Gitche Gumee on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe
 The
The
 Lake Superior has a surface area of , which is approximately the size of
Lake Superior has a surface area of , which is approximately the size of
 Lake Superior is fed by more than 200 rivers, including the
Lake Superior is fed by more than 200 rivers, including the
 The lake's average surface elevation is
The lake's average surface elevation is
 The largest island in Lake Superior is
The largest island in Lake Superior is
 The rocks of Lake Superior's northern shore date back to the early history of the earth. During the
The rocks of Lake Superior's northern shore date back to the early history of the earth. During the 
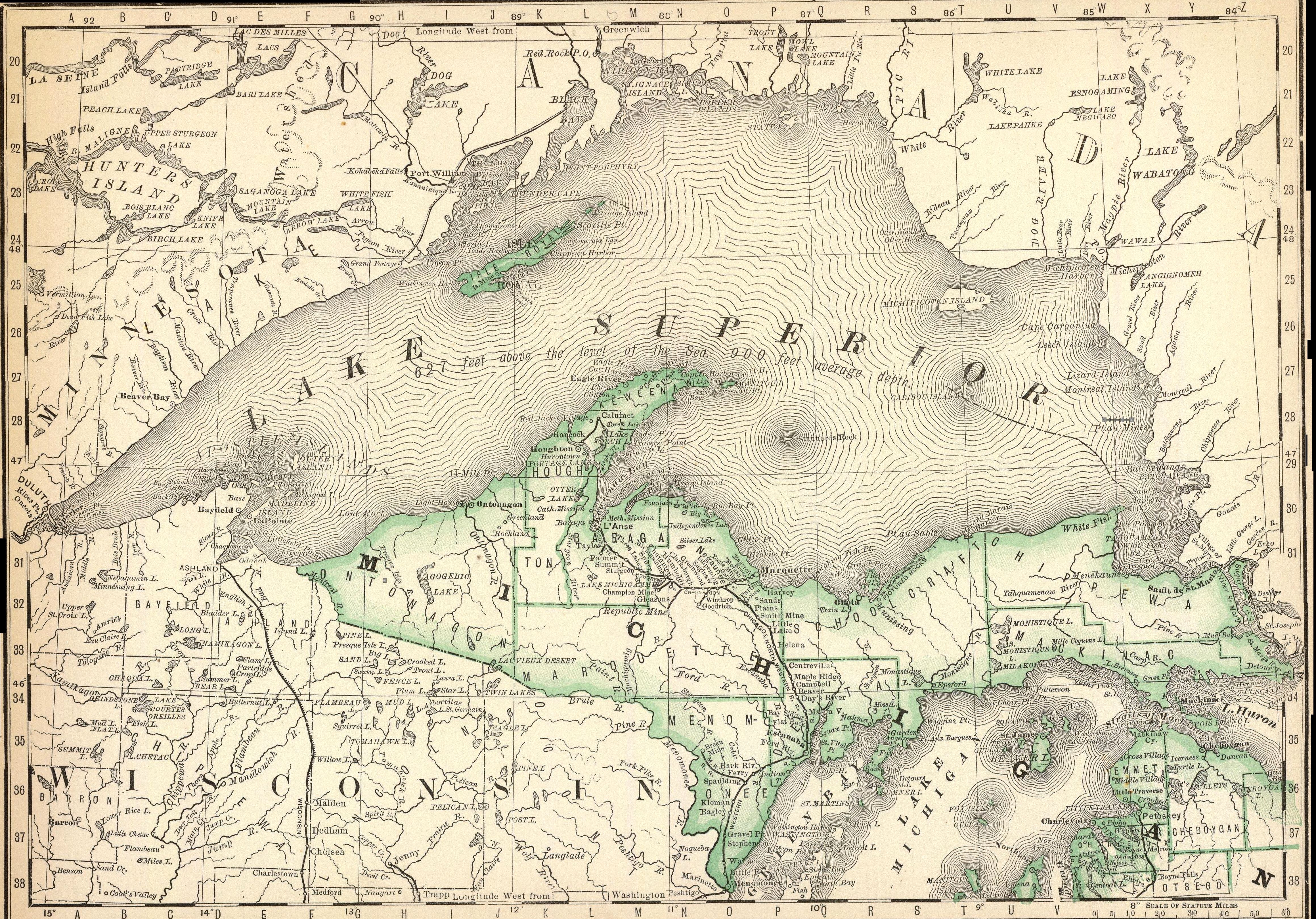 The first people came to the Lake Superior region 10,000 years ago after the retreat of the glaciers in the Last Glacial Period. They are known as the Plano, and they used stone-tipped spears to hunt caribou on the northwestern side of Lake Minong. The Shield
The first people came to the Lake Superior region 10,000 years ago after the retreat of the glaciers in the Last Glacial Period. They are known as the Plano, and they used stone-tipped spears to hunt caribou on the northwestern side of Lake Minong. The Shield  The
The  In the 18th century, as the booming fur trade supplied Europe with
In the 18th century, as the booming fur trade supplied Europe with


Lake Superior NOAA nautical chart #14961 online
International Lake Superior Board of Control
Great Lakes Coast Watch
Parks Canada - Lake Superior National Marine Conservation Area
Minnesota Sea Grant Lake Superior Page
Lake Superior Trials
{{DEFAULTSORT:Superior, Lake Lakes of Michigan Lakes of Wisconsin Lakes of Minnesota Lakes of Ontario Great Lakes Waterway Upper Peninsula of Michigan Lakes of Algoma District Lakes of Thunder Bay District Mesoproterozoic rifts and grabens Canada–United States border International lakes of North America *Superior
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad s ...
is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh water. The northern and westernmost of the Great Lakes of North America
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lake ...
, it straddles the Canada–United States border
The border between Canada and the United States is the longest international border in the world. The terrestrial boundary (including boundaries in the Great Lakes, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is long. The land border has two sections: Can ...
with the province of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
to the north and east, and the states of Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minne ...
to the northwest and Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
and Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
to the south. It drains into Lake Huron
Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrologically, it comprises the easterly portion of Lake Michigan–Huron, having the same surface elevation as Lake Michigan, to which it is connected by the , Straits of Ma ...
via St. Marys River, then through the lower Great Lakes to the St. Lawrence River and the Atlantic Ocean.
Name
 The
The Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
name for the lake is ''gichi-gami'' (in syllabics: , pronounced ''gitchi-gami'' or ''kitchi-gami'' in different dialects), meaning "great sea". Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (February 27, 1807 – March 24, 1882) was an American poet and educator. His original works include " Paul Revere's Ride", '' The Song of Hiawatha'', and '' Evangeline''. He was the first American to completely tra ...
wrote this name as "Gitche Gumee" in the poem ''The Song of Hiawatha
''The Song of Hiawatha'' is an 1855 epic poem in trochaic tetrameter by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow which features Native American characters. The epic relates the fictional adventures of an Ojibwe warrior named Hiawatha and the tragedy of his ...
'', as did Gordon Lightfoot
Gordon Meredith Lightfoot Jr. (born November 17, 1938) is a Canadian singer-songwriter and guitarist who achieved international success in folk, folk-rock, and country music. He is credited with helping to define the folk-pop sound of the 19 ...
in his song " The Wreck of the ''Edmund Fitzgerald''".
According to other sources, the full Ojibwe name is ''Ojibwe Gichigami'' ("Ojibwe's Great Sea") or ''Anishinaabe Gichigami'' ("Anishinaabe
The Anishinaabeg (adjectival: Anishinaabe) are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe (including Saulteaux and Oji-Cree), Odawa, Potawato ...
's Great Sea"). The 1878 dictionary by Father Frederic Baraga, the first one written for the Ojibway language, gives the Ojibwe name as ''Otchipwe-kitchi-gami'' (a transliteration of ''Ojibwe Gichigami'').
In the 17th century, the first French explorers approached the great inland sea by way of the Ottawa River
The Ottawa River (french: Rivière des Outaouais, Algonquin: ''Kichi-Sìbì/Kitchissippi'') is a river in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. It is named after the Algonquin word 'to trade', as it was the major trade route of Eastern ...
and Lake Huron; they referred to their discovery as ''le lac supérieur'' (the upper lake, i.e. above Lake Huron). Some 17th-century Jesuit missionaries referred to it as ''Lac Tracy'' (for Alexandre de Prouville de Tracy
Marquis Alexandre de Prouville de Tracy (c. 1596 or 1603 – 1670) was a French aristocrat, statesman, and military leader. He was the seigneur of Tracy-le-Val and Tracy-le-Mont (Picardy).
Life
The Marquis de Tracy first made his name as a regi ...
). After taking control of the region from the French in the 1760s following their defeat in the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the st ...
, the British anglicized
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influen ...
the lake's name to ''Superior'', "on account of its being superior in magnitude to any of the lakes on that vast continent".
Hydrography
Lake Superior empties into Lake Huron via the St. Marys River and theSoo Locks
The Soo Locks (sometimes spelled Sault Locks but pronounced "soo") are a set of parallel locks, operated and maintained by the United States Army Corps of Engineers, Detroit District, that enable ships to travel between Lake Superior and the low ...
(Sault Ste. Marie locks). Lake Superior is the largest freshwater lake in the world in area and the third largest in volume, behind Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, I ...
in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
and Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika () is an African Great Lake. It is the second-oldest freshwater lake in the world, the second-largest by volume, and the second-deepest, in all cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. It is the world's longest freshwater lake. T ...
in East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the histori ...
. The Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad s ...
, while larger than Lake Superior in both surface area and volume, is brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
. Though presently isolated, prehistorically the Caspian has been repeatedly connected to and then isolated from the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
via the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
.
 Lake Superior has a surface area of , which is approximately the size of
Lake Superior has a surface area of , which is approximately the size of South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = "Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = G ...
or Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. It has a maximum length of and maximum breadth of . Its average depth is with a maximum depth of . Lake Superior contains 2,900 cubic miles (12,100 km³) of water. There is enough water in Lake Superior to cover the entire land mass
A landmass, or land mass, is a large region or area of land. The term is often used to refer to lands surrounded by an ocean or sea, such as a continent or a large island. In the field of geology, a landmass is a defined section of continenta ...
of North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''no ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
to a depth of . North America (2.47 km²) and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
(1.78 km²) combined cover 4.26 km². Lake Superior's volume (1.20 km³) over 4.26 km² gives a depth of 0.282 m. The shoreline of the lake stretches (including islands).
American limnologist
Limnology ( ; from Greek λίμνη, ''limne'', "lake" and λόγος, ''logos'', "knowledge") is the study of inland aquatic ecosystems.
The study of limnology includes aspects of the biological, chemical, physical, and geological characteris ...
J. Val Klump was the first person to reach the lowest depth of Lake Superior on July 30, 1985, as part of a scientific expedition, which at 122 fathoms 1 foot () below sea level is the second-lowest spot in the continental interior of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
and the third-lowest spot in the interior of the North American continent after Great Slave Lake
Great Slave Lake (french: Grand lac des Esclaves), known traditionally as Tıdeè in Tłı̨chǫ Yatıì (Dogrib), Tinde’e in Wıìlıìdeh Yatii / Tetsǫ́t’ıné Yatıé (Dogrib / Chipewyan), Tu Nedhé in Dëne Sųłıné Yatıé (Chi ...
in the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
of Canada ( below sea level) and Iliamna Lake
Iliamna Lake or Lake Iliamna (Yup'ik: ''Nanvarpak''; Dena'ina Athabascan: ''Nila Vena'') is a lake in southwest Alaska, at the north end of the Alaska Peninsula, between Kvichak Bay and Cook Inlet, about west of Seldovia, Alaska. It shares a n ...
in Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
(942 feet 87 m 87 may refer to:
* 87 (number)
* one of the years 87 BC, AD 87, 1987, 2087, etc.
* Atomic number 87: francium
* Intel 8087, a floating-point coprocessor
See also
*
* List of highways numbered
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or ...
below sea level). (Though Crater Lake
Crater Lake (Klamath: ''Giiwas'') is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The lake partly fills ...
is the deepest lake in the United States and deeper than Lake Superior, Crater Lake's elevation is higher and consequently its deepest point is ''above'' sea level.)
While the temperature of the surface of Lake Superior varies seasonally, the temperature below is an almost constant 39 °F (4 °C). This variation in temperature makes the lake seasonally stratified
Stratification may refer to:
Mathematics
* Stratification (mathematics), any consistent assignment of numbers to predicate symbols
* Data stratification in statistics
Earth sciences
* Stable and unstable stratification
* Stratification, or s ...
. Twice per year, however, the water column
A water column is a conceptual column of water from the surface of a sea, river or lake to the bottom sediment.Munson, B.H., Axler, R., Hagley C., Host G., Merrick G., Richards C. (2004).Glossary. ''Water on the Web''. University of Minnesota-D ...
reaches a uniform temperature of 39 °F (4 °C) from top to bottom, and the lake waters thoroughly mix. This feature makes the lake dimictic. Because of its volume, Lake Superior has a retention time
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a ...
of 191 years.
Annual storms on Lake Superior regularly feature wave heights of over . Waves well over have been recorded.
Tributaries
 Lake Superior is fed by more than 200 rivers, including the
Lake Superior is fed by more than 200 rivers, including the Nipigon River
The Nipigon River is located in Thunder Bay District in Northwestern Ontario, Canada. The river is about long (or when measured to the head of Ombabika River) and , and flows from Lake Nipigon to Nipigon Bay on Lake Superior at the community ...
, the St. Louis River, the Pigeon River, the Pic River, the White River, the Michipicoten River
The Michipicoten River is a river in Algoma District of northern Ontario, Canada, which flows from Dog Lake and joins with the Magpie River to empty into Michipicoten Bay on Lake Superior near the town of Wawa. This river is in length (includi ...
, the Bois Brule River
The Bois Brule River (most often referred to as the Brule River) is located in Douglas County, Wisconsin, United States, near the county's eastern border with Bayfield County. The river is long.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Datase ...
and the Kaministiquia River
The Kaministiquia River is a river which flows into western Lake Superior at the city of Thunder Bay, Ontario. ''Kaministiquia'' (''Gaa-ministigweyaa'') is an Ojibwe word meaning "where a stream flows in island" due to two large islands (McKellar ...
. The lake's outlet at St. Marys River has a relatively steep gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p is the "direction and rate of fastest increase". If the gr ...
with rapids. The Soo Locks enable ships to bypass the rapids and to overcome the height difference between Lakes Superior and Huron.
Water levels
 The lake's average surface elevation is
The lake's average surface elevation is above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as '' orthometric heights''.
The ...
. Until approximately 1887, the natural hydraulic conveyance through the St. Marys River rapids determined the outflow from Lake Superior. By 1921, development in support of transportation and hydroelectric power resulted in gates, locks, power canals and other control structures completely spanning St. Marys rapids. The regulating structure is known as the Compensating Works and is operated according to a regulation plan known as Plan 1977-A. Water levels, including diversions of water from the Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
watershed, are regulated by the International Lake Superior Board of Control
Lake Superior in central North America is the List of lakes by area, largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the List of lakes by volume, third-largest by volum ...
, which was established in 1914 by the International Joint Commission
The International Joint Commission (french: Commission mixte internationale) is a bi-national organization established by the governments of the United States and Canada under the Boundary Waters Treaty of 1909. Its responsibilities were expa ...
.
Lake Superior's water level was at a new record low in September 2007, slightly less than the previous record low in 1926. Water levels recovered within a few days.
Historic high water
The lake's water level fluctuates from month to month, with the highest lake levels in October and November. The normal high-water mark is above datum (601.1 ft or 183.2 m). In the summer of 1985, Lake Superior reached its highest recorded level at above datum. 2019 and 2020 set new high-water records in nearly every month.
Historic low water
The lake's lowest levels occur in March and April. The normal low-water mark is below datum. In the winter of 1926 Lake Superior reached its lowest recorded level at below datum. Additionally, the entire first half of the year (January to June) included record low months. The low water was a continuation of the dropping lake levels from the previous year, 1925, which set low-water records for October through December. During the nine-month period of October 1925 to June 1926, water levels ranged from to below Chart Datum. In the summer of 2007 monthly historic lows were set; August at , September at .
Climate change
According to a study by professors at theUniversity of Minnesota Duluth
The University of Minnesota Duluth (UMD) is a public university in Duluth, Minnesota. It is part of the University of Minnesota system and offers 16 bachelor's degrees in 88 majors, graduate programs in 25 different fields, and a two-year pr ...
, Lake Superior may have warmed faster than its surrounding area. Summer surface temperatures in the lake appeared to have increased by about between 1979 and 2007, compared with an approximately increase in the surrounding average air temperature. The increase in the lake's surface temperature may be related to the decreasing ice cover. Less winter ice cover allows more solar radiation
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area ( surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre ...
to penetrate and warm the water. If trends continue, Lake Superior, which freezes over completely once every 20 years, could routinely be ice-free by 2040 although more current data through 2021 does not support this trend.
Warmer temperatures could lead to more snow in the lake effect snow belts along the shores of the lake, especially in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by ...
. Two recent consecutive winters (2013–2014 and 2014–2015) brought high ice coverage to the Great Lakes, and on March 6, 2014, overall ice coverage peaked at 92.5%, the second-highest in recorded history. Lake Superior's ice coverage further beat 2014's record in 2019, reaching 95% coverage.
Geography
 The largest island in Lake Superior is
The largest island in Lake Superior is Isle Royale
Isle Royale National Park is an American national park consisting of Isle Royale – known as Minong to the native Ojibwe – along with more than 400 small adjacent islands and the surrounding waters of Lake Superior, in the state of Michig ...
in Michigan. Isle Royale contains several lakes, some of which also contain islands. Other well-known islands include Madeline Island
''Madeline'' is a media franchise that originated as a series of children's books written and illustrated by Ludwig Bemelmans, an Austrian-American author. The books have been adapted into numerous formats, spawning telefilms, television series a ...
in Wisconsin, Michipicoten Island
Michipicoten Island is an island in Ontario, Canada, in the northeastern part of Lake Superior, about northwest of Sault Ste. Marie and southwest of Wawa, Ontario. At its closest point to mainland Ontario, the island is located about from th ...
in Ontario, and Grand Island (the location of the Grand Island National Recreation Area
The Grand Island National Recreation Area is a national recreation area in Hiawatha National Forest under jurisdiction of the U.S. Forest Service. Located on Grand Island, Michigan offshore from Munising, Michigan, the Grand Island National Recrea ...
) in Michigan.
The larger cities on Lake Superior include the twin ports of Duluth, Minnesota
, settlement_type = City
, nicknames = Twin Ports (with Superior), Zenith City
, motto =
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top: urban Duluth skyline; Minnesota ...
, and Superior, Wisconsin
, native_name_lang = oj
, nickname =
, total_type =
, motto =
, image_skyline = Tower Avenue.jpg
, imagesize =
, image_caption = Downtown Superior
, ima ...
; Thunder Bay
Thunder Bay is a city in and the seat of Thunder Bay District, Ontario, Canada. It is the most populous municipality in Northwestern Ontario and the second most populous (after Greater Sudbury) municipality in Northern Ontario; its populatio ...
, Ontario; Marquette, Michigan
Marquette ( ) is a city in Marquette County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 20,629 at the 2020 United States Census, which makes it the largest city in the Upper Peninsula. Marquette serves as the seat of government of Marquet ...
; and the twin cities of Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan
Sault Ste. Marie ( ') is the only city in, and county seat of, Chippewa County in the U.S. state of Michigan. With a population of 13,337 at the 2020 census, it is the second-most populated city in the Upper Peninsula after Marquette. It i ...
, and Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario
Sault Ste. Marie ( ) is a city in Ontario, Canada. It is at the St. Mary's River on the Canada–US border. It is the third largest city in Northern Ontario, after Sudbury and Thunder Bay.
The Ojibwe, the indigenous Anishinaabe inhabitants of ...
. Duluth-Superior
The Duluth MN-WI Metropolitan Area, commonly called the Twin Ports, is a small metropolitan area centered around the cities of Duluth, Minnesota and Superior, Wisconsin. The Twin Ports are located at the western part of Lake Superior (the we ...
, at the western end of Lake Superior, is the most inland point on the Saint Lawrence Seaway
The St. Lawrence Seaway (french: la Voie Maritime du Saint-Laurent) is a system of locks, canals, and channels in Canada and the United States that permits oceangoing vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes of North Ameri ...
and the most inland port in the world.
Among the scenic places on the lake are Apostle Islands National Lakeshore
The Apostle Islands National Lakeshore is a U.S. national lakeshore consisting of 21 islands (Apostle Islands) and shoreline encompassing on the northern tip of Wisconsin on the shore of Lake Superior.
It is known for its collection of historic l ...
, Brockway Mountain Drive
Brockway Mountain Drive is an scenic roadway just west of Copper Harbor in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan in the United States. Drivers can access the road from State Highway M-26 on either end near Eagle Harbor to the west or Copper Harbor ...
on the Keweenaw Peninsula
The Keweenaw Peninsula ( , sometimes locally ) is the northernmost part of Michigan's Upper Peninsula. It projects into Lake Superior and was the site of the first copper boom in the United States, leading to its moniker of " Copper Country." As ...
, Isle Royale National Park
Isle Royale National Park is an American national park consisting of Isle Royale – known as Minong to the native Ojibwe – along with more than 400 small adjacent islands and the surrounding waters of Lake Superior, in the state of Michigan. ...
, Porcupine Mountains Wilderness State Park
The Porcupine Mountains, or Porkies, are a group of small mountains spanning the northwestern Upper Peninsula of Michigan in Ontonagon and Gogebic counties, near the shore of Lake Superior. The Porcupine Mountains were named by the native O ...
, Pukaskwa National Park
Pukaskwa National Park ( ) is a national park located south of the town of Marathon, Ontario in the Thunder Bay District of northern Ontario, Canada. Established in 1978, Pukaskwa is known for its vistas of Lake Superior and boreal forests. The pa ...
, Lake Superior Provincial Park
Lake Superior Provincial Park is one of the largest provincial parks in Ontario, covering about along the northeastern shores of Lake Superior between Sault Ste. Marie and Wawa in Algoma District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. Ontario Hi ...
, Grand Island National Recreation Area, Sleeping Giant (Ontario) and Pictured Rocks National Lakeshore
Pictured Rocks National Lakeshore is a U.S. National Lakeshore in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, United States. It extends for 42 miles (67 km) along the shore of Lake Superior and covers . The park has extensive views of the hilly shor ...
. The Great Lakes Circle Tour
The Great Lakes Circle Tour is a designated scenic road system connecting all of the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River. It consists of routes for circumnavigating the lakes, either individually or collectively. It was designated by the Gre ...
is a designated scenic road system connecting all of the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River.
Climate
Lake Superior's size reduces the severity of the seasons of itshumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(more typically seen in locations like Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native En ...
). The water surface's slow reaction to temperature changes, seasonally ranging between 32 and 55 °F (0–13 °C) around 1970, helps to moderate surrounding air temperatures in the summer (cooler with frequent sea breeze
A sea breeze or onshore breeze is any wind that blows from a large body of water toward or onto a landmass; it develops due to differences in air pressure created by the differing heat capacities of water and dry land. As such, sea breezes ar ...
formations) and winter, and creates lake-effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated up by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises up through ...
in colder months. The hills and mountains that border the lake hold moisture and fog, particularly in the fall.
Geology
 The rocks of Lake Superior's northern shore date back to the early history of the earth. During the
The rocks of Lake Superior's northern shore date back to the early history of the earth. During the Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of th ...
(between 4.5 billion and 540 million years ago) magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natura ...
forcing its way to the surface created the intrusive granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
s of the Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield (french: Bouclier canadien ), also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), the anc ...
. These ancient granites can be seen on the North Shore today. It was during the Penokean orogeny The Penokean orogeny was a mountain-building episode that occurred in the early Proterozoic about 1.86 to 1.83 billion years ago, in the area of Lake Superior, North America. The core of this orogeny, the Churchill Craton, is composed of terranes ...
, part of the process that created the Great Lakes tectonic zone, that many valuable metals were deposited. The region surrounding the lake has proved to be rich in minerals, with copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
, iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
and nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
the most frequently mined. Notable production includes gold from the Hemlo mine near Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of , usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There are also wheelchair di ...
, copper from the Keweenaw Peninsula
The Keweenaw Peninsula ( , sometimes locally ) is the northernmost part of Michigan's Upper Peninsula. It projects into Lake Superior and was the site of the first copper boom in the United States, leading to its moniker of " Copper Country." As ...
and the Mamainse Point Formation The Mamainse Point Formation is a geologic formation in Algoma District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is located north of Sault Ste. Marie along Lake Superior. The rocks comprising the Mamainse Point Formation are volcanic in origin, having ...
, iron from the Gogebic Range
The Gogebic Range is an elongated area of iron ore deposits located within a range of hills in northern Michigan and Wisconsin just south of Lake Superior. It extends from Lake Namakagon in Wisconsin eastward to Lake Gogebic in Michigan, or al ...
, silver at Silver Islet, and uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly ...
at Theano Point.
The mountains steadily eroded, depositing layers of sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
s that compacted and became limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
, dolomite, taconite
Taconite () is a variety of iron formation, an iron-bearing (over 15% iron) sedimentary rock, in which the iron minerals are interlayered with quartz, chert, or carbonate. The name "taconyte" was coined by Horace Vaughn Winchell (1865–1923) � ...
and the shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especia ...
at Kakabeka Falls
Kakabeka Falls is a waterfall on the Kaministiquia River, located beside the village of Kakabeka Falls in the municipality of Oliver Paipoonge, Ontario, west of the city of Thunder Bay.
The falls have a drop of , cascading into a gorge carved o ...
. The continental crust was later riven
''Riven'' is a puzzle adventure video game. It is the sequel to '' Myst'' and second in the ''Myst'' series of games. Developed by Cyan Worlds, it was initially published by Red Orb Entertainment, a division of Broderbund. ''Riven'' was dis ...
, creating one of the deepest rifts in the world. The lake lies in this long-extinct Mesoproterozoic
The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from . The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth's history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era (the Paleoproterozoic ...
rift valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear de ...
, the Midcontinent Rift
The Midcontinent Rift System (MRS) or Keweenawan Rift is a long geological rift in the center of the North American continent and south-central part of the North American plate. It formed when the continent's core, the North American craton, b ...
. Magma was injected between layers of sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particle ...
, forming diabase
Diabase (), also called dolerite () or microgabbro,
is a mafic, holocrystalline, subvolcanic rock equivalent to volcanic basalt or plutonic gabbro. Diabase dikes and sills are typically shallow intrusive bodies and often exhibit fine-gra ...
sills. This hard diabase protects the layers of sedimentary rock below, forming the flat-topped mesas in the Thunder Bay
Thunder Bay is a city in and the seat of Thunder Bay District, Ontario, Canada. It is the most populous municipality in Northwestern Ontario and the second most populous (after Greater Sudbury) municipality in Northern Ontario; its populatio ...
area. Amethyst
Amethyst is a violet variety of quartz. The name comes from the Koine Greek αμέθυστος ''amethystos'' from α- ''a-'', "not" and μεθύσκω (Ancient Greek) / μεθώ (Modern Greek), "intoxicate", a reference to the belief that ...
formed in some of the cavities created by the Midcontinent Rift, and there are several amethyst mines in the Thunder Bay area.
Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock ( magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or ...
erupted from the rift and formed the black basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
rock of Michipicoten Island, Black Bay Peninsula, and St. Ignace Island
St. Ignace Island (French: Île Saint-Ignace), in northern Lake Superior in Ontario, Canada, is the Lake island#Naturally occurring lake islands, by area, eleventh-largest lake island in the world. With an area of , it is also the second-largest ...
.
In the most recent geological history, during the Wisconsin glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cor ...
10,000 years ago, ice covered the region at a thickness of . The land contours familiar today were carved by the advance and retreat of the ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at ...
. The retreat left gravel, sand, clay and boulder deposits. Glacial meltwaters gathered in the Superior basin creating Lake Minong, a precursor to Lake Superior. Without the immense weight of the ice, the land rebounded, and a drainage outlet formed at Sault Ste. Marie, becoming today's St. Mary's River.
History
 The first people came to the Lake Superior region 10,000 years ago after the retreat of the glaciers in the Last Glacial Period. They are known as the Plano, and they used stone-tipped spears to hunt caribou on the northwestern side of Lake Minong. The Shield
The first people came to the Lake Superior region 10,000 years ago after the retreat of the glaciers in the Last Glacial Period. They are known as the Plano, and they used stone-tipped spears to hunt caribou on the northwestern side of Lake Minong. The Shield Archaic
Archaic is a period of time preceding a designated classical period, or something from an older period of time that is also not found or used currently:
*List of archaeological periods
**Archaic Sumerian language, spoken between 31st - 26th cent ...
peoples arrived around 5000 BC; evidence of this culture can be found at the eastern and western ends of the Canadian shore. They used bows and arrows, paddled dugout canoes, fished, hunted, mined copper for tools and weapons, and established trading networks. They are believed to be the direct ancestors of the Ojibwe and Cree.. The people of the Laurel complex
The Laurel complex or Laurel tradition is an archaeological culture which was present in what is now southern Quebec, southern and northwestern Ontario and east-central Manitoba in Canada, and northern Michigan, northwestern Wisconsin and northe ...
(c. 500 BC to AD 500) developed seine net
Seine fishing (or seine-haul fishing; ) is a method of fishing that employs a surrounding net, called a seine, that hangs vertically in the water with its bottom edge held down by weights and its top edge buoyed by floats. Seine nets can be de ...
fishing, evidence being found at rivers around Superior such as the Pic and Michipicoten. The people of the Terminal Woodland period
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeo ...
were evident in the area from 900 AD to 1650. They were Algonquian peoples
The Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American native language groups. Historically, the peoples were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and into the interior along the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes ...
who hunted, fished and gathered berries. They used snowshoe
Snowshoes are specialized outdoor gear for walking over snow. Their large footprint spreads the user's weight out and allows them to travel largely on top of rather than through snow. Adjustable bindings attach them to appropriate winter footwe ...
s, birch bark
Birch bark or birchbark is the bark of several Eurasian and North American birch trees of the genus ''Betula''.
The strong and water-resistant cardboard-like bark can be easily cut, bent, and sewn, which has made it a valuable building, crafti ...
canoes and conical or domed lodges. At the mouth of the Michipicoten River, nine layers of encampments have been discovered. Most of the Pukaskwa Pit Pukaskwa Pits are rock-lined depressions near the northern shore of Lake Superior dug by early inhabitants, ancestors of the Ojibwa, named after the Pukaskwa River in Ontario, Canada. Estimates of their age range from as recent as 1100-1600 CE, to ...
s were likely made during this time.
 The
The Anishinaabe
The Anishinaabeg (adjectival: Anishinaabe) are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe (including Saulteaux and Oji-Cree), Odawa, Potawato ...
people, which includes the Ojibwe or Chippewa, have inhabited the Lake Superior region for over five hundred years and were preceded by the Dakota
Dakota may refer to:
* Dakota people, a sub-tribe of the Sioux
** Dakota language, their language
Dakota may also refer to:
Places United States
* Dakota, Georgia, an unincorporated community
* Dakota, Illinois, a town
* Dakota, Minnesota ...
, Fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelv ...
, Menominee
The Menominee (; mez, omǣqnomenēwak meaning ''"Menominee People"'', also spelled Menomini, derived from the Ojibwe language word for "Wild Rice People"; known as ''Mamaceqtaw'', "the people", in the Menominee language) are a federally reco ...
, Nipigon, Noquet and Gros Ventres
The Gros Ventre ( , ; meaning "big belly"), also known as the Aaniiih, A'aninin, Haaninin, Atsina, and White Clay, are a historically Algonquian-speaking Native American tribe located in north central Montana. Today the Gros Ventre people are ...
. After the arrival of Europeans, the Anishinaabe made themselves middle-men between the French fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mo ...
rs and other Native peoples. They soon became the dominant Native American nation in the region: they forced out the Sioux
The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin (; Dakota language, Dakota: Help:IPA, /otʃʰeːtʰi ʃakoːwĩ/) are groups of Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes and First Nations in Canada, First Nations peoples in North America. The ...
and Fox and won a victory against the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
west of Sault Ste. Marie in 1662. By the mid-18th century, the Ojibwe occupied all of Lake Superior's shores.
 In the 18th century, as the booming fur trade supplied Europe with
In the 18th century, as the booming fur trade supplied Europe with beaver hat
A beaver hat is a hat made from felted beaver fur. They were fashionable across much of Europe during the period 1550–1850 because the soft yet resilient material could be easily combed to make a variety of hat shapes (including the familiar top ...
s, the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trade, fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake b ...
had a virtual monopoly in the region until 1783, when the rival North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great we ...
was formed. The North West Company built forts on Lake Superior at Grand Portage
Grand Portage National Monument is a United States National Monument located on the north shore of Lake Superior in northeastern Minnesota that preserves a vital center of fur trade activity and Anishinaabeg Ojibwe heritage. The area became one o ...
, Fort William, Nipigon, the Pic River, the Michipicoten River, and Sault Ste. Marie. But by 1821, with competition harming the profits of both, the companies merged under the Hudson's Bay Company name. Many towns around the lake are current or former mining areas, or engaged in processing or shipping. Today, tourism is another significant industry: the sparsely populated Lake Superior country, with its rugged shorelines and wilderness, attracts vacationers and adventurers.
Shipping
Lake Superior has been an important link in theGreat Lakes Waterway
The Great Lakes Waterway (GLW) is a system of natural channels and artificial canals which enable navigation between the North American Great Lakes. Though all of the lakes are naturally connected as a chain, water travel between the lakes was i ...
, providing a route for the transportation of iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the ...
as well as grain and other mined and manufactured materials. Large cargo vessels called lake freighter
Lake freighters, or lakers, are bulk carrier vessels that operate on the Great Lakes of North America. These vessels are traditionally called boats, although classified as ships.
Since the late 19th century, lakers have carried bulk cargoes of ma ...
s, as well as smaller ocean-going freighters, transport these commodities across Lake Superior. Shipping was slow to arrive at Lake Superior in the 19th century. The first steamboat to run on the lake was the ''Independence'' in 1847, whereas the first steamers on the other Great Lakes began sailing in 1816. Ice closes the lake shipping from mid-January to late March. Exact dates for the shipping season vary each year, depending on weather conditions that form and break the ice.
Shipwrecks
The southern shore of Lake Superior betweenGrand Marais, Michigan
Grand Marais ( ) is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Alger County in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is located within Burt Township on the shores of Lake Superior, and the community is the eastern gateway to the ...
, and Whitefish Point
Whitefish Point is a cape of Michigan's Upper Peninsula, United States, marking the entry point of Whitefish Bay. It is north of the unincorporated community of Paradise, Michigan.
Whitefish Point is known for the Great Lakes Shipwreck Museum, ...
is known as the "Graveyard of the Great Lakes;" more ships have been lost around the Whitefish Point area than any other part of Lake Superior. These shipwrecks are now protected by the Whitefish Point Underwater Preserve
The Whitefish Point Underwater Preserve was established in 1987 to protect and conserve shipwrecks and historical resources on of Lake Superior bottomlands in Whitefish Bay and around Whitefish Point, Michigan. The formation of the Michigan U ...
. Storms that claimed multiple ships include the Mataafa Storm
The Mataafa Storm of 1905, was a storm that occurred on the Great Lakes on November 27–28, 1905. The system moved across the Great Basin with moderate depth on November 26 and November 27, then east-northeastward across the Great Lakes on Novemb ...
in November 1905 and the Great Lakes Storm of 1913
The Great Lakes Storm of 1913 (historically referred to as the "Big Blow", the "Freshwater Fury", and the "White Hurricane") was a blizzard with hurricane-force winds that devastated the Great Lakes Basin in the Midwestern United States and Sou ...
.
Wreckage of —a ore carrier that sank on October 11, 1907, during a Lake Superior storm in 77 fathoms () of water—was located in August 2007. Built in Lorain, Ohio
Lorain () is a city in Lorain County, Ohio, United States. The municipality is located in northeastern Ohio on Lake Erie, at the mouth of the Black River, about 30 miles west of Cleveland. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of ...
, ''Cyprus'' was launched August 17, 1907, and was lost on her second voyage hauling iron ore from Superior, Wisconsin, to Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is the second-largest city in the U.S. state of New York (behind only New York City) and the seat of Erie County. It is at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of the Niagara River, and is across the Canadian border from Sou ...
, with the sole survivor among her 23 crew being Charles G. Pitz. In 1918 the last warships to sink in the Great Lakes, French minesweepers ''Inkerman'' and ''Cerisoles'', vanished in a Lake Superior storm, perhaps upon striking the uncharted danger of the Superior Shoal
The Superior Shoal is a geologic shoal of approximately located north of Copper Harbor, Michigan in the middle of Lake Superior, the highest point of which lies only below the lake's surface. The shoal is a hump of Keweenawan basaltic lava fl ...
in an otherwise deep part of the lake. With 78 crewmembers dead, their sinking marked the largest loss of life on Lake Superior to date.
was the latest ship to sink in Lake Superior, from Whitefish Point in a storm on November 10, 1975. The wreck was immortalized by Gordon Lightfoot
Gordon Meredith Lightfoot Jr. (born November 17, 1938) is a Canadian singer-songwriter and guitarist who achieved international success in folk, folk-rock, and country music. He is credited with helping to define the folk-pop sound of the 19 ...
in his ballad "The Wreck of the ''Edmund Fitzgerald''". All 29 crew members died, and no bodies were recovered. ''Edmund Fitzgerald'' was battered so intensely by Lake Superior that the ship split in half; her two pieces lie approximately apart at a depth of 88 fathoms ().
Lightfoot sings that "Superior, they said, never gives up her dead". This is because of the unusually cold water, under on average around 1970. Normally, bacteria decaying a sunken body will bloat it with gas, causing it to float to the surface after a few days. But Lake Superior's water is cold enough year-round to inhibit bacterial growth
250px, Growth is shown as ''L'' = log(numbers) where numbers is the number of colony forming units per ml, versus ''T'' (time.)
Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providin ...
, and bodies tend to sink and never resurface. Joe MacInnis reported that in July 1994, explorer Frederick Shannon's Expedition 94 to the wreck of ''Edmund Fitzgerald'' discovered a man's body near the port side of her pilothouse, not far from the open door, "fully clothed, wearing an orange life jacket, and lying face down in the sediment".


Ecology
More than 80 species of fish have been found in Lake Superior. Species native to the lake includebanded killifish
The banded killifish (''Fundulus diaphanus'') is a North American species of temperate freshwater killifish belonging to the genus ''Fundulus'' of the family Fundulidae. Its natural geographic range extends from Newfoundland to South Carolina, a ...
, bloater, brook trout, burbot
The burbot (''Lota lota'') is the only gadiformes, gadiform (cod-like) freshwater fish. It is also known as bubbot, mariah, loche, cusk, freshwater cod, freshwater ling, freshwater cusk, the lawyer, coney-fish, lingcod, and eelpout. The species ...
, cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational corporation, multinational digital communications technology conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develo ...
, lake sturgeon
The lake sturgeon (''Acipenser fulvescens''), also known as the rock sturgeon, is a North American temperate freshwater fish, one of about 25 species of sturgeon. Like other sturgeons, this species is a bottom feeder with evolutionarily basal ...
, lake trout
The lake trout (''Salvelinus namaycush'') is a freshwater char living mainly in lakes in northern North America. Other names for it include mackinaw, namaycush, lake char (or charr), touladi, togue, and grey trout. In Lake Superior, it can als ...
, lake whitefish
The lake whitefish (''Coregonus clupeaformis'') is a species of freshwater whitefish from North America. Lake whitefish are found throughout much of Canada and parts of the northern United States, including all of the Great Lakes. The lake whit ...
, longnose sucker
The longnose sucker (''Catostomus catostomus'') is a species of cypriniform freshwater fish in the family Catostomidae. It is native to North America from the northern United States to the top of the continent. It is also found in Russia in ...
, muskellunge
The muskellunge ''(Esox masquinongy)'', often shortened to muskie, musky or lunge is a species of large freshwater predatory fish native to North America. It is the largest member of the pike family, Esocidae.
Origin of name
The name "muskel ...
, northern pike
The northern pike (''Esox lucius'') is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus ''Esox'' (the pikes). They are typical of brackish water, brackish and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere (''i.e.'' holarctic in distribution). They are kno ...
, pumpkinseed
The pumpkinseed (''Lepomis gibbosus''), also referred to as pond perch, common sunfish, punkie, sunfish, sunny, and kivver, is a small/medium-sized North American freshwater fish of the genus '' Lepomis'' (true sunfishes), from family Centrar ...
, rock bass
The rock bass (''Ambloplites rupestris''), also known as the rock perch, goggle-eye, red eye, and black perch, is a freshwater fish native to east-central North America. This red eyed creature is a species of freshwater fish in the sunfish fam ...
, round whitefish
The round whitefish (''Prosopium cylindraceum'') is a freshwater species of fish that is found in lakes from Alaska to New England, including the Great Lakes. It has an olive-brown back with light silvery sides and underside and its length is ge ...
, smallmouth bass, walleye
The walleye (''Sander vitreus'', synonym ''Stizostedion vitreum''), also called the yellow pike or yellow pickerel, is a freshwater perciform fish native to most of Canada and to the Northern United States. It is a North American close relat ...
, white sucker
The white sucker (''Catostomus commersonii)'' is a species of freshwater cypriniform fish inhabiting the upper Midwest and Northeast in North America, but it is also found as far south as Georgia and as far west as New Mexico. The fish is commo ...
and yellow perch
The yellow perch (''Perca flavescens''), commonly referred to as perch, striped perch, American perch, American river perch or preacher is a freshwater perciform fish native to much of North America. The yellow perch was described in 1814 by S ...
. In addition, many fish species have been either intentionally or accidentally introduced to Lake Superior: Atlantic salmon, brown trout
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a European species of salmonid fish that has been widely introduced into suitable environments globally. It includes purely freshwater populations, referred to as the riverine ecotype, ''Salmo trutta'' morp ...
, carp
Carp are various species of oily freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large group of fish native to Europe and Asia. While carp is consumed in many parts of the world, they are generally considered an invasive species in parts of ...
, chinook salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon in North America, as well as the largest in the genus '' Oncorhynchus''. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other ...
, coho salmon
The coho salmon (''Oncorhynchus kisutch;'' Karuk: achvuun) is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family and one of the five Pacific salmon species. Coho salmon are also known as silver salmon or "silvers". The scientific species n ...
, freshwater drum
The freshwater drum, ''Aplodinotus grunniens'', is a fish endemic to North and Central America. It is the only species in the genus ''Aplodinotus'', and is a member of the family Sciaenidae. It is the only North American member of the group that ...
, pink salmon
Pink salmon or humpback salmon (''Oncorhynchus gorbuscha'') is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family. It is the smallest and most abundant of the Pacific salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name fo ...
, rainbow smelt
The rainbow smelt (''Osmerus mordax'') is a North American species of fish of the family Osmeridae. Walleye, trout, and other larger fish prey on these smelt. The rainbow smelt prefer juvenile ciscoes, zooplankton such as calanoid copepods ('' ...
, rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coast ...
, round goby
The round goby (''Neogobius melanostomus'') is a fish. Defined as a euryhaline bottom-dwelling goby of the family Gobiidae, it is native to Central Eurasia, including the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. Round gobies have established large non-n ...
, ruffe
The Eurasian ruffe (''Gymnocephalus cernua''), also known as ruffe or pope, is a freshwater fish found in temperate regions of Europe and northern Asia. It has been introduced into the Great Lakes of North America, reportedly with unfortun ...
, sea lamprey
The sea lamprey (''Petromyzon marinus'') is a parasitic lamprey native to the Northern Hemisphere. It is sometimes referred to as the "vampire fish".
Description
The sea lamprey has an eel-like body without paired fins. Its mouth is jawless, ...
and white perch
The white perch (''Morone americana'') is not a true perch but is a fish of the temperate bass family, Moronidae, notable as a food and game fish in eastern North America. In some places it is referred to as "Silver Bass".
The name "White pe ...
.
Lake Superior has fewer dissolved nutrients relative to its water volume than the other Great Lakes and so is less productive in terms of fish populations and is an oligotrophic lake
The Trophic State Index (TSI) is a classification system designed to rate water bodies based on the amount of biological productivity they sustain. Although the term "trophic index" is commonly applied to lakes, any surface water body may be ind ...
. This is a result of the underdeveloped soils found in its relatively small watershed. It is also a reflection of relatively small human population and small amount of agriculture in its watershed. However, nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insoluble ...
concentrations in the lake have been continuously rising for more than a century. They are still much lower than levels considered dangerous to human health; but this steady, long-term rise is an unusual record of environmental nitrogen buildup. It may relate to anthropogenic alternations to the regional nitrogen cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biolo ...
, but researchers are still unsure of the causes of this change to the lake's ecology.
As for other Great Lakes fish, populations have also been affected by the accidental or intentional introduction of foreign species such as the sea lamprey and Eurasian ruffe. Accidental introductions have occurred in part by the removal of natural barriers to navigation between the Great Lakes. Overfishing has also been a factor in the decline of fish populations.
See also
*List of lakes in Ontario
This is an incomplete list of lakes in Ontario, a province of Canada. There are over 250,000 lakes in Ontario, constituting around 20% of the world's fresh water supply.
Larger lake statistics
This is a list of lakes of Ontario with an ar ...
* North Shore North Shore or Northshore may refer to:
Geographic features Australia
*North Shore (Sydney), a suburban region of Sydney
**Electoral district of North Shore
**North Shore railway line, Sydney
*Noosa North Shore, Queensland
* North Shore, New So ...
of Lake Superior
* South Shore of Lake Superior
General
*Great Lakes Areas of Concern
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
* Great Lakes census statistical areas
* Great Lakes Commission
The Great Lakes Commission is a United States interstate agency established in 1955 through the Great Lakes Basin Compact, in order to "promote the orderly, integrated and comprehensive development, use and conservation of the water resources of ...
* Great Recycling and Northern Development Canal
The Great Recycling and Northern Development (GRAND) Canal of North America or GCNA is a water management proposal designed by Newfoundland engineer Thomas Kierans to alleviate North American freshwater shortage problems. It proposed damming Ja ...
* International Boundary Waters Treaty
The Boundary Waters Treaty is the 1909 treaty between the United States and Canada providing mechanisms for resolving any dispute over any waters bordering the two countries. The treaty covers the
Canada, as a dominion of the Crown of Britain ...
* List of cities along the Great Lakes
* Seiche
A seiche ( ) is a standing wave in an enclosed or partially enclosed body of water. Seiches and seiche-related phenomena have been observed on lakes, reservoirs, swimming pools, bays, harbors, caves and seas. The key requirement for formation o ...
* Shipwrecks of the 1913 Great Lakes storm
This is a list of shipwrecks during the Great Lakes Storm of 1913.
Vessels gallery
File:Leafield before the 1913 Great Lakes storm.png, "Leafield"
File:Henry B Smith LOC det 4a16048.jpg, "Henry B Smith"
File:Argus before 1913 Great Lakes st ...
* Sixty Years' War
The Sixty Years' War (1754–1815) was a military struggle for control of the North American Great Lakes region, including Lake Champlain and Lake George, encompassing a number of wars over multiple generations. The term ''Sixty Years' War'' ...
for control of the Great Lakes
* Third Coast
Third Coast is an American colloquialism used to describe coastal regions distinct from the East Coast and the West Coast of the United States. Generally, the term "Third Coast" refers to either the Great Lakes region or in some circles the Gulf ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*Lake Superior NOAA nautical chart #14961 online
International Lake Superior Board of Control
Great Lakes Coast Watch
Parks Canada - Lake Superior National Marine Conservation Area
Minnesota Sea Grant Lake Superior Page
Lake Superior Trials
{{DEFAULTSORT:Superior, Lake Lakes of Michigan Lakes of Wisconsin Lakes of Minnesota Lakes of Ontario Great Lakes Waterway Upper Peninsula of Michigan Lakes of Algoma District Lakes of Thunder Bay District Mesoproterozoic rifts and grabens Canada–United States border International lakes of North America *Superior