Gibraltar Strait on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the
 The seabed of the Strait is composed of synorogenic Betic-Rif
The seabed of the Strait is composed of synorogenic Betic-Rif
 Evidence of the first human habitation of the area by
Evidence of the first human habitation of the area by
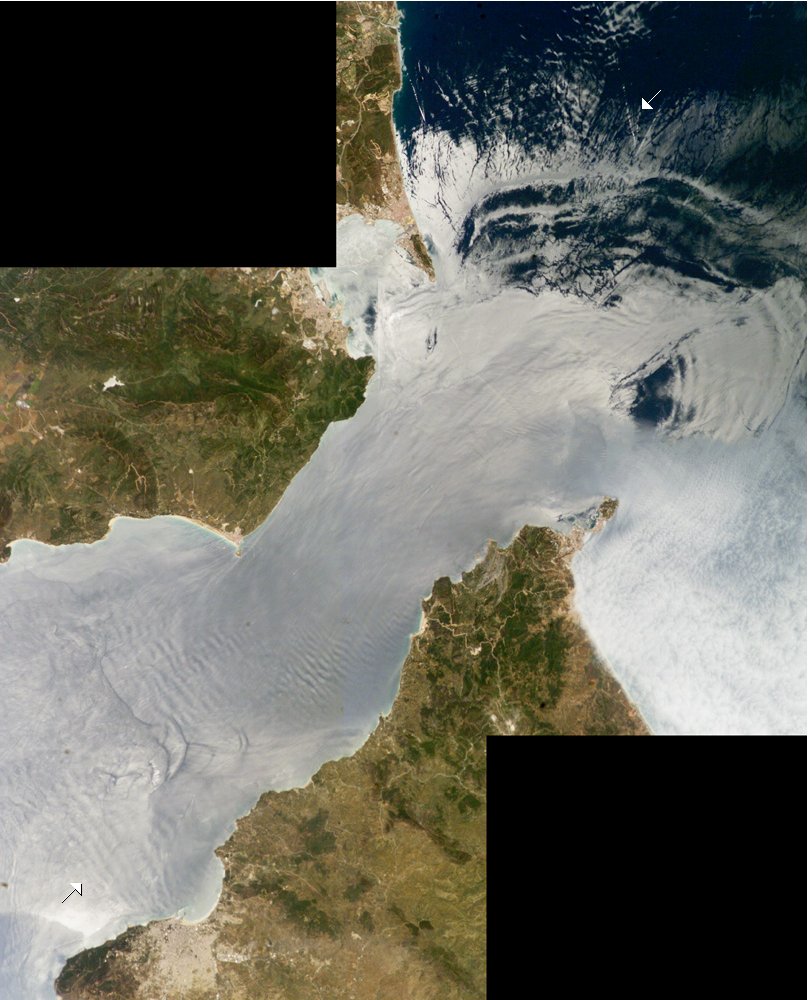 Water flows through the Strait more or less continuously, both eastwards and westwards. A smaller amount of deeper, saltier and therefore denser waters continually flow westwards (the Mediterranean outflow), while a larger amount of surface waters with lower salinity and density continually flow eastwards (the Mediterranean inflow). These general flow tendencies may be occasionally interrupted for brief periods by temporary tidal flows, depending on various lunar and solar alignments. The balance of the water flow is eastwards, since the evaporation rate within the Mediterranean basin is higher than the combined inflow of all the rivers that empty into it, plus the total precipitation of rain or snow that falls on it. At the Strait's far western end is the Camarinal Sill, the Strait's shallowest point which limits mixing between the cold, less saline Atlantic water and the warmer, more saline Mediterranean waters.
The Mediterranean waters are so much saltier than the Atlantic waters that they sink below the constantly incoming water and form a highly saline ('' thermohaline'', both warm and salty) layer of bottom water. This layer of bottom-water constantly works its way out into the Atlantic as the Mediterranean outflow. On the Atlantic side of the Strait, a density boundary separates the Mediterranean outflow waters from the rest at about depth. These waters flow out and down the continental slope, losing salinity, until they begin to mix and equilibrate more rapidly, much farther out at a depth of about . The Mediterranean outflow water layer can be traced for thousands of kilometres west of the Strait, before completely losing its identity.
During the
Water flows through the Strait more or less continuously, both eastwards and westwards. A smaller amount of deeper, saltier and therefore denser waters continually flow westwards (the Mediterranean outflow), while a larger amount of surface waters with lower salinity and density continually flow eastwards (the Mediterranean inflow). These general flow tendencies may be occasionally interrupted for brief periods by temporary tidal flows, depending on various lunar and solar alignments. The balance of the water flow is eastwards, since the evaporation rate within the Mediterranean basin is higher than the combined inflow of all the rivers that empty into it, plus the total precipitation of rain or snow that falls on it. At the Strait's far western end is the Camarinal Sill, the Strait's shallowest point which limits mixing between the cold, less saline Atlantic water and the warmer, more saline Mediterranean waters.
The Mediterranean waters are so much saltier than the Atlantic waters that they sink below the constantly incoming water and form a highly saline ('' thermohaline'', both warm and salty) layer of bottom water. This layer of bottom-water constantly works its way out into the Atlantic as the Mediterranean outflow. On the Atlantic side of the Strait, a density boundary separates the Mediterranean outflow waters from the rest at about depth. These waters flow out and down the continental slope, losing salinity, until they begin to mix and equilibrate more rapidly, much farther out at a depth of about . The Mediterranean outflow water layer can be traced for thousands of kilometres west of the Strait, before completely losing its identity.
During the
Climate Control Requires a Dam at the Strait of Gibraltar
—American Geophysical Union, 1997. Accessed 26 February 2006. Gone 12 February 2010. Dam design at http://www.agu.org/sci_soc/eosrjohnsonf3.gif Building the dam and letting the Mediterranean Sea completely evaporate would raise Sea Level 15 meters over 1,000 years. Evaporating the first 100 meters or so would raise Sea Level 1 meter in about 100 years.
Project for a Europe-Africa permanent link through the Strait of Gibraltar
��United Nations Economic and Social Council, 2001. Accessed 26 February 2006.
��La Universidad de Tetuán and La Universidad de Sevilla. Accessed 26 February 2006. * *
Old maps of the Strait of Gibraltar
Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The National Library of Israel
HOW TO SWIM ACROSS THE STRAIT OF GIBRALTAR
By ACNEG The Straits of Gibraltar Swimming Association. {{DEFAULTSORT:Gibraltar
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
to the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
and separates Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
from Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical mile
A nautical mile is a unit of length used in air, marine, and space navigation, and for the definition of territorial waters. Historically, it was defined as the meridian arc length corresponding to one minute ( of a degree) of latitude at t ...
s (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Ferries cross between the two continents every day in as little as 35 minutes. The Strait's depth ranges between .
The strait lies in the territorial waters of Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, and the British overseas territory
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs) or alternatively referred to as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs) are the fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom that, ...
of Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
. Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international treaty that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 169 sov ...
, foreign vessels and aircraft have the freedom of navigation and overflight to cross the strait of Gibraltar in case of continuous transit.
Names and etymology
The name comes from theRock of Gibraltar
The Rock of Gibraltar (from the Arabic name Jabal Ṭāriq , meaning "Mountain of Tariq ibn Ziyad, Tariq") is a monolithic limestone mountain high dominating the western entrance to the Mediterranean Sea. It is situated near the end of a nar ...
, which in turn originates from the Arabic (meaning "Tariq's Mount"), named after Tariq ibn Ziyad. It is also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, the Gut of Gibraltar (although this is mostly archaic), the STROG (STRait Of Gibraltar) in naval use.
Another Arabic name is ''Bāb al- ''maghrib'''' (), meaning "Gate of the West" or "Gate of the sunset", and furthermore "Gate of the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
" or "Gate of Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
". In the Middle Ages it was called in Arabic ( 'the Passage'), or ( 'the passage sea') and by the Romans (Strait of Cadiz).
In Latin it has been called , based on the name from antiquity "Pillars of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules are the promontory, promontories that flank the entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar. The northern Pillar, Calpe Mons, is the Rock of Gibraltar. A corresponding North African peak not being predominant, the identity of ...
" (), referring to the mountains as pillars, such as Gibraltar, flanking the strait.
Location
On the northern side of the Strait areSpain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
and Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
(a British overseas territory in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
). On the southern side are Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
and Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ) is an Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous city of Spain on the North African coast. Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta is one of th ...
(a Spanish autonomous city in northern Africa).
Due to its location, the Strait is commonly used for illegal immigration from Africa to Europe.
Extent
TheInternational Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) (French: ''Organisation Hydrographique Internationale'') is an intergovernmental organization representing hydrography. the IHO comprised 102 member states.
A principal aim of the IHO is to ...
defines the limits of the Strait of Gibraltar as follows:
Geology
clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
ey flysch covered by Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
calcareous sediments, sourced from thriving cold water coral communities. Exposed bedrock surfaces, coarse sediments and local sand dunes attest to the strong bottom current conditions at the present time.
Around 5.9 million years ago, the connection between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean along the Betic and Rifan Corridor was progressively restricted until its total closure, effectively causing the salinity of the Mediterranean to rise periodically within the gypsum and salt deposition range, during what is known as the Messinian salinity crisis. In this water chemistry environment, dissolved mineral concentrations, temperature and stilled water currents combined and occurred regularly to precipitate many mineral salts in layers on the seabed. The resultant accumulation of various huge salt and mineral deposits about the Mediterranean basin are directly linked to this era. It is believed that this process took a short time, by geological standards, lasting between 500,000 and 600,000 years.
It is estimated that, were the Strait closed even at today's higher sea level, most water in the Mediterranean basin would evaporate within a thousand years, as it is believed to have done then, and such an event would lay down mineral deposits like the salt deposits now found under the sea floor all over the Mediterranean.
After a lengthy period of restricted intermittent or no water exchange between the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean basin, approximately 5.33 million years ago, the Atlantic–Mediterranean connection was completely reestablished through the Strait of Gibraltar by the Zanclean flood, and has remained open ever since. The erosion produced by the incoming waters seems to be the main cause for the present depth of the Strait ( at the narrows, at the Camarinal Sill). The Strait is expected to close again as the African Plate moves northward relative to the Eurasian Plate, but on geological rather than human timescales.
Biodiversity
The Strait has been identified as an Important Bird Area byBirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding i ...
because of the hundreds of thousands of seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adaptation, adapted to life within the marine ecosystem, marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent ...
s which use it every year to migrate between the Mediterranean and the Atlantic, including significant numbers of Scopoli's and Balearic shearwaters, Audouin's and lesser black-backed gulls, razorbills, and Atlantic puffin
The Atlantic puffin ('), also known as the common puffin, is a species of seabird in the auk family (biology), family. It is the only puffin native to the Atlantic Ocean; two related species, the tufted puffin and the horned puffin being found ...
s.
A resident orca pod of some 36 individuals lives around the Strait, one of the few that are left in Western European waters. The pod may be facing extinction in the coming decades due to long term effects of PCB pollution.
History
 Evidence of the first human habitation of the area by
Evidence of the first human habitation of the area by Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
s dates back to 125,000 years ago. It is believed that the Rock of Gibraltar
The Rock of Gibraltar (from the Arabic name Jabal Ṭāriq , meaning "Mountain of Tariq ibn Ziyad, Tariq") is a monolithic limestone mountain high dominating the western entrance to the Mediterranean Sea. It is situated near the end of a nar ...
may have been one of the last outposts of Neanderthal habitation in the world, with evidence of their presence there dating to as recently as 24,000 years ago. Archaeological evidence of ''Homo sapiens'' habitation of the area dates back years.
The relatively short distance between the two shores has served as a quick crossing point for various groups and civilizations throughout history, including Carthaginians
The Punic people, usually known as the Carthaginians (and sometimes as Western Phoenicians), were a Semitic people, Semitic people who Phoenician settlement of North Africa, migrated from Phoenicia to the Western Mediterranean during the Iron ...
campaigning against Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, Romans travelling between the provinces of Hispania and Mauritania, Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vand ...
raiding south from Germania through Western Rome and into North Africa in the 5th century, Moors
The term Moor is an Endonym and exonym, exonym used in European languages to designate the Muslims, Muslim populations of North Africa (the Maghreb) and the Iberian Peninsula (particularly al-Andalus) during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a s ...
and Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
in the 8th–11th centuries, and Spain and Portugal in the 16th century.
Beginning in 1492, the Strait began to play a certain cultural role in acting as a barrier against cross-channel conquest and the flow of culture and language that would naturally follow such a conquest. In that year, the last Muslim government north of the Strait was overthrown by a Spanish force. Since that time, the Strait has come to foster the development of two very distinct and varied cultures on either side of it after sharing much the same culture for over 500 years from the 8th century to the early 13th century.
On the northern side, Christian-European culture has remained dominant since the expulsion of the last Muslim kingdom in 1492, along with the Romance Spanish language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, gl ...
, while on the southern side, Muslim-Arabic/Mediterranean has been dominant since the spread of Islam into North Africa in the 700s, along with the Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
language.
The small British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
enclave of the city of Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
presents a third cultural group found in the Strait. This enclave was ceded in perpetuity to Britain in the Peace of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
. Gibraltar has since been used by the United Kingdom to act as a surety for control of the sea lanes into and out of the Mediterranean.
Following the Spanish coup of July 1936 the Spanish Republican Navy tried to blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are ...
the Strait of Gibraltar to hamper the transport of Army of Africa troops from Spanish Morocco to Peninsular Spain. On 5 August 1936 the so-called Convoy de la Victoria was able to bring at least 2,500 men across the Strait, breaking the republican blockade.
Communications
The Strait is an important shipping route from theMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
to the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
. Ferries
A ferry is a boat or ship that transports passengers, and occasionally vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A small passenger ferry with multiple stops, like those in Venice, Italy, is sometimes referred to as a water taxi or water bus.
...
operate between Spain and Morocco across the Strait, as well as between Spain and Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ) is an Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous city of Spain on the North African coast. Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta is one of th ...
and Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
to Tangier
Tangier ( ; , , ) is a city in northwestern Morocco, on the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The city is the capital city, capital of the Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima region, as well as the Tangier-Assilah Prefecture of Moroc ...
.
Tunnel across the Strait
Discussion between Spain and Morocco of a tunnel under the strait began in the 1980s. In December 2003, both countries agreed to explore the construction of an undersea railtunnel
A tunnel is an underground or undersea passageway. It is dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, or laid under water, and is usually completely enclosed except for the two portals common at each end, though there may be access and ve ...
to connect their rail systems across the Strait. The gauge of the rail would be to match the proposed construction and conversion of significant parts of the existing broad gauge system to standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
. While the project remained in a planning phase, Spanish and Moroccan officials met to discuss it occasionally, including in 2012. Those talks led to nothing constructive happening, but in April 2021 ministers from both countries agreed to a joint intergovernmental meeting to be held in Casablanca
Casablanca (, ) is the largest city in Morocco and the country's economic and business centre. Located on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Chaouia (Morocco), Chaouia plain in the central-western part of Morocco, the city has a populatio ...
in the coming months. This was in order to resume discussions on a tunnel. Earlier, in January 2021, the UK government had studied plans for a tunnel to link Gibraltar with Tangiers that would replace the Spanish-Moroccan project that until then had had no tangible results after over 40 years of discussions.
Special flow and wave patterns
The Strait of Gibraltar links the Atlantic Ocean directly to the Mediterranean Sea. This direct linkage creates certain unique flow and wave patterns. These unique patterns are created due to the interaction of various regional and global evaporative forces, water temperatures, tidal forces, and wind forces.Inflow and outflow
 Water flows through the Strait more or less continuously, both eastwards and westwards. A smaller amount of deeper, saltier and therefore denser waters continually flow westwards (the Mediterranean outflow), while a larger amount of surface waters with lower salinity and density continually flow eastwards (the Mediterranean inflow). These general flow tendencies may be occasionally interrupted for brief periods by temporary tidal flows, depending on various lunar and solar alignments. The balance of the water flow is eastwards, since the evaporation rate within the Mediterranean basin is higher than the combined inflow of all the rivers that empty into it, plus the total precipitation of rain or snow that falls on it. At the Strait's far western end is the Camarinal Sill, the Strait's shallowest point which limits mixing between the cold, less saline Atlantic water and the warmer, more saline Mediterranean waters.
The Mediterranean waters are so much saltier than the Atlantic waters that they sink below the constantly incoming water and form a highly saline ('' thermohaline'', both warm and salty) layer of bottom water. This layer of bottom-water constantly works its way out into the Atlantic as the Mediterranean outflow. On the Atlantic side of the Strait, a density boundary separates the Mediterranean outflow waters from the rest at about depth. These waters flow out and down the continental slope, losing salinity, until they begin to mix and equilibrate more rapidly, much farther out at a depth of about . The Mediterranean outflow water layer can be traced for thousands of kilometres west of the Strait, before completely losing its identity.
During the
Water flows through the Strait more or less continuously, both eastwards and westwards. A smaller amount of deeper, saltier and therefore denser waters continually flow westwards (the Mediterranean outflow), while a larger amount of surface waters with lower salinity and density continually flow eastwards (the Mediterranean inflow). These general flow tendencies may be occasionally interrupted for brief periods by temporary tidal flows, depending on various lunar and solar alignments. The balance of the water flow is eastwards, since the evaporation rate within the Mediterranean basin is higher than the combined inflow of all the rivers that empty into it, plus the total precipitation of rain or snow that falls on it. At the Strait's far western end is the Camarinal Sill, the Strait's shallowest point which limits mixing between the cold, less saline Atlantic water and the warmer, more saline Mediterranean waters.
The Mediterranean waters are so much saltier than the Atlantic waters that they sink below the constantly incoming water and form a highly saline ('' thermohaline'', both warm and salty) layer of bottom water. This layer of bottom-water constantly works its way out into the Atlantic as the Mediterranean outflow. On the Atlantic side of the Strait, a density boundary separates the Mediterranean outflow waters from the rest at about depth. These waters flow out and down the continental slope, losing salinity, until they begin to mix and equilibrate more rapidly, much farther out at a depth of about . The Mediterranean outflow water layer can be traced for thousands of kilometres west of the Strait, before completely losing its identity.
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, German U-boats used the currents to pass into the Mediterranean Sea without detection, by maintaining silence with engines off. From September 1941 to May 1944 Germany managed to send 62 U-boats into the Mediterranean. All these boats had to navigate the British-controlled Strait of Gibraltar where nine U-boats were sunk while attempting passage and 10 more had to break off their run due to damage.
Internal waves
Internal waves (waves at the density boundary layer) are often produced by the Strait. Like traffic merging on a highway, the water flow is constricted in both directions because it must pass over the Camarinal Sill. When large tidal flows enter the Strait and the high tide relaxes, internal waves are generated at the Camarinal Sill and proceed eastwards. Even though the waves may occur down to great depths, occasionally the waves are almost imperceptible at the surface, at other times they can be seen clearly in satellite imagery. These ''internal waves'' continue to flow eastward and to refract around coastal features. They can sometimes be traced for as much as , and sometimes create interference patterns with refracted waves.Territorial waters
Except for its far eastern end, the Strait lies within theterritorial waters
Territorial waters are informally an area of water where a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potentially the extended continental shelf ( ...
of Spain and Morocco. The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
claims around Gibraltar on the northern side of the Strait, putting part of it inside British territorial waters. As this is less than the maximum, it means, according to the British claim, that part of the Strait lies in international waters
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
. The ownership of Gibraltar and its territorial waters is disputed by Spain. Similarly, Morocco disputes Spanish sovereignty over Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ) is an Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous city of Spain on the North African coast. Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta is one of th ...
on the southern coast. There are several islets, such as the disputed Isla Perejil, that are claimed by both Morocco and Spain.
Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international treaty that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 169 sov ...
, vessels passing through the strait do so under the regime of transit passage
Transit passage is a concept of the law of the sea, which allows a vessel or aircraft the freedom of navigation or overflight solely for the purpose of continuous and expeditious transit of a strait between one part of the high seas or exclusive ...
, rather than the more limited innocent passage allowed in most territorial waters. Therefore, a vessel or aircraft has the freedom of navigation or overflight for the purpose of crossing the strait of Gibraltar.
Power generation
Some studies have proposed the possibility of erecting tidal power generating stations within the Strait, to be powered from the predictable current at the Strait. In the 1920s and 1930s, the Atlantropa project proposed damming the Strait to generate large amounts of electricity and lower the sea level of the Mediterranean by several hundreds of meters to create large new lands for settlement. This proposal would however have devastating effects on the local climate and ecology and would dramatically change the strength of the West African Monsoon.History of Strait crossings
Some adventurers crossed the Strait of Gibraltar byswimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, such as saltwater or freshwater environments, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Swimmers achieve locomotion by coordinating limb and body movements to achieve hydrody ...
, powered paragliding
Powered paragliding, also known as paramotoring or PPG, is a form of ultralight aviation where the pilot wears a back-pack motor (a paramotor) which provides enough thrust to take off using a paraglider. It can be launched in still air, and on ...
and Paddleboarding.
By swimming
Mercedes Gleitze was the first known person to swim across the Strait of Gibraltar on 6 April 1928. It took her 12 hours and 50 minutes to cross the stretch of water. This was her sixth attempt to swim the Strait of Gibraltar, her first having been made in December 1927.By powered paraglider
Francesco Stipo was the first known person to cross the Strait of Gibraltar with a powered paraglider on 11 July 1995. According to Spanish newspaper Europa Sur, Stipo crossed the Strait from Tarifa toCeuta
Ceuta (, , ; ) is an Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous city of Spain on the North African coast. Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta is one of th ...
in less than one hour, followed by the Red Cross boat "Salvamar Tarifa", and landed on a street near the Port of Ceuta.
By stand up paddleboard
Chris Ziaja and Nik Benner were the first known people to cross the Strait of Gibraltar with a stand up paddleboard on 4 October 2010. They set out from Punta Carnero and reachedCeuta
Ceuta (, , ; ) is an Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous city of Spain on the North African coast. Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta is one of th ...
four and a half hours later.
See also
* Vendavel, Westerly wind * Perdicaris Park * Floating suspension bridge * Mediterranean Basin * List of straitsReferences
External links
Climate Control Requires a Dam at the Strait of Gibraltar
—American Geophysical Union, 1997. Accessed 26 February 2006. Gone 12 February 2010. Dam design at http://www.agu.org/sci_soc/eosrjohnsonf3.gif Building the dam and letting the Mediterranean Sea completely evaporate would raise Sea Level 15 meters over 1,000 years. Evaporating the first 100 meters or so would raise Sea Level 1 meter in about 100 years.
Project for a Europe-Africa permanent link through the Strait of Gibraltar
��United Nations Economic and Social Council, 2001. Accessed 26 February 2006.
��La Universidad de Tetuán and La Universidad de Sevilla. Accessed 26 February 2006. * *
Old maps of the Strait of Gibraltar
Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The National Library of Israel
HOW TO SWIM ACROSS THE STRAIT OF GIBRALTAR
By ACNEG The Straits of Gibraltar Swimming Association. {{DEFAULTSORT:Gibraltar
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
International straits
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
Straits of Africa
Straits of Europe
Straits of the Mediterranean Sea
Geography of Europe
Geography of North Africa