Gerhard Hauptmann on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gerhart Johann Robert Hauptmann (; 15 November 1862 ã 6 June 1946) was a German dramatist and novelist. He is counted among the most important promoters of
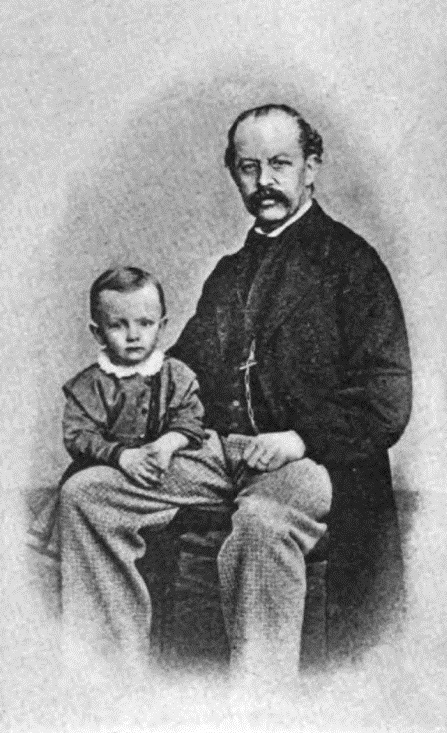 In the spring of 1878, Hauptmann left the
In the spring of 1878, Hauptmann left the
 Hauptmann married Marie Thienemann in
Hauptmann married Marie Thienemann in  During this period he began to write. His 1887 novella '' BahnwûÊrter Thiel'' was published the following year. His first play, ''Before Sunrise'', was first staged in 1889, directed by
During this period he began to write. His 1887 novella '' BahnwûÊrter Thiel'' was published the following year. His first play, ''Before Sunrise'', was first staged in 1889, directed by
 In 1910, Hauptmann's first full-length novel was published, ''The Fool in Christ, Emanuel Quint'', which told the story of a wandering preacher who mixed sun worship with Christianity. His 1912 novel, ''Atlantis'', became the basis for a Danish silent film of the same name. The novel was written one month before the RMS ''Titanic'' disaster, and the film's 1913 release was less than one year after the event.
The storyline for both involved a romance aboard a doomed ocean liner, and the similarity to the disaster became obvious. This coincidental untimeliness caused the film to be banned in Norway, due to perceived insensitivity. Nevertheless, excited by the possibilities of this new medium, Hauptmann wrote several screenplays, none of which were ever filmed.
Around the turn of the century, Hauptmann began to receive official recognition. Three times he was awarded the Austrian Franz-Grillparzer-Preis. He also received honorary doctorates from
In 1910, Hauptmann's first full-length novel was published, ''The Fool in Christ, Emanuel Quint'', which told the story of a wandering preacher who mixed sun worship with Christianity. His 1912 novel, ''Atlantis'', became the basis for a Danish silent film of the same name. The novel was written one month before the RMS ''Titanic'' disaster, and the film's 1913 release was less than one year after the event.
The storyline for both involved a romance aboard a doomed ocean liner, and the similarity to the disaster became obvious. This coincidental untimeliness caused the film to be banned in Norway, due to perceived insensitivity. Nevertheless, excited by the possibilities of this new medium, Hauptmann wrote several screenplays, none of which were ever filmed.
Around the turn of the century, Hauptmann began to receive official recognition. Three times he was awarded the Austrian Franz-Grillparzer-Preis. He also received honorary doctorates from 
 At the beginning of May 1946, Hauptmann learned that the Polish government was insisting on the expulsion of all Germans without exception. On 6 June, he died of
At the beginning of May 1946, Hauptmann learned that the Polish government was insisting on the expulsion of all Germans without exception. On 6 June, he died of
 At the end of the 1880s, he was confronted with the incipient anti-socialist movement. The first of the
At the end of the 1880s, he was confronted with the incipient anti-socialist movement. The first of the
 After his death, the fame he had enjoyed in life began to fade. His reputation was further diminished by his uncritical attitude toward the Nazis. Nevertheless, centenary celebrations were held in many German cities in 1962, and his works continued to be performed on West German stages into the 1970s, especially ''Der Biberpelz'' and ''Die Ratten''.
After his death, the fame he had enjoyed in life began to fade. His reputation was further diminished by his uncritical attitude toward the Nazis. Nevertheless, centenary celebrations were held in many German cities in 1962, and his works continued to be performed on West German stages into the 1970s, especially ''Der Biberpelz'' and ''Die Ratten''.
''Hannele. A Dream Poem''
(1894)
''Lonely Lives''
(1898)
''The Sunken Bell''
(1899).
''The Coming of Peace''
(1900)
''And Pippa Dances''
(1907)
''The Reconciliation''
(1910)
''The Fool in Christ, Emanuel Quint''
(1911)
''Atlantis''
(1912).
''Parsival''
(1915) * The Dramatic Works: *
''Social Dramas''
(1912) *
''Social Dramas''
(1913) *
''Domestic Dramas''
(1914) *
''Symbolic and Legendary Dramas''
(1914) *
''Symbolic and Legendary Dramas''
(1915) *
''Later Dramas in Prose''
(1915) *
''Miscellaneous Dramas''
(1917)
''Phantom''
(1922) * ''The Heretic of Soana'' (1923) * ''Lineman Thiel and Other Tales'' (1989)
''Witness of Deceit. Gerhart Hauptmann as Critic of Society.''
Berkeley: University of California Press. * Skrine, Peter N. (1989). ''Hauptmann, Wedekind, and Schnitzler.'' New York: St. Martin's Press.
''Modern Dramatists.''
London: Frank Palmer. * Dussû´re, Carolyn (1980). "An Interpretation of Gerhart Hauptmann's 'Parsival'," ''Colloquia Germanica,'' Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 233ã245. * Campbell, T.M. (1924). "Gerhart HauptmannãChristian or Pagan?," ''The Modern Language Journal,'' Vol. 8, No. 6, pp. 353ã361. * Coates, William Ames (1945). "Dostoyevski and Gerhart Hauptmann," ''The American Slavic and East European Review,'' Vol. 4, No. 3/4, pp. 107ã127. * Ewen, David (1935). "Conversations with Gerhart Hauptmann," ''Books Abroad,'' Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 253ã254. * Hale, Edward Everett (1905)
"Hauptmann."
In: ''Dramatists of Today.'' New York: Henry Holt & Company, pp. 37ã61. * Heller, Otto (1905)
"Gerhart Hauptmann."
In: ''Studies in Modern German Literature.'' Boston: Ginn & Company, pp. 117ã128. * Heuser, F.W.J.(1926). "Hauptmann and Novalis," ''Germanic Review,'' Vol. 1, pp. 125ã131. * Huneker, James (1919)
"Gerhart Hauptmann."
In: ''Iconoclasts.'' New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, pp. 182ã210. * Kobbûˋ, Gustav (1898)
"The Dramas of Gerhart Hauptmann,"
''The Forum,'' Vol. 24, pp. 432ã441. * Lewisohn, Ludwig (1912)
"Introduction."
In: ''The Dramatic Works,'' Vol. 1. London: Martin Secker, pp. ixãxxxvii. * Maurer, Warren R. (1979). "Gerhart Hauptmann's Character Names," ''The German Quarterly,'' Vol. 52, No. 4, pp. 457ã471. * Muller, Siegfried H. (1952). "Gerhart Hauptmann's Relation to American Literature and His Concept of America," ''Monatshefte,'' Vol. 44, No. 7, pp. 333ã339. * Reichart, Walter A. (1946). "The Totality of Hauptmann's Work," ''Germanic Review,'' Vol. 21, pp. 143ã149. * Reichart, Walter A. (1962). "Hauptmann Study in America: A Continuation Bibliography," ''Monatshefte,'' Vol. 54, No. 6, pp. 297ã310. * Robertson, John G. (1902)
''A History of German Literature.''
New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons. * Scholz, Karl W.H. (1918)
''The Art of Translation.''
Philadelphia: Americana Germanica Press. * Thompson, Nesta M. (1920). "Naturalism and the Dream Motive as Observed in the Works of Gerhart Hauptmann," ''Washington University Studies,'' Vol. 8, pp. 77ã101. * Wahr, F.B. (1946). "Hauptmann's Hellenism," ''Journal of English and Germanic Philology,'' Vol. 33, pp. 421ã451. * Wiehr, Josef (1906)
"The Naturalistic Plays of Gerhart Hauptmann,"
''The Journal of English and Germanic Philology,'' Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 1ã71
Part II
Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 531ã575. * Witkowski, Georg (1909)
''The German Drama of the Nineteenth-century.''
London: George Bell & Sons. * Youngman, Paul A. (2005). "Gerhart Hauptmann." In: ''Black Devil and Iron Angel. The Railway in Nineteenth-century German Realism.'' Washington, D.C.: Catholic University of America Press, pp. 109ã127. * Schweissinger, Marc: Gerhart Hauptmann's Hamlet `translation`, In: Anglistica Pisana 8(2), pp. 11ã24.
Works by Gerhart Hauptmann
at
List of Works
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Hauptmann, Gerhart 1862 births 1946 deaths 19th-century German dramatists and playwrights 19th-century German male writers 20th-century German dramatists and playwrights German Nobel laureates 19th-century German novelists 20th-century German novelists German poets German male short story writers German autobiographers Nobel laureates in Literature Writers from the Province of Silesia People from Waébrzych County Recipients of the Pour le Mûˋrite (civil class) University of Jena alumni German male poets German male novelists German male dramatists and playwrights 19th-century German short story writers 20th-century German short story writers
literary naturalism
Naturalism is a literary movement beginning in the late nineteenth century, similar to literary realism in its rejection of Romanticism, but distinct in its embrace of determinism, detachment, scientific objectivism, and social commentary. Litera ...
, though he integrated other styles into his work as well. He received the Nobel Prize in Literature
The Nobel Prize in Literature, here meaning ''for'' Literature (), is a Swedish literature prize that is awarded annually, since 1901, to an author from any country who has, in the words of the will of Swedish industrialist Alfred Nobel, "in ...
in 1912.
Life
Childhood and youth
Gerhart Hauptmann was born in 1862 in Obersalzbrunn, now known asSzczawno-Zdrû°j
Szczawno-Zdrû°j (, until 1935 ''Ober Salzbrunn'') is a spa town in Waébrzych County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland.
Geography
The town in the historic Lower Silesia region is situated north of the Central Sudetes mountai ...
, in Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ) is a historical and geographical region mostly located in Poland with small portions in the Czech Republic and Germany. It is the western part of the region of Silesia. Its largest city is Wrocéaw.
The first ...
(then a part of the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
, now a part of Poland). His parents were Robert and Marie Hauptmann, who ran a hotel in the area. As a youth, Hauptmann had a reputation of being loose with the truth. His elder brother was Carl Hauptmann.
Beginning in 1868, he attended the village school and then, in 1874, the Realschule
Real school (, ) is a type of secondary school in Germany, Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It has also existed in Croatia (''realna gimnazija''), the Austrian Empire, the German Empire, Denmark and Norway (''realskole''), Sweden (''realskola''), F ...
in Breslau for which he had only barely passed the qualifying exam. Hauptmann had difficulties adjusting himself to his new surroundings in the city. He lived, along with his brother Carl, in a somewhat run-down student boarding house before finding lodging with a pastor.
He ran into problems with the Prussian-influenced school. Above all were the strictness of the teachers and the better treatment of his noble classmates. His dislike and numerous illnesses kept him from attending class, which led to his having to repeat his first year. Over time, he came to appreciate Breslau because of the opportunity to visit the theater.
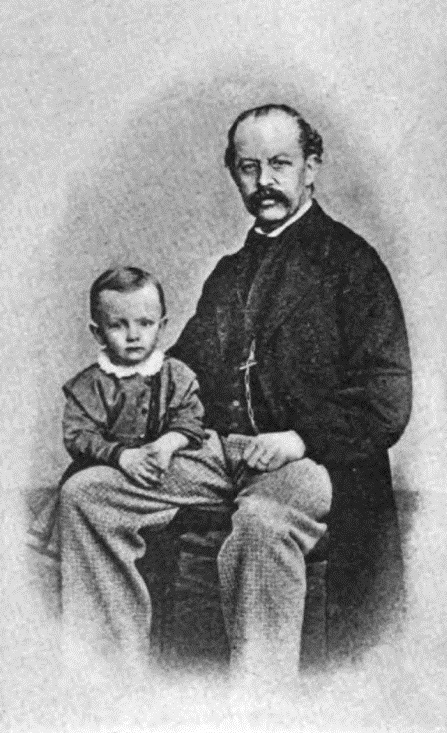 In the spring of 1878, Hauptmann left the
In the spring of 1878, Hauptmann left the Realschule
Real school (, ) is a type of secondary school in Germany, Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It has also existed in Croatia (''realna gimnazija''), the Austrian Empire, the German Empire, Denmark and Norway (''realskole''), Sweden (''realskola''), F ...
to learn agriculture on his uncle's farm in Lohnig (today éagiewniki éredzkie
éagiewniki éredzkie is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Udanin, within éroda élá
ska County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Lower Silesian Voivodeship (, ) in southwestern Poland, is one of the 16 Voivodeships of Poland, voivo ...
in Gmina Udanin
__NOTOC__
Gmina Udanin is a rural gmina (administrative district) in éroda élá
ska County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. Its seat is the village of Udanin, which lies approximately south-west of éroda élá
ska, and west ...
, Poland). After a year and a half, however, he had to break off his training. He was not physically prepared for the work and he had contracted a life-threatening lung ailment that troubled him for the next twenty months.
Studies and life as a sculptor
After he failed to pass an officer entry exam for the Prussian Army, Hauptmann entered the sculpture school at the Royal Art and Vocational School in Breslau in 1880. There he metJosef Block
Josef Block (27 November 1863 ã 20 December 1943) was a German painter.
Life and career
Block was born in Bernstadt an der Weide (Bierutû°w) in Prussian Silesia. He was a scholar of the Breslau (Wrocéaw) Art Academy, where his lifelong frie ...
who became a lifelong friend. He was temporarily expelled for "poor behavior and insufficient diligence," but quickly reinstated on the recommendation of the sculptor and Professor Robert HûÊrtel. Hauptmann left the school in 1882.
For his brother's wedding, he wrote a short play, ''Liebesfrû¥hling'', which was performed on the night before. Also at the wedding, he met the bride's sister, Marie Thienemann. They became secretly engaged and she began supporting him financially, which enabled him to begin a semester of philosophy and literary history
The history of literature is the historical development of writings in prose or poetry that attempt to provide entertainment or education to the reader, as well as the development of the literary techniques used in the communication of these pie ...
at the University of Jena
The University of Jena, officially the Friedrich Schiller University Jena (, abbreviated FSU, shortened form ''Uni Jena''), is a public research university located in Jena, Thuringia, Germany.
The university was established in 1558 and is cou ...
, which he soon quit.
After he left Jena, Marie financed a Mediterranean trip, which he undertook with his brother Carl. There he decided to settle in Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
as a sculptor, but with little success. His attempt to establish himself as part of Rome's German expatriate community also failed and his large clay sculpture of a German warrior collapsed. Hauptmann returned disappointed to Germany, where he began a brief stint at the Royal Academy in Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''DrûÊsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most p ...
before beginning to study history at the University of Berlin. While there, he devoted his interests to the theater rather than to his studies. In 1891 he moved to Schreiberhau in Silesia.
Marriage and beginning as a writer
 Hauptmann married Marie Thienemann in
Hauptmann married Marie Thienemann in Radebeul
Radebeul (; ) is a town (''groûe Kreisstadt'') in the Elbe valley in the district of Meiûen (district), Meiûen in Saxony, Germany, a suburb of Dresden. It is well known for its viticulture, a Karl May Museum, museum dedicated to writer Karl ...
on 5 May 1885. In July, they took their honeymoon to Rû¥gen
Rû¥gen (; Rani: ''Rà₤jana'', ''Rána''; , ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rû¥gen island is the Hanseatic ci ...
along with Carl and his wife, Marie's sister, Martha. They visited the island of Hiddensee
Hiddensee () is a Auto-free zone, car-free island in the Baltic Sea, located west of Germany's largest island, Rû¥gen, on the Germany, German coast.
The island has about 1,000 inhabitants. It was a holiday destination for East Germany, East Germ ...
, which would become a favorite retreat of Hauptmann's. Because the city air bothered Gerhart's lungs, the couple spent the first four years of their marriage in the town of Erkner
Erkner () is a town in the Oder-Spree District of Brandenburg, Germany, located on the south-eastern edge of the German capital city Berlin.
Geography
The town is located between the lakes DûÊmeritzsee, a part of the river Spree (river), Spree, a ...
, where their three sons were born. In 1889, they moved to Charlottenburg
Charlottenburg () is a Boroughs and localities of Berlin, locality of Berlin within the borough of Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf. Established as a German town law, town in 1705 and named after Sophia Charlotte of Hanover, Queen consort of Kingdom ...
in Berlin. There he joined the naturalist literary club "Durch", which included among others Karl Bleibtreu
Karl August Bleibtreu (January 13, 1859 ã January 30, 1928) was a German writer who promoted Naturalism (literature), naturalism in German literature. He was noted for his aggressive and dogmatic style of criticism, linked to a nationalistic and ...
and Wilhelm BûÑlsche
Wilhelm BûÑlsche (2 January 1861 – 31 August 1939) was a German author, editor and publicist. He was among the early promoters of nature conservation and committed to popularizing science.
Life
BûÑlsche was born in Cologne on 2 January 1861 ...
.
 During this period he began to write. His 1887 novella '' BahnwûÊrter Thiel'' was published the following year. His first play, ''Before Sunrise'', was first staged in 1889, directed by
During this period he began to write. His 1887 novella '' BahnwûÊrter Thiel'' was published the following year. His first play, ''Before Sunrise'', was first staged in 1889, directed by Otto Brahm
Otto Brahm (born Otto Abrahamsohn on 5 February 1856 in Hamburg; died 28 November 1912 in Berlin) was a German drama and literary critic, theatre manager and director. His productions were noted for being accurate and realistic. He was involved i ...
. It inaugurated the naturalistic movement in modern German literature
German literature () comprises those literature, literary texts written in the German language. This includes literature written in Germany, Austria, the German parts of Switzerland and Belgium, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, South Tyrol in Italy ...
. It was followed by ''The Reconciliation'' (1890), ''Lonely People'' (1891) and ''The Weavers'' (1892), a powerful drama depicting the rising of the Silesian weavers in 1844, for which he is best known outside of Germany. His work also included comedies, including ''Colleague Crampton'' (1891) and ''The Beaver Coat
''The Beaver Coat'' () is a satirical play by Gerhart Hauptmann premiered in Berlin in 1893.
The work is an example of a German naturalistic ''DiebskomûÑdie'', or 'thief's comedy'. The drama takes place "somewhere in Berlin... around the end of ...
'' (1893).
In 1893, he also took actress Margarete Marschalk as his lover. In order to get some distance, Marie moved to the US with their sons. Hauptmann prepared the first French performance of his play ''The Assumption of Hannele
''The Ascension of Little Hannele'' (), also known simply as ''Hannele'', is an 1893 play by the German playwright Gerhart Hauptmann.Hartnoll (1983, 377). In contrast to Hauptmann's naturalistic dramas, ''The Assumption of Hannele'' adopts a mo ...
'' and then went after Marie, without even staying for the premiere. The rift, however, was not to be bridged. After several years of separation, the marriage was ended in July 1904. However, Marie continued to live in the villa Hauptmann had built in Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''DrûÊsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most p ...
.
Recognition and World War I
From 1901, Hauptmann lived with Margarete Marschalk in Agnetendorf (today Jagniá tkû°w in Poland). He called it ''"the mystical protective sheathing of my soul"''. In the preceding year, Margarete had borne him a son, Benvenuto. In September 1904, they were married; this second marriage lasted until his death, though it was thrown into a serious crisis in 1905 and 1906 by his affair with a 16-year-old actress, Ida Orloff. In 1910, Hauptmann's first full-length novel was published, ''The Fool in Christ, Emanuel Quint'', which told the story of a wandering preacher who mixed sun worship with Christianity. His 1912 novel, ''Atlantis'', became the basis for a Danish silent film of the same name. The novel was written one month before the RMS ''Titanic'' disaster, and the film's 1913 release was less than one year after the event.
The storyline for both involved a romance aboard a doomed ocean liner, and the similarity to the disaster became obvious. This coincidental untimeliness caused the film to be banned in Norway, due to perceived insensitivity. Nevertheless, excited by the possibilities of this new medium, Hauptmann wrote several screenplays, none of which were ever filmed.
Around the turn of the century, Hauptmann began to receive official recognition. Three times he was awarded the Austrian Franz-Grillparzer-Preis. He also received honorary doctorates from
In 1910, Hauptmann's first full-length novel was published, ''The Fool in Christ, Emanuel Quint'', which told the story of a wandering preacher who mixed sun worship with Christianity. His 1912 novel, ''Atlantis'', became the basis for a Danish silent film of the same name. The novel was written one month before the RMS ''Titanic'' disaster, and the film's 1913 release was less than one year after the event.
The storyline for both involved a romance aboard a doomed ocean liner, and the similarity to the disaster became obvious. This coincidental untimeliness caused the film to be banned in Norway, due to perceived insensitivity. Nevertheless, excited by the possibilities of this new medium, Hauptmann wrote several screenplays, none of which were ever filmed.
Around the turn of the century, Hauptmann began to receive official recognition. Three times he was awarded the Austrian Franz-Grillparzer-Preis. He also received honorary doctorates from Worcester College
Worcester College ( ) is a constituent college of the University of Oxford in England. The college was founded in 1714 by the benefaction of Sir Thomas Cookes, 2nd Baronet (1648ã1701) of Norgrove, Worcestershire, whose coat of arms was ad ...
at Oxford in 1905 and from the University of Leipzig
Leipzig University (), in Leipzig in Saxony, Germany, is one of the world's oldest universities and the second-oldest university (by consecutive years of existence) in Germany. The university was founded on 2 December 1409 by Frederick I, Electo ...
in 1909. In 1912, he was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature
The Nobel Prize in Literature, here meaning ''for'' Literature (), is a Swedish literature prize that is awarded annually, since 1901, to an author from any country who has, in the words of the will of Swedish industrialist Alfred Nobel, "in t ...
"primarily in recognition of his fruitful, varied and outstanding production in the realm of dramatic art", after he had been nominated in that year by Erich Schmidt, member of the Prussian Academy of Science
The Royal Prussian Academy of Sciences () was an academy established in Berlin, Germany on 11 July 1700, four years after the Prussian Academy of Arts, or "Arts Academy," to which "Berlin Academy" may also refer. In the 18th century, when French ...
.

Kaiser Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia from 1888 until his abdication in 1918, which marked the end of the German Empire as well as the Hohenzollern dynasty ...
, however, did not care for the "social democratic" poet. He vetoed the awarding of the 1896 Schiller Preis (for ''The Assumption of Hannele'') and at the instigation of his son, Crown Prince Wilhelm
Wilhelm, German Crown Prince, Crown Prince of Prussia (Friedrich Wilhelm Victor August Ernst; 6 May 1882 ã 20 July 1951) was the eldest child of the last German emperor, Wilhelm II, and his consort Augusta Victoria of Schleswig-Holstein, an ...
, in 1913, a Breslau production of Hauptmann's play ''Commemoration Masque'' (''Festspiel in deutschen Reimen'') was canceled, because in it the hundredth anniversary of the Liberation of Germany from Napoleon was depicted with a pacifistic rather than patriotic tone. However, the very same Hauptmann who had criticized militarism in the ''Masque'', the very next year was among those who supported the war.
Hauptmann signed the Manifesto of the Ninety-Three
The "Manifesto of the Ninety-Three" (; originally "To the Civilized World," , by "Professors of Germany") is a 4 October 1914 proclamation by 93 prominent Germans supporting Germany in the start of World War I. The Manifesto galvanized support for ...
, a manifesto signed by 93 German scientists, scholars and artists, declaring their unequivocal support of German military actions at the beginning of World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 ã 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. He published supportive poems (many of which read as unintentional satires and which he later crossed out in the manuscript).
In 1915, Wilhelm II awarded him the Order of the Red Eagle
The Order of the Red Eagle () was an order of chivalry of the Kingdom of Prussia. It was awarded to both military personnel and civilians, to recognize valor in combat, excellence in military leadership, long and faithful service to the kingdom, o ...
, Fourth Class. After Germany's military defeat and the fall of the monarchy, Hauptmann fled to the pacifist colony Monte Veritû
Monte Veritû (Italian; German 'Berg Wahrheit', meaning "Mount Truth" or "Mountain of Truth") is a hill standing 321 Metres above the Sea (Switzerland), metres above sea level and a cultural-historical ensemble in the Swiss canton of Ticino. The ...
in Locarno
Locarno (; ; Ticinese dialect, Ticinese: ; formerly in ) is a southern Switzerland, Swiss List of towns in Switzerland, town and Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district Locarno (district), Locarno (of which it is the capita ...
, Switzerland. Several years later, he wrote ''Till Eulenspiegel'', a poetic memorial to Hans Paasche, the pacifist and reformer who was assassinated by ultra-nationalists.
Representative poet of Germany
In 1918, he joined a declaration, signed by a number of German intellectuals and published in the ''Berliner Tageblatt'' newspaper, showing solidarity with theRepublic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
. During the early years of the republic, he was considered as a candidate for the ReichsprûÊsident and offered the position of Reichskanzler, which he turned down.
In the following years, he was the first recipient of the Adlerschild des Deutschen Reiches
The ''Adlerschild des Deutschen Reiches'' () was an honorary award () granted by the German president for scholarly or artistic achievements. It was introduced during the Weimar Republic, under President Friedrich Ebert and continued under Nazi Ge ...
(The Eagle Shield of the German Reich) an award for scholarly or artistic achievement. During this period, the demand for Hauptmann's work had declined, to the point where, in order to maintain his lifestyle, he had begun to do films and serializations. Despite this, he continued to enjoy popularity. He was seen abroad as the representative of German Literature. In 1932, in honor of the centenary of Goethe
Johann Wolfgang (von) Goethe (28 August 1749 ã 22 March 1832) was a German polymath who is widely regarded as the most influential writer in the German language. His work has had a wide-ranging influence on Western literature, literary, Polit ...
's death, he went on a lecture tour of the United States and was awarded and honorary doctorate from Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York, commonly referred to as Columbia University, is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Churc ...
. In addition he was awarded the Goethe Prize of the city of Frankfurt am Main
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
.
On his 70th birthday, he was awarded several honorary citizenships. There were countless exhibitions and performances of his work, many with well-known performers. Max Reinhardt
Max Reinhardt (; born Maximilian Goldmann; 9 September 1873 ã 30 October 1943) was an Austrian-born Theatre director, theatre and film director, theater manager, intendant, and theatrical producer. With his radically innovative and avant-gard ...
played the lead in the premiere of Hauptmann's new play ''Before Sunset.'' From 1926 to 1943, Hauptmann summered with his family in Hiddensee
Hiddensee () is a Auto-free zone, car-free island in the Baltic Sea, located west of Germany's largest island, Rû¥gen, on the Germany, German coast.
The island has about 1,000 inhabitants. It was a holiday destination for East Germany, East Germ ...
.
The Nazi era
After the Nazis came to power in Germany in 1933, Hauptmann signed a loyalty oath of the German Academy of Literature, a section of thePrussian Academy of Arts
The Prussian Academy of Arts () was a state arts academy first established in 1694 by prince-elector Frederick III of Electorate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg in Berlin, in personal union Duke Frederick I of Prussia, and later king in Kingdom of ...
.Ernst Klee
Ernst Klee (15 March 1942, Frankfurt ã 18 May 2013, Frankfurt) was a German journalist and author. As a writer on Germany's history, he was best known for his exposure and documentation of medical crimes in Nazi Germany, much of which was conce ...
: ''Das Kulturlexikon zum Dritten Reich. Wer war was vor und nach 1945''. S. Fischer, Frankfurt am Main 2007, , S. 223. In the summer of the same year, according to writer and historian Ernst Klee
Ernst Klee (15 March 1942, Frankfurt ã 18 May 2013, Frankfurt) was a German journalist and author. As a writer on Germany's history, he was best known for his exposure and documentation of medical crimes in Nazi Germany, much of which was conce ...
, he applied for membership in the Nazi party but his application was denied by the regional party office.
Hauptmann's copy of ''Mein Kampf
(; ) is a 1925 Autobiography, autobiographical manifesto by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler. The book outlines many of Political views of Adolf Hitler, Hitler's political beliefs, his political ideology and future plans for Nazi Germany, Ge ...
'', which can now be found in the Hauptmann collection at the Berlin State Library
The Berlin State Library (; officially abbreviated as ''SBB'', colloquially ''Stabi'') is a universal library in Berlin, Germany, and a property of the German public cultural organization the Prussian Cultural Heritage Foundation ().
Founded in ...
, was heavily annotated. He regarded himself as being fundamentally a poet, above the political fray; and certainly nothing from the Nazi ideology was incorporated into his works.Ulrich Lauterbach, Eberhard Siebert: ''Einleitung.'' In: ''Wirklichkeit und Traum, Gerhart Hauptmann 1862ã1946. Ausstellungskatalog der Staatsbibliothek Preuûischer Kulturbesitz.'' Berlin 1987, p. 7ã12 However, he had earlier been a founding member of the eugenics
Eugenics is a set of largely discredited beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter the frequency of various human phenotypes by inhibiting the fer ...
organization the German Society for Racial Hygiene
The German Society for Racial Hygiene () was a German eugenic organization founded on 22 June 1905 by the physician Alfred Ploetz in Berlin. Its goal was "for society to return to a healthy and blooming, strong and beautiful life" as Ploetz put i ...
, in Berlin in 1905, and his play ''Before Sunrise'' is deeply concerned with hereditary alcoholism, a popular idea with eugenicists, and the main character rejects his fiancûˋe due to concerns about his potential children's genetics.
Because Hauptmann remained highly regarded by the German people, the Nazis did everything to keep him from leaving the country, despite the emigration of many of his colleagues. At times he suffered from official disapproval. The censors of the Propaganda Minister Goebbels
Paul Joseph Goebbels (; 29 October 1897 ã 1 May 1945) was a German Nazi politician and philologist who was the ''Gauleiter'' (district leader) of Berlin, chief propagandist for the Nazi Party, and then Reich Minister of Propaganda ...
kept an eye on Hauptmann's work and even banned a new edition of his novella ''The Shot in the Park'' because it featured a black character. Hauptmann was told that reprinting was impossible because of a paper shortage. The film versions of ''The Beaver Coat'' and ''Before Sunrise'' were censored, and the film adaptation of ''Schluck and Jau'' was banned. For Hauptmann's 80th birthday, in 1942, representatives of the Nazi regime cooperated with honors, celebrations, and celebratory performances. Hauptmann was presented by his publisher with the first copy of his 17-volume Complete Works.
Hauptmann lived through the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 ã 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
at his house, Wiesenstein. In 1944, he published his Atreus
In Greek mythology, Atreus (, ) was a king of Mycenae in the Peloponnese, the son of Pelops and Hippodamia (daughter of Oenomaus), Hippodamia, and the father of Agamemnon and Menelaus. His descendants became known collectively as the Atreidae ...
Tetralogy, which he had been working on for four years. It comprises ''Iphigenia in Delphi'', ''Iphigenia in Aulis'', ''Agamemnon's Death'', and ''Electra''. In 1944, Hauptmann's name was included in the Gottbegnadeten list
The ''Gottbegnadeten-Liste'' ("God-gifted list" or "Important Artist Exempt List") was a 36-page list of artists considered crucial to National Socialist culture. The list was assembled in September 1944 by Joseph Goebbels, the head of the Mi ...
(the "God-gifted list"), a list of artists considered crucial to the German culture, who were therefore exempt from mobilization in the war effort. He was one of the six most important writers in the special list of the "irreplaceable artists.".
During the bombing of Dresden
The bombing of Dresden was a joint British and American aerial bombing attack on the city of Dresden, the capital of the German state of Saxony, during World War II. In four raids between 13 and 15 February 1945, 772 heavy bombers of the Ro ...
, Hauptmann was staying at a Dresden sanatorium
A sanatorium (from Latin '' sánáre'' 'to heal'), also sanitarium or sanitorium, is a historic name for a specialised hospital for the treatment of specific diseases, related ailments, and convalescence.
Sanatoriums are often in a health ...
due to severe pneumonia. He said of the inferno, "Whoever had forgotten how to cry learned again at the destruction of Dresden. I stand at the end of my life and envy my dead comrades, who were spared this experience."
After the war, Silesia, where Hauptmann was living, became part of Poland, but Hauptmann was temporarily allowed to stay due to a letter of protection. Then, on 7 April 1946, he was informed by the Soviet military authorities that the Polish government was insisting on his resettlement. Before his expulsion, he became very ill.
Death
bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
in Agnieszkû°w (present-day Jagniá
tkû°w, a part of ''Hirschberg im Riesengebirge'', now Jelenia Gû°ra
Jelenia Gû°ra (; ; ) is a historic city in southwestern Poland, within the historical region of Lower Silesia. Jelenia Gû°ra is situated in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship, close to the Karkonosze mountain range running along the Polish-Czech bo ...
). His last words were reported to be, "Am I still in my house?" Despite his final wishes, as expressed in his last will
A will and testament is a legal document that expresses a person's (testator) wishes as to how their property ( estate) is to be distributed after their death and as to which person (executor) is to manage the property until its final distribut ...
, Hauptmann was not buried at his home.
An official letter from the Soviet Administration in favor of the writer, who was highly regarded in the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, proved ineffective, though the family was permitted to take its belongings. Only an hour after his death, the local militia had gathered outside the window directly under his deathbed and banging pots and pans and blowing whistles and trumpets.
Funeral
At a funeral service held inStralsund
Stralsund (; Swedish language, Swedish: ''StrûËlsund''), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Stralsund (German language, German: ''Hansestadt Stralsund''), is the fifth-largest city in the northeastern German federal state of Mecklen ...
, near Hauptmann's summer home on Hiddensee
Hiddensee () is a Auto-free zone, car-free island in the Baltic Sea, located west of Germany's largest island, Rû¥gen, on the Germany, German coast.
The island has about 1,000 inhabitants. It was a holiday destination for East Germany, East Germ ...
island, Wilhelm Pieck
Friedrich Wilhelm Reinhold Pieck (; 3 January 1876 ã 7 September 1960) was a German communist politician who served as the Leadership of East Germany, chairman of the Socialist Unity Party from 1946 to 1950 and as the only president of the Ger ...
, then co-chairman of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany
The Socialist Unity Party of Germany (, ; SED, ) was the founding and ruling party of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) from the country's foundation in 1949 until its dissolution after the Peaceful Revolution in 1989. It was a Mar ...
in the Soviet occupation zone of Germany
The Soviet occupation zone in Germany ( or , ; ) was an area of Germany that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a communist area, established as a result of the Potsdam Agreement on 2 August 1945. On 7 October 1949 the German Democratic Republ ...
spoke, along with poet Johannes R. Becher, and Soviet official Sergei Ivanovich Tiulpanov all spoke.
On the morning of 28 July, 52 days after his death, he was buried before sunrise at the cemetery in Hiddensee. His widow mixed a small sack of earth from the Riesengebirge/Karkonosze Mountains (KrkonoéÀe
The Giant Mountains, KrkonoéÀe, or Karkonosze (Czech: , , ), are a mountain range located in the north of the Czech Republic and the south-west of Poland, part of the Sudetes mountain system (part of the Bohemian Massif). The CzechãPolish bor ...
) in Silesia with the sandy soil of the Baltic coast where he was buried. In 1951, a granite block was unveiled as the grave stone. It bears, as per Hauptmann's wish, only his name. In 1983, his wife Margarete's remains were moved to lie beside her husband's, though she had died in 1957.
Work
Influences
Hauptmann first encountered the various representatives of the naturalist movement through theavant-garde
In the arts and literature, the term ''avant-garde'' ( meaning or ) identifies an experimental genre or work of art, and the artist who created it, which usually is aesthetically innovative, whilst initially being ideologically unacceptable ...
society "Durch" in 1885, which was an important influence. The society hearkened back to historical examples from the Sturm und Drang
(, ; usually translated as "storm and stress") was a proto-Romanticism, Romantic movement in German literature and Music of Germany, music that occurred between the late 1760s and early 1780s. Within the movement, individual subjectivity an ...
movement, especially the circle centered on the Hart Brothers up until the VormûÊrz
' (; English: ''pre-March'') was a period in the history of Germany preceding the 1848 March Revolution in the states of the German Confederation. The beginning of the period is less well-defined. Some place the starting point directly after ...
period before the revolutions of 1848
The revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the springtime of the peoples or the springtime of nations, were a series of revolutions throughout Europe over the course of more than one year, from 1848 to 1849. It remains the most widespre ...
.
At their meetings, aesthetic questions about idealism
Idealism in philosophy, also known as philosophical realism or metaphysical idealism, is the set of metaphysics, metaphysical perspectives asserting that, most fundamentally, reality is equivalent to mind, Spirit (vital essence), spirit, or ...
, Realism
Realism, Realistic, or Realists may refer to:
In the arts
*Realism (arts), the general attempt to depict subjects truthfully in different forms of the arts
Arts movements related to realism include:
*American Realism
*Classical Realism
*Liter ...
and the naturalist movement were discussed. Hauptmann gave a lecture about the theretofore largely forgotten poet and dramatist Georg Bû¥chner
Karl Georg Bû¥chner (17 October 1813 ã 19 February 1837) was a German dramatist and writer of poetry and prose, considered part of the Young Germany movement. He was also a revolutionary and the brother of physician and philosopher Ludwig Bû¥chn ...
. With that, he also established his naturalistic orientation.
 At the end of the 1880s, he was confronted with the incipient anti-socialist movement. The first of the
At the end of the 1880s, he was confronted with the incipient anti-socialist movement. The first of the Anti-Socialist Laws
The Anti-Socialist Laws or Socialist Laws (; officially , approximately "Law against the public danger of Social Democratic endeavours") were a series of acts of the parliament of the German Empire, the first of which was passed on 19 October 187 ...
was passed in 1878 and strengthened in 1887. Hauptmann was in 1887 called before the court in Breslau, because he had been a follower of the "Icharians," whose ideas hearkened back to the ideas of French communist Etienne Cabet.
He sought refuge in his brother's house in Zurich in order to avoid prosecution. While there he encountered psychiatrist August Forel and the preacher Johannes Guttzeit, whose ideas influenced ''Before Sunrise''. Hauptmann's early dream of a utopian-socialist community were further fed by his encounter with the poet Gusto GrûÊser, whose communal colony Hauptmann would visit several times in 1919. The story ''The Heretic of Soana'', the novel ''The Fool in Christ Emmanuel Quint'', and the final chapter of ''Till Eulenspiegel'' deal with his experience of a Dionysian
The Apollonian and the Dionysian are philosophical and literary concepts represented by a duality between the figures of Apollo and Dionysus from Greek mythology. Its popularization is widely attributed to the work ''The Birth of Tragedy'' by Fri ...
- Jesuanic itinerant prophet.
Naturalism
Hauptmann began producing naturalistic works in Zurich. From there, he sent the manuscript of ''BahnwûÊrter Thiel'', his first naturalistic work, toMunich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
to be read by the critic Michael Georg Conrad. Hauptmann's 1889 play ''Before Sunrise'' caused one of the largest scandals in German theater history. The bourgeois audience was shocked by the frank depictions of alcoholism and sexuality.
According to Franz-Josef Payrhuber, ''Before Sunrise'' was an epoch-making work, but it is not the representative example of naturalistic drama, that label would go to ''Die Familie Selicke'' by Arno Holz
Arno Hermann Oscar Alfred Holz (26 April 1863 ã October 1929) was a German naturalist poet and dramatist. He is best known for his poetry collection ''Phantasus'' (1898). He was nominated for a Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel prize in litera ...
and Johannes Schlaf
Johannes Schlaf (21 June 1862 in Querfurt ã 2 February 1941 in Querfurt) was a German playwright, author, and translator and an important exponent of Naturalism. As a translator he was important for exposing the German-speaking world to the wo ...
.Franz-Josef Payrhuber: ''Literaturwissen Gerhart Hauptmann.'' Stuttgart 1998, p. 20. Hauptmann however did have an important role, with the support of Otto Brahm
Otto Brahm (born Otto Abrahamsohn on 5 February 1856 in Hamburg; died 28 November 1912 in Berlin) was a German drama and literary critic, theatre manager and director. His productions were noted for being accurate and realistic. He was involved i ...
, in establishing naturalistic drama on the German stage. Theaters under Brahm's leadership premiered 17 of Hauptmann's plays.Peter Sprengel: ''Gerhart Hauptmann.'' In Hartmut Steinecke
Hartmut Steinecke (12 March 1940 ã 25 January 2020Traueranz ...
(ed.): ''Deutsche Dichter des 20. Jahrhunderts.'' Berlin 1996, p. 31ã42 Those plays, and the numerous performances across Germany, gave Naturalism its first broad exposure and social impact.Letter of 19. Februar 1885 addressed to the Danish literary critic Georg Brandes. Quoted in: Peter Sprengel: ''Gerhart Hauptmann.'' In: Gunter E. Grimm, Frank Rainer Max (Ed.): ''Deutsche Dichter.'' Stuttgart 1993, p. 525.
With his most important play, ''The Weavers'', which he had already been contemplating during his stay in Zurich, Hauptmann achieved world renown and reached the high point of his Naturalistic phase.
Critical reception
Hauptmann's early work received differing reviews. Conservative circles and also the government were not excited about his socially critical dramas, which made itself felt through censorship. His position in the opposition raised his profile in progressive, intellectual circles, which appreciated these aspects of his work. After many naturalistic-influenced works, Hauptmann's style changed and he grew increasingly well-received among the educated and upper classes. Nevertheless, he was still in demand as a writer and was regarded abroad as the representative poet of Germany. The Hungarian philosopher and literature critic,Georg Lukacs
Georg may refer to:
* ''Georg'' (film), 1997
*Georg (musical), Estonian musical
* Georg (given name)
* Georg (surname)
* , a Kriegsmarine coastal tanker
* Spiders Georg, an Internet meme
See also
* George (disambiguation)
George may refer to:
...
later called Hauptmann the "representative poet of bourgeois Germany," by which he did not mean to underscore Hauptmann's prominent position. Rather, he expressed displeasure with Hauptmann's fickleness and lack of attachment to his "revolutionary beginnings."Georg LukûÀcs: ''Gerhart Hauptmann.'' In: Hans Joachim Schrimpf (Ed.): ''Georg Hauptmann'', Darmstadt 1976, p. 82ã95. Despite his preeminence, the sale of his works steadily declined as other poets and playwrights took the spotlight.
Hauptmann had taken up a lavish lifestyle, lived in expensive hotels, often received guests, and took trips to Italy. He summered in his large house on the Hiddensee, that Gû¥nter Kunert called a "do-it-yourself Olympia." Thomas Mann
Paul Thomas Mann ( , ; ; 6 June 1875 ã 12 August 1955) was a German novelist, short story writer, social critic, philanthropist, essayist, and the 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature laureate. His highly symbolic and ironic epic novels and novell ...
referred to this lavish lifestyle when he called him in 1922 the "King of the Republic." Mann met Hauptmann at an Alpine resort and wrote to his brother, "I hobnob every evening with Hauptmann, who is a really good fellow." In addition Mann adapted some of Hauptmann's traits for his character Mynheer Peeperkorn in his book ''The Magic Mountain
''The Magic Mountain'' (, ) is a novel by Thomas Mann. It was first published in Germany in November 1924. Since then, it has gone through numerous editions and been translated into many languages. It is widely considered a seminal work of 20t ...
''.
When Hauptmann continued to live in Germany after the Nazis came to power, they attempted to use Hauptmann for their own purposes. Various works that displeased the party leaders were banned but others continued to be performed. At his 80th birthday, in 1942 he was honored by the government with a festival and tributes, which he accepted. Hauptmann's ebb-and-flow character was highlighted in William L. Shirer's ''The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich
''The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich: A History of Nazi Germany'' is a book by American journalist William L. Shirer in which the author chronicles the rise and fall of Nazi Germany from the birth of Adolf Hitler in 1889 to the end of World W ...
''. Shirer offered in a first-person account:
 After his death, the fame he had enjoyed in life began to fade. His reputation was further diminished by his uncritical attitude toward the Nazis. Nevertheless, centenary celebrations were held in many German cities in 1962, and his works continued to be performed on West German stages into the 1970s, especially ''Der Biberpelz'' and ''Die Ratten''.
After his death, the fame he had enjoyed in life began to fade. His reputation was further diminished by his uncritical attitude toward the Nazis. Nevertheless, centenary celebrations were held in many German cities in 1962, and his works continued to be performed on West German stages into the 1970s, especially ''Der Biberpelz'' and ''Die Ratten''.
Publications
Novels * ''Der Narr in Christo Emanuel Quint'' (1910) * ''Atlantis'' (1912) * ''Wanda'' ''Der DûÊmon'' (1926) * ''Die Insel der grossen Mutter'' (1928) * ''Um Volk und Geist'' (1932) * ''Im Wirbel der Berufung'' (1936) * ''Das Abenteuer meiner Jugend'' (1937) Short novels * ''BahnwûÊrter Thiel'' (1888) * ''Der Ketzer von Soana'' (1918) * ''Phantom'' (1923) * ''Marginalien'' (selected works, reports: 1887ã1927) * ''Das Meerwunder'' (1934) * ''Sonnen'' (1938) * ''Der Schuss im Park'' (1939) Verse novels * ''Promethidenlos'' (1885) * ''Anna'' (1921) * ''Die blaue Blume'' (1924) * ''Till Eulenspiegel'' (1927) * ''Der grosse Traum'' (1912ã42) Plays * ''Before Sunrise'' (''Vor Sonnenaufgang'', 1889) * ''The Reconciliation'' (''Das Friedensfest'', 1890) * ''Lonely People'' (''Einsame Menschen'', 1891)Also translated as ''Lonely Lives''. * ''The Weavers
The Weavers were an American folk music quartet based in the Greenwich Village area of New York City originally consisting of Lee Hays, Pete Seeger, Ronnie Gilbert, and Fred Hellerman. Founded in 1948, the group sang traditional folk songs from ...
'' (''Die Weber'', 1892)
* ''Colleague Crampton'' (''College Cramption'', 1892)
* ''The Beaver Coat
''The Beaver Coat'' () is a satirical play by Gerhart Hauptmann premiered in Berlin in 1893.
The work is an example of a German naturalistic ''DiebskomûÑdie'', or 'thief's comedy'. The drama takes place "somewhere in Berlin... around the end of ...
'' (''Der Biberpelz'', 1893)
* ''The Assumption of Hannele
''The Ascension of Little Hannele'' (), also known simply as ''Hannele'', is an 1893 play by the German playwright Gerhart Hauptmann.Hartnoll (1983, 377). In contrast to Hauptmann's naturalistic dramas, ''The Assumption of Hannele'' adopts a mo ...
'' (''Hanneles Himmelfahrt'', 1893)
* ''Florian Geyer'' (1896)
* ''Elga'' (1896)
* ''Helios'' (1896) fragment
* ''The Sunken Bell
''The Sunken Bell'' () is a poetic play in blank verse
Blank verse is poetry written with regular metre (poetry), metrical but rhyme, unrhymed lines, usually in iambic pentameter. It has been described as "probably the most common and influ ...
'' (''Die versunkene Glocke'', 1896)
* ''Pastoral'' (''Das Hirtenlied'', 1898) fragment
* ''Drayman Henschel
''Drayman Henschel'' (), also known as ''Carter Henschel'', is an 1898 five-act naturalistic play by the German playwright Gerhart Hauptmann. Unlike his 1892 play ''The Weavers'', Hauptmann focuses on the story's psychological rather than social ...
'' (''Fuhrmann Henschel'', 1898)
* ''Schluck and Jau'' (''Schluck und Jau'', 1900)
* ''Michael Kramer'' (1900)
* '' The Conflagration'' (''Der rote Hahn'', 1901)
* ''Henry of Auû¨'' (''Der arme Heinrich'', 1902)
* '' Rose Bernd'' (1903)
* ''And Pippa Dances'' (''Und Pippa tanzt!'', 1906)
* ''The Maidens of the Mount'' (''Die Jungfern von Bischofsberg'', 1907)
* ''Charlemagne's Hostage'' (''Kaiser Karls Geisel'', 1908)
* ''The White Savior'' or ''Montezuma'' (''Der weiûe Heiland'', 1908)
* ''Griselda'' (1909)
* '' The Rats'' (''Die Ratten'', 1911)
* ''Gabriel Schilling's Flight'' (''Gabriel Schillings Flucht'', 1912)
* ''Peter Brauer'' (1912)
* ''Commemoration Masque'' (''Festspiel in deutschen Reimen'', 1913)
* ''The Bow of Odysseus'' (''Der Bogen des Odysseus'', 1914)
* ''Magnus Garbe'' (1914, second version: 1942)
* ''Indipohdi'' (1920)
* ''Veland'' (1925)
* ''Herbert Engelmann'' (1921ã26)
* ''Spuk'' (two plays: ''Die schwarze Maske'' and ''Hexenritt'', 1928)
* ''Die goldene Harfe'' (1933)
* ''Hamlet in Wittenberg'' (''Hamlet im Wittenberg'', 1935)
* ''Die Finsternisse'' (1937)
* ''Ulrich von Lichtenstein'' (1936ã37)
* ''Die Tochter der Kathedrale'' (1935ã38)
* ''Die Atriden-Tetralogie'':
#''Iphigenie in Aulis'' (1944)
#''Agamemnons Tod'' (1948; written in 1942)
#''Elektra'' (1948; written in 1944)
#''Iphigenie in Delphi'' (1941)
In English translation
''Hannele. A Dream Poem''
(1894)
''Lonely Lives''
(1898)
''The Sunken Bell''
(1899).
''The Coming of Peace''
(1900)
''And Pippa Dances''
(1907)
''The Reconciliation''
(1910)
''The Fool in Christ, Emanuel Quint''
(1911)
''Atlantis''
(1912).
''Parsival''
(1915) * The Dramatic Works: *
''Social Dramas''
(1912) *
''Social Dramas''
(1913) *
''Domestic Dramas''
(1914) *
''Symbolic and Legendary Dramas''
(1914) *
''Symbolic and Legendary Dramas''
(1915) *
''Later Dramas in Prose''
(1915) *
''Miscellaneous Dramas''
(1917)
''Phantom''
(1922) * ''The Heretic of Soana'' (1923) * ''Lineman Thiel and Other Tales'' (1989)
See also
* 8381 Hauptmann, a minor planet discovered in 1992, named for Hauptmann * Hauptmann (crater), a crater on Mercury, named for HauptmannReferences
Sources * Garten, H.F. (1954). ''Gerhart Hauptmann.'' New Haven: Yale University Press. * Holl, Karl (1913). ''Gregarious Hauptmann, his life and his work, 1862ã1912.'' * Marshall, Alan (1982). ''The German Naturalists and Gerhart Hauptmann.'' Frankfurt am Main: Peter Lang. * Maurer, Warren R. (1992). ''Understanding Gerhart Hauptmann.'' Columbia, S.C.: University of South Carolina Press. * Mellen, Philip A. (1984). ''Gerhart Hauptmann. Religious Syncretism and Eastern Religions.'' New York: Peter Lang. * Osborne, John (1998). ''Gerhart Hauptmann and the Naturalist Drama.'' Amsterdam: Harwood Academic. * Pohl, Gerhart (1962). ''Gerhart Hauptmann and Silesia.'' Grand Forks: University of North Dakota Press. * Shaw, Leroy R. (1958)''Witness of Deceit. Gerhart Hauptmann as Critic of Society.''
Berkeley: University of California Press. * Skrine, Peter N. (1989). ''Hauptmann, Wedekind, and Schnitzler.'' New York: St. Martin's Press.
Further reading
* Downs, Brian W. (1926). "Gerhart Hauptmann," ''The North American Review,'' Vol. 223, No. 830, pp. 102ã115. * Dukes, Ashley (1911)''Modern Dramatists.''
London: Frank Palmer. * Dussû´re, Carolyn (1980). "An Interpretation of Gerhart Hauptmann's 'Parsival'," ''Colloquia Germanica,'' Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 233ã245. * Campbell, T.M. (1924). "Gerhart HauptmannãChristian or Pagan?," ''The Modern Language Journal,'' Vol. 8, No. 6, pp. 353ã361. * Coates, William Ames (1945). "Dostoyevski and Gerhart Hauptmann," ''The American Slavic and East European Review,'' Vol. 4, No. 3/4, pp. 107ã127. * Ewen, David (1935). "Conversations with Gerhart Hauptmann," ''Books Abroad,'' Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 253ã254. * Hale, Edward Everett (1905)
"Hauptmann."
In: ''Dramatists of Today.'' New York: Henry Holt & Company, pp. 37ã61. * Heller, Otto (1905)
"Gerhart Hauptmann."
In: ''Studies in Modern German Literature.'' Boston: Ginn & Company, pp. 117ã128. * Heuser, F.W.J.(1926). "Hauptmann and Novalis," ''Germanic Review,'' Vol. 1, pp. 125ã131. * Huneker, James (1919)
"Gerhart Hauptmann."
In: ''Iconoclasts.'' New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, pp. 182ã210. * Kobbûˋ, Gustav (1898)
"The Dramas of Gerhart Hauptmann,"
''The Forum,'' Vol. 24, pp. 432ã441. * Lewisohn, Ludwig (1912)
"Introduction."
In: ''The Dramatic Works,'' Vol. 1. London: Martin Secker, pp. ixãxxxvii. * Maurer, Warren R. (1979). "Gerhart Hauptmann's Character Names," ''The German Quarterly,'' Vol. 52, No. 4, pp. 457ã471. * Muller, Siegfried H. (1952). "Gerhart Hauptmann's Relation to American Literature and His Concept of America," ''Monatshefte,'' Vol. 44, No. 7, pp. 333ã339. * Reichart, Walter A. (1946). "The Totality of Hauptmann's Work," ''Germanic Review,'' Vol. 21, pp. 143ã149. * Reichart, Walter A. (1962). "Hauptmann Study in America: A Continuation Bibliography," ''Monatshefte,'' Vol. 54, No. 6, pp. 297ã310. * Robertson, John G. (1902)
''A History of German Literature.''
New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons. * Scholz, Karl W.H. (1918)
''The Art of Translation.''
Philadelphia: Americana Germanica Press. * Thompson, Nesta M. (1920). "Naturalism and the Dream Motive as Observed in the Works of Gerhart Hauptmann," ''Washington University Studies,'' Vol. 8, pp. 77ã101. * Wahr, F.B. (1946). "Hauptmann's Hellenism," ''Journal of English and Germanic Philology,'' Vol. 33, pp. 421ã451. * Wiehr, Josef (1906)
"The Naturalistic Plays of Gerhart Hauptmann,"
''The Journal of English and Germanic Philology,'' Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 1ã71
Part II
Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 531ã575. * Witkowski, Georg (1909)
''The German Drama of the Nineteenth-century.''
London: George Bell & Sons. * Youngman, Paul A. (2005). "Gerhart Hauptmann." In: ''Black Devil and Iron Angel. The Railway in Nineteenth-century German Realism.'' Washington, D.C.: Catholic University of America Press, pp. 109ã127. * Schweissinger, Marc: Gerhart Hauptmann's Hamlet `translation`, In: Anglistica Pisana 8(2), pp. 11ã24.
External links
* * * * *Works by Gerhart Hauptmann
at
Hathi Trust
HathiTrust Digital Library is a large-scale collaborative repository of digital content from research libraries. Its holdings include content digitized via Google Books and the Internet Archive digitization initiatives, as well as content digit ...
List of Works
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Hauptmann, Gerhart 1862 births 1946 deaths 19th-century German dramatists and playwrights 19th-century German male writers 20th-century German dramatists and playwrights German Nobel laureates 19th-century German novelists 20th-century German novelists German poets German male short story writers German autobiographers Nobel laureates in Literature Writers from the Province of Silesia People from Waébrzych County Recipients of the Pour le Mûˋrite (civil class) University of Jena alumni German male poets German male novelists German male dramatists and playwrights 19th-century German short story writers 20th-century German short story writers