to 30% of total catches in some important fisheries.
Illegal fishing takes p ...
. It threatens marine ecosystems, puts food security and regional stability at risk, and is linked to major human rights violations and even organized crime.
Increased ocean temperatures and oxygen loss act concurrently with
ocean acidification and constitute the "deadly trio" of climate change pressures on the marine environment.

One indicator (14.1.1b) under Goal 14 specifically relates to reducing impacts from
marine plastic pollution.
Goal 15: Life on land
SDG 15 is to: "Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
s, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land
degradation and halt
biodiversity loss". The proportion of forest area fell, from 31.9 per cent of total land area in 2000 to 31.2 per cent in 2020, representing a net loss of nearly 100 million ha of the world's forests.
This was due to decreasing forest area decreased in Latin America, sub-Saharan Africa and South-Eastern Asia, driven by deforestation for agriculture.
Desertification affects as much as one-sixth of the world's population, 70% of all drylands, and one-quarter of the total land area of the world. It also leads to spreading
poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse < ...
and the
degradation of billion hectares of
cropland. A report in 2020 stated that globally, the
species extinction risk has worsened by about 10 per cent over the past three decades.
Goal 16: Peace, justice and strong institutions
SDG 16 is to: "Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels". With more than a quarter of children under 5 unregistered worldwide as of 2015, about 1 in 5 countries will need to accelerate progress to achieve universal birth registration by 2030.
Data from 38 countries over the past decade suggest that high-income countries have the lowest prevalence of
bribery
Bribery is the offering, giving, receiving, or soliciting of any item of value to influence the actions of an official, or other person, in charge of a public or legal duty. With regard to governmental operations, essentially, bribery is "Co ...
(an average of 3.7 per cent), while lower-income countries have high levels of bribery when accessing public services (22.3 per cent).
Goal 17: Partnership for the goals
SDG 17
Sustainable Development Goal 17 (SDG 17 or Global Goal 17) is about "partnerships for the goals." One of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015, the official wording is: "Strengthen the means of implement ...
is to: "Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development". This goal has 19 outcome targets and 24 indicators. Increasing
international cooperation is seen as vital to achieving each of the 16 previous goals.
Goal 17 is included to assure that countries and organizations cooperate instead of compete. Developing multi-stakeholder partnerships to share knowledge, expertise,
technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scie ...
, and financial support is seen as critical to overall success of the SDGs. The goal encompasses improving north–south and
South-South cooperation, and
public-private partnerships which involve civil societies are specifically mentioned.
With US$5 trillion to $7 trillion in annual investment required to achieve the SDGs, total official
development assistance reached US$147.2 billion in 2017. This, although steady, is below the set target.
In 2016, six countries met the international target to keep official development assistance at or above 0.7 percent of
gross national income.
brought on by conflict or
natural disasters have continued to demand more financial resources and
aid. Even so, many countries also require official development assistance to encourage growth and trade.
Cross-cutting issues and synergies

To achieve
sustainable development, three aspects or dimensions need to come together: The economic, socio-political, and environmental dimensions are all critically important and interdependent.
Progress will require
multidisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several other fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, ec ...
and
trans-disciplinary research across all three sectors. This proves difficult when major governments fail to support it.
Sustainable development can enhance sectoral integration and social inclusion (robust evidence, high agreement). Inclusion merits attention because equity within and across countries is critical to transitions that are not simply rapid but also sustainable and just. Resource shortages, social divisions, inequitable distributions of wealth, poor infrastructure and limited access to advanced technologies can constrain the options and capacities for developing countries to achieve sustainable and just transitions (medium evidence, high agreement) .
According to the UN, the target is to reach the community farthest behind. Commitments should be transformed into effective actions requiring a correct perception of target populations. Data or information must address all vulnerable groups such as children, elderly folks,
persons with disabilities
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physical, s ...
,
refugee
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution. s,
indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
,
migrants
Migrant may refer to:
Human migration
*Human migration
*Emigration, leaving one's resident country with the intent to settle elsewhere
*Immigration, movement into a country with the intent to settle
* Economic migrant, someone who emigrates from o ...
, and
internally-displaced persons.
Cross cutting issues include for example gender equality, education, culture and health. These are just some examples of various interlinkages inherent in the SDGs.
Gender equality
The widespread consensus is that progress on all of the SDGs will be stalled if women's empowerment and gender equality are not prioritized, and treated holistically. The SDGs look to policy makers as well as private sector executives and board members to work toward gender equality.
Statements from diverse sources, such as the
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD),
UN Women and the
World Pensions Forum, have noted that investments in women and girls have positive impacts on economies. National and global development investments in women and girls often exceed their initial scope.
Gender equality is mainstreamed throughout the SDG framework by ensuring that as much sex-disaggregated data as possible are collected.
[UNESCO (2019]
Culture , 2030 Indicators
, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Paris, France, , CC-BY-ND 3.0 IGO
Education
 Education for sustainable development
Education for sustainable development (ESD) is explicitly recognized in the SDGs as part of Target 4.7 of the SDG on education.
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
promotes the
Global Citizenship Education (GCED) as a complementary approach. At the same time, it is important to emphasize ESD's importance for all the other 16 SDGs. With its overall aim to develop cross-cutting
sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livin ...
competencies in learners, ESD is an essential contribution to all efforts to achieve the SDGs. This would enable individuals to contribute to sustainable development by promoting societal, economic and political change as well as by transforming their own behavior.
Culture
Culture is explicitly referenced in
SDG 11 Target 4 ("Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world's cultural and natural heritage"). However, culture is seen as a cross-cutting theme because it impacts several SDGs.
For example, culture plays a role in SDGs related to:
* environment and resilience (Targets 11.4 Cultural & natural heritage, 11.7 Inclusive public spaces, 12.b Sustainable tourism management, 16.4 Recovery of stolen assets),
* prosperity and livelihoods (Targets 8.3 Jobs, entrepreneurship & innovation; 8.9 Policies for sustainable tourism),
* knowledge and skills,
* inclusion and participation (Targets 11.7 Inclusive public spaces, 16.7 Participatory decision-making).
Health
SDGs 1 to 6 directly address
health disparities
Health equity arises from access to the social determinants of health, specifically from wealth, power and prestige. Individuals who have consistently been deprived of these three determinants are significantly disadvantaged from health inequiti ...
, primarily in developing countries.
These six goals address key issues in
Global Public Health,
Poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse < ...
, Hunger and
Food security, Health, Education, Gender equality and
women's empowerment
Women's empowerment (or female empowerment) may be defined in several ways, including accepting women's viewpoints, making an effort to seek them and raising the status of women through education, awareness, literacy, and training.Kabeer, Naila ...
, and
water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
and
sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation syste ...
.
Public health officials can use these goals to set their own agenda and plan for smaller scale initiatives for their organizations. These goals are designed to lessen the burden of disease and inequality faced by developing countries and lead to a healthier future.
The links between the various sustainable development goals and
public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
are numerous and well established:
* Living below the poverty line is attributed to poorer health outcomes and can be even worse for persons living in developing countries where
extreme poverty
Extreme poverty, deep poverty, abject poverty, absolute poverty, destitution, or penury, is the most severe type of poverty, defined by the United Nations (UN) as "a condition characterized by severe deprivation of basic human needs, includi ...
is more common. A child born into poverty is twice as likely to die before the age of five compared to a child from a wealthier family.
* The detrimental effects of hunger and
malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
that can arise from systemic challenges with food security are enormous. The
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
estimates that 12.9 percent of the population in developing countries is undernourished.
* Health challenges in the developing world are enormous, with "only half of the women in developing nations receiving the recommended amount of healthcare they need.
*
Educational equity has yet to be reached in the world. Public health efforts are impeded by this, as a lack of education can lead to poorer health outcomes. This is shown by children of mothers who have no education having a lower survival rate compared to children born to mothers with primary or greater levels of education.
Cultural differences in the role of women vary by country, many
gender inequalities are found in developing nations. Combating these inequalities has shown to also lead to a better public health outcome.
* In studies done by the
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
on populations in developing countries, it was found that when women had more control over household resources, the children benefit through better access to food, healthcare, and education.
* Basic
sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation syste ...
resources and access to clean sources of water are a basic
human right
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
. However, 1.8 billion people globally use a source of drinking water that is contaminated by
feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a rela ...
, and 2.4 billion people lack access to basic sanitation facilities like
toilet
A toilet is a piece of sanitary hardware that collects human urine and Human feces, feces, and sometimes toilet paper, usually for disposal. Flush toilets use water, while dry toilet, dry or non-flush toilets do not. They can be designed for ...
s or
pit latrines.
A lack of these resources is what causes approximately 1000 children a day to die from
diarrheal diseases
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin wi ...
that could have been prevented from better water and
sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation syste ...
infrastructure.
Synergies
Synergies amongst the SDGs are "the good
antagonists of trade-offs".
With regards to SDG 13 on climate action, the
IPCC sees robust synergies particularly for the SDGs 3 (health), 7 (clean energy), 11 (cities and communities), 12 (responsible consumption and production) and 14 (oceans).
[IPCC, 2018]
Global Warming of 1.5°C.An IPCC Special Report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, H.-O. Pörtner, D. Roberts, J. Skea, P.R. Shukla, A. Pirani, W. Moufouma-Okia, C. Péan, R. Pidcock, S. Connors, J.B.R. Matthews, Y. Chen, X. Zhou, M.I. Gomis, E. Lonnoy, T. Maycock, M. Tignor, and T. Waterfield (eds.)]. In Press
To meet SDG 13 and other SDGs, sustained long-term investment in green innovation is required: to Decarbonization, decarbonize the physical capital stock – energy, industry, and transportation infrastructure – and ensure its resilience to a changing future climate; to preserve and enhance
natural capital – forests, oceans, and wetlands; and to train people to work in a climate-neutral economy.
Conceptual problem areas
Competing and too many goals
A commentary in ''
The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Econ ...
'' in 2015 argued that 169 targets for the SDGs is too many, describing them as "sprawling, misconceived" and "a mess" compared to the eight
Millennium Development Goals (MDGs).
The goals are said to ignore local context. All other 16 goals might be contingent on achieving SDG 1, ending poverty, which should have been at the top of a very short list of goals.
The
trade-off
A trade-off (or tradeoff) is a situational decision that involves diminishing or losing one quality, quantity, or property of a set or design in return for gains in other aspects. In simple terms, a tradeoff is where one thing increases, and anot ...
s among the 17 SDGs are a difficult barrier to
sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livin ...
and might even prevent their realization.
For example these are three difficult trade-offs to consider: "How can ending hunger be reconciled with environmental sustainability? (SDG targets 2.3 and 15.2) How can economic growth be reconciled with environmental sustainability? (SDG targets 9.2 and 9.4) How can income inequality be reconciled with economic growth? (SDG targets 10.1 and 8.1)."
Weak on environmental sustainability

Scholars have criticized that the Sustainable Development Goals fail to recognize that planetary, people and prosperity concerns are all part of one earth system, and that the protection of
planetary integrity should not be a means to an end, but an end in itself.
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
/ref> A principal concern is that the SDGs remain fixated on the idea that economic growth is foundational to achieve all pillars of sustainable development.environmental protection
Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment by individuals, organizations and governments. Its objectives are to conserve natural resources and the existing natural environment and, where possible, to repair da ...
arise not only from their ability to steer, but also from the fact that they do not seem to prioritize environmental protection in the first place.Goal 13
Sustainable Development Goal 13 (SDG 13 or Global Goal 13) is about climate action and is one of 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015. The official mission statement of this goal is to "Take ...
, 14 and 15. While including these explicit environmental goals might advance environmental protection, some also argue that Goals 13, 14 and 15 could compartmentalize environmental issues (climate, land and oceans). The goals do not pursue planetary integrity as such, but do recognize the importance of protecting environmental aspects such as climate, land and the oceans.trade-off
A trade-off (or tradeoff) is a situational decision that involves diminishing or losing one quality, quantity, or property of a set or design in return for gains in other aspects. In simple terms, a tradeoff is where one thing increases, and anot ...
s, root causes of poverty and environmental degradation, and social justice issues".river delta
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, or (more ra ...
s, mountain areas)
* Better understanding of feedbacks across scales in space (e.g., through globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences), is the process of foreign relation ...
) and time (e.g., affecting future generations) that could ultimately determine the success or failure of the SDGs.
Ethical orientation
There are concerns about the ethical orientation of the SDGs: their focus seems to remain on "growth and use of resources ... and tdeparts from an individual, not collective, point of view"; and they remain "underpinned by strong (Western) modernist notions of development: sovereignty of humans over their environment (anthropocentricism), individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote the exercise of one's goals and desires and to value independence and self-relia ...
, competition, freedom (rights rather than duties), self-interest, belief in the market leading to collective welfare, private property (protected by legal systems), rewards based on merit, materialism
Materialism is a form of philosophical monism which holds matter to be the fundamental substance in nature, and all things, including mental states and consciousness, are results of material interactions. According to philosophical material ...
, quantification of value, and instrumentalization of labor".
Difficulties with tracking qualitative indicators
Regarding the targets of the SDGs, there is generally weak evidence linking the "means of implementation" to outcomes.
Difficulties in achieving impact
There is a lack of impact of the SDGs so far, especially in the are of protecting planetary integrity.economic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals a ...
-oriented sustainable development as their core orientation.
Monitoring mechanism
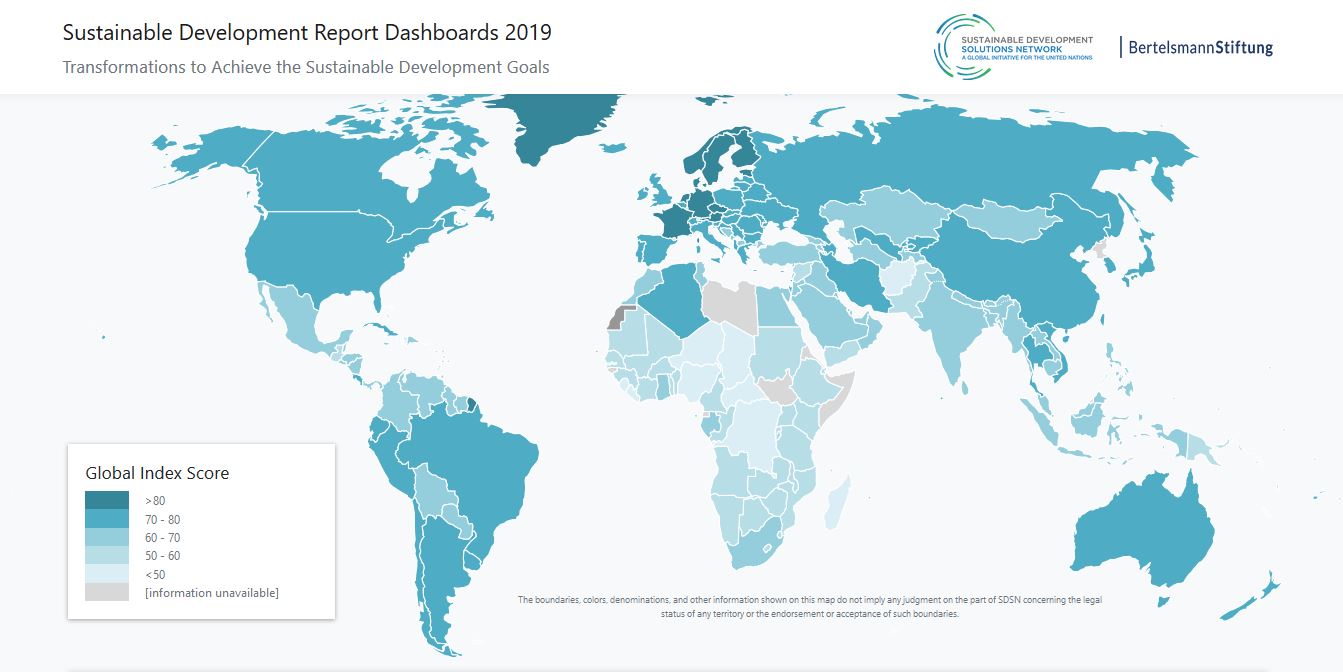
UN High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development (HLPF)
As part of a larger reform, governments decided to terminate the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development
The United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), also known as the Rio Conference or the Earth Summit (Portuguese: ECO92), was a major United Nations conference held in Rio de Janeiro from June 3 to June 14, 1992.
Earth S ...
and to establish in its place a High-level Political Forum on Sustainable Development.United Nations economic and Social Council
The United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC; french: links=no, Conseil économique et social des Nations unies, ) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, responsible for coordinating the economic and social fields ...
. In July 2020 the meeting took place online for the first time due to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified ...
. The theme was "Accelerated action and transformative pathways: realizing the decade of action and delivery for sustainable development" and a ministerial declaration was adopted.national interest
The national interest is a sovereign state's goals and ambitions (economic, military, cultural, or otherwise), taken to be the aim of government.
Etymology
The Italian phrase ''ragione degli stati'' was first used by Giovanni della Casa around ...
s.
Monitoring tools and websites
The online publication SDG-Tracker was launched in June 2018 and presents data across all available indicators.Our World in Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, climate change, war, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Change Data Lab, a r ...
database and is also based at the University of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the world's second-oldest university in contin ...
.[Ritchie, Roser, Mispy, Ortiz-Ospina. "Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals." ]
SDG-Tracker.org
, website'' (2018). The publication has global coverage and tracks whether the world is making progress towards the SDGs. It aims to make the data on the 17 goals available and understandable to a wide audience.
Reporting on progress
Overall status
Overall status reports made the following statements regarding  SDG 2 is to: "End
SDG 2 is to: "End 
 SDG 7 is to: "Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all". Progress in expanding access to electricity has been made in several countries, notably
SDG 7 is to: "Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all". Progress in expanding access to electricity has been made in several countries, notably  One indicator (14.1.1b) under Goal 14 specifically relates to reducing impacts from marine plastic pollution.
One indicator (14.1.1b) under Goal 14 specifically relates to reducing impacts from marine plastic pollution.
 To achieve sustainable development, three aspects or dimensions need to come together: The economic, socio-political, and environmental dimensions are all critically important and interdependent. Progress will require
To achieve sustainable development, three aspects or dimensions need to come together: The economic, socio-political, and environmental dimensions are all critically important and interdependent. Progress will require  Scholars have criticized that the Sustainable Development Goals fail to recognize that planetary, people and prosperity concerns are all part of one earth system, and that the protection of planetary integrity should not be a means to an end, but an end in itself.
Scholars have criticized that the Sustainable Development Goals fail to recognize that planetary, people and prosperity concerns are all part of one earth system, and that the protection of planetary integrity should not be a means to an end, but an end in itself.